IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis

Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
India’s First Green Energy Convergence Project
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment
In news
- Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), a joint venture of PSUs under the Ministry of Power and Department of New & Renewable Energy (DNRE), Goa, have signed a MOU to implement India’s first Convergence Project in the State.
Key takeaways
- Under the MoU, EESL and DNRE will carry-out the feasibility studies and subsequent implementation of decentralized solar energy projects.
- EESL shall implement the solar energy projects including; (1) establishment of 100 MW of decentralized ground mounted Solar Power projects on government lands to be used for agricultural pumping; (2) replacing approximately 6,300 agricultural pumps with BEE star rated energy efficient pumps; (3) distribute approximately 16 Lakh LED bulbs for rural domestic households.
- The projects will accelerate the usage of renewable energy sources, especially for agricultural and rural power consumption in the State.
7th round of Foreign Office Consultations between India and Kazakhstan held
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- The 7th round of Foreign Office Consultations between India and Kazakhstan was held recently.
Key takeaways
- During the consultations, the two sides reviewed the entire scope of bilateral cooperation within the framework of their Strategic Partnership.
- The consultations covered political, economic and commercial, energy, defence, space, consular and cultural matters.
- A MoU on “Indian Grant Assistance for Implementation of High Impact Community Development Projects in Kazakhstan” was signed.
Indian Army rejects report on Microwave Weapons
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- The Indian Army has rejected a report which claimed that the Chinese army had used microwave weapons to drive Indian soldiers away from their positions in eastern Ladakh.
Key takeaways
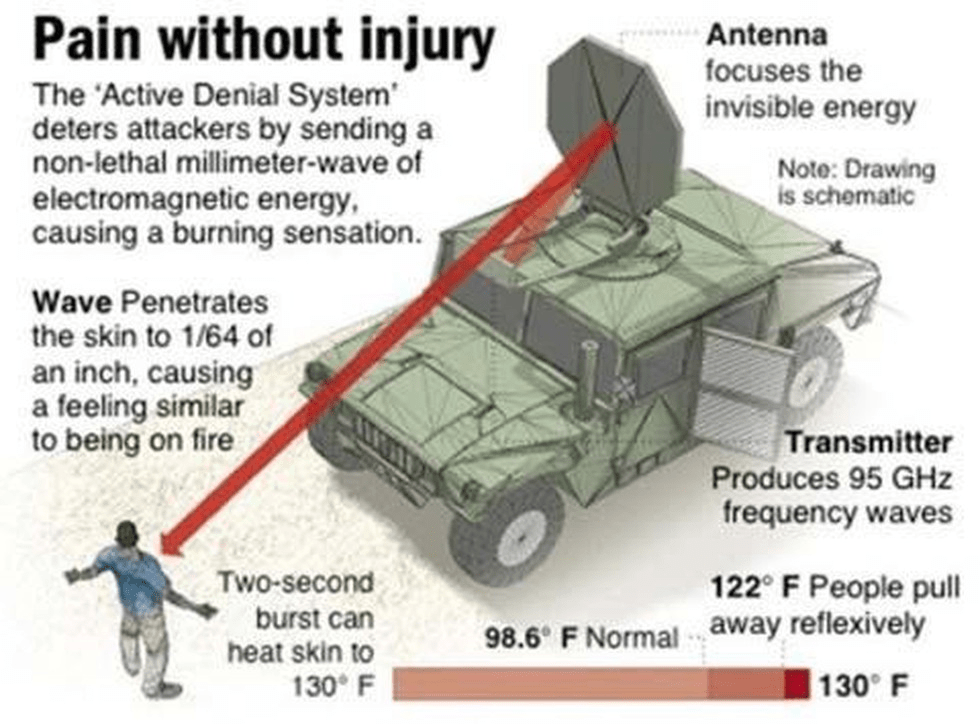
- These are supposed to be a type of direct energy weapons.
- They aim highly focused energy in the form of sonic, laser, or microwaves, at a target.
- They use beams of high-frequency electromagnetic radiation to heat the water in a human target’s skin, causing pain and discomfort.
- A number of countries are thought to have developed these weapons to target both humans and electronic systems.
- Concerns have been raised on whether they can damage the eyes, or have a carcinogenic impact in the long term.
Do you know?
- China had first put on display its “microwave weapon”, called Poly WB-1, at an air show in 2014.
- The United States has also developed a prototype microwave-style weapon, which it calls the “Active Denial System”.
- The US apparently deployed such a weapon in Afghanistan, but withdrew it without ever using it against human targets.
Important value additions
- In a microwave oven, an electron tube called a magnetron produces electromagnetic waves (microwaves) that bounce around the metal interior of the appliance, and are absorbed by the food.
- The microwaves agitate the water molecules in the food, and their vibration produces heat that cooks the food.
- Foods with high water content cook faster in a microwave often than drier foods.
Capacity building component of PM-FME Scheme inaugurated
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- Union Minister for Food Processing Industries inaugurated the capacity building component of the Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises scheme (PM-FME Scheme).
Important value additions
PM-FME Scheme
- It was launched under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme.
- Aim: (1) To enhance the competitiveness of existing individual micro-enterprises in the unorganized segment of the food processing industry; (2) To promote formalization of the sector; (3) To provide support to Farmer Producer Organizations, Self Help Groups, and Producers Cooperatives along their entire value chain.
- Vision: To directly assist the 2,00,000 micro food processing units for providing financial, technical, and business support for upgradation of existing micro food processing enterprises with an outlay of Rs. 10,000 crore over a period of five years from 2020-21 to 2024-25.
GIS One District One Product (ODOP) Digital Map Of India
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The Ministry of Food Processing launched the GIS One District One Product (ODOP) digital map of India.
Key takeaways
- The digital ODOP map provides detailed information about ODOP products to all states and facilitates the stakeholders.
- The digital map also has indicators for tribal, SC, ST, and aspirational districts.
- It will enable stakeholders to make concerted efforts for its value chain development.

Miscellaneous
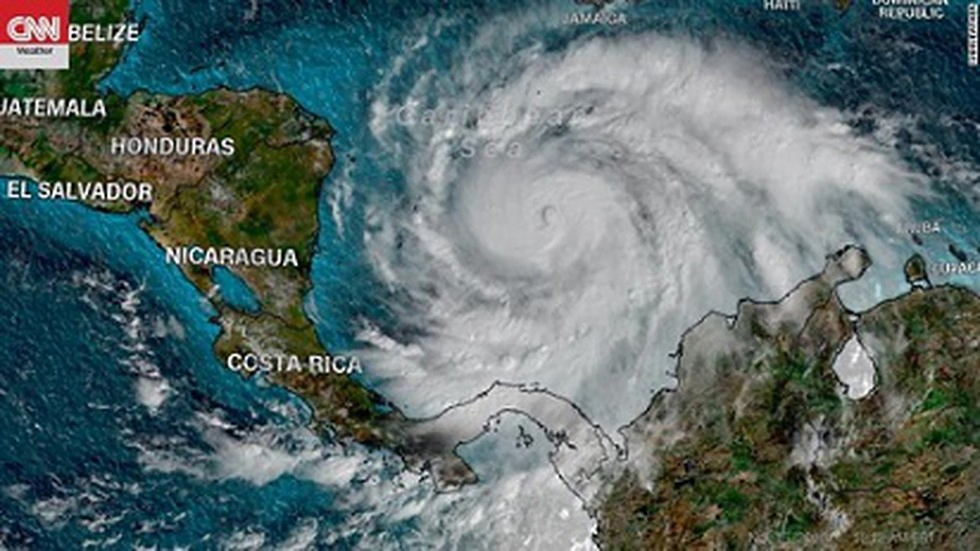
Hurricane Iota
- Hurricane Iota made landfall in Nicaragua in Central America recently.
- It developed into a category five storm.
- The Atlantic Hurricane season runs from June to November and covers the Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico.
- The Eastern Pacific Hurricane season runs from May 15 to November 30.

Tropical cyclones or hurricanes
- Such Cyclones use warm, moist air as fuel.
- Therefore, they form over warm ocean waters near the equator.
- The tropical cyclones that form over the Atlantic Ocean or the eastern Pacific Ocean are called hurricanes.
- The ones that form in the Northwest Pacific are called typhoons.
- Tropical storms that form in the Bay of Bengal or the Arabian Sea are called cyclones.
- Hurricanes are categorised on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, which rates them on a scale of 1 to 5 based on wind speed.
- Hurricanes that reach category three or higher are called ‘major hurricanes’ because of their potential to cause devastating damage to life and property.
(MAINS FOCUS)
FEDERALISM/ SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure
- Internal Security
Unrest along Assam-Mizoram border
Context: The recent violence and tension on the Assam-Mizoram border underlines the differences the two States have about their borders.
Do You Know?
- In 1972 Mizoram was carved out of Assam as a Union Territory.
- Mizoram became a State in 1987.
- National Highway 306 (Earlier NH 54) connects the State of Assam and Mizoram.
- Mizoram ferries all its essentials, food grains, transport fuel and various other goods and machines through NH 306 and hence is called the lifeline of Mizoram
What triggered the unrest?
- Three districts of southern Assam’s Barak Valley — Cachar, Hailakandi and Karimganj — border Kolasib and Mamit districts of Mizoram.
- On October 9, a farm hut and a betel nut plantation belonging to two Mizoram residents were set on fire in an area bordering Karimganj (Assam) and Mamit districts(Mizoram)
- Some people from Assam allegedly pelted stones at Mizoram police personnel the following day and Mizoram residents retaliated.
- Assam-based organisations blocked NH306 and other roads leading to Mizoram. The blockade was lifted on October 22 after negotiations between the two States and intervention by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- But Mizoram police’s refusal to withdraw from the disputed areas led to another blockade from October 28.
- The situation threatened to get out of control when an Assamese man named Imtiaz Ali Laskar died in custody in Mizoram. While Mizoram claimed he was a drug peddler, Assam said he was a poor firewood collector.
Has the tension eased now?
- The tension eased when personnel of the Border Security Force and Sashastra Seema Bal began patrolling three flashpoints on the border.
- The blockade was lifted on November 9.
Was it a one-off conflict?
- No. The last instance of violence along the Assam-Mizoram border was in February 2018, when the Mizo Zirlai Pawl (students’ union) had built a wooden rest-house for farmers in a forest.
- Assam police and forest officials demolished the structure, claiming it was in Assam’s territory.
- Members of Mizo Student’s union clashed with Assam police personnel, which led to the escalation of tensions. The scale of the violence was larger than earlier intermittent conflicts along the border.
Is there any other border conflict of Mizoram?
- Mizoram has also had border issues with Tripura, particularly over claims and counter-claims over Phuldungsei village in North Tripura district.
- The Phuldungsei issue, involving a bid to reconstruct an old temple by the Bru tribal people, had flared up almost at the same time as the 2020 Oct blockade.
What is the genesis of the trouble?
| Assam’s argument | Mizoram’s Argument |
| Authorities in Assam say the contested land belongs to Assam according to revenue records. | Authorities from Mizoram said people from Assam violated the status quo – as agreed upon between the two State governments a few years ago – in “no man’s land” to trigger the present crisis. |
| Officials and locals in Assam claim Mizos have been squatting in areas 1-3 km from the inter-State border. | Mizoram groups disagree, claiming that the authorities in Assam have been using “illegal Bangladeshis” to move 10-12 km inside their territory |
| Assam follows British-era notification of 1933 for demarcation of boundaries. | Mizo leaders say this 1933 notification is not acceptable as their ancestors had not been consulted.
Mizoram insists that the boundary should be demarcated on the basis of a notification in 1875 that distinguished the Lushai Hills (present-day Mizoram and erstwhile district of Assam) from the plains of Cachar. The notification is derived from the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation Act, 1873 that makes it obligatory for Indians from outside to possess a travel document to enter Mizoram. |
Are there other boundary issues in the northeast?
- Assam has had boundary problems with all its north-eastern neighbours, except Manipur and Tripura that had existed as separate entities.
- State Reorganisation Post Independence: The primary reason is that the other States, which were all part of Assam during the British rule, have contested the boundaries since they separated from Assam and became full-fledged States over a period of time (Nagaland Statehood in 1963; Meghalaya, Tripura & Manipur Statehood in 1971; Arunachal Pradesh & Mizoram Statehood in 1987)
- Constitutional Solution Vs Historical grounds: Assam has accepted several recommendations of border commissions set up by the Supreme Court, but other States have been sticking to “historical boundaries” that go back to the period before 1826, when the British annexed undivided Assam and included the hills as its provinces.
- Issue of Nagaland: The Nagaland government has been insisting that a 16-point agreement of 1960, which led to the creation of Nagaland, also included “restoration” of all Naga territories that had been transferred out of the Naga Hills after the British annexed Assam in 1826.
- Issue of Meghalaya: Meghalaya has challenged the Assam Reorganisation Act of 1971, claiming that two blocks in Assam’s Karbi Anglong district belonged to the erstwhile United Khasi and Jaintia Hills created in 1835.
- Assam’s point of view: Assam says its neighbours have encroached upon more than 75,000 hectares of land. Revenue records of the Assam government say Nagaland has encroached upon 19,819.62 hectares, Arunachal Pradesh 5,756.02 hectares and Meghalaya 65.62 hectares since 2001.
Way Forward
- Burden borne by common man: The border residents will continue to bear the brunt of the unrest unless an acceptable solution is arrived at.
- Joint patrolling by police personnel of both the States with Central forces along the inter-State border.
- Maintaining Peace & Order: Apart from drawing up the standard operating procedure for guarding the contentious boundary, state governments need to strengthen coordination between the Superintendents of Police of the border districts for prompt action against criminals and anti-social activities that add to the border tension.
Connecting the dots:
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Lakshmi Vilas Bank (LVB) Crisis
Context: After the failures of IL&FS, Punjab & Maharashtra Cooperative Bank and DHFL, and the bailout of Yes Bank, the RBI has now decided to impose a 30-day moratorium on Lakshmi Vilas Bank Ltd (LVB).
RBI has also put in place a draft scheme for amalgamation of LVB with DBS Bank India, a subsidiary of DBS of Singapore and has raised concerns about the safety of the financial system.
Why was LVB put under moratorium and amalgamated with DBS Bank?
- Continuous Losses: The RBI said the financial position of the Chennai-based LVB, which has a network of 563 branches and deposits of Rs 20,973 crore, has undergone a steady decline, with continuous losses over the last three years eroding the bank’s net-worth. LVB posted a net loss of Rs 397 crore in the September quarter of FY21, as against a loss of Rs 112 crore in the June quarter
- Rising NPAs: Serious governance issues in recent years have led to deterioration in its performance. Almost one fourth of the bank’s advances have turned bad assets. Its gross non-performing assets (NPAs) stood 25.4% of its advances as of June 2020, as against 17.3% a year ago.
- Low Liquidity: It was also experiencing continuous withdrawal of deposits and low levels of liquidity.
- Unable to raise Capital: The bank has not been able to raise adequate capital to address these issues. The bank management had indicated to the RBI that it was in talks with certain investors, but failed to submit any concrete proposal
Are depositors and the financial system safe?
- Assurance & Insurance by RBI: The RBI, which put a cap of Rs 25,000 on withdrawals, has assured depositors of the bank that their interest will be protected. One safety net for small depositors is the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC), an RBI subsidiary, which gives insurance cover on up to Rs 5 lakh deposits in banks.
- Amalgamation will prevent further slide: The combined balance sheet of DBS India and LVB would remain healthy after the proposed amalgamation, with Capital to Risk Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) at 12.51% and Common Equity Tier-1 (CET-1) capital at 9.61%, without taking into account the infusion of additional capital.
Rising Crisis in Banking Sector
- The collapse of IL&FS in 2018 had set off a chain reaction in the financial sector, leading to liquidity issues and defaults
- Punjab & Maharashtra Co-op Bank was hit by a loan scam involving HDIL promoters and the bank is yet to be bailed out.
- The near-death experience of Yes Bank in March 2020 sent jitters among depositors. The RBI bailed out Yes Bank through a scheme backed by State Bank of India and other banks.
- Shareholders of LVB and Dhanlaxmi Bank recently firing their chief executive officers in the span of a week.
What happens to investors in these banks?
- Bad Experience for Yes Bank Investors: Shareholders in Yes Bank faced a significant erosion in wealth as the stock price crashed below Rs 10 per share from a peak of Rs 400 per share
- Near total loss for existing shareholders of LVB: In the case of LVB, equity capital is being fully written off. This means existing shareholders face a total loss on their investments unless there are buyers in the secondary market who may ascribe some value to these.
- In its draft scheme for the amalgamation, the RBI said that “On and from the appointed date, the entire amount of the paid-up share capital and reserves and surplus, including the balances in the share/securities premium account of the transferor bank, shall stand written off.”
Issues facing old-generation private banks- Lack of strong promoters
- The functioning of many such banks has been under scrutiny in the last couple of years, as most of them do not have strong promoters, making them targets for mergers or forced amalgamation.
- Two other South-based banks – South Indian Bank and Federal Bank – have been operating as board-driven banks without a promoter.
- In Karur Vysya Bank, the promoter stake is 2.11% and in Karnataka Bank, there’s no promoter.
- The problems in LVB follow the similar challenges faced by Yes Bank as well as Punjab & Maharashtra Co-operative Bank in recent times.
What has been the regulatory response to these failures?
- On July 24, 2004, the RBI, then headed by Y V Reddy, announced a moratorium on private sector lender Global Trust Bank, which was then reeling under huge losses and bad loans. The bank was merged with public sector Oriental Bank of Commerce within 48 hours under an RBI-led rescue plan.
- Nearly 16 years later, the RBI has followed a somewhat similar approach on resuscitation of the troubled lenders of Yes Bank and now LVB.
- The moratorium announcement was followed by a reconstruction plan for Yes Bank and capital infusion by banks and financial institutions, with SBI, ICICI Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank, HDFC, Axis Bank and others putting in equity capital in the reconstructed entity.
Will loan stress caused by the pandemic impact the banking system?
- Business Cycle disrupted: NPAs in the banking sector are expected to increase as the pandemic affects cash flows of people and companies.
- Differential Impact of Pandemic on Sectors: However, the impact will differ depending upon the sector, as segments like pharmaceuticals and IT seem to have benefited in terms of revenues. NPA accretion in cash-rich sectors like IT, pharmaceuticals, FMCG, chemicals, automobiles is expected to be smaller when compared to areas like hospitality, tourism, aviation and other services.
- K V Kamath Committee recently came out with recommendations on the financial parameters required for a one-time loan restructuring window for corporate borrowers under stress due to the pandemic.
Conclusion
- While banking observers agree that the RBI has acted whenever a bank or an NBFC faced trouble, the question remains whether it made the interventions swiftly.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in the comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in the next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements:
- Tropical cyclones that form over the Eastern Pacific Ocean are called typhoons.
- Tropical cyclones that form over the Northwest Pacific Ocean are called hurricanes.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 India’s first green energy conversions project will be implemented in which of the following state of India?
- Goa
- Rajasthan
- Himachal Pradesh
- Odisha
Q.3 GIS one district one product digital map of India was recently launched by which of the following Ministry?
- Ministry of Food Processing
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium enterprises
- Ministry of Science and Technology
ANSWERS FOR 18th November 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | D |
Must Read
About New Challenges: India and Joe Biden:
About Urban Planning and disease spread:
About Myanmar’s election results:











