IASbaba's Press Information Bureau, UPSC Articles
Press Information Bureau (PIB) IAS UPSC – 8th June to 13th June – 2020
GS-1
World Day against Child Labour
(Topic: Social empowerment (Children); Mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of vulnerable sections (Children))
On: 12th June
Theme: ‘Covid-19: Protect Children from Child Labour, now more than ever!’
According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), there are about 152 million children globally who are engaged in child labour, 72 million of whom are in hazardous work. With the coronavirus pandemic set to lead the world into a recession, these children are now at an even greater risk of facing circumstances even more difficult and working longer hours.
The Covid-19 crisis has pushed thousands of vulnerable children into child labour. As the pandemic wreaks havoc on family incomes, without support, many could resort to child labour. In times of crisis, child labour becomes a coping mechanism for many families
India has
- Increased the NCLP training centres stipends to Rs 400 from Rs 150 per month per child
- The ratification of ILO conventions 182 and 138 reflects India’s commitment towards this cause
- The Supreme Court said policing alone will not help prevent child labour and suggested that measures should be put in place to prevent contractors from employing children.
Sustainable Development Goal for ending child labour
- SDG Goal 8 (decent work and economic growth): focuses on promoting sustained, inclusive and sustainable growth and full and productive employment and decent work for all.
- SDG Target 8.7 aims to “take immediate and effective measures to eradicate forced labour, end modern slavery and human trafficking and secure the prohibition and elimination of the worst forms of child labour, including recruitment and use of child soldiers, and by 2025 end child labour in all its forms.”
Under the SDG agenda, UN member states, employers’ and workers’ organizations, as well as civil society organizations urged to eliminate child labour by 2025, and forced labour, modern slavery and human trafficking by 2030.
Four systemic failures that underpin the lack of progress:
- Absence of an effective national legislation: There is a need for an efficient national legislation to give effect to global conventions on the employment of children in hazardous industries, as well as on the minimum age of work.
- Lack of harmony between global commitments and domestic priorities.
- Lack of effective labour inspections in the informal economy: A strong legal framework that mandates punitive action against offending firms and recruitment of youth and adults are important tools to guarantee the protection of children.
- Absence of strong collective bargaining mechanisms and effective social protection policies from the cradle to the end of their lives.
Measures to tackle
- Elimination of school fees
- Boost social protections and provide easier access to credit for poor households
- Better economic opportunities for parents
- Conduct surprise checks at various industrial units and shops to keep child labour in check
- Improving migration governance
- Addressing gender considerations and tackling modern slavery as part of humanitarian actions in areas of fragility, conflict and crisis.
GS-2
All North Eastern States to have e-office
(Topic: e-governance)
E-offices will be set up in all 8 North Eastern States in a stipulated timeframe.
- A part of an initiative on “Minimum Government, Maximum Governance”
- Will ensure ease of administration, transparency and citizen-centric delivery mechanism
- E-office project is also a cardinal pillar of Digital India
Shillong Declaration: Promotion of e-office and quality of its services
The implementation of e-Office in State Secretariats of North Eastern States will result in
- Creation of paperless State Secretariats in a time bound manner where officers would be empowered with virtual private networks, digital signature certificates
- Promotion of less contact governance – work from home will be possible
The infrastructure bottlenecks:
- Network connectivity
- Lack of funds to implement the e-office project
India and Denmark sign MOU for developing cooperation between two countries in the power sector
(Topic: India’s relations with other countries)
Aim: To develop a strong, deep and long-term co-operation between two countries in the power sector on the basis of equality, reciprocity and mutual benefit
The MoU provides for collaboration in areas like
- Offshore wind
- Long term energy planning
- Forecasting
- Flexibility in the grid
- Consolidation of grid codes to integrate and operate efficiently variable generation options
- Flexibility in the power purchase agreements
- Incentivize power plant flexibility
- Variability in renewable energy production
GS-3
Efforts to enhance cultivation of Heeng and Saffron
(Topic: Crops)
Saffron and Heeng (asafoetida) are the most valuable spices of the world and widely used in Indian cuisine since time immemorial. In India, the annual demand for Saffron spice is 100 tons per year but its average production is about 6-7 tons per year. Hence a large amount of Saffron is being imported. Similarly, there is no production of heeng in India and currently about 1200 tons of raw heeng worth Rs 600 crore is being imported from Afghanistan, Iran, and Uzbekistan.
- A state-of-the-art tissue-culture lab will be established for large-scale production of quality planting material of these crops.
- Along with reduction in import, it will also lead to increased farm income, improve the farmer well-being by providing better income prospects and the state will be benefited by cultivation of these high-value crops along with rural development.
Streamline the process for import and possession of exotic live species in India
(Topic: Environment and Conservation)
Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has decided to collect stock information from the holders of exotic species through voluntary disclosure in next six months.
The registration will be done for the stock of animals, new progeny, as well as for import and exchange. The declarer would not be required to produce any documentation in relation to the exotic live species if the same has been declared within six months of the date of issue of the advisory. For any declaration made after 6 months, the declarer shall be required to comply with the documentation requirement under the extant laws and regulations.
This will help in
- Better management of the species and guide the holders about proper veterinary care, housing and other aspects of well-being of the species
- Controlling and management of zoonotic diseases on which guidance would be available from time to time to ensure safety of animals and humans
Why: Exotic live species are animal or plant species moved from their original range (location) to a new one. These species are introduced to a new location most often by people. Many citizen of the country have kept CITES (Convention of International Trade in Endangered Species) enlisted exotic animal species in their possession but there is no unified information system available of such stock of species at the State/Central level.
Indians can make efforts to strengthen the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES)
- In light of COVID-19, there is a need for greater scrutiny of wet(animal) markets in China, south-east Asia, and many other countries around the world.
- There is also a need to eradicate animal farms that breed and trade exotic species.
- Such wet markets and breeding centres increases the potential for zoonotic transmission of unknown, deadly viruses and hence a need for greater monitoring.
- Efforts need to be made to pass and enforce legislation to control the domestic consumption of wild animals, which also contributes to environmental conservation
About CITES
- It came into force in July 1975 and currently has 183 signatories
- Aim: Ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants does not threaten their survival.
- The CITES Secretariat is administered by UNEP and is located at Geneva, Switzerland.
- The CITES is as an international legally binding agreement aimed at ensuring “that international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants does not threaten their survival”. However, it does not take the place of national laws.
- Rather, it provides a framework to be respected by each Party, which has to adopt its own domestic legislation to ensure that CITES is implemented at the national level.
- The International Consortium on Combating Wildlife Crime (ICCWC), a consortium of the CITES Secretariat, INTERPOL, UN Office on Drugs and Crime, World Bank and the World Customs Organization has been established to tackle illegal wildlife trade.
Appendix:
- Appendix I includes species “threatened with extinction”. Trade in specimens of these species is permitted only in exceptional circumstances.
- Appendix II provides a lower level of protection.
- Appendix III contains species that are protected in at least one country, which has asked other CITES Parties for assistance in controlling the trade.
State-of-the-art Flood Warning System for Mumbai Launched
(Topic: Disaster Management)
iFLOWS- Mumbai, a state-of the-art Integrated Flood Warning System for Mumbai has been launched
Mumbai has been facing floods with increased periodicity which brings the city to a standstill in spite of its natural and storm water drainage systems. In a bid to aid in the mitigation of the flood prone city, Disaster Management Department of Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai (MCGM) approached the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) to develop an Integrated Flood Warning System for Mumbai, on the lines of a similar system developed for Chennai earlier. MoES initiated the development of the flood warning system in July 2019 using the expertise of Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting (NCMRWF), Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) and National Centre for Coastal Research (NCCR), in close coordination with Disaster Management Department of MCGM.
Features
- The system will help make the city become more resilient, by providing early warning for flooding especially during high rainfall events and cyclones.
- Using this, it will be possible to have an estimate of the flood inundation 3 days in advance, along with 3 hours – 6 hours Now cast (immediate weather updates).
- It will be very useful, especially if people need to be evacuated from low-lying areas as we will be able to forecast 12 hours in advance that a particular spot may get flooded.
- The system will also forecast the rainfall in each pocket.
How does the Prediction System Works?
The sophisticated system has been developed by the Ministry of Earth Sciences using its in-house expertise, in close collaboration with the Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai (BMC).
- The system uses rain gauge data and local data such as data on land use, land topography, drainage systems, water bodies in the city, tide levels, infrastructure and population, which has been provided by BMC.
- Using these as inputs, the prediction system models weather, rainfall, runoff and water movement, tide and storm surge impacts based on which early Flood Warnings for the city will be provided.
- It will address the flood inundation due to rainfall, river bank breach, storm surge, obstruction of flow due to roads, buildings, rail lines, high tides and sea level rise.
I-FLOWS is built on a modular structure and comprises seven modules.
- The Data Assimilation Module gathers a variety of dynamic data including IMD weather forecasts and under-water depth of rivers and lakes across Mumbai city.
- The Inundation Module will use the data to forecast flood inundation 3 days in advance, while the Flood Module will predict how the water will move across areas expected to be flooded.
- The Vulnerability and Risk Modules, which together comprise the Decision Support System, enables the administration to take smart decisions to manage the situation based on a scientific and holistic assessment of flooding risks.
- The Dissemination Module makes information available to field officials through various communication channels, enabling them to take prompt and informed field action.
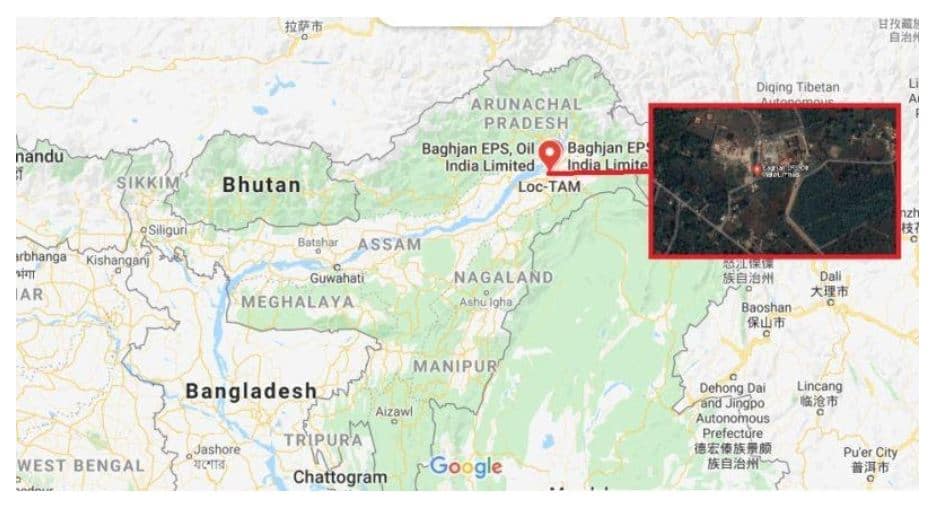
Baghjan fire tragedy
(Topic: Disaster Management)
Location: Tinsukia district of Assam, close to Dibru-Saikhowa National Park
The incident
- On May 26, workover was going on at the Baghjan oil well site to enhance the production of crude oil from the oil field.
- According to the Standard operation Procedure (SOP) drilling can be carried out only after 48 hours. However, the official who was in charge of production and services gave the order for drilling on the said oil well only after 14 hours.
- There was a blowout in the oil well owing to immense pressure when the pipes were inserted for drilling into the Baghjan 5 oil well
- Baghjan and Barekuri oil field in Tinsukia are the two major oil fields of Oil India Limited which produces maximum crude oil.
“The well was planned to be capped by following the advice of experts and taking all safety precautions. While the clearing operations were going on at the well site, the well caught fire on 9 June 2020 around noon time, spreading the fire in an area of about 200 meters around the well site. The cause of the fire has not been ascertained till now,” the petroleum ministry statement said.
Source: https://thekootneeti.in/2020/06/12/fire-at-assams-baghjan-oil-well/
The effect
Ecological: The gas leak has caused extensive devastation in the Dibru-Saikhowa National Park (known for its feral horses) and Maguri-Motapung wetland and forced villagers in the neighbourhood to flee the area — over 7,000 persons are now lodged in relief camps.
No disaster management structure or mechanism in place: India’s second-largest hydro-carbon exploration and production PSU did not have an adequate safety and disaster management plan in place. The toll in Tinsukia may not be limited to the two brave firefighters. A biosphere reserve faces the prospect of extinction because of the accident.
Livelihoods: Farmlands with standing crops, as well as ponds and wetlands in the adjoining villages have also been badly affected and the threat is growing with every passing day. People engaged in farming would face fertility issue of land as the land had been contaminated. People who earned their livelihood through fisheries are now left with no option as the water bodies are polluted and aquatic species have died in numbers. Those who are involved in animal rearing have been majorly affected too. This is not just an environmental crisis but has turned to be in an employment crisis for the locals.
Health: Locals have complained of headaches, itching in eyes, blockage of nasal passages, various respiratory problems after this blowout. Locals have been evacuated from the site and have been displaced into relief camps by the concerned authorities. This problem had become graver because of the Covid-19 restrictions as well. People living in the COVID relief camps had to evacuate their places as soon as possible. As the impact spread, the National Disaster Response Force was called and 2,500 people were taken to relief camps.
While Baghjan has been the most affected by the blowout due to its proximity to the well, villages located further downstream like Notungaon, Milanpur, Hatibagh, Bebejia and Barekuri have also suffered. Droplets of condensate (which is the residue from gas condensing after coming in contact with water) have reportedly spread up to a radius of 5 km, falling on trees, tea gardens making them unsuited for the markets, grasslands, water bodies, and on the roofs of houses making it more difficult for people living there.
Indians have not reacted: While each disaster should get its due coverage, the blind eye turned to the Assam oil leak has reignited the old grudge people from the Northeast have regarding mainland India ignoring its issues.
India and Industrial Tragedies
- A toxic gas leak at LG Polymers’ facility last month killed 11 people at Vishakhapatnam, in one of the deadliest industrial accidents since the Bhopal tragedy of 1984.
- In November 2017, there was a blast in the boiler area of state-run NTPC Ltd’s Unchahar power plant in Raebareli that also claimed many lives.
Conclusion:
Public safety and sensitivity to the local environment have to be an integral part of its managerial vision.
This year has witnessed many natural disasters from a global pandemic to tremors to locust attacks. The rich biodiversity and ecology are in danger and nature calls out for an immediate collective sustainable strategy towards it, not just by people but also government and industrialists.
Scaling up technology for reducing CO2 to methanol & other useful chemicals
(Topic: Environment; Technology)
An agreement has been signed between Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR), an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and Breathe Applied Sciences, a company incubated at JNCASR for transfer of technology based on lab-scale research on reducing CO2 to methanol and other useful chemicals and fuels.
- The MOU will help in smooth translation of the research in the area of CO2 reduction to useful chemicals and fuels from the laboratory scale to pilot scale economically
- Highlight the scientific contribution of a research institute translating to the industry to solve the problems associated with renewable energy and environmental pollution
- It will also help in developing an indigenous technology in line with government policy.
Why is it important: Conversion of CO2 to clean fuels such as methanol and other useful chemicals on scale with cost-effectiveness is the holy grail of science to address sustainable development, environmental and climate.
Activities that will be undertaken
- Development of efficient catalysts for the conversion of CO2 to methanol and other chemicals
- Improvisation of the process engineering to enhance the production of chemicals and fuels from anthropogenic CO2 generated from various sources including coal and natural gas power generation sectors, steel industry, cement industry, and chemical industries
- Integrating multiple components involved in the CCUS (Carbon capture, utilization, and sequestration) to develop a complete solution for the environmental issues due to global warming.
New study may help develop therapeutics for tongue cancer
(Topic: Technology)
A team of researchers have identified a specific microRNA (miRNAs) called ‘miR-155’ that is over-expressed in tongue cancer. This finding is important in that molecular strategies can potentially be devised to manipulate miR-155 expression to develop therapeutics for tongue cancer.
- MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small Ribo Nucleic Acid. They are non-coding RNAs involved in the regulation of a variety of biological and pathological processes, including the formation and development of cancer.
- The miRNAs associated with cancer are called ‘Oncomirs’.”
- The main function of miRNA is to silence the expression of the other genes. If the silence oncogenes then the cancer will be suppressed.
- On the other hand, if they suppress tumour suppressor gene, the cancer will progress. Accordingly, miRNA can act as oncogenes or tumour suppressor genes depending on what they act upon.
- If the miRNA acts as tumour suppressor genes, then you want to introduce to the system so that tumour can be suppressed; such therapy is called miRNA replacement therapy
miRNA manipulation is being combined with conventional cancer treatment methods such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy, and the study reported by collaborative team can enable such emerging therapeutics for cancer.
Please Note
World Accreditation Day: 9th June
- To highlight as well as promote the role of accreditation in trade & economy
- The theme for WAD 2020 is “Accreditation: Improving Food Safety”, as decided by the International Accreditation Forum (IAF) and the International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation (ILAC).
National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) under Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has gone ‘Fully Digital’, with the launch of unique cloud based and Artificial Intelligence powered Big Data Analytics platform – Data Lake and Project Management Software.
Launch of Aarogyapath, a web-based solution for the healthcare supply chain: To provide real-time availability of critical healthcare supplies
- During the present national health emergency arising out of the COVID-19 pandemic, where there is severe disruption in supply chain, the ability to produce and deliver the critical items may be compromised due to a variety of reasons.
- This integrated public platform that provides single-point availability of key healthcare goodscan be helpful to customers in tackling a number of routinely experienced issues.
- These issues include dependence on limited suppliers, time-consuming processes to identify good quality products, limited access to suppliers who can supply standardized products at reasonable prices within desired timelines, lack of awareness about the latest product launches, etc.
DST constitutes joint Science Communication Forum
Aim: To facilitate interaction, cooperation, and coordination amongst various public sector science communication institutions and agencies
- The Forum brings together science communication efforts spread across various institutions and can help adoption of a common policy and best practices at a wider scale, ultimately aiming towards a national science communication framework.
- The Forum would work upon strategies for effective planning and implementation of science communication programmes at macro and micro level in the country to spread scientific awareness and inculcate scientific temper amongst the masses leading to an innovation-driven society that contributes towards an ecosystem for Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Launch of Sahakar Mitra: Scheme on Internship Programme
Initiative by: National Cooperative Development Corporation has embarked upon a series of initiatives in the cooperative sector entrepreneurship development ecosystem through capacity development, paid internship to youth and assured project loans on liberalized terms to young cooperators on start-up mode.
To assist cooperative institutions access new and innovative ideas of young professionals while the interns gain experience of working in the field giving confidence to be self-reliant. It is expected to be a win-win situation both for cooperatives as well as for the young professionals.
Quality Council of India
- A non-profit autonomous society, under the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT)
- To establish an accreditation structure in the country
- To spread quality movement in India by undertaking a National Quality Campaign
- The Mission of QCI is to lead nationwide quality movement in India by involving all stakeholders for emphasis on adherence to quality standards in all spheres of activities primarily for promoting and protecting interests of the nation and its citizens.
Why is it important today?
- Quality consciousness will have to percolate to the level of the common man, and quality culture imbibed and cultivated in all aspects of our life.
- The quality evaluation and certification should be rational, transparent, reliable, and free from any manipulation or malpractices.
- The quality standards should be of high class and implementable.
Enhanced Import Duty on Bamboo Sticks to give a big boost to Agarbatti and Bamboo Industries in India
- Increase in import duty on bamboo sticks from 10% to 25% – will open up new avenues of self-employment in the country
- Will lead to creation of at least one lakh new jobs in the Agarbatti industry, a major activity under the village industry sector in India
India is the 2nd largest producer of bamboo in the world but ironically, it is also the 2nd largest importer of bamboo and its products. The hike in import duty on bamboo sticks from 10% to 25% will curb heavy import from China and encourage local manufacture in Agarbatti and bamboo industries.
Heavy import of bamboo sticks from China and Vietnam caused huge employment loss in India. This decision will pave the way for setting up of new agarbatti stick manufacturing units to meet the ever-growing demand of Agarbatti in India.
- Consumption of incense sticks in India is pegged at a whopping 1490 tons per day but only 760 tons per day is locally produced. Hence, the huge gap between the demand and supply resulted in heavy import of raw agarbatti.
- Consequently, the import of raw agarbatti increased from just 2% in 2009 to 80% in 2019. In monetary terms, the import of raw agarbatti in India increased exponentially from Rs 31 crore in 2009 to Rs 546 crore in 2019 due to reduction of import duty in 2011 from 30 % to 10 %.
- This hit the Indian agarbatti manufacturers hard and resulted in closure of nearly 25% of the total units
Agarbatti making industry is a part of the Village Industry, which requires a very small capital and less technical skill. This industry employs mostly women workers. In the post Covid scenario, this industry will prove to be a boon for the migrant workers.
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY- PDMC)
Annual allotment of Rs. 4000 crore made to State Governments under ‘Per Drop More Crop’ component of Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY- PDMC) for the year 2020-21.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) has been formulated with the vision of extending the coverage of irrigation ‘Har Khet ko pani’ and improving water use efficiency ‘More crop per drop’ in a focused manner with end to end solution on source creation, distribution, management, field application and extension activities.
- PMKSY has been formulated amalgamating ongoing schemes viz. Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP) of the Ministry of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation (MoWR,RD&GR), Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP) of Department of Land Resources (DoLR) and the On Farm Water Management (OFWM) of Department of Agriculture and Cooperation (DAC).
The major objective of PMKSY is to –
- Achieve convergence of investments in irrigation at the field level,
- Expand cultivable area under assured irrigation,
- Improve on-farm water use efficiency to reduce wastage of water,
- Enhance the adoption of precision-irrigation and other water saving technologies (More crop per drop),
- Enhance recharge of aquifers and
- Introduce sustainable water conservation practices
Concept of ‘more crop per drop’
- As part of Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) Government of India has been implementing Centrally Sponsored Scheme on Micro Irrigation with the objective to enhance water use efficiency in the agriculture sector by promoting appropriate technological interventions like drip & sprinkler irrigation technologies and encourage the farmers to use water saving and conservation technologies.
- “Per Drop More Crop”, an integral component of PMKSY focuses on maximizing water use efficiency at the farm level. Major activities under Per Drop More Crop can be categorized into “Micro Irrigation” including Drip, Sprinkler, Micro Sprinklers etc; and “Supplementary Water Management Activities (SWMA)/ Other Interventions”.
- SWMA activities include farm level secondary storage structures such as individual or community water storage, Drought proofing structures such as water harvesting or recharge or ground water development, renovation of existing water bodies, enhancing water conveyance efficiency and water lifting devices.
Indian Air Force Inducts Indigenous Airborne Rescue Pod for Isolated Transportation (ARPIT): The Indian Air Force has designed, developed and inducted an Airborne Rescue Pod for Isolated Transportation (ARPIT). This pod will be utilised for evacuation of critical patients with infectious diseases including COVID-19 from high altitude area, isolated and remote places.
- The system has been developed as a lightweight isolation system made from aviation certified material.
- It has a transparent and durable cast Perspex for enhanced patient visibility which is larger, higher and wider than the existing models.
- The isolation system caters for suitable number of air exchanges, integration of medical monitoring instruments, and ventilation to an intubated patient.
- In addition, it generates high constant negative pressure in the isolation chamber for prevention of infection risk to aircrew, ground crew and health care workers involved in air transportation.
Jal Jeevan Mission
Government of India has restructured and subsumed the ongoing National Rural Drinking Water Programme (NRDWP) into Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) to provide Functional Household Tap Connection (FHTC) to every rural household i.e., Har Ghar Nal Se Jal (HGNSJ) by 2024.
Proposed Jal Jeevan Mission will be a decentralised, community-managed and sustainable water management scheme –
- Out of 17.87 crore rural households in the country about 14.6 crore which accounts for 81.67 percent are yet to have household tap connections for water.
- JJM envisages a structural change in the provision of drinking water supply services. The service provision should change to ‘utility based approach’ centered on ‘service delivery’
- The government had also integrated different ministries and departments dealing with water into one ministry — the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
Work to be taken up under JJM:
- In-village water supply (PWS) infrastructure for tap water connection to every household
- Reliable drinking water source development/ augmentation of existing sources
- Transfer of water (multi-village scheme; where quantity & quality issues are there in the local water sources)
- Technological intervention for treatment to make water potable (where water quality is an issue, but quantity is sufficient)
- Retrofitting of completed and ongoing piped water supply schemes to provide FHTC and raise the service level
- Grey water management
- Capacity building of various stakeholders and support activities to facilitate the implementation
73rd Amendment of Constitution of India: Gram Panchayats or its sub-committees will play a crucial role in planning, designing, execution, operations and maintenance of the in-village infrastructure under the Jal Jeevan Mission – Every village is to prepare a village action plan (VAP) which will be essentially having three components namely;
- Water source & its maintenance
- Water supply and
- Grey water management
With women playing a leadership role in managing their community’s water resources, minus the drudgery of walking for miles to fetch water for their families, the Jal Jeevan Mission will provide a massive fillip to the ease of living for women, and they will no longer be beasts of burden.













