IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Property Cards to be distributed under SVAMITVA scheme
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions
In news
- Indian Prime Minister will launch the physical distribution of Property Cards under the SVAMITVA Scheme on October 11, 2020 to transform rural India.
Important value additions
SVAMITVA scheme
- It was launched in April 2020.
- Aim: To provide the record of rights to village household owners in rural areas and issue Property Cards.
- It is being implemented across India in a phased manner over a period of four years.
- It will cover around 6.62 lakh villages
- The launch will enable around 1 lakh property holders to download their Property Cards through the SMS link delivered on their mobile phones.
- This would be followed by physical distribution of the Property Cards by the respective State governments.
- The move will pave the way for using property as a financial asset by villagers for taking loans and other financial benefits.
Nobel Peace Prize For 2020 announced
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Poverty; Hunger; Global Organisations
In news
- The Nobel Peace Prize for 2020 will be given to the World Food Programme (WFP) for its efforts to combat hunger.
Key takeaways
- In 2019, the WFP provided assistance to close to 100 million people in 88 countries who are victims of acute food insecurity and hunger.
- The World Food Programme was an active participant in the diplomatic process that culminated in May 2018 in the UN Security Council’s unanimous adoption of Resolution 2417, which for the first time explicitly addressed the link between conflict and hunger.
Do you know?
- The World Food Programme (WFP) is the food-assistance branch of the United Nations.
- It is the world’s largest humanitarian organization focused on hunger and food security.
- In 2015, eradicating hunger was adopted as one of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals.
- The WFP is the UN’s primary instrument for achieving this goal.
- Founded in: 1961.
- Headquarter: Rome
Contraction in GDP of India in 2020-21: World Bank
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- Recently, the World Bank has released its South Asia Economic Focus report which estimated that India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) can contract by 9.6% for the year 2020-21.
Key takeaways
- This estimate is lower than the earlier forecast of 3.2% contraction which was made in June, 2020 .
- It is due to the impact of the national lockdown against the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Households and small urban service firms experienced income shock .
- The manufacturing and exporting industries may face reduced growth.
- The construction sector may also face slowdown.
- These disruptions to jobs will increase the poverty rate. 2020 rates may go back to levels in 2016.
- The economic slowdown could lead to rising loan non-repayment and risk aversion impacting the financial markets also.
- However, India’s growth is estimated to rebound to 5.4% in 2021-22.
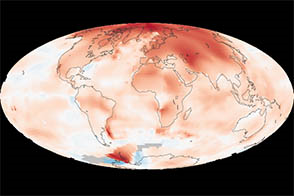
Arctic Amplification phenomenon
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; Climate change
In news
- A team of scientists have identified iodic acid (HIO3) which is driver of new aerosol particle formation in the Arctic.
- This is responsible for Arctic Amplification or Arctic Warming.
- Also, presence of Iodic acid in the region had not been observed previously.
- Over the past 30 years, the Arctic has warmed at roughly twice the rate as the entire globe. This phenomenon is known as Arctic amplification.
- Global warming and climate change are impacting the Arctic more than the rest of the world.
- Changes have become much more pronounced since the 1980s.
Key takeaways
- These aerosol particles influence the formation of clouds.
- These clouds reflect solar radiation which is known as Aerosol Radiative Forcing.
- Also, clouds can retain heat on the Earth’s surface. Thus, they have an influence on the warming of the Arctic.
Reasons for Arctic Amplification
- Change in Albedo: It is a measure of how much light that hits a surface is reflected without being absorbed.
- Changing Ocean currents: Ocean currents normally bring in warmer water from the Pacific, and colder water exits out of the Arctic into the Atlantic. However, such currents may be changing because more melting ice is injecting the Arctic Ocean with freshwater.
- Changing Weather: Ocean currents also drive the polar jet stream, which moves hot and cold air masses around the Northern Hemisphere. This happens due to temperature differences between the Arctic and the tropics. But as the Arctic warms, the jet stream now undulates wildly north and south due to which the Arctic gets warm air.
Do you know?
- There is no Antarctic amplification.
- Antarctic warming is not as alarming as Arctic Warming.
- This is so because Antarctica is surrounded by the vast Southern Ocean, which is soaking up much of the atmosphere’s excess heat.
(MAINS FOCUS)
WOMEN/ GOVERNANCE/ SCIENCE & TECH
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
- Mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections.
Assisted Reproductive Technology Bill – Part II
Context: Union Health Minister introduced the Assisted Reproductive Technology (Regulation) Bill, 2020 (Bill) in the Lok Sabha on September 14.
Click here for Part I (containing elaborate provisions of the Bill)
The ART Bill has shifted to an altruistic model of gamete donation and fails to respond to the needs of the 27 million infertile Indian couples.
Critical Analysis of the provisions of Bill
- Exclusion of segment of society to access ART
- The Bill allows for a married heterosexual couple and a woman above the age of marriage to use ARTs. It excludes single men, cohabiting heterosexual couples and LGBTQI individuals and couples from accessing ARTs.
- This violates Article 14 (Right to Equality) of the Constitution
- It also violates the right to privacy jurisprudence of Puttaswamy case.
- Unlike the Surrogacy Regulation Bill, there is no prohibition on foreign citizens accessing ARTs. Foreigners can access ART but not Indian citizens in loving relationships.
- The egg donor’s interests are subordinated
- The Bill requires an egg donor’s written consent but does not provide for her counselling or the ability to withdraw her consent before or during the procedure (unlike for commissioning parties).
- She receives no compensation or reimbursement of expenses for loss of salary, time and effort.
- Failing to pay for bodily services constitutes unfree labour, which is prohibited by Article 23 of the Constitution.
- The commissioning parties only need to obtain an insurance policy in her name for medical complications or death; no amount or duration is specified.
- Elements of Patriarchy
- The Bill restricts egg donation to a married woman with a child (at least three years old).
- Even here, egg donation as an altruistic act is possible only once a woman has fulfilled her duties to the patriarchal institution of marriage.
- More Safeguards needed with regard to testing of embryos
- The Bill requires pre-implantation genetic testing and where the embryo suffers from “pre-existing, heritable, life-threatening or genetic diseases”, it can be donated for research with the commissioning parties’ permission.
- These disorders need specification or the Bill risks promoting an impermissible programme of eugenics.
- Prior versions of the Bill regulated research using embryos, which must be brought back.
- SRB Bill and ART Bill needs further synchronisation
- Definitions of commissioning “couple”, “infertility”, “ART clinics” and “banks” need to be synchronised between the Bills.
- A single woman cannot commission surrogacy but can access ART.
- Both Bills set up multiple bodies for registration which will result in duplication or worse, lack of regulation (e.g. surrogacy clinic is not required to report surrogacy to National Registry).
- Also, the same offending behaviours under both Bills are punished differently + punishments under the SRB are greater
- Offences under the ART Bill are bailable but not under the SRB.
- Records have to be maintained for 10 years under the ART Bill but for 25 years under the SRB
- Other issues
- Children born from ART do not have the right to know their parentage, which is crucial to their best interests and protected under previous drafts.
- The Bill requires clinics and banks to maintain a grievance cell but these will be one-sided. Clinics must instead have ethics committees.
- Mandated counselling services should also be independent of the clinic.
- The Bill’s prohibition on the sale, transfer, or use of gametes and embryos is poorly worded and will confuse foreign and domestic parents relying on donated gametes.
Conclusion
The Bill raises several constitutional, medico-legal, ethical and regulatory concerns, affecting millions and must be thoroughly reviewed before passage.
Connecting the dots:
- Surrogacy Regulation Bill
- Indian Human Genome Project
HEALTH/ GOVERNANCE/ SOCIETY
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Government policies and interventions for development in Health sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Boosting India’s Mental Health Care Apparatus
Context: From being the neglected and stigmatised domain of health care, mental health has gained significance in the wake of the socio-economic upheaval caused by Covid-19.
What are the myths associated with Mental Health Problems?
- Those who face mental health problems are weak
- Seeking help for mental health issues makes one dependent
- Psychiatric medicines prescribed by Mental Health Doctor are addictive;
- Psychotherapy and counselling can alter people’s thinking instantly.
Do You Know?
- In 2017, there were 197.3 million people with mental disorders, comprising 14·3% of India’s total population
- Mental disorders contributed 4.7% to the total Disability Adjusted Life Years (DALY) in India in 2017 as compared to approximately 2·5% in 1990 (one DALY essentially being one lost year of “healthy” life)
What are the issues associated with mental health care services?
- Low Spending: India spends 1.3% of its health budget on mental health
- Low Accessibility: Access to psychological and social interventions for mental health problems is not available to most people. The treatment gap for mental health is as high as 95%. Treatment, even when available, is largely focussed on medicines
- Inequity in Access to Mental Health Services: The more vulnerable — children, women, homeless, people in conflict areas, those facing identity based discrimination — are the least likely to have access to mental health services.
- Shortage of Manpower: One of the key barriers to access is the lack of mental health human resources. WHO’s Mental Health Atlas in 2017 documents that India has around a total of 25,000 mental health worker for 1.3 billion population
- Inefficient Strategy for developing human resource: These are focussed primarily on training more psychiatrists, clinical psychologists, psychiatric nurses and psychiatric social workers, whose numbers are woefully inadequate.
What Strategy should be used to increase Mental Health Human resources?
India needs to work towards a three-tiered mental health workforce comprising associates, practitioners and specialists.
- Associates
- The associates would be the primary level workers for mental health interventions at the village or urban cluster-level.
- They would make up a new cadre of frontline community mental health workers which can be set up by repurposing the present Accredited Social Health Activist (Asha) cadre or women SHGs
- The mental health associates would be the first point of contact, and would be able to form empathetic relationships, support people in decision-making and work with an individual or a group of individuals under supervision.
- They would also work towards increasing awareness and linking people to crisis intervention and secondary and tertiary mental health services.
- Practitioners
- The next level, practitioners, would form the spine of mental health service delivery and would be graduates with specific training in community mental health.
- Their competencies would include supporting adaptive coping programmes; providing online behavioural and cognitive interventions; supporting care and protection processes in residential and community settings and facilitating informed choices
- These practitioners would also start conversations and galvanise communities around initiatives to challenge stigma and facilitate inclusion.
- Specialists
- The specialists would include the current mental health professionals, but would also strategically allow post-graduates in psychology and social work to upgrade their skills through an advanced diploma in community mental health.
- They will provide leadership, training, tertiary services and supervision.
Conclusion
- If all commissions for women, child care and protection organisations, schools, universities and neighbourhood clinics were to integrate mental health in the services they provide (as required by the law), the need for mental health human resources would be a few hundred thousand skilled professionals.
- The current pandemic should precipitate a disruptive change to lay the foundations for a more comprehensive network of mental health services in India.
Connecting the dots:
- Mental health care Act 2017
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 SVAMITVA scheme is associated with which of the following?
- Issuance of property cards in rural and urban areas.
- Issuance of property cards in rural areas only.
- Issuance of property cards in urban areas only.
- Issuance of property cards to businesswomen in both urban and rural areas.
Q.2 World Food Programme recently won Nobel Peace Prize for 2020 for its efforts to combat hunger. Consider the following statements regarding it:
- It is a private not-for-profit organization.
- It is headquartered in Rome.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Arctic Amplification could be due to which of the following factors?
- Change in weather
- Change in ocean currents
- Increased fishing
- Decrease in biodiversity
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2 and 4 only
ANSWERS FOR 9th October 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
About impending US elections:
About Caste Atrocity in Hathras Rape Case:
About Monetary Policy Committee’s recent meeting:











