IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis

IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 6th March 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
EC moots linking Aadhar with Voter-ID
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II-Constitutional Bodies
In News:
- Election Commission has mooted this idea to ensure preparation of an error free electoral roll, and to prevent duplication of entries
- The proposal requires an amendment to the Representation of People’s Act 1951
- The move would allow migrant labour and workers to vote even if they are away from their homes at the time of elections.
- It would also allow automatic inclusion of citizens into electoral roll once the person attains 18 years of age.
Value addition for Prelims
- The Election Commission of India is an autonomous constitutional authority established under Article 324 responsible for administering election processes of offices of President and Vice-President of India and Parliament and State Legislatures
- Article 324-329 deals with provisions of elections and ECI
- Originally the commission had only one election commissioner but after the Election Commissioner Amendment Act 1989, it has been made a multi-member body.
- The commission now consists of one Chief Election Commissioner and two Election Commissioners.
- A similar independent constitutional authority has been created to conduct elections to municipalities, Panchayats and other local bodies (Articles 243 K and 243 ZA).
Chief Information Commissioner (CIC)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II-Quasi-Judicial Bodies
In News:
- President appoints Information Commissioner Bimal Julka as CIC
- Central Information Commission is presently at a reduced strength of six information commissioners, against the sanctioned strength of 11 (including the CIC).
Value addition for Prelims
- The Chief Information Commissioner(CIC) and Information Commissioners(CI) shall be appointed by the President on the recommendation of a committee consisting of
-
- The Prime Minister, who shall be the Chairperson of the committee.
- The Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha.
- A Union Cabinet Minister to be nominated by the Prime Minister.
- Section 12(5) of the RTI Act 2005 provides that the CIC and IC shall be persons of eminence in public life with wide knowledge and experience in law, science and technology, social service, management, journalism, mass media or administration and governance.
- Also, CIC/IC shall not be a MP or MLA, or hold any other office of profit or connected with any political party or carrying on any business or pursuing any profession.
- CIC shall hold office for a term of five years from the date on which he enters upon his office and shall not be eligible for reappointment
- Salaries and allowances payable to and other terms and conditions of service of the CIC shall be the same as that of the Chief Election Commissioner and that of ICs shall be the same as that of Election Commissioner
- Information Commissioner(IC) shall also hold office for a term of five years from the date on which he enters upon his office and shall not be eligible for reappointment of IC. However, IC is eligible for appointment as CIC
- Where the Information Commissioner is appointed as the Chief Information Commissioner, his term of office shall not be more than five years in aggregate as the Information Commissioner and the Chief Information Commissioner.
Freedom in the World 2020 report
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I-Society; GS-II-Governance
In News:
- It is released by Freedom House, a US-based NGO which has been tracking global political and civil liberties for almost half a century
- The report derives its methodology from the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, adopted by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in 1948.
- The 2020 report has ranked India at the 83rd position along with Timor-Leste and Senegal.
- India is near the bottom of the pile among the countries categorised as “Free”, with only Tunisia receiving a lower score.

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 6th March 2020
Pic Source: The Hindu
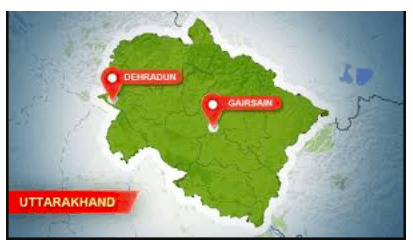
Gairsain
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I- Geography
In News:
- Uttarakhand Chief Minister named Gairsain as the new summer capital of the state
- Gairsain is situated at the eastern edge of the Dudhatoli mountain range.
- Uttarakhand was carved out as a separate state from Uttar Pradesh in 1998
- Statehood activists had long contended that Gairsain, a tehsil in Chamoli district, was best suited to be the capital of the mountainous state as it was a hilly region falling on the border of Kumaon and Garhwal regions.
- The state Assembly is located in Dehradun, but sessions are held in Gairsain as well.
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 6th March 2020
Pic Source: Catch News
Gender Parity Index
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I-Society; GS-II- Governance
In News:
- Gender Parity Index in education is the ratio of the number of female students enrolled to the number of male students in each level of education.
- In short, GPI at various levels reflect equitable participation of girls in the School system.
- GPI is released by UNESCO as a part of its Global Education Monitoring Report.
- A GPI of 1 indicates parity between the sexes; GPI below 1 indicated disparity in favour of males and GPI above 1 indicated disparity in favour of females
- India’s GPI for the year 2018-19 at different levels of School Education is as follows:
- Primary Education: 1.03
- Upper Primary Education: 1.12
- Secondary Education: 1.04
- Higher Secondary Education: 1.04
- India’s GPI indicates that the number of girls is more than the number of boys at all levels of school Education.
Internet Shutdowns
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Governance
In News:
- The Software Freedom Law Centre (SFLC) released data on internet shutdown in India.
- Internet in India was shut down for 314 times between 2017 & 2019 and 95 of these lasted more than a day
- There were at least 147 instances over these three years for which there is no data on the duration of the shutdowns as there is lack of any form of communication on these blockades.
- There is a rising trend to use Section 144 of the Code Of Criminal Procedure to justify the communications blockade and the continuance of it
Did You Know about the rules on suspension of the internet?
- Under the Indian Telegraph Act of 1885, only the Home Secretary of the central or the state government can pass orders to enforce an internet shutdown in any area.
- The order must include the detailed reasons for the shutdown and must be sent to a review committee the next day.
- The committee shall, within five days, submit its report and only if the shutdown is justified even after that will the communications blockade continue.
126th Constitutional Amendment: Anglo-Indians Protest at Jantar Mantar
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Indian Polity
In News:
- The Amendment act allows for continuing the reservation of seats for SC & STs in the Lok Sabha (Article 330) and state assemblies (Article 332)for another 10 years, upto January 25, 2030 which was due to end on 25th Jan 2020.
- The reservation for Anglo-Indians in the form of “nomination” (Article 331 & 333) is set to expire on 25th Jan 2020 as this Bill does not extend the facility to the community.
- Currently, only some state Assemblies like Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand etc. have one Anglo-Indian member each. The Amendment does away with this as well.
- Article 334 originally provided that reservation of seats would cease 10 years after the commencement of Constitution. But this was extended every 10 years (8th,23rd,45th,62nd,79th and 95th amendments)
(MAINS FOCUS)
Governance
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
Competition policy: Online Versus Offline
Context: The online marketplace or the platform/intermediation service market is now largely characterised by duopolies where several of these companies have come under the scrutiny of the Competition Commission of India (CCI).
Some of the sectors where duopolies exist in online marketplace are:
- E-commerce: Amazon and Flipkart
- Transport: Uber and Ola
- Food service: Zomato and Swiggy
- Travel bookings: MakeMyTrip and Yatra
The emergence of duopolies does not bode well because:
- Possibility of collusion– It is possible that at some point, the players will find it in their interest to venture into some sort of agreement that allows both of them to survive, rather than be engaged in a race to the bottom — as has seemingly happened in the telecom sector.
- Increased Lobbying with Political Class to keep the regulatory framework in their favour. This is highly possible in societies where Democracies are not matured.
- As result innovation in the sector begins to decline, as both market players are assured of their position & revenues
The issues involved with duopoly online space have far reaching ramifications for both online and off-line market places, some of which are:
- Impact of such market structures on online competition – Duopolies be it any sector may create barriers for entry of new players
- Players engaging in predatory pricing through deep discounting & offers
- Impact on offline competition – as a result of predatory pricing offered by these online companies
- Impact on Consumer Welfare –
- They are able to access variety of goods at much cheaper cost (discounted by companies).
- Consumers do benefit in the short run but once the competition is driven out, the platform starts raising prices to recoup previous losses.
- Also, their data is being mined without their explicit consent which is being used for behavioural manipulation regarding consumer spending
Assessing whether a platform is engaged in predatory pricing may not be a straightforward exercise. This is because of
- The dynamics of online pricing (prices change over time), their unique cost structures as well as the impact of economies of scale and organisational efficiency in lowering costs, all need to be factored in.
- Besides, one would also have to take into account that even offline firms engage in deep discounting to clear inventories.
- It is quite likely that once competition is eliminated and the platform starts to raise prices, new players will enter the market, attracted by higher prices. Thus, deep discounting strategies cannot be used for extended periods of time
In theory, the online market structure should facilitate greater competition given the lower barriers to entry. But this may not be the case due to reasons like:
- Mechanism of positive feedback loop: As these digital companies grow, more the users coming on board these platforms greater is the benefit due to positive feedback loop. This leads to market concentration.
- Given the network effects, which are common in digital spaces, it becomes difficult for new players to enter these spaces, and gain market share as there isn’t much space for many such networks.
- Another reason is that the online space is highly capital intensive. Deep pockets are required to fund the discounts to get customers on board initially. Duopoly incumbents having access to huge capital engage in various strategies (mergers & acquisitions) to restrict entry and thus competition.
Therefore, it is presumed that competition in online space is likely to be restricted and new entrants in the will be rare, unless facilitated by:
- Technological changes i.e. innovation
- Regulatory intervention
- Through deep discount pricing backed by deep pocketed firm
Way Forward:
- If regulatory intervention is required to check predatory pricing, it could kick in before market power or dominance is established. A
- Alternatively, the definition of market dominance could be expanded to take into account deep pockets.
- Competition policy should be driven by safeguarding competition, not competitors. It should seek to bring about greater transparency in pricing and reduce information asymmetry.
Connecting the Dots
- Net Neutrality
- Duopoly in Beverages – Pepsi and Coca-Cola- Has it led to collusion?
Society
Topic: General Studies 1 & 2:
- Social empowerment
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Human Resources.
Student Suicides: Young Lives Matter:
Context: India has the highest suicide rate amongst 15-29-year-olds globally and this rate has been increasing
Present Scenario of Student Suicides
- Overall, India saw 1.3 lakh suicides in 2018, of which students made up 8%, almost the same as those involved in the farming sector, while 10% of them were unemployed people.
- While 28,000 students committed suicide between 1999-2003, by 2014-18 this number had increased to 46,554
- Every hour one student commits suicide in India, with about 28 such suicides reported every day, according to data compiled by NCRB
- The NCRB data shows that 10,159 students died by suicide in 2018, an increase from 9,905 in 2017, and 9,478 in 2016.
- Maharashtra had the highest number of student suicides in 2018 with 1,448 — almost 4 suicides every day — followed by Tamil Nadu with 953 and Madhya Pradesh with 862.
Reasons for Students Committing Suicide:
- Academic Stress- A quarter of the student suicides in 2018 were because of “failure in exams”. Suicides even in premier institutes such as IITs hold a mirror to the stressful education system.
- Relationship breakdown is another leading cause.
- Lack of adequate support: A student commits suicide when he doesn’t get emotional support at the time of crisis
- High expectations from Students: Parental and peer pressure also have an adverse effect on mental health of students which leads to suicidal tendencies. Kota, primarily known as a coaching centre hub, has seen a series of student deaths every year. 58 students ended their lives in Kota between 2013 and 2017.
- Social Stigma: not enough discussion around depression and suicides
- Mental Issues: Anxiety disorder, depression, personality disorder — all these result in mental illness that leads a student towards suicide.
Steps that can be taken
- Social Awareness: The first step is to start a serious debate on the issue in schools and colleges
- Academic Support Groups by College administration: Teachers and College staff should form groups which identifies people who are not performing well in academics and provide them with special coaching/guidance.
- Counselling centres in Colleges: This may help student have an avenue to get proper psychiatric guidance on dealing with their emotional/mental issues
- Helplines by NGO and Civil Society Groups: This can help those who are having suicidal tendencies
- Leveraging Social media groups: while technology is rightly blamed for increasing self-imposed isolation and alienation, especially among the young, it can also be part of the solution—chatbots that are intended to fight depression among humans by addressing loneliness are an example.
Connecting the Dots
- Farmer Suicides
- Mental Health Act – that has decriminalised suicidal attempts
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q 1. Consider the following statements about Chief Information Commissioner(CIC)
- CIC is appointed by Prime Minister after clearance from Cabinet Committee on Appointment
- Salaries and allowances payable to and other terms and conditions of service of the CIC shall be the same as that of the Chief Election Commissioner
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 2. Consider the following statements Information Commissioner(IC)
- Salaries and allowances payable to and other terms and conditions of service of the IC shall be the same as that of Election Commissioner
- When IC is appointed as Chief Information Commissioner his/her term of office shall not be more than five years in aggregate as the Information Commissioner and the Chief Information Commissioner
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 3. Article 324 of the Indian Constitution deals with which of the following ?
- Comptroller and Auditor-General of India
- Special Provision related to National Capital Territory of Delhi
- Imposition of President’s rule in State upon recommendation by concerned Governor
- None of the above
Q 4. Freedom in the World report is released by which body/organisation?
- World Economic Forum
- Transparency International
- Amnesty International
- Freedom House
Q 5. Consider the following statements about 126th Constitutional Amendment Bill
- It deals with reservation of SC & ST in Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies
- It falls within the purview of Article 368of the Constitution and is hence required to be ratified by the Legislature of not less than half of the States by simple majority.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 6. Consider the following statements about Gender Parity Index (GPI)
- It is released by UNICEF in collaboration with NITI Aayog
- India’s GPI indicates that the number of girls is more than the number of boys at all levels of school Education.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 05 March 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | C |
| 4 | B |
Must Read
About Coronavirus:
Article by Former PM-Manmohan Singh about present Indian Situation:
About Sedition Law debates: