IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 7th March 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Suspension of Members of Lok Sabha
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Governance
In News:
- Seven Congress members were suspended, for the remainder of the Budget Session, which ends on April 3, for unruly behaviour in the Lok Sabha.
- Rules under which MPs in Lok Sabha can be suspended
- Rule Number 373 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business – Here Speaker may direct the member of House to withdraw from proceeding for the remainder of day’s sittings
- Rule 374 – Member named by speaker for suspension and the same needs to be passed by motion of the House. The member will thence be suspended from the service of the House for a period not exceeding the remainder of the session.
- Rule 374A – It is invoked by Speaker for automatic suspension of member of the House – for five consecutive sittings or the remainder of the session, whichever is less in the event of grave disorder occasioned by a Member
- While the Speaker is empowered to place a Member under suspension, the authority for revocation of this order is not vested in her.
- It is for the House, if it so desires, to resolve on a motion to revoke the suspension
SC order on Land Acquisition
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Governance
In News:
- SC upheld Section 24 (2) of Right to Fair Compensation and Transparency in Land Acquisition, Rehabilitation and Resettlement Act of 2013 (LARR-2013)
- The 2013 Act replaced the Land Acquisition Act, 1894 and provides for higher compensation to those deprived of land by the government for both public and private sector projects.
- It also mandates consent of a majority of land-owners and contains provisions for rehabilitation and resettlement.
What did the section 24(2) of LARR-2013 deal with?
- It dealt with land acquisition compensation awards made five years “prior or more” to the coming of existence of the 2013 Act
- The provision said that in such cases, if the physical possession has not been taken “or” the compensation is not paid, the acquisition proceeding is “deemed to have lapsed”.
- The government, if it so wishes, would have to initiate fresh acquisition proceedings under the new Act of 2013, which provides for fair compensation
What did SC rule?
- The land acquisition proceeding under Section 24(2) would only lapse if the authorities have neither taken physical possession nor paid the compensation due to the landowner for five or more years prior to January 1, 2014.
- In Other words, an “or” in the Section was “interpreted” as an “and”.
- Thus, there is no lapse if possession has been taken and compensation has not been paid. Similarly, there is no lapse if compensation has been paid and possession not taken of the land.
Indian Ocean Commission (OC)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- International Affairs
In News:
- India joined IOC as an Observer State
- IOC is five-nation grouping in the Western Indian Ocean, which includes Madagascar, Comoros, Seychelles, Mauritius and French Reunion.
- Significance of IOC: For its geographical location, as the islands sit around a “key choke-point” in the Indian Ocean — the Mozambique Channel
- This channel is being watched more closely as the U.S.-Iran tensions threaten the Strait of Hormuz.

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 7th March 2020
Pic Source
Did You Know?
- In December 2019, the Ministry of External Affairs decided to include Madagascar, Comoros and Reunion as part of the IOR (Indian Ocean Region) desk along with Sri Lanka, Maldives, Mauritius and Seychelles
- China was made an observer of IOC in 2016
- International Organisation of the Francophonie (the 54-nation French-speaking collective), the European Union (EU) and Malta became observers of IOC in 2017
Solar Charkha Mission
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Polity & Governance
In News:
- It was launched by Ministry of Micro Small & Medium Enterprises (MSME) in 2018.
- Solar Charkha units is an innovative way of cotton production by using solar energy. They have been classified as Village Industries.
- The mission will oversee the implementation of 50 Solar Charkha Clusters across the country with a budget of Rs.550 crore for the year 2018-19 and 2019-20.
- The scheme is envisaged to generate direct employment nearly to one lakh persons in the approved clusters.
Objectives of the scheme
- To create awareness about Khadi by bringing up the sales from Rs. 26,000 crores to Rs. 1 lakh crores.
- To have an eco-friendly environment.
- To revitalize the cotton industry.
- To extend self-employment in rural and urban areas.
- To make cotton generation a reliable and profitable business.

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 7th March 2020
Pic Source: India.Com
Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Polity & Governance
In News:
- INCOIS is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- It is located in Hyderabad & was established in 1999.
- It is mandated to provide the best possible ocean information and advisory services to society, industry, government agencies and the scientific community through sustained ocean observations and constant improvement through systematic and focused research.
- It is a unit of the Earth System Science Organization (ESSO), New Delhi. ESSO operates as an executive arm of MoES
(MAINS FOCUS)
Science and Technology
Topic: General Studies 2 & 3:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
- Awareness in the field of IT
Cryptocurrencies, Blockchain and Regulations
Context: SC lifts Ban on virtual currencies that was imposed by RBI
Virtual Currency
- There is no globally accepted definition of what exactly is virtual currency.
- Basically, virtual currency is the larger umbrella term for all forms of non-fiat currency being traded online.
- Virtual Currencies are mostly created, distributed and accepted in local virtual networks.
- Virtual currency also includes Cryptocurrencies that have an extra layer of security, in the form of encryption algorithms
CryptoCurrency
- It is a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange that uses strong cryptography to control the creation of additional units, to secure financial transactions and verify the transfer of assets
- These transactions are verified by network nodes and recorded in public distributed ledger called blockchain
- They are being transferred, stored or traded electronically.
- Thus, Crypto Currencies are type of unregulated digital money.
- They are neither issued by central bank/public authority, nor is necessarily attached to fiat currency, but is used and accepted among the members of a specific virtual community
Blockchain Technology:
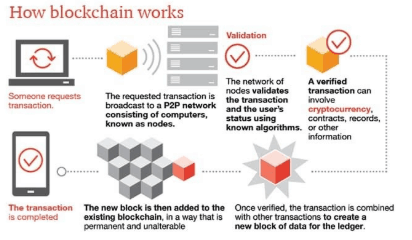
- Block chain is a decentralised digital ledger
- It was invented by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 for use in the cryptocurrency bitcoin
- Blockchains achieve consensus among distributed nodes, allowing the transfer of digital goods without the need for centralized authorisation of transactions.
- Its working can be represented through the below diagram.

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 7th March 2020
- The Internet allows computers to exchange information; Blockchain allows computers to record information. Both use a lot of computers (nodes).
- The technology thus allows transactions to be simultaneously anonymous and secure, peer-to-peer, instant and frictionless.
Dinesh Sharma Committee
- It was an inter-disciplinary committee set up in April 2017 by Finance Ministry to look into cryptocurrency legitimacy.
- The committee recommended a total ban on cryptocurrency in India
Subhash Chandra Garg committee
- It was formed in Nov 2017 to draft regulations for cryptocurrencies.
- It also recommended banning cryptocurrencies in India, citing risks and volatility in prices
- It recommended heavy penalties of up to Rs 25 crore and a jail term up to 10 years for anyone who mines, generates, holds, sells, transfers or issues cryptocurrency.
Criticism of Crypto Currencies:
- Highly speculative nature of assessing their value. For ex: the cryptocurrency traded at a peak of $20,000 in mid-2018 before crashing to $3,000 by the end of the year.
- It is not backed by any central institution but derives trust from its intricate blockchain ledger system.
- Bitcoins, with their assured anonymity is used in illicit transactions over the “dark web”.
Merits of cryptocurrencies
- Cryptocurrencies have now been adopted by international trading firms for use in lending, raising funds for other cryptoprojects
- It facilitates easier cross-border payments
- European Union has not out rightly banned the instrument but have sought to regulate its functioning.
- The 2019 Bill on Cryptocurrency even proposed the creation of a “digital rupee” as official currency.
Arguments made by Petitioners in SC against RBI ban
- The ban choked the agencies that sought to provide a platform to facilitate trading in cryptocurrencies by cutting them off from banks.
- This had a chilling effect on the fledgling cryptocurrency exchanges industry in India and went against their entrepreneurial right to operate a business enshrined in Article 19(1)(g).
- Article 19(1)(g) states that all citizens of the country will have the right to practise any profession, or carry on any occupation or trade and business.
Key Highlights of the Supreme Court Judgement
- The court found the ban did not pass the “proportionality” test as mentioned in Article 19(2)
- Besides, RBI had not considered the availability of alternatives before issuing the order i.e. achieving the same objective by imposing a less drastic restraint.
- Till date, the RBI has not come out with a stand that any of the entities regulated by it have suffered any loss or adverse effect directly or indirectly, on account of VC exchanges.
Conclusion
It is now imperative on authorities to find the right “regulatory balance” on cryptocurrencies, task that is easier thought than done, considering their ever-evolving nature due to technological innovation.
Connecting the dots
- Applications of Block Chain Technology in other sectors
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q 1. Consider the following statements about suspension of MP
- The Speaker of Lok Sabha is empowered to place a Member under suspension, however, the authority for revocation of this order is not vested in her
- Unlike the Speaker, however, the Rajya Sabha Chairman does not have the power to suspend a Member
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 2. Consider the following statements about Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS)
- INCOIS is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- It is located in Hyderabad & was established in 1999
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 3. Solar Charka Mission is a scheme by which Ministry ?
- Ministry of Textiles
- Ministry of Power
- Ministry of Micro Small & Medium Enterprises
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy
Q 4. Which of the following are the member countries of Indian Ocean Commission?
- Madagascar
- Reunion Island
- Mauritius
- India
- Seychelles
Select the correct answer from the codes given below
- 1,2 and 3 Only
- 1,2,3 and 4 Only
- 1,2,3 and 5 Only
- 1,2,3,4 and 5
ANSWERS FOR 06 March 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | C |
| 5 | C |
| 6 | B |
Must Read
About Judiciary:
About Delhi Violence:
About Bailout of Yes Bank: