IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis

Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
UN Special Rapporteurs on EIA 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Global Groupings & GS-III- Environment
In news
- Recently, a group of Special Rapporteurs to the United Nations (UN) has expressed concerns over the draft Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) notification, 2020.
Analysis of EIA draft, 2020 Part I
Analysis of EIA Draft, 2020 Part II
Key takeaways
- The group has highlighted that the proposed notification appeared to have clauses that obstructed people’s rights to a safe, clean and healthy environment.
- There are clauses which exempt several large industries and projects from the public consultation.
- It does not require publication of information or holding of public consultation for projects labelled by the Central government as ‘involving strategic considerations’.
- It allows for post-facto approval for projects. It means that the clearances for projects can be awarded even if they have started construction or have been running phase without securing environmental clearances.
- The group has sought the government’s response on how the provisions of the notification are consonant with India’s obligations under international law.
Indian Government’s Response
- The Environment Ministry has held that nothing in the proposed EIA, 2020 violates the UN Declaration of Human Rights and that the rapporteurs’ concerns are misplaced.
- It is still a draft and was issued for public consultation.
- The imperfections in the existing EIA would be amended in the new notification.
Do you know?
- Special Rapporteurs are independent experts working on behalf of the UN. They work on a country or a thematic mandate specified by the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC).
Impact of Lockdown on Indian Corporates
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy; Corporate sector
In news
- Recently a credit rating agency analysis looked into the effect of prolonged nationwide lockdown on Indian corporate sector.
Key takeaways
- Around 500 companies were surveyed.
- They have shown aggregate revenues contracting by 31.1% year-on-year basis in the first quarter of Financial Year 2021.
- Sectors which were most-impacted: Consumer-oriented sectors, airlines, hotels, retail, automotive and consumer durables, Industrial and infrastructure-oriented sectors, non-pharma exporters, real estate and construction companies and Banking Sector.
- Sectors which were less impacted: FMCG, consumer foods, IT, telecom, sugar and pharmaceuticals
Significance of Dead Coral Reef
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; Biodiversity
In news
- According to a recent study by researchers from University of Queensland (UQ), Australia, more life can be supported by dead coral remains than live corals.
Key takeaways
- The researchers designed three-dimensional-printed coral stacks called RUbble Biodiversity Samplers (RUBS) to survey cryptic organisms.
- The researchers found the missing link in the coral reef food webs.
- This data fills important knowledge gaps, such as how small cryptic animals support coral reefs from the bottom of the food chain, all the way up to bigger predators
Important value additions
Coral Reefs
- They are large underwater structures composed of the skeletons of colonial marine invertebrates called coral.
- Corals extract calcium carbonate from seawater to create a hard, durable exoskeleton that protects their soft, sac-like bodies.
- These exoskeleton remains of millions of corals pile up with time to form coral reefs.
- The corals have a symbiotic relationship with algae called the zooxanthellae.
- These algae live inside the coral polyp’s body and provide the coral with food. The polyps, in turn, provide a home and carbon dioxide for the algae.
- These algae are responsible for the variety of colours of corals.
Do you know?
- Coral reefs cover less than 1% of the ocean floor but they are among the most productive and diverse ecosystems on Earth.
- They are referred to as “the rainforests of the sea” for their biodiversity,
- When corals become stressed due to any changes, including pollution or global warming, they can expel algae and get bleached, meaning the ‘death’ of the coral reef.
- Dead coral reefs support cryptic organisms like hidden sea creatures, including fishes, snails, tiny crabs and worms, who hide under its rubble to save themselves from predation.

Image source: Click here
Project Dolphin announced
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; Biodiversity
In news
- The Indian Prime Minister had announced the government’s plan to launch a Project Dolphin in his recent Independence Day Speech.
- Aim: To save both river and marine dolphins.
- Implemented by: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Project Dolphin will be on the lines of Project Tiger.

Important value additions
Gangetic Dolphin
- Scientific Name: Platanista gangetica
- These are generally blind.
- They catch their prey by emitting an ultrasonic sound which reaches the prey.
- These are also called Susu.
- It is found mainly in the Indian subcontinent, particularly in Ganga-Brahmaputra-Meghna and Karnaphuli-Sangu river systems and in the Ganga’s tributaries.
- Threats: Construction of dams, Pollution, excessive silting and sand mining.
- It has been recognized by the Indian Government as its National Aquatic Animal
- It is the official animal of the Guwahati, Assam.
- IUCN Status: Endangered
Do you know?
- They are included in Appendix I (most endangered) of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES).
- They are also included in Appendix II of the Convention on Migratory Species (CMS).
- The National Mission for Clean Ganga celebrates 5th October as National Ganga River Dolphin Day.
Ease Banking Reforms Index
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Banking; Economy
In news
- Union Minister of Finance recently inaugurated Doorstep Banking Services by Public Sector Banks (PSBs).
- Best performing banks on EASE Banking Reforms Index were also facilitated.
Key takeaways
- Doorstep Banking Services are part of EASE Reforms.
- It is envisaged to provide convenience of banking services to the customers at their doorstep through the universal touch points of Call Centre, Web Portal or Mobile App.
- Customers can also track their service request through these channels.
- The services shall be rendered by the Doorstep Banking Agents deployed by the selected Service Providers at 100 centres across the country.
- The services can be availed by customers of Public Sector Banks at nominal charges.
Important value additions
EASE 2.0 Banking Reforms Index
- It is a common reform agenda for PSBs.
- Aim: Institutionalizing clean and smart banking.
- Launched in: January 2018.
- PSBs have shown a healthy trajectory in their performance over four quarters since the launch of EASE 2.0 Reforms Agenda.
- Top Performing Banks: (1) Bank of Baroda, (2) State Bank of India, (3) Oriental Bank of Commerce
- Top Improvers: (1) Bank of Maharashtra, (2) Central Bank of India, (3) Corporation Bank.

Climate Smart Cities Assessment Framework (CSCAF) 2.0 launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions & GS-III – Climate change
In news
- Recently, Climate Smart Cities Assessment Framework (CSCAF) 2.0 and ‘Streets for People Challenge’ were launched.
- Ministry: Ministry for Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
Important value additions
Climate Smart Cities Assessment Framework (CSCAF) 2.0
- Objective: (1) To provide a clear roadmap for cities towards combating Climate Change while planning and implementing their actions, including investments; (2) To inculcate a climate-sensitive approach to urban planning and development in India.
- The framework has 28 indicators across five categories namely; (i) Energy and Green Buildings, (ii) Urban Planning, Green Cover & Biodiversity, (iii) Mobility and Air Quality, (iv) Water Management and (v) Waste Management.
- Implemented by: The Climate Centre for Cities under National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA) and MoHUA
Streets for People Challenge
- It is the response to the need for making the cities more walkable and pedestrian friendly.
- It builds on the advisory issued by the MoHUA.
- It will support cities across the country to develop a unified vision of streets for people in consultation with stakeholders and citizens.
- Fit India Mission, under Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports and the India program of the Institute for Transport Development and Policy (ITDP) have partnered with the Smart Cities Mission to support the challenge.
Living Planet Report 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; Climate change
In news
- The WWF’s Living Planet Report 2020 was recently released.
Key takeaways from the Report
- There has been a reduction of 68 % in the global wildlife population between 1970 and 2016.
- 75 % of the Earth’s ice-free land surface has already been significantly altered.
- Most of the oceans are polluted.
- More than 85% of the area of wetlands has been lost during this period.
- The most important cause of biodiversity loss: Land-use change – conversion of pristine habitats into agricultural systems and oceans have been overfished.
- The highest biodiversity loss due to land use change: (1) Europe and Central Asia at 57.9 %; (2) North America at 52.5 %; (3) Latin America and Caribbean at 51.2 %; (4) Africa at 45.9 %; (5) Asia at 43 %.
- The largest wildlife population loss: Latin America at an alarming 94 %.
- One of the most threatened biodiversity: Freshwater biodiversity (declining faster than that in oceans or forests).
Do you know?
- Global mapping has recently revealed the extent to which humans have altered millions of kilometres of rivers.
- India, a “mega diverse country” with over 45,000 species of plants in only 2.4 % of the world’s land area, has already lost six plant species to extinction, according to the IUCN Red List.
Miscellaneous
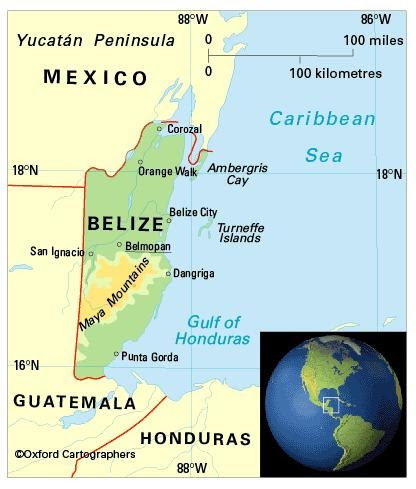
Hurricane Nana
-
Atlantic Hurricane Nana has made a landfall on the coast of Belize.
- The country Belize is located on the northeast coast of Central America.
- Few days back, Hurricane Laura made landfall in south-western Louisiana (South Central United States).
(MAINS FOCUS)
JUDICIARY / GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Structure, organization and functioning of the Judiciary
- Fundamental Rights
Judiciary and Housing Rights of Urban Poor
Context: Supreme Court of India on 31 August 2020 ordered the removal of about 48,000 slum dwellings situated along the railway tracks in Delhi within three months.
The hearing was based on a report filed by the Environment Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority (EPCA), which said Railways is not following the Solid Waste Management Rules.
What are the other directives of SC order?
- The court declared no interference, political or otherwise, should be there against their removal.
- It said any order of interim stay passed by any court against the removal of these encroachment shall be deemed ineffective.
- The court further directed the Railways and local authorities in Delhi to remove plastic waste, garbage, etc, piled up alongside the tracks within three months.
Criticisms of the SC Order
- Court ignores the specific issues of Pollution raised in PIL & proceeds on a tangential topic
-
- The order was passed in the long-running case, M.C. Mehta vs. Union of India & Ors., regarding pollution in Delhi and related report filed by EPCA
- However, neither this case nor the report concerns itself with the legality of informal settlements
- Still, the Court made an unconvincing connection between the piling of garbage and the presence of slums and gave an eviction order
- Court has ignored principles of natural justice
-
- The order violates principles of natural justice and due process since it decided on the removal of jhuggi jhopris without hearing the affected party, the jhuggi dwellers.
- Court ignores judicial precedents on the right to shelter
-
- In Olga Tellis & Ors vs. Bombay Municipal Corporation & Ors. (1985), five-judge bench SC held that the right to life also includes the “right to livelihood” and that no eviction shall take place without notice and hearing those affected
- In Chameli Singh vs. State Of U.P. (1995), the Supreme Court recognised the “right to shelter” as a component of the right to life under Article 21 and freedom of movement under Article 19(1)(e).
- In Ajay Maken & Ors. vs Union Of India & Ors. (2019), a case concerning the demolition of Shakur Basti on railway land, the Delhi High Court invoked the idea of the “Right to the City” to uphold the housing rights of slum dwellers.
- Court has also ignored state policies governing evictions.
-
- In Sudama Singh & Others vs Government Of Delhi & Anr. (2010), the High Court of Delhi held that prior to any eviction, a survey must be conducted and those evicted should have a right to “meaningful engagement” with the relocation plans.
- The procedure laid down in this judgment formed the basis for the Delhi Slum and JJ Rehabilitation and Relocation Policy, 2015, which has not been referred by the court
- Order considered insensitive in the time of Pandemic
-
- The pandemic makes urban informal livelihoods more vulnerable and Supreme Court order threatens to leave lakhs of people homeless amid a health and economic emergency
Way Ahead
- The affected residents would now need to employ a combination of political and legal strategies to protect their housing rights and ensure that no eviction or rehabilitation is conducted without their prior informed consent.
Connecting the dots:
- National Green Tribunal
- Smart City Mission (How City beautification projects are impacting Slum dwellers)
POLITY / GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Autonomous Bodies
Context: The Union textile ministry recently abolished the All India Handicrafts Board, Handloom Board and the Power Loom Board.
The ministry also changed the status of the eight Textile Research Associations to “approved bodies”, instead of the earlier “affiliated bodies”. Thereafter, the government withdrew the officials of the ministry of textiles from the governing bodies of these textile associations.
What are the objectives behind this decision?
- It in consonance with the government’s vision of minimum government, maximum governance
- It is a step in achieving leaner government machinery
- Government through these measures wants to introduce systematic rationalisation of government bodies.
What are Autonomous Bodies(AB)?
- Objective: Autonomous Bodies are set up whenever it is felt that certain functions need to be discharged outside the governmental set up with some amount of independence and flexibility without day-to-day interference of the Governmental machinery.
- Establishment: These are set up by the Ministries/Departments concerned with the subject matter and are funded through grants-in-aid, either fully or partially, depending on the extent which such institutes generate internal resources of their own
- Nature of these Bodies: They are mostly registered as societies under the Societies Registration Act and in certain cases they have been set up as statutory institutions under the provisions contained in various Acts.
- Functions: They are engaged in diverse activities, ranging from formulating frameworks for policies, conducting research, and preserving the cultural heritage, etc. Institutes imparting technical, medical and higher education fall in this category
- Governance: The apex administrative body of ABs is called governing council or governing body and is chaired by the minister or the secretary of the respective ministry.
- Accountability: These Autonomous Bodies are audited by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG), and the annual report is presented in the Parliament every year.
What are the issues of Autonomous Bodies that needs review?
- Extent of Flexibility: Since these bodies are funded by taxpayer’s money, it is argued that they should follow the policies of the government and be accountable the way the government departments are. Others claim that they being “autonomous” have the right to make their own financial and administrative policies
- The exact count of ABs is not known, with estimates ranging from 400 to 650 plus. Then, ABs employ a considerable number. For example, the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, an AB under the ministry of agriculture, has almost 17,000 employees.
- Lacks Uniformity in Recruitment: Unlike the government and PSUs, in which the recruitment rules are uniform and the recruitment is done by a centralised body such SSC, UPSC and the Public Enterprise Selection Board, there is no such body for Central AB recruitments
- Accountability issue: In place of Senior Ministry Officials, Junior officials attend meeting who lack jurisdiction to take meaningful decisions. Also, Some ABs are audited by CAG whereas many are done by chartered accountants.
Way Ahead
- Proper Definition: A legal framework to describe an AB should be drawn up, which defines the boundaries of its working, its autonomy, and the various policies that it must follow.
- Rationalisation of their numbers: ABs that have outlived the cause for which they were established may need to be closed or merged with a similar organisation or their memorandum altered as per the new charter.
- Uniformity in their Policies: In order to bring about uniformity in the policies, a task force needs to be set up under a pan-Indian agency such as SSC or UPSC to streamline the recruitment rules, salary structure, allowance and perks paid to employees, and mode of recruitment.
- Changes in Functioning: To ensure the participation of ministry officials, committee meetings of similar ABs should be held together so that the appropriate authorities could provide meaningful suggestions.
- Performance Audit of AB: CAG had done an exhaustive performance audit of autonomous scientific bodies in 2016, highlighting the gaps in their performance. Such a theme-based audit should be done for other ABs as wel
Connecting the dots:
- Tribunals and their utility
- Regulatory Bodies and their functioning
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following sectors were most impacted by nationwide lockdown due to COVID-19:
- Consumer-oriented
- Pharmaceuticals
- Airline
- Tourism
- Real Estate
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 3 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3, 4 and 5 only
- 2 and 5 only
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Coral reefs:
- Coral Reefs are large underwater structures composed of the skeletons of colonial marine invertebrates called coral.
- The corals have a symbiotic relationship with algae called the zooxanthellae.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Gangetic Dolphin:
- It has been recognized by the Indian Government as its National Aquatic Animal.
- It is the official animal of the Guwahati, Assam.
- Its IUCN Status is Vulnerable
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 2 only
ANSWERS FOR 11th September 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | C |
Must Read
About India-China Five point Consensus:
About US revoking Visa to Chinese Students:
About suspension of Oxford trials:











