IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 11th December 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Appointment of judges
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II–Judiciary
In News
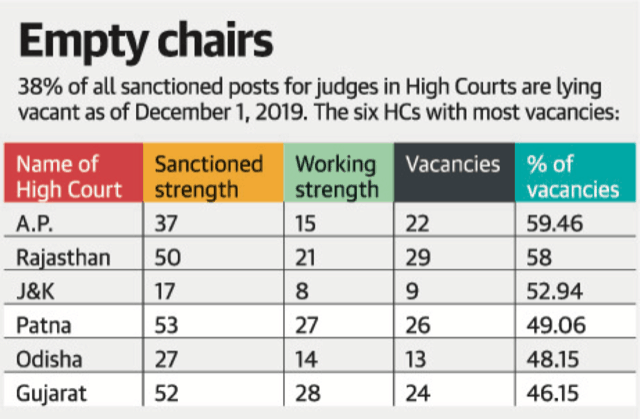
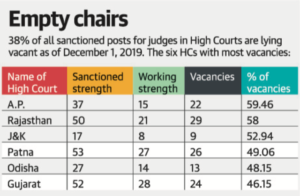
- 213 names recommended for appointment to various High Courts are pending with the government/Supreme Court Collegium
- Supreme Court has said in a judicial order, at least the names on which the Supreme Court Collegium, the High Courts and the governments had agreed upon should be appointed within six months.
- The High Courts are functioning at nearly 50% of their sanctioned judicial strength. Of a total 1,079 judges sanctioned in the High Courts, there are 410 vacancies.
- There were three SC judgments which made it crystal clear that the government had no option but to make the appointments if the collegium reiterated them after the government returned the names with objections.
- On the Supreme Court collegium clearing the recommendees, the Union Law Ministry has to put up within three weeks the recommendations to the Prime Minister who would advise the President on the appointment. However, no time limit has been prescribed for action by the Prime Minister and the President.
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 11th December 2019
Land Boundary Agreement
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II – International Relations
In News
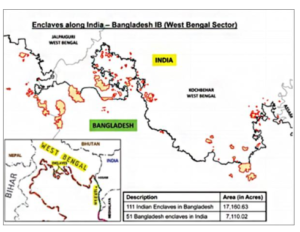
- More than four years after the historic Land Boundary Agreement (LBA) between India and Bangladesh, a report released by civil rights organisation – Masum- on the situation in erstwhile enclaves states that protest and resistance have become an essential part of their survival in India.
- The report says that the condition of the people is far from what they had imagined. They are yet to get land records and nothing has been done for providing them employment
- The report calls for a comprehensive survey should be undertaken to identify and assimilate the people whose names have been left out of the headcount previously, and all the benefits of being a citizen in India should be extended to them
- LBA settles land boundary dispute which dates back to colonial times as India transfers 111 border enclaves to Bangladesh in exchange for 51 enclaves.
- It also settles the question of citizenship for over 50,000 people in these enclaves.
For more details, refer: https://iasbaba.com/2015/05/big-picture-india-bangladesh-land-boundary-agreement/
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 11th December 2019
Defamation Case
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II – Governance
In News
- Supreme Court has held that internet intermediaries like Google cannot be protected from criminal defamation cases registered against them prior to October 27, 2009.
- It was only on October 27, 2009 that Parliament amended the Information Technology Act of 2000 to protect online intermediaries from liability for criminally defamatory content published in them by third parties.
- The amended Section 79 of the 2000 Act provided that “an intermediary shall not be liable for any third party information, data, or communication link made available or hosted by him.”
- The amendment gave almost blanket protection to intermediaries from legal action under Section 499/500 (criminal defamation) of the Indian Penal Code.
- In India, defamation cases can be filed under two heads. It is either civil or criminal.
- In civil defamation, a person who is defamed can move either the High Court or the subordinate courts and seek damages in the form of monetary compensation. There is no punishment in the form of jail sentence
- In criminal defamation, the person against whom a defamation case is filed might be sentenced to two years’ imprisonment or fined or both.
Gandhipedia
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains I- Society
In News
- The Government is developing ‘Gandhi Encyclopedia’ to spread awareness in the society.
- Ministry of Culture has approved a project for development of GandhiPaedia by National Council of Science Museums, Kolkata.
- The objective of the initiative is promotion of Gandhian philosophy and thoughts through social media platforms
- Government is providing financial assistance of Rs. 5.25 cr for this project and has released an amount of Rs. 2.95 cr against first installment.
U.S. International Commission on Religious Freedom (USCIRF)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Affairs
In News
- In the wake of the passage of the Citizenship Amendment Bill (CAB) in the Lok Sabha, USCIRF has expressed concern over it and considered recommending sanctions against Home Minister Amit Shah and other top leaders.
- USCIRF fears that the Indian government is creating a religious test for Indian citizenship through CAB that would strip citizenship from millions of Muslims
- In response, the External Affairs Ministry said India had the prerogative to validate its citizenry through various policies like any other country.
About USCIRF
- The USCIRF is an independent, bipartisan US federal government commission- an advisory body, which advises the US Congress and the administration on issues pertaining to international religious freedom
- In practice, the USCIRF has little teeth in implementation, but acts as a conscience-keeper for the two branches in the US government — the legislature and the executive.
- It often takes maximalist or extreme positions, and has been used by civil society groups to put pressure on US Congress members and administration officials.
Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment Conservation
In News
- CCPI measures the emissions, renewable energy share and climate policies of 57 countries and the European Union, collectively responsible for about 90% of the global GHG emissions.
- It is released annually after analysing four parameters – greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, renewable energy, climate policy and energy use
- The CCPI 2020 is released by three international NGOs – German watch, New Climate Institute and Climate Action Network
- India for the first time ranks among the top ten countries in the index. It has improved its ranking from 11th last year to ninth this year
- It found the U.S. ranks last, followed by Saudi Arabia and Australia, although several countries did report falls in emissions last year, largely due to an industry-wide fade out of coal
- While climate performance varied greatly, the report found that none of the countries surveyed were currently on a path compatible with the Paris climate goals.
- The 2015 Paris accord saw nations agree to work towards limiting global temperature rises to “well below” two degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
(MAINS FOCUS)
INDIA’S FOREIGN RELATION
TOPIC: General Studies 2:
- India-Australia signed Mutual Logistics Support Agreement
Context
- India and Australia moved closer to closing in on the Logistics Support Agreement (LSA), as the Foreign and Defence Secretaries from both countries met recently.
- The dialogue comes ahead of Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison’s scheduled January 13-16 trip to India.
- The first such two-plus-two meeting happened in December 2017.
- The LSA will be one of the key agenda points during Prime Minister Morrison’s visit.
- The Agreement will allow the two countries to use each other’s military bases for logistics support, including food, water, and petroleum.
- During their meeting, the two sides carried out a comprehensive review of their strategic engagement and the regional security scenario, which is continuously evolving given China’s military expansion and economic influence.
India-Australia bilateral relations
- When it comes to defence, India and Australia share a common concern over China.
- While Australia is worried about China’s presence in the Pacific, India is worried about China’s increasing activities and influence in the Indian Ocean.
- Earlier this year, the Australian and Indian navies concluded a two-week-long bilateral maritime exercise code-named AUSINDEX.
- The exercise was conducted to strengthen and enhance mutual cooperation and interoperability between the IN (Indian Navy) and RAN (Royal Australian Navy), providing opportunities for interaction and exchange of professional views between the personnel of the two navies.
- From 2016-18, the armies of the countries conducted a joint military exercise dubbed “AUSTRA HIND”.
- Significantly, for the first time in 2017, Australia’s Foreign Policy White Paper identified India as being at the “front rank” of Australia’s international partnerships, “on par with the US, Japan, Indonesia, and China”.
The Quad
- The informal strategic Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QSD) that was initiated by Japan’s Prime Minister Shinzo Abe in 2007 was largely in response to China’s growing power and influence.
- Initially, the “Quad” members included India, Japan, the US, and Australia; however Australia chose to withdraw when Kevin Rudd was Prime Minister, since it did not want to be a part of an anti-China alliance at the time.
- However, Australia later rejoined the dialogue in 2017 on the sidelines of the ASEAN Summit, signalling a re-ignition in Australia’s interest in the dialogue.
Connecting the dots:
- 2+2 dialogue will further cement India-Japan strategic relations. Critically examine.
POLITY
TOPIC: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Arms Amendment Bill, 2019
Context:
- Parliament recently approved a legislation providing for a maximum punishment of life imprisonment for manufacturing and carrying illegal arms.
- The Bill seeks to amend the Arms Act, 1959.
- It seeks to decrease the number of licensed firearms allowed per person and increase penalties for certain offences under the Act.
- It also introduces new categories of offences.
Features:
- License for acquiring firearms: Under the Act, a license must be obtained to acquire, possess, or carry any firearm. A person can obtain a license for up to three firearms. The Bill reduces the number of permitted firearms from three to one.
- The validity of a firearm license will be from three years to five years.
- Ban on firearms: The Act bans manufacture, sale, use, transfer, conversion, testing or proofing of firearms without license. The Bill additionally prohibits obtaining or procuring un-licensed firearms.
- Increase in punishment: The Bill increases the punishment related to un-licensed firearms and various other offences to between seven years and life imprisonment, along with a fine.
- New offences: The Bill adds news offences. These include: (i) forcefully taking a firearm from police or armed forces (ii) using firearms in a celebratory gunfire which endangers human life or personal safety of others. Celebratory gunfire refers to use of firearms in public gatherings, religious places, marriages or other functions to fire ammunition.
- Tracking of firearms: The central government may make rules to track firearms and ammunition from manufacturer to purchaser to detect, investigate, and analyse illicit manufacturing and trafficking.
- heirloom or heritage weapons could be kept if they have been de-activated.
- The bill has also accorded special status to sportsperson who need firearms and ammunition for practice and participating in tournaments.
- As per the bill, those who own more than two firearms will have to deposit the third one with police station concerned or authorised gun dealers.
- The new legislation has a provision for life imprisonment for those who snatch or loot arms and ammunition from police or other security forces.
- The Bill amends a Section of the Arms Act, 1959, to give punishment from the usual life term of 14 years to “imprisonment for the remainder of that person’s life” for manufacturing, selling, repairing and possessing “prohibited” arms.
- The minimum punishment under this section will be 14 years.
- According to an estimate, India has a total of around 35 lakh gun licences. Thirteen lakh people have licences to carry weapons in Uttar Pradesh, followed by militancy-hit Jammu and Kashmir, where 3.7 lakh people possess arms licences, most of which were taken in the name of personal security.
- Punjab, which witnessed terrorism in 1980s and 1990s, has around 3.6 lakh active gun licences, most of which were issued during the two decades of strife.
Connecting the dots:
- Arms Amendment Bill, 2019 will ensure effective control over arms and ammunition which is very important for safety and security in the country. Critically analyse.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1) Constitution (100th Amendment) Act,2015 deals with which of the following provision?
- National Judicial Appointments Committee
- Goods and Services Tax
- Constitutional status to National Commission on Backward Classes
- Land Boundary Agreement between India & Bangladesh
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Appointments of Judges to Supreme Court/High Court
- Appointment of Judges to High Court is done on the basis of recommendation by Supreme Court Collegium whereas appointment of Judges to Supreme Court is done on the basis of recommendation by National Judicial Appointments Committee.
- When the Supreme Court collegium clears the name for appointment as a Judge of High Court, Prime Minister & President have to act within the six months of receiving the recommendation from Supreme Court Collegium.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements about Gandhipedia
- It is being developed by NITI Aayog in collaboration with Ministry of Culture.
- The objective is to promote Gandhian philosophy and thoughts in society
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4) Consider the following statements about Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI)
- It is released by Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change in Collaboration with United Nations
- India for the first time ranks among the top ten countries in the 2020 released index
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 10 DEC 2019 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | A |
| 4 | C |
| 5 | D |
MUST READ
Instant reward: On Karnataka defection politics
Doping to win: On Russia’s ban from global sporting events
A patently unconstitutional piece of legislation
Wholly subordinated to the majoritarian nation
Citizenship Amendment Bill continues long tradition of welcoming persecuted minorities
Religious basis of citizenship would be a negation of secularism, liberalism, equality and justice











