IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 18th January 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Yada Yada alphavirus
In news:
Scientists named a novel virus after Seinfeld catchphrase “yada yada,” because it isn’t that big a deal as far as humans are concerned.
From Prelims Point of View:
- Yada Yada is an alphavirus, a group of viruses that the researchers described as “small, single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses (that) include species important to human and animal health, such as Chikungunya virus and Eastern equine encephalitis virus
- Alphavirus are transmitted primarily by mosquitoes and (are) pathogenic in their vertebrate hosts”.
- Yada Yada does not pose a threat to human beings.
Green clearance for onshore and offshore oil and gas exploration
In news:
The Environment Ministry has exempted oil and gas firms, looking to conduct exploratory drilling, from seeking an environmental clearance (both on-shore and offshore drilling explorations)
From Prelims Point of View:
Environment impact assessment (EIA):
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a process of evaluating the likely environmental impacts of a proposed project or development, taking into account inter-related socio-economic, cultural and human-health impacts, both beneficial and adverse.
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC):
- Indian Multinational Crude Oil and Gas Corporation
- It is the largest oil and gas exploration and production company in the country.
- It produces around 70% of India’s crude oil (equivalent to around 57% of the country’s total demand) and around 84% of its natural gas
- Maharatna status
A new Centre of Excellence (CoE) for Blockchain Technology in Bangalore
In news:
- A new Centre of Excellence (CoE) for Blockchain Technology, which will strive to adapt emerging technology to create e-governance solutions is established in Bangalore
- The CoE by National Informatics Centre (NIC) is the third such centre, following CoE for Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence.
From Prelims Point of View:
Blockchain Technology:
- Blockchains are a new data structure that is secure, cryptography-based, and distributed across a network.
- The technology supports cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, and the transfer of any data or digital asset.
- Spearheaded by Bitcoin, blockchains achieve consensus among distributed nodes, allowing the transfer of digital goods without the need for centralized authorisation of transactions.
National Informatics Centre (NIC):
- National Informatics Centre (NIC under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India.
- NIC provides infrastructure to help support delivery of Government IT services and delivery of some of the initiatives of Digital India.
China’s coronavirus
In news:
A new virus has been identified by Chinese researchers which is responsible for a new pneumonia-like illness.
From Prelims Point of View:
Coronavirus
- Coronaviruses are a specific family of viruses, with some of them causing less-severe damage, such as the common cold, and others causing respiratory and intestinal diseases.
- A coronavirus has many “regularly arranged” protrusions on its surface, because of which the entire virus particle looks like an emperor’s crown, hence the name “coronavirus”.
- Apart from human beings, coronaviruses can affect mammals including pigs, cattle, cats, dogs, martens, camels, hedgehogs and some birds.
- So far, there are four known disease-causing coronaviruses, among which the best known are the SARS coronavirus and the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) coronavirus, both of which can cause severe respiratory diseases.
(MAINS FOCUS)
International Affairs
General Studies 2:
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interest
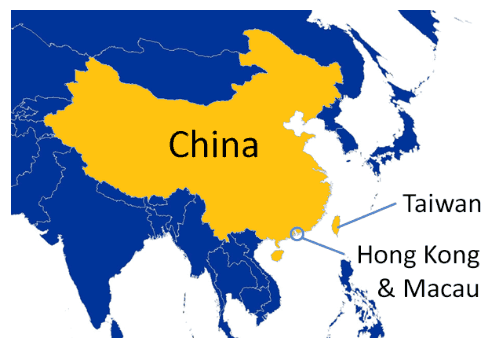
Taiwan, Hongkong and China

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 18th January 2020
Context:
The landslide re-election victory for the Democratic Progressive Party’s (DPP) Tsai Ing-wen in Taiwan has presented Beijing with a second pressing challenge in its backyard (along with ongoing protests in Hongkong)
Also, pro-democratic political parties swept the local district council elections in Hong Kong, which were widely seen as a referendum on the protests happening in Hongkong pressing for wider Democratic reforms
Brief Background of Taiwan
- China’s nationalist government, which was defeated in a civil war by the communists in 1949, had been exiled to Taiwan.
- Taiwan has been entirely self-ruled since then, however, China claims the island as a part of its territory
- Taiwan has a thriving democracy and has held direct elections to choose its leaders since 1996. China is Taiwan’s largest trade partner.
China’s One Country- Two system model
- This policy was originally proposed by Deng Xiaoping shortly after he took the reins of the country in the late 1970s. Deng’s plan was to unify China and Taiwan under the One Country Two Systems policy which provided autonomy to Taiwan
- Under this system, Taiwan could follow its capitalist economic system, run a separate administration and keep its own army but under Chinese sovereignty. Taiwan, however, rejected the Communist Party’s offer.
- The idea of two systems in one country is replicated again in Hong Kong and Macau when Britain and Portugal, who were running these territories under lease (since colonial times) returned it to China in 1997 & 1999 respectively. These territories was also given autonomy in its functioning in return for recognition of China’s Sovereignty over these areas.
Election results in Taiwan a referendum on China
- If the local elections in Hong Kong were a referendum on the protests, the elections in Taiwan ended up becoming a referendum on China — and specifically, on the “one country, two systems”
- The events in Hongkong whereby Chinese authorities were criticized for their handling of protestors (not calling for peace talks) revitalized the anti-China campaign in Taiwan (Independence from China)
- The opposition KMT (pro-China) – in power from 2008-16- had chosen to build economic and political bridges with China. The KMT’s stance was based on need to boost Taiwan’s economic opportunities.
- Polls conducted in Taiwan by the National Chengchi University in June 2019 showed that 56.9% identify as being only ‘Taiwanese’, up from 54.5% a year earlier
- On the choice between independence and reunification, 86.1% favoured maintaining the status quo (Not accede to China’s model)
Consequences for Taiwan
- With Ms. Tsai who is at the helm of Taiwan since 2016 and her stated anti-China views, Beijing has pushed with vigour an international strategy aimed at isolating Taiwan.
- By the end of 2019, Taiwan was left with only 14 UN member states that maintain diplomatic relations, after losing the Solomon Islands and Kiribati which both shifted to recognising Beijing.
- China believe that the country’s “great rejuvenation”, which President Mr. Xi has declared as the “China dream”, will not be complete without Taiwan’s return
Consequences for China
- China believe the tide of history is on their side (with economic & military might), and that the island (Taiwan) of 23 million people (roughly the population of Beijing) will inevitably return to the fold.
- However, China needs to offer more than the stability, security, and economic growth that its model promises, when issues of identity, suffrage and values are involved
- With China aggressively pushing its mega infrastructure project Belt & Road initiative and aiming at superpower status, it has to show to the world that it is able to solve its own internal problems in a peaceful manner before embarking on taking up Global leader status.
Lessons for India
- India also follows asymmetric Federalism where by many states enjoy greater autonomy in their functioning as compared to other states (Article 371, Schedule V & VI).
- These special provision are also intended to deal with issues to identity & culture. India thus needs to handle these in a democratic manner so as to not see Taiwan/Hongkong type of protests happening in India
- In International Politics: India can always use the leverage of Taiwan and Hongkong whenever China meddles in India’s own internal issues like Kashmir/ Naga unrest.
Connecting the dots
- China’s other internal issues – Tibet and Xinjiang province
- Why there are no protests in Macau which also enjoys special powers under the One Country-Two system mode
- How US is trying to exploit this situation? Resolution/laws passed by US legislature aimed at Hongkong/Xinjiang.
Governance: Education
General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
- Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes;
ASER lessons: Fix early learning in govt schools
Context:
ASER 2019 shows how poor the quality of education in government schools is even at the foundational levels.
About Annual Status of Education Report (ASER)
- This is an annual survey (since 2005) that aims to provide reliable estimates of children’s enrolment and basic learning levels across rural India ( Statewise and district wise)
- ASER is a household-based rather than school-based survey. This design enables all children to be included – those who have never been to school or have dropped out, as well as those who are in government schools, private schools, religious schools or anywhere else.
- Children in the age group 3 to 16 are surveyed to find out their enrollment status in school or pre-school. Children in the age group 5 to 16 are assessed one-on-one to understand their basic reading and arithmetic abilities.
- It is the largest citizen-led survey in India facilitated by Pratham NGO. It is also the only annual source of information on children’s learning outcomes available in India today
About 2019 report
- The 2019 report focuses on ‘Early Years’ (ages 4-8) since these are critical to later-stage learning
- Overall. More than 90% of young children in the age group of 4-8 year enrolled in some type of educational institution (91.3% at 4 years to 99.5 at 8 years)
- Gender gaps are visible even among these young children with more girls than boys enrolled in government institutions and more boys than girls enrolled in private institutions
- Disparity between Government & Private schools:
- Only 6.7% of government school students in Std I who were aged 4-5 could correctly do early language tasks, this figure was 24.1% for private schools
- Similarly, only 16.5% of 4&5-year-olds in Std I in government schools could demonstrate early numeracy competency, compared with 35.3% in private schools.
- In cognitive skills, too, government institutions lagged their private peers by six to 18 percentage points when performance of 5-year-olds was compared
Implication
- The Right to Education law and the new National Education Policy both set 6 years as the age when a child should enter formal schooling (Standard I)
- Cognitive development in the pre-school years is key to learning outcomes in school.
- Disparity in learning levels: A higher population of 4&5-year-olds study in standard I in government schools (26.1%) compared with private schools (15.7%)—largely because of the lack of affordable and accessible pre-primary institutions—it can be argued, the feedstock in government schools sets them up for the disparity in learning levels.
- High dropout rates at higher level: With the poor learning levels at the primary level (combined with no detention till class 8) many students simply may not be able to cope with the curriculum at the secondary and senior secondary levels thus leading to high dropout rate
Reasons for poor early learning outcomes is primarily two-fold
- India’s Anganwadi scheme: India has one of the largest pre-school care programmes in the world—the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), but it remains primarily focussed on nutrition/healthcare/immunisation, with early learning often neglected at the anganwadis.
- Distorted Pedagogy: Content knowledge and instruction us the preferred method when research shows that play-based activities geared towards building memory, reasoning, and problem-solving abilities have a much larger impact on building the foundation for later learning.
Way Ahead:
- Funding: India needs to aggressively bolster its early education programme—in FY20, the Centre budgeted $3.9 billion for the umbrella ICDS programme while in 2017, China was spending nearly $19 billion on just early childhood education
- Reorient Anganwadi centres as not just centres for nutrition but also centres for early learning
- Teaching Pedagogy should be relied more upn play based learning rather than instructional methodology
- Revisit State and National norms for age entry to school: Performance on congnitive, early language, early numeracy, and social & emotional learning tasks is closely related to children’s age, with older children doing better than younger ones. Permitting underage children into primary grades puts them at learning disadvantage which is difficult to overcome
Connecting the Dots
- New Educational Policy
- Operation Digital Board
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q 1. Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing?
- Chikungunya
- Hepatitis B
- HIV-AIDS
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q 2. Consider the following statements:
- NTPC is the largest power utility in India
- ONGC accounts for half of the LPG production of India
- Indian Oil Corporation operates all the refineries in India
- The Indian Ordinance Factory is the largest departmentally run industrial undertakings in the country
Which of these statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Q 3. Consider the following pairs of Terms sometimes seen in news vs Context /Topic:
- Belle II experiment: Artificial Intelligence
- Blockchain technology: Digital/ Cryptocurrency
- CRISPR – Cas9: Particle Physics
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched ?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q 4. With reference to ‘Bitcoins’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- Bitcoins are tracked by the Central Banks of the countries.
- Anyone with a Bitcoin address can send and receive Bitcoins from anyone else with a Bitcoin address.
- Online payments can be sent without either side knowing the identity of the other.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
ANSWERS FOR 17 JAN 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | C |
| 4 | D |
MUST READ
About Child deaths in Rajasthan
About need for continuity of governmental policies
About fighting radicalization











