UPSC Articles
SECURITY/ GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Security challenges and their management in border areas
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors
Drug abuse amidst pandemic
Context: In Punjab, there has been 23% rise in addict registrations since Covid outbreak
Did You Know?
- Around 269 million people used drugs in 2018, up 30% from 2009, with adolescents and young adults accounting for the largest share of users
- Development assistance dedicated to drug control fell by some 90% between 2000-2017.
Why India is vulnerable to trafficking of narcotics?
- India is sandwiched between the ‘Golden Crescent’ and the ‘Golden Triangle’, the major opium production regions in the world
- The Golden Crescent region of the South Asia comprises Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan.
- The Golden Triangle is the area where the borders of Thailand, Laos and Myanmar meet at the confluence of the Ruak and Mekong rivers.
- The bumper harvests of opium in Afghanistan for the last few years have given rise to increased supply of heroin in the subcontinent
- The combination of darknet and courier/postal deliveries have made the narco/psychotropic trafficking more anonymous in nature
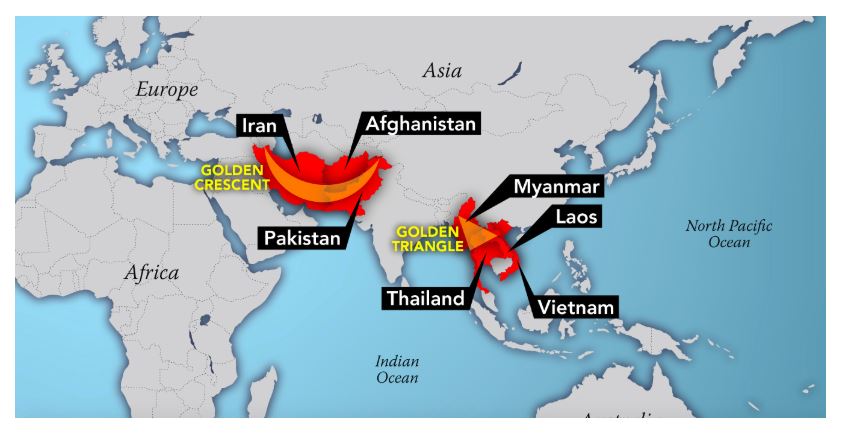
Image Source: Here
Consequences of pandemic on Drugs usage
- Increased Substance abuse: The economic downturn caused by the global pandemic may drive more people to substance abuse
- Anti-social activities: Many people will be vulnerable to involvement in drug trafficking and related crime as their incomes became dry during lockdown period
- Inattention and neglect: Governments will reduce budgets to deal with drug-related problems in the wake of reduced government revenues post-COVID-19 pandemic
- Dangers of increase in use of synthetic drugs: In the global recession that followed the 2008 financial crisis, drug users sought out cheaper synthetic substances and patterns of use shifted towards injecting drugs.
- Increase in drug use disorders: Only one out of eight people who need drug-related treatment receive it, according to the World Drug Report 2020. Some 35.6 million people suffer from drug use disorders globally.
- Prevents shift by farmers: Assistance for alternative development — creating viable, legal forms of income to enable poor farmers to stop growing illicit opium poppy or coca — will remain low.
- Increased transnational drug trafficking: National governments efforts will be focused on reviving domestic economies and this may hamper multi-lateral cooperation on cracking drug trade
- Disproportionate impact on weaker sections:
- One out of three drug users is a woman but women represent only one out of five people in treatment.
- People in prison settings, minorities, immigrants and displaced people also face barriers to treatment due to discrimination and stigma.
Way Ahead
- Greater investment in evidence-based prevention, as well as treatment and other services for drug use disorders
- International cooperation to increase access to controlled drugs for medical purposes and to strengthen law enforcement action to dismantle the transnational organised crime networks.
- Health-centred, rights-based and gender-responsive approaches to drug use and related diseases deliver better public health outcomes.











