IASbaba's Press Information Bureau
Press Information Bureau (PIB) IAS UPSC – 1st April to 6th April – 2019
GS-2
Health Ministry forms a Solidarity Human Chain; reaffirms commitment towards Universal Health Care
(Topic: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources)
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare along with World Health Organization (WHO) formed a Solidarity Human Chain as part of the World Health Day celebrations to reaffirm their commitment to bridging gaps and working collaboratively towards Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
World Health Day: April 7th
The theme of World Health Day 2019 is Universal Health Coverage: Everyone, Everywhere.
Ayushmaan Bharat – An attempt to transform India’s Healthcare Map
Innovative and path-breaking scheme in the history of public health in India. It may have a transformative impact if implemented in an effective and coordinated manner.
- Aim: To make path-breaking interventions to address health holistically, in primary, secondary and tertiary care systems
- Objective: Prevention + Promotion (Health & Wellness)
- Full proof mechanism while allowing States to accommodate the existing schemes, keeping the flavour of Digital India intact
Two major initiatives:
- Health and Wellness Centre: Foundation of India’s health system
- 1.5 lakh centres will provide – comprehensive health care, including for non-communicable diseases and maternal and child health services, provide free essential drugs and diagnostic services
- The budget has allocated Rs.1200 crore for this flagship programme
- Contribution of the private sector through CSR and philanthropic institutions in adopting these centres is also envisaged.
- National Health Protection Scheme:
-
- Will cover over 10 crore poor and vulnerable families (approximately 50 crore beneficiaries)
- Coverage of up to ₹5 lakh a family a year will be provided for secondary- and tertiary-care hospitalization (50 crore beneficiaries)
Facts:
- Data of families will be derived from the SECC Data
- Increase in Health budget over the previous one: Approximately 11.50%
Ayushmaan Bharat Vs. Rashtriya Swasthiya Bhima Yojana: The new scheme builds on the already existing Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojna (with the entitlement of up to Rs 30,000 per annum for diseases requiring hospitalization) but has a bigger outreach plan.
A well-equipped primary health care delivery system is the key to achieving universal health coverage. This will require bringing quality care closer to people; strengthening peripheral health centres with linkages to secondary and tertiary care; and equipping primary health care providers to effectively deliver a package of preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative services.
Rise in non-communicable diseases
(Topic: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources)
At the turn of the century, chronic noncommunicable diseases were not widely recognized as a barrier to development and were not included in the Millennium Development Goals. In terms of gaining attention and financial support, these diseases were overshadowed by the devastating epidemics of HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria and the large number of maternal and childhood deaths.
Of all the major health threats to emerge, none has challenged the very foundations of public health so profoundly as the rise of chronic noncommunicable diseases. Heart disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases, once linked only to affluent societies, are now global, and the poor suffer the most. These diseases share four risk factors: tobacco use, the harmful use of alcohol, unhealthy diets, and physical inactivity. All four lie in non-health sectors, requiring collaboration across all of government and all of society to combat them.
A report in The Lancet last week found that India is among the more than half the world’s countries that are unlikely to meet the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) for 2030 to reduce, by one-third, premature deaths due to four major non-communicable diseases (NCDs) — cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases and diabetes. The study, led by Imperial College London researchers, found that the probability of death of one of these four NCDs between the ages of 30 and 70, in India, was 20% for women and 27% for men. In 2016, 1 million women and 1.46 million men in that age group died due to NCDs in India.
The Way Ahead
Decisive new action is urgently needed to halt the tsunami effect of NCDs – on people, families, communities, and economies. Over the coming decade, millions will lose loved ones to avoidable and early death. Millions more will suffer pain, disability and anguish because of lack of diagnosis and treatment. Millions more will struggle with entrenched poverty caused by catastrophic out of pocket expenditures.
- Actions to curb tobacco and alcohol consumption will help reduce future risk of NCD in the under-30 age group, while reducing mortality at all ages, and help create a healthier society which will yield inter-generational benefits well beyond 2030.
- Actions related to reduction of blood pressure, control of diabetes and provision of competent primary care supplemented by cost-effective specialist clinical care for treatable NCDs will benefit all age groups, with the highest benefits in the 30-80 age group.
- Energetic implementation of public health policies and NCD-inclusive health services under UHC are what the country needs. India’s efforts in these areas certainly merit the UN commendation.
- Actions to save lives are simple and extremely cost-effective; investing in the tried-and-tested WHO Best Buy interventions yields a seven-fold return in low and lower-middle-income countries. When it comes to NCD prevention, Best Buys interventions include taxation, regulation and legislation and the much-publicised taxes on Sugar, Tobacco and Alcohol (STAX). Implementing the 16 Best Buys worldwide would save 9.6 million lives by 2025, according to new data by WHO.
Solve: Is the world sleepwalking into a sick future? Discuss.
Indian Advance Pricing Agreement regime moves forward with signing of 18 APAs by CBDT
(Topic: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests)
The total number of APAs entered into by the CBDT as of now stands at 271, which inter alia includes 31 BAPAs.
The BAPAs entered into during the month of March 2019 were with the following treaty partners: –
- Australia – 1
- Netherlands – 1
- USA – 1
The International Transactions covered in all these Agreements, inter alia, include the following, –
- Contract manufacturing
- Provision of software development services
- Back office engineering support service
- Provision of back office (ITeS) support services
- Provision of marketing support services
- Payment of royalty for use of technology and brand
- Trading
- Payment of interest
The progress of the APA scheme strengthens the Government’s resolve of fostering a non-adversarial tax regime. The Indian APA programme has been appreciated nationally and internationally for being able to address complex transfer pricing issues in a fair and transparent manner.
Prelims oriented News:
AUSINDEX: Australia – India Maritime Exercise
Chile
- A South American country occupying a long, narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west.
- It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south.
- The arid Atacama Desert in northern Chile contains great mineral wealth, principally copper.
- Chile is a founding member of the United Nations
Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles II (FAME II) scheme
For: Promotion of Electric Mobility in the country
Objective of the scheme:
- To encourage faster adoption of Electric and hybrid vehicle by way of offering upfront Incentive on purchase of Electric vehicles and also by way of establishing a necessary charging Infrastructure for electric vehicles.
- The scheme will help in addressing the issue of environmental pollution and fuel security.
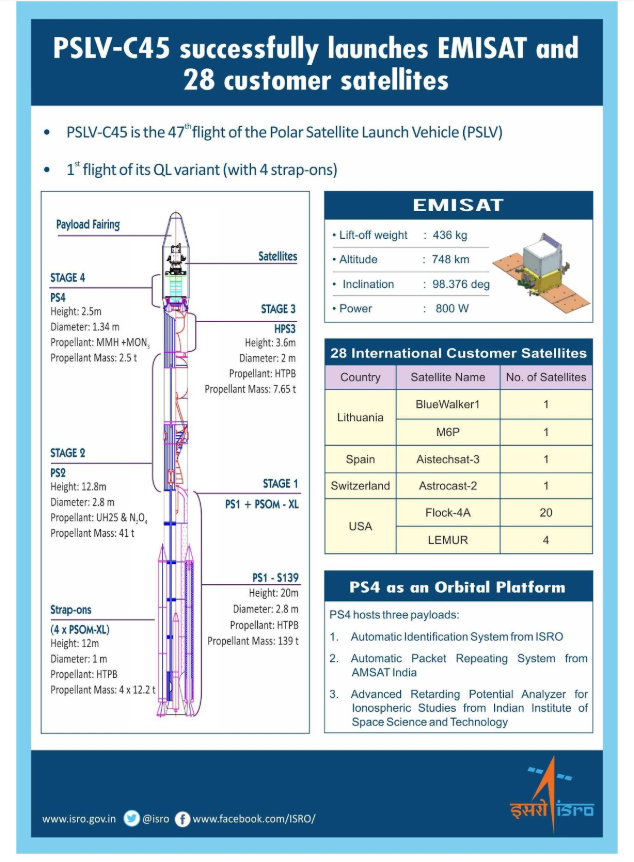
PSLV-C45 successfully launches EMISAT and 28 customer satellites
- This flight marked the first mission of PSLV-QL, a new variant of PSLV with four strap-on motors.
- EMISAT is a satellite built around ISRO’s Mini Satellite-2 bus weighing about 436 kg. The satellite is intended for electromagnetic spectrum measurement.
- The 28 international customer satellites, together weighing about 220 kg, are from four countries, namely, Lithuania (2), Spain (1), Switzerland (1) and USA (24). These foreign satellites were launched as part of commercial arrangements.
Quotes:
The Vice President of India, Shri M. Venkaiah Naidu
On Rural Entrepreneurship
- Create an ecosystem for rural entrepreneurship to thrive. Entrepreneurship was valuable only if it had a multiplier effect on the prosperity of our local communities, especially in rural areas
- Bridging the urban rural divide essential for overall development
- Reinvent and re-imagine ‘Brand India’ and revive dying industries through spirited young entrepreneurs
- Women empowerment should not only be a national goal but a global agenda. Pointing out that women constitute only 14% of the total entrepreneurship i.e. 8.05 million out of the total 58.5 million entrepreneurs, he said there was an urgent need to encourage more women to embark on the path of entrepreneurship.
- There is a need to create the relevant infrastructure and impart the right skill sets for them to successfully overcome the challenges posed by the technology-dependent world.
- Stressed on the need for making agriculture sustainable and profitable, creating market for rural artisans, empowering woman entrepreneurs to sell their crafts by way of online platforms and ensuring access to affordable education and healthcare.
- MSMEs contribute 6.11 per cent of manufacturing GDP and 24.6 per cent of services GDP. These industries which are often located in rural areas play a vital role in preserving India’s traditional skills and products such as handicrafts and handlooms
On Climate Change
- Promote new & renewable energy to ensure energy security, to protect climate & to reduce pollution
- Encourage environment friendly modes of transport
- Educate common man on the need to cut down GHG emissions & use RNE
- Adequate growth in renewable energy would serve dual purpose – firstly, it would contribute towards achieving energy security to the nation and it would address the environmental concerns, which need to be tackled on a war-footing
- Urged technologists to find new methods for tapping the huge potential in the renewable energy sector and also wanted them to educate the common man on the need to cut down GHG emissions.
- Pointing that connectivity and electricity were key to development, stressed upon the need to address challenges such as pilferages in transmission and distribution. There should begin a process of developing a suitable transmission and distribution system to facilitate renewable integration.











