IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 4th October 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
PRAKASH PORTAL
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Economy
In News
- PRAKASH stands for ‘Power Rail Koyla Availability through Supply Harmony’.
- The Union Minister for Power and the Union Minister for Coal & Mines jointly launched PRAKASH portal for transparency and better coordination in coal supplies to power plants.
- The Portal aims at bringing better coordination for coal supplies among all stakeholders viz – Ministry of Power, Ministry of Coal, Coal India, Railways and power utilities.
- PRAKASH Portal is developed by NTPC and sources data from different stakeholders such as Central Electricity Authority (CEA), Centre for Railway Information System (CRIS) and coal companies.
VANDE BHARAT EXPRESS
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-III -Infrastructure
In News
-
- Union government started New Delhi-Katra ‘Vande Bharat’ Express to give boost to religious tourism in Jammu.
- Katra is a small townlocated 42 km from the city of Jammu which serves as the base camp for pilgrims who visit Vaishno Devi.
- The coaches of this train are indigenously manufactured at the Chennai Rail coach factory.
- Vande Bharat Express has been tested at 180 kmph and can run upto maximum speed of 160 kmph on passenger service. All Coaches are equipped with automatic doors; GPS based audio-visual passenger information system, onboard hotspot, wi-fi for entertainment purposes, and very comfortable seating.
- This is the second ‘Vande Bharat’ express after the New Delhi – Varanasi semi-high speed train was started in February this year.
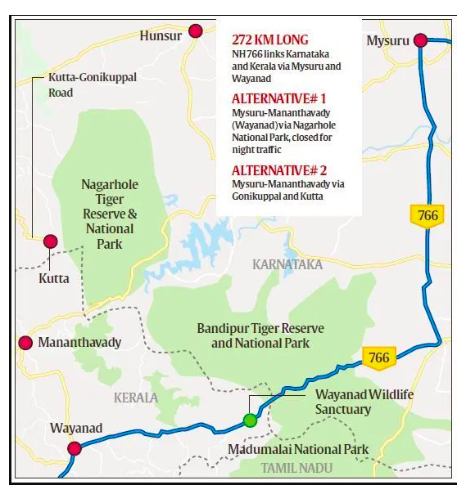
NH 766
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III – Environment Conservation
In News
- NH 766 is a key highway between Karnataka and Kerala that passes through the Bandipur Tiger Reserve in Karnataka.
- Kerala’s Wayanad district has witnessed a series of protests against a ban on night traffic on the forest stretch of NH 766.
- Although the night ban was first enforced a decade ago, the immediate trigger for the current agitation was a recent Supreme Court direction to the Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change and NHAI to suggest alternative routes so that NH 766 could be shut down permanently
Bandipur Tiger Reserve:
- Spread over 990.51 sq km, Bandipur Tiger Reserve is part of interconnected forests that include Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu), Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (Kerala) and Nagarhole National Park (Karnataka).
- A large variety of wildlife including the elephant moves from one stretch to another, cutting the states.
Do You Know?
- Night traffic would affect behaviour biology such as breeding and parental care of animals, disrupt their life cycle and make them stray to human habitats.
- Using the central Motor Vehicle Act read with the Karnataka Motor Vehicle Rules, traffic was banned from both sides of stretch from 9 pm to 6 am
https://images.indianexpress.com/2019/10/forest.jpg?w=759&h=797&imflag=true
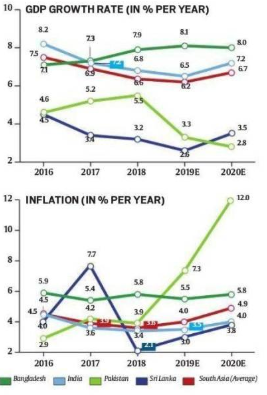
In economic growth, Bangladesh leads South Asian group
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II –International Relations
In News
- Since 2016, Bangladesh has been growing at 7%-plus every year, and its growth is likely to cross the 8% mark both in this and the coming year, according to the Asian Development Bankreport.
- Garments accounted for 84.2% of Bangladesh exports
- Over this same period, India has seen a secular decline in growth rates, even though an uptick is expected in the coming year.
- Sri Lanka has been the worst performing South Asian economy in terms of growth
Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank established on 19 December 1966.
- ADB is headquartered in Manila, Philippines. It aims to promote social and economic development in Asia.
- ADB now has 67 members, of which 48 are from within Asia and the Pacific and 19 outside.
- It is modeled on the World Bank and has a similar weighted voting system where votes are distributed based on member’s capital subscriptions.
- As of 31 December 2018, Japan and United States hold the largest proportion of shares at 15.571%. China holds 6.43%, India holds 6.32%, and Australia holds 5.77%.
- ADB provides financing to both Sovereign Nations and private companies.
Drone cameras threatening Nilgiris wildlife
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III – Environment Conservation
In News
- Birds may get injured when they attack drones of photographers which may lead to endangering of species and abandoning nesting sites,
- Use of drone cameras or Unmanned Aerial Vehicles mounted with filming equipment in forest areas, without the permission of the Chief Wildlife Warden is a criminal offence.
Niligiris
- The Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve was the first biosphere reserve in India established in the year 1986
- It forms a part of Western Ghats shared among Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka
- Main vegetation of the region is montane grasslands and shrub lands interspersed with shola forests
- Niligir Tahr (enadangered species) is endemic to Nilgiri hills. It is also State animal of Tamil Nadu
Miscellaneous
Blood4Pet – mobile app that brings together canine blood donors
- In order to bridge the gap between canine-blood demand & supply, Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University (Tanuvas)has launched a mobile app — Blood4Pet — to bring ‘pet-parents’ together across the country.
- There’s also a provision in the app for calculating the amount of blood required. A dog can safely donate blood once in three weeks.
- The app will help both pet owners and veterinarians to find suitable donors for dogs and thus help save lives of dogs
Repatriation Mizoram Bru refugees
- Over 30,000 Bru, also known as Reang, refugees are now housed in camps in north Tripura, since they fled ethnic violence in Mizoram in September 1997.
- Initiatives to repatriate the Mizoram Bru refugees back to their homes in Mizoram have failed as the refugee leaders refused to return citing mainly security reasons in their home State.
(MAINS FOCUS)
NATIONAL
TOPIC: General Studies 2:
- Development processes and the development industry- the role of NGOs, SHGs, various groups and associations, donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders
Non-Government Organisations (NGOs) under RTI Purview
Context:
- Non-Government Organisations (NGOs) receiving substantial financing from the government are bound to give information to the public under the RTI Act, the Supreme Court.( D.A.V. College Trust and Management Society Vs. Director of Public Instructions)
- Institutions like schools, colleges and hospitals which receive substantial aid from the government both directly or indirectly in the form of land at discounted rate are also bound to give information to the citizens under the Right to Information (RTI) Act.
Why?
- Several schools and colleges and associations running this educational institution have moved the apex court claiming that NGOs are not covered under the RTI Act
Do you know?
- Non-governmental organisations which were substantially financed by the appropriate government fall within the ambit of ‘public authority’ under Section 2(h) of the Right to Information Act, 2005.
- Under this section of the RTI Act, ‘public authority’ means “any authority or body or institution of self-government established or constituted by or under the Constitution and included… any non-government organisation substantially financed directly or indirectly by funds provided by the appropriate government.”
- ‘Substantial’ means a large portion which can be both, direct or indirect.
For instance, if land in a city is given free of cost or at a heavily subsidised rate to hospitals, educational institutions or other bodies, it can qualify as substantial financing.
Political parties:
- The Law Commission opines that political parties are the lifeblood of our entire constitutional system.
- Political parties act as a conduit through which interests and issues of the people get represented in Parliament.
- Since elections are predominantly contested on party lines in our parliamentary democratic polity, the agenda of the potential government is set by them.
Transparency in Political parties:
- In 2010, the Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR) filed an application under the RTI to all national parties, seeking information about the “10 maximum voluntary contributions”.
- None of the national political parties volunteered to disclose the information.
- Consequently, ADR and RTI activist Subhash Agarwal filed a petition with the Central Information Commission (CIC).
- In 2013, a full bench of the CIC delivered a historic judgment by declaring that all national parties came under ‘public authorities’ and were within the purview of the RTI Act.
- Notwithstanding the binding value of the CIC’s, none of the six political parties complied with it
- Finally, in 2019, a PIL was filed in the Supreme Court seeking a declaration of political parties as ‘public authority’ and the matter is sub judice
Ambedkar’s remarks:
“The working of a Constitution does not depend wholly upon the nature of the Constitution. The Constitution can provide only the organs of State…The factors on which the working of those organs of the State depend are the people and the political parties they will set up as their instruments to carry out their wishes and their politics.”
Implication:
- It can be argued that national parties are ‘substantially’ financed by the Central government.
- If an entity gets substantial finance from the government, there is no reason why any citizen cannot ask for information to find out whether his/her money which has been given to the entity is being used for the requisite purpose or not.
Connecting the dots:
- The creation of an ‘informed’ citizenry, containment of corruption and holding of government and its instrumentalities accountable to the governed is a need of hour .Justify.
ECONOMY
TOPIC: General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and related issues
- Investment models
Foreign Direct Investment 2.0
Context :
Recently, the Union Cabinet has approved the proposal for the review of Foreign Direct Investment in various sectors.
- This will result in making India a more attractive FDI destination, leading to benefits of increased investments, employment and growth.
- As of now (March 2019), Singapore remains India’s top FDI source, twice that from Mauritius.
Situation demanding policy response:
- Emergence of Internet Multinational Companies (MNCs) such as Microsoft, Google, Facebook and Twitter that are based on ‘winner-takes-all’ platform business models. These firms are characterised essentially by inequitable dynamics, since they distribute most gains to themselves vis-à-vis their host countries.
- In 1978, the Indian government adopted a policy that required equity dilution by 100% foreign-owned companies. This led to the ‘Listing of MNCs’, and many of which then provided handsome returns to both MNCs and Indian shareholders.
In China:
- China banned Internet MNCs.
- China strategically deploys a quid pro quo policy.
- MNC firms are mandated to transfer technology, share patents and enter into 50:50 joint ventures with Chinese partners in return for market access.
Foreign direct investment (FDI)
- It is an investment from a party in one country into a business or corporation in another country with the intention of establishing a lasting interest.
- Lasting interest differentiates FDI from foreign portfolio investments, where investors passively hold securities from a foreign country.
- Foreign direct investment can be made by expanding one’s business into a foreign country or by becoming the owner of a company in another country.
FDI 2.0
- 100% FDI under automatic route is permitted for sale of coal, for coal mining activities including associated processing infrastructure.
- The government has allowed 100% FDI through the automatic route for contract manufacturing.
- It will augment the Make in India initiative and will attract global companies in India looking to establish alternative manufacturing hubs
Merit:
FDI 2.0 could deploy ‘List or Trade in India’ as a strategic policy tool to enable Indian citizens become shareholders in MNCs such as Google, Facebook, Samsung, Huawei and others, thus capturing the ‘upside’ they create for their platforms and companies. This is equitable to all, since Indian consumers contribute to the market value of MNCs.
Proposals:
- (List in India): Majority (more than 51%) foreign-owned Indian-listed MNCs could be eligible to domestic company tax rate whereas unlisted MNC subsidiaries could be subjected to a higher tax rate. Many countries such as Bangladesh, Vietnam and Thailand have used tax incentives to attract listing by MNCs.
- (‘Trade in India’ i.e. U.S. dollar-denominated parent MNC Shares to be ‘Admitted for Trading’ on Indian bourses): In , Indian investors could buy shares of parent MNCs (where global profits and value get consolidated). This can be permitted within the $250,000 Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) limit.
What needs to be done?
- Indian bourses could admit only S&P 500 stocks. The Mexican Stock Exchange allows trading of international shares listed in other stock exchanges. India could replicate such models
Measures for successful implementation of above mentioned “Trade in India”:
- Permit Indian bourses to implement international trading system on the lines of Mexico.
- Parent MNCs in S&P 500 with business interests in India could be mandated to facilitate trading of their shares in India. MNCs would readily agree as it does not envisage listing in India.
- For taxation purposes, no distinction should be made between transactions in comparable domestic and foreign securities.
- LRS implementation for buying foreign stocks in GIFT City/NSE/BSE could be simplified and work as single click functionality.
- Educate Indian investors about the value of diversification of their portfolio in international stocks for achieving better risk adjusted returns.
Problem with implementation:
- For Indian citizens, U.S. estate taxes @40% apply above portfolio value of $60,000.
Solution:
- National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) could design a sovereign trust for holding parent MNC stocks.
- The NSDL could then issue BharatShares to retail investors. Nominees of the government of India would get voting rights in parent MNCs.
- In addition, the government could make available a ‘Fully Disclosed Model’ for holding foreign stocks in line with our NSDL/Central Depository Services Ltd (CDSL) system.
- The prevalent ‘Omnibus model’ carries the risk of U.S broker default because investors’ shares are held in the U.S. broker’s name. For this reason, it could also lead to higher tax liabilities in Indi
What is the Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) of USD 2,50,000?
- Under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme, all resident individuals, including minors, are allowed to freely remit up to USD 2,50,000 per financial year (April – March) for any permissible current or capital account transaction or a combination of both.
- Further, resident individuals can avail of foreign exchange facilities for the purposes mentioned in Para 1 of Schedule III of Foreign Exchange Management(Current Account Transactions) Amendment Rules 2015, within the limit of USD 2,50,000 only.
Way forward:
- Increasing Indian equity ownership of MNCs would offer diversification benefits and make Indians more prosperous.
- Wealth distribution through mutual funds would create a virtuous cycle of innovative ideas, entrepreneurship, employment, consumption, higher taxes, social and physical infrastructure for the benefit of Indian society.
- MNCs would earn the goodwill of Indian consumers while expanding their investor base.
Connecting the dots:
- List or trade in India’ should be used as a strategic policy tool to enable Indians to become shareholders in MNCs. Comment.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) NH 766 often seen in news passes through which of the following States of India?
- Assam and Arunachal Pradesh
- Gujarat and Maharashtra
- Karnataka and Kerala
- None of the above
Q.2) Consider the following statements Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- Japan and India hold the largest proportion of shares ADB
- It provides financing to both Sovereign Nations and private companies.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements about Nilgiris
- The Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve was the first biosphere reserve in India established in the year 1986
- Itsmain vegetation of the region is montane grasslands and shrub lands interspersed with shola forests
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4) PRAKASH PORTALoften seen in news is related to which of the following area?
- Management of Waste
- Promotion of energy efficient LED lights
- Coal supply to Power plants
- None of the above.
MUST READ
Toilet targets: On ending open defecation
Co-operative banks: Is dual regulation the problem?
How to read RBI’s monetary policy review
Subdued GST collections, lower tax devolution will impact state finances, pose macro risks











