IASbaba Daily Prelims Quiz
For Previous Daily Quiz (ARCHIVES) – CLICK HERE
The Current Affairs questions are based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, which are very important sources for UPSC Prelims Exam. The questions are focused on both the concepts and facts. The topics covered here are generally different from what is being covered under ‘Daily Current Affairs/Daily News Analysis (DNA) and Daily Static Quiz’ to avoid duplication. The questions would be published from Monday to Saturday before 2 PM. One should not spend more than 10 minutes on this initiative.
This is a part of our recently launched, NEW INITIATIVE IASbaba’s INTEGRATED REVISION PLAN (IRP) 2020 – Road Map for the next 100 Days! FREE INITIATIVE!
We will make sure, in the next 4 months not a single day is wasted. All your energies are channelized in the right direction. Trust us! This will make a huge difference in your results this time, provided that you follow this plan sincerely every day without fail.
Gear up and Make the Best Use of this initiative.
Do remember that, “the difference between Ordinary and EXTRA-Ordinary is PRACTICE!!”
To Know More about the Initiative -> CLICK HERE
SCHEDULE/DETAILED PLAN – > CLICK HERE
Important Note:
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- After completing the 5 questions, click on ‘View Questions’ to check your score, time taken and solutions.
Test-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
Which of the following countries does not share border with Baltic sea?
Correct
Solution (d)
The countries bounding the Baltic are Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, and Germany. The countries bounding the Baltic are Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, and Germany.
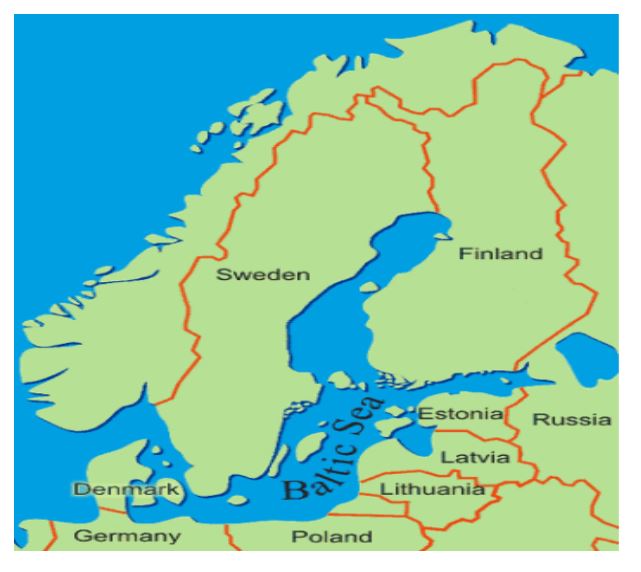 Incorrect
Incorrect
Solution (d)
The countries bounding the Baltic are Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, and Germany. The countries bounding the Baltic are Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, and Germany.

-
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana:
- It is an entitlement-based scheme that targets the beneficiaries as identified by latest Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data.
- National health agency is an implementing body of PMJAY.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- PMJAY offers a sum insured of ? 5 lakh per family for secondary care (which doesn’t involve a super specialist) as well as tertiary care (which does). For the beneficiaries, this is a free scheme.
- It is an entitlement-based scheme that targets the beneficiaries as identified by latest Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data.
- Individuals can walk into any empanelled hospital that can process cashless payments.
- Once identified by the database, the beneficiary is considered insured.
- The insurance cost is shared by the centre and the state mostly in the ratio of 60:40.
- Empanelled hospitals agree to the packaged rates under PMJAY—there are about 1,400 packaged rates for various medical procedures under the scheme.
- These packaged rates also mention the number of average days of hospitalization for a medical procedure and supporting documents that are needed.
- These rates are flexible, but once fixed hospitals can’t change it and under no circumstances can they charge the beneficiary. The scheme also has prescribed a daily limit for medical management.
- National Health Agency has been constituted as an autonomous entity under the Society Registration Act, 1860 for effective implementation of PMJAY in alliance with state governments.
- Inter-alia, this will include, formulation of PMJAY policies, development of operational guidelines, implementation mechanisms, coordination with state governments, monitoring and oversight of PMJAY amongst other.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- PMJAY offers a sum insured of ? 5 lakh per family for secondary care (which doesn’t involve a super specialist) as well as tertiary care (which does). For the beneficiaries, this is a free scheme.
- It is an entitlement-based scheme that targets the beneficiaries as identified by latest Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data.
- Individuals can walk into any empanelled hospital that can process cashless payments.
- Once identified by the database, the beneficiary is considered insured.
- The insurance cost is shared by the centre and the state mostly in the ratio of 60:40.
- Empanelled hospitals agree to the packaged rates under PMJAY—there are about 1,400 packaged rates for various medical procedures under the scheme.
- These packaged rates also mention the number of average days of hospitalization for a medical procedure and supporting documents that are needed.
- These rates are flexible, but once fixed hospitals can’t change it and under no circumstances can they charge the beneficiary. The scheme also has prescribed a daily limit for medical management.
- National Health Agency has been constituted as an autonomous entity under the Society Registration Act, 1860 for effective implementation of PMJAY in alliance with state governments.
- Inter-alia, this will include, formulation of PMJAY policies, development of operational guidelines, implementation mechanisms, coordination with state governments, monitoring and oversight of PMJAY amongst other.
-
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
Which of the following statements is not correct with respect to Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever (CCHF):
Correct
Solution (b)
Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever (CCHF):
- Congo fever was first discovered in Crimea in 1944 and was named Crimean hemorrhagic fever.
- Cause: The CCHF is a widespread disease caused by a tick-borne virus (Nairovirus) of the Bunyaviridae family.
Transmission:
-
- The virus is transmitted through bite of Hyalomma tick, an external parasite, living by feeding on the blood of mammals, birds etc.
- It can also be contracted through contact with viraemic animal tissues (animal tissue where the virus has entered the bloodstream) during and immediately post-slaughter of animals.
- Human-to-human transmission: It can occur resulting from close contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected persons.
- Hospital-acquired infections can also occur due to improper sterilisation of medical equipment, reuse of needles and contamination of medical supplies.
- Fatality: CCHF outbreaks constitute a threat to public health services as the virus can lead to epidemics, with a high case fatality ratio (10-40%).
- Case fatality rate (CFR) is a measure of the severity of a disease and is defined as the proportion of cases of a specified disease or condition which are fatal within a specified time.
- CCHF is endemic in all of Africa, the Balkans, the Middle East and in Asia.
Symptoms:
- Fever, muscle ache, dizziness, neck pain, backache, headache, sore eyes and photophobia (sensitivity to light).
- There may be nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain and sore throat early on, followed by sharp mood swings, confusion, depression and liver enlargement.
Treatment:
- General supportive care with treatment of symptoms is the main approach to managing CCHF in people.
- The antiviral drug ribavirin has been used to treat CCHF infection with apparent benefit.
- There are no vaccines widely available for human or animal use.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever (CCHF):
- Congo fever was first discovered in Crimea in 1944 and was named Crimean hemorrhagic fever.
- Cause: The CCHF is a widespread disease caused by a tick-borne virus (Nairovirus) of the Bunyaviridae family.
Transmission:
-
- The virus is transmitted through bite of Hyalomma tick, an external parasite, living by feeding on the blood of mammals, birds etc.
- It can also be contracted through contact with viraemic animal tissues (animal tissue where the virus has entered the bloodstream) during and immediately post-slaughter of animals.
- Human-to-human transmission: It can occur resulting from close contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected persons.
- Hospital-acquired infections can also occur due to improper sterilisation of medical equipment, reuse of needles and contamination of medical supplies.
- Fatality: CCHF outbreaks constitute a threat to public health services as the virus can lead to epidemics, with a high case fatality ratio (10-40%).
- Case fatality rate (CFR) is a measure of the severity of a disease and is defined as the proportion of cases of a specified disease or condition which are fatal within a specified time.
- CCHF is endemic in all of Africa, the Balkans, the Middle East and in Asia.
Symptoms:
- Fever, muscle ache, dizziness, neck pain, backache, headache, sore eyes and photophobia (sensitivity to light).
- There may be nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain and sore throat early on, followed by sharp mood swings, confusion, depression and liver enlargement.
Treatment:
- General supportive care with treatment of symptoms is the main approach to managing CCHF in people.
- The antiviral drug ribavirin has been used to treat CCHF infection with apparent benefit.
- There are no vaccines widely available for human or animal use.
-
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to Amnesty International:
- It is a global level Inter-governmental Organization which works for Human rights globally
- it was awarded the Nobel Prize for Peace in 1977
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
- It is an international Non-Governmental Organisation (NGO) founded in London (UK) in 1961.
- It seeks to publicize violations by governments and other entities of rights recognized in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948), especially freedom of speech and of conscience and the right against torture.
- In 1977, it was awarded the Nobel Prize for Peace.
- AI India is a part of the global human rights movement spearheaded by Amnesty International. It has its registered office in Bangalore (Karnataka).
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- It is an international Non-Governmental Organisation (NGO) founded in London (UK) in 1961.
- It seeks to publicize violations by governments and other entities of rights recognized in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948), especially freedom of speech and of conscience and the right against torture.
- In 1977, it was awarded the Nobel Prize for Peace.
- AI India is a part of the global human rights movement spearheaded by Amnesty International. It has its registered office in Bangalore (Karnataka).
-
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to geographical location of UAE:
- Tropic of cancer passes below UAE
- UAE shares land border with only two countries
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
The United Arab Emirates is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the west and south and by Oman to the east and northeast.
Tropic of cancer passes through Eight Asian countries they are: Myanmar, Oman, Bangladesh, UAE, Saudi Arabia, India, China, and Taiwan.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
The United Arab Emirates is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the west and south and by Oman to the east and northeast.
Tropic of cancer passes through Eight Asian countries they are: Myanmar, Oman, Bangladesh, UAE, Saudi Arabia, India, China, and Taiwan.











