IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2020 to be held virtually
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Science and technology
In news
- The fourth edition of the India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2020 is scheduled to be held in December.
- It will be held virtually this year given the ongoing pandemic.
- Ministry: Minister of Information Technology
Key takeaways
- Jointly organized by: The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) and Cellular Operators Association of India (COAT).
- The event will see 50+ participating countries, 110 + Global Speakers, Start-ups over the three day programme.
- Theme: “Inclusive Innovation – Smart, Secure, Sustainable”
- IMC is considered the largest Digital Technology Forum in Asia for bringing together the industry, Government, academia, and other ecosystem players to discuss the latest industry technology trends around major themes such as SG, Artificial Intelligence (Al), Internet of things (loT) etc.
Do you know?
- COAI was constituted in 1995 as a registered, non-governmental society.
- Vision: To establish India as the global leader of mobile communications infrastructure, products and services and achieving a national tele density of 100%, including broadband.
All the Electricity Distribution Companies (DISCOMs) to be covered under the Energy Conservation (EC) Act, 2001
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Energy sector
In news
- The Union Ministry of Power, Government of India has issued a notification to cover all the Electricity Distribution Companies (DISCOMs) under the preview of the Energy Conservation (EC) Act, 2001.
Key takeaways
- The notification was formulated in consultation with Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
- According to it, all entities having issued distribution license by State/Joint Electricity Regulatory Commission under the Electricity Act, 2003 (36 of 2003)” are notified as Designated Consumers (DCs).
- After this notification, all the DISCOMs will be governed under the various provisions of EC Act, such as Appointment of Energy Manager, Energy Accounting & Auditing etc. for each DISCOMs.
- Earlier, the DISCOMs whose annual energy losses were equal to or above 1000 MU were only covered as DCs.
- Now with this notification, the number of DISCOMs covered under the EC Act will increase from 44 to 102.
Important value additions
Bureau of Energy Efficiency
- It is a statutory body under the Ministry of Power, Government of India.
- It assists in developing policies and strategies.
- Objective: Reducing the energy intensity of the Indian economy.
Saffron bowl to expand to the North East soon
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I – Geography & GS-III – Agriculture
In news
- The saffron bowl, which was so far confined to Kashmir, may soon expand to the North East of India.
- Plants which were transported from Kashmir to Sikkim, acclimatized there and are now flowering in Yangyang in the Southern part of Sikkim.
Key takeaways
- Saffron production has long been restricted to a limited geographical area in the Union territory of J&K.
- Though the National Mission on Saffron focused on several measures to improve its farming, the measures were still limited to the specified areas of Kashmir.
- North East Centre For Technology Application and Reach (NECTAR), an autonomous body under the Department of Science & Technology, Government of India supported a pilot project to explore the feasibility of growing saffron in North East region of India, with the same quality and higher quantity.
- The Botany and Horticulture department of Sikkim Central University carried out tests to understand the soil and actual pH conditions of Yangyang of Sikkim and found it comparable to saffron growing places of Kashmir.
Important value additions
Saffron
- It is a plant whose dried stigmas (thread-like parts of the flower) are used to make saffron spice.
- Saffron cultivation is believed to have been introduced in Kashmir by Central Asian immigrants around the 1st Century BCE.
- It represents the rich cultural heritage of the J&K region.
- It is a very precious and costly product.
- It is referred to as ‘bahukam’ in ancient Sanskrit literature.
- It is cultivated and harvested in the Karewa (highlands) of J&K.
- Uses: (1) It rejuvenates health; (2) It is used in cosmetics and for medicinal purposes.
- It is usually cultivated during June and July and at some places in August and September.
- Saffron grows well at an altitude of 2000 meters above sea level.
- It needs 12 hours of sunlight.
- It grows in many different soil types but thrives best in calcareous (soil that has calcium carbonate in abundance), humus-rich and well-drained soil with a pH between 6 and 8.
- Temperature: Ranging from 35 or 40 degree Celsius in summer to about –15 or –20 degree Celsius in winter.
- It also requires adequate rainfall that is 1000-1500 mm per annum.
Do you know?
- Pampore region, in India, commonly known as Saffron bowl of Kashmir, is the main contributor to saffron production, followed by Budgam, Srinagar, and Kishtiwar districts.
Denmark records SARS-CoV-2 infections that are associated with farmed minks
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Biodiversity
In news
- Denmark, which has recorded more than 55,000 cases of COVID-19, has also recorded over 200 human cases infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants that are associated with farmed minks.

Important value additions
Mink
- These are dark-colored, semiaquatic, carnivorous mammals.
- Genera: Neovison and Mustela.
- Family: Mustelidae.
- This family also includes weasels, otters and ferrets.
- There are two extant species referred to as “mink”: the American mink and the European mink.
- The European mink is listed by the IUCN as Critically Endangered due to an ongoing reduction in numbers.
Do you know?
- Denmark is the world’s largest mink producer, with a 15-17 million strong mink population across 1,100 farms.
Peace Deal brokered Between Armenia And Azerbaijan
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations; Health
In news
- Russia brokered a new peace deal between Armenia and Azerbaijan.
- The two countries have been in a military conflict for over six weeks over the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh in the South Caucasus.
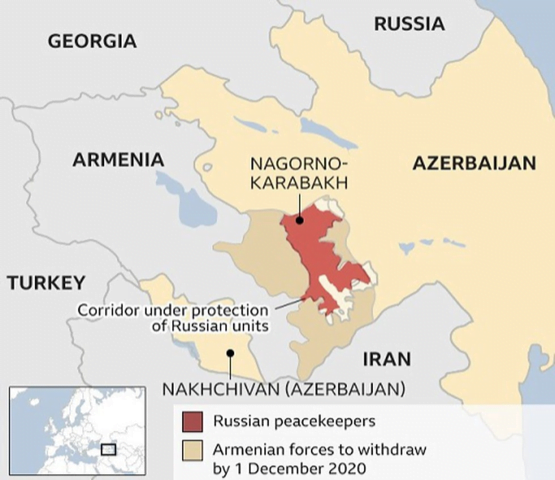
Key takeaways
- As per the new peace deal, both sides will now maintain positions in the areas that they currently hold.
- It means a significant gain for Azerbaijan as it has reclaimed over 15-20% of its lost territory during the recent conflict.
- Further, under this agreement, all military operations are suspended.
- Russian peacekeepers will be deployed along the line of contact in Nagorno-Karabakh and along the Lachin corridor that connects the region to Armenia.
Important value additions
Collective Security Treaty Organisation (CSTO)
- Russia’s role in the conflict has been somewhat opaque since it supplies arms to both countries and is in a military alliance with Armenia called the Collective Security Treaty Organisation (CSTO).
- CSTO is an intergovernmental military alliance that was signed on 15 May 1992.
- In 1992, six post-Soviet states belonging to the Commonwealth of Independent States signed the Collective Security Treaty (also referred to as the “Tashkent Pact” or “Tashkent Treaty”).
- Members: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan.
- Headquarters: Moscow, Russia.
Thirty Meter Telescope
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Science and technology; Space
In news
- 2020 Physics Nobel Laureate Prof. Andrea Ghez had worked closely with Indian astronomers on the design of back-end instruments and possible science prospects of the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) project being installed at Maunakea in Hawaii.
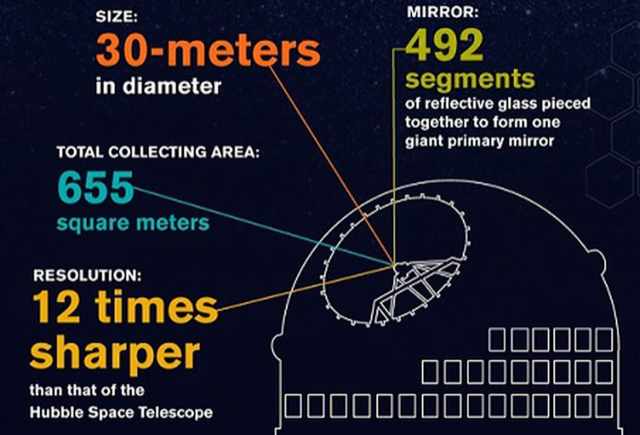
Key takeaways
- TMT project is an international partnership between CalTech, Universities of California, Canada, Japan, China, and India.
- “Thirty Metre” refers to the 30-metre diameter of the mirror, with 492 segments of glass pieced together.
- Once completed, it would be three times as wide as the world’s largest existing visible-light telescope.
- The larger the mirror, the more light a telescope can collect, which means, in turn, that it can “see” farther, fainter objects.
- It would be more than 200 times more sensitive than current telescopes.
- It would be able to resolve objects 12 times better than the Hubble Space Telescope.
- Application: The study of exoplanets
Do you know?
- Already the site of a number of observatories and 13 large telescopes, Mauna Kea is considered sacred by native Hawaiians who believe that such constructions defile the Mauna Kea Mountain.
- If the Thirty Metre Telescope cannot be built on Mauna Kea Mountain in Hawaii, Spain’s Canary Islands is a backup site.
(MAINS FOCUS)
HEALTH/ ECONOMY/ DISASTER MANAGEMENT
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Issues relating to Health and disaster management
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Strengthening public health capacities in disasters
Context: Much of Europe is witnessing a menacing second wave of COVID-19, which is seemingly worse than the first.
Second Wave and Challenges
- Desensitised Public: Living with the pandemic for months together has had a desensitising effect on the collective psyche.
- Reduced Urgency: Owing to such ‘desensitisation’, disasters that are not sudden and striking – like the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic- tend to be minimised.
- Impacting Disaster Management Framework: Unfortunately, the above two has characterised and thus weakened India’s disaster management framework in dealing with many pressing public health issues.
India’s Disaster Management Framework
- In 2005, India enacted the Disaster Management Act(DMA), which laid an institutional framework for managing disasters across the country
- What hitherto comprised largely of reactive, ad hoc measures applied in the event of a disaster, was to be replaced under the Act with a systematic scheme for prevention, mitigation, and responding to disasters of all kinds.
- Disaster management considerations were to be incorporated into every aspect of development and the activities of different sectors, including health.
- The Disaster Management Act is one of the few laws invoked since the early days of COVID-19 to further a range of measures — from imposing lockdowns to price control of masks and medical services.
- Concerns w.r.t Disaster Management Framework: While some headway has indeed been achieved with the enactment of Act, the approach continues to be largely reactive, under-emphasizing of Public Health concern and presence of significant gaps in terms of medical preparedness for disasters.
Experience of using DMA during Pandemic and lessons learnt
- Drawbacks in private sector
- Health services and their continuing development are oblivious to the possibility of disaster-imposed pressures.
- Non-dependability of Private Sector during Crisis times: Since the capping of treatment prices in private hospitals in May, many instances of overcharging by hospitals in India have surfaced, in some cases even leading to suspension of licences.
- Private Sector Significance in future road map of Public Health Policy: Dependability of private sector is important since the future development of hospital care services is being envisaged chiefly under publicly financed health insurance, which would very likely be private-sector led
- Structural Weakness in Private Sector: A large majority of private hospitals in the country are small enterprises which cannot meet the inclusion criteria for insurance. Many of these small hospitals are also unsuitable for meeting disaster-related care needs.
- Incompatibility between Disaster Preparedness and Profit: Disaster preparedness does not make a strong “business case” for hospitals, which prefer to invest in more profitable areas
- Lesson Learnt: Strong public sector capacities are therefore imperative for dealing with disasters. There is a strong case for introducing a legal mandate to strengthen public sector capacities via disaster legislation
- Weakness in DMA
- DMA fails to identify progressive events (which nevertheless cause substantial damage, often more than sudden catastrophes) as disasters, thus neglecting pressing public health issues such as tuberculosis and recurrent dengue outbreaks
- Had they been identified as disasters, they would have attracted stronger action in terms of prevention, preparedness, and response
- Inadequate Integration with primary care: Primary care stands for things such as multisectoral action, community engagement, disease surveillance, and essential health-care provision, all of which are central to disaster management. This area of disaster management, especially relevant for low-income setting, has been overlooked.
- Lesson Learnt: Making primary health care central to disaster management can be a significant step towards building health system and community resilience to disasters. Also, synergies with the National Health Mission with the Disaster Management Act in 2005, could be worth exploring.
Conclusion
- While the novel coronavirus pandemic has waned both in objective severity and subjective seriousness, valuable messages and lessons lie scattered around. It is for us to not lose sight and pick them up.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 India Mobile Congress is jointly organised by which of the following?
- Department of Telecommunications
- Cellular Operators Association of India
- Council of Scientific & Industrial Research
- Both (a) and (b)
Q.2 Saffron plants were recently transported from J&K to one of the North eastern regions of India where they acclimatized and flowered. Where were the plants transported?
- Sikkim
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Tripura
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding growth conditions of Saffron:
- It needs 8 hours of daily sunlight.
- It grows well only in summer.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 10th November 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | A |
Must Read
About 15th Finance Commission’s report:
About India and COVID-19 vaccine:
About Central Bank Policy and Judicial Review:











