IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Himachal Pradesh government trying to obtain GIs for products native to the State
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – GI tags
In news
- The Himachal Pradesh government is trying to obtain GIs (Geographical Indication) tags for five products from the state.
- These are Karsog Kulth, Thangi of Pangi, Chamba Metal Crafts, Chamba Chukh, and Rajmah of Bharmour.
Key takeaways
- Karsog Kulth: Kulthi or Kulth (horse gram) is a legume grown as a kharif crop in Himachal Pradesh. Kulth grown in the Karsog area of Mandi district is believed to be particularly rich in amino acids.
- Pangi ki Thangi: It is a type of hazelnut which grows in Pangi valley located in the north-western edge of Himachal. It is known for its unique flavour and sweetness.
- Chamba metal crafts: These include items such as metal idols and brass utensils which were made by skilled artisans in the courts of kings of Chamba.
- Chamba Chukh: It’s a chutney made from green and red chillies grown in Chamba, and prepared in traditional and unique ways.
- Bharmouri Rajmah: It’s more specifically called the Kugtalu Rajmah, since it grows in the area around Kugti Pass in the Bharmour region of Chamba district. It is rich in proteins and has a unique flavour.
Do you know?
- Himachal pradesh currently has GI tags in four handicrafts (Kullu Shawl, Chamba Rumal, Kinnauri Shawl and Kangra Paintings), three agricultural products (Kangra Tea, Basmati and Himachali Kala Zeera) and one manufactured product (Himachali Chulli Oil).
Petroleum Board’s notifies New Unified Tariff Structure
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) has notified a new tariff structure for 14 natural gas pipelines.
- The aim is to reduce the cost of natural gas for users further away from sources of natural gas and LNG terminals on the west coast of the country.
Key takeaways
- Under the new unified tariff structure, buyers will be charged a fixed tariff for the transport of gas within 300 kms of a source and a fixed tariff for the transport of gas beyond 300 kms on a single pipeline network.
- This would be significantly cheaper for buyers further away from the source of gas who were earlier charged on the basis of the number of pipelines used and the distance from the source of gas.
- Therefore, a buyer using multiple pipelines would likely benefit significantly from this change.
- The changes in the tariffs will likely incentivise greater investment into gas transmission infrastructure as natural gas becomes more affordable for users further away from the west coast of the country.
Do you know?
- The Indian government is aiming to boost the consumption of natural gas which currently accounts for 6.2% of India’s energy basket to 15% by 2030.
Ayush Export Promotion Council to be set up
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions; Health & GS-III – Trade
In news
- Ministry of Commerce and Industry and Ministry of AYUSH have decided to set up an AYUSH Export Promotion Council to boost AYUSH exports.
Key takeaways
- Both Ministries will work together for establishing an AYUSH Export Promotion Council (AEPC).
- The proposed AEPC can be housed at Ministry of AYUSH.
- Standardisation of HS code for AYUSH will be expedited.
- Ministry of AYUSH will work in collaboration with Bureau of Indian standards to develop international standards for AYUSH products as well as services.
- AYUSH industry will work on ensuring quality and standards of AYUSH products as well as to become price-competitive.
- AYUSH will also figure in the Brand India activities.
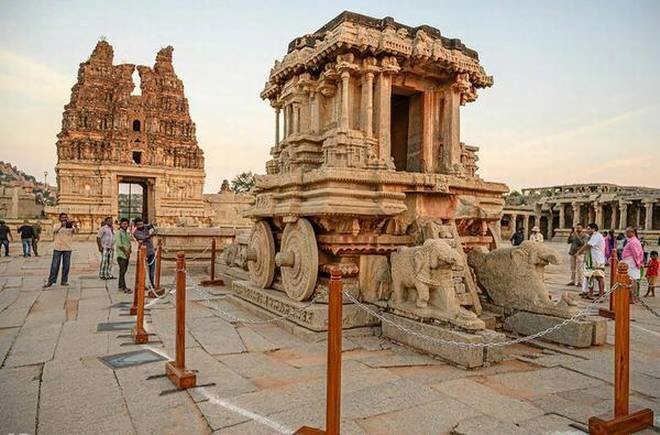
Hampi Stone Chariot
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I – Temple and Architecture
In news
- The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has taken steps to protect the stone chariot inside Vittala Temple complex at the UNESCO World Heritage site of Hampi, Karnataka.
- Tourists can no longer get too close to the iconic stone chariot.

Important value addition
Hampi chariot
- The chariot inside the temple complex is a shrine dedicated to Garuda, but the sculpture of Garuda is now missing.
- The Hampi chariot is one among the three famous stone chariots in India.
- The other two are in Konark (Odisha) and Mahabalipuram (Tamil Nadu).
- It was built in the 16th century by the orders of King Krishnadevaraya, a Vijayanagara ruler.
- The delicately carved chariot at Hampi reflects skill of temple architecture under the patronage of Vijayanagara rulers who reigned from 14th to 17th century CE.
Vittala Temple
- It was built in the 15th century during the rule of Devaraya II, one of the rulers of the Vijayanagara Empire.
- It is dedicated to Vittala.
- Vittala is said to be an incarnation of Lord Vishnu.
- Dravidian style adorns the built of the complex, which is further enhanced with elaborate carvings.
Moolamylliang recovers from rat-hole mining
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I – Key natural resources & GS-III – Environment
In news
- Moolamylliang, a village in Meghalaya’s East Jaintia Hills district, is making progress in becoming a greener place amid abandoned pits from the rat-hole mining.
Key takeaways
- National Green Tribunal (NGT) banned hazardous rat-hole coal mining in Meghalaya in April 2014 and set a time limit for transporting the coal already mined till that time.
- The Jaintia Coal Miners and Dealers’ Association claims there are some 60,000 coal mines across 360 villages in East Jaintia Hills district.
- Moolamylliang used to be one such village until the National Green Tribunal’s ban.
Do you know?
- Rat-hole Mining is a term used for a hazardous and arduous mining technique where miners crawl into winding underground tunnels that are just 4-5 feet in diameter to extract coal from the deep seams with a pickaxe.
IRDAI standardises health policies for Robotic and bariatric surgeries
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions; Health & GS-III – Trade
In news
- The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has standardised all health policies to include robotic and bariatric surgeries as well.
Key takeaways
- Robotic surgery holds significant promise in the field of healthcare.
- The introduction of such surgeries has made the performance of complicated procedures much easier.
- They allow doctors to perform different types of complex procedures with more precision, flexibility, and control.
- The benefits of such procedures in India come at a lower cost than in developed nations, making it easily accessible to a larger section of the population.
- Robotic surgeries reduce the trauma caused to the patient by allowing surgery to be performed through small ports or ‘keyholes’ rather than via large incisions.
- The instruments can access hard-to-reach areas of a patient’s body more easily through smaller incisions compared with traditional open and laparoscopic surgeries.
- This helps in shorter recovery times, with fewer complications and a shorter hospital stay.
- They are minimally invasive, painless and have a bigger cosmetic advantage.
- Lower cost of the surgery would mean lower premium to be paid for such cover, too.
Do you know?
- Bariatric surgery is an operation that helps lose weight by making changes to the digestive system.
- Insurance Regulatory Development Authority of India (IRDAI) is a regulatory body created with the aim of protecting the interests of the insurance customers.
- It regulates and sees to the development of the insurance industry while monitoring insurance-related activities.
Jupiter and Saturn to be seen in Great Conjunction
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Sci & Tech
In news
- In a rare celestial event, Jupiter and Saturn will be seen very close to each other (conjunction) on 21st December 2020, appearing like one bright star.
Key takeaways
- Conjunction occurs when two celestial bodies visually appear close to each other from Earth.
- Astronomers use the term great conjunction to describe meetings of the two biggest worlds in the solar system, Jupiter and Saturn.
- It happens about every 20 years.
- The conjunction is the result of the orbital paths of Jupiter and Saturn coming into line, as viewed from Earth.
- Jupiter orbits the sun about every 12 years, and Saturn about every 29 years.
- It will be the closest alignment of Saturn and Jupiter since 1623, in terms of distance.
- The next time the planets will be this close is 2080.
- They will appear to be close together, however, they will be more than 400 million miles apart.
(Mains Focus)
GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources
DUET (Decentralised Urban Employment and Training) for urban areas
Context
- There is a crisis of employment in the urban informal sector, as millions of workers have lost their job due to periodic lockdowns, and may or may not retrieve it soon.
- Our public institutions and public spaces (schools, colleges, health centres, bus stands, jails, shelters, hostels, parks, museums, offices, etc.) have a chronic problem of poor maintenance.
- There is growing interest in an employment guarantee act, but little experience of relief works in urban areas. Decentralised Urban Employment and Training’ (DUET) could act as a step towards urban employment guarantee.
The basic idea of DUET
- The state government issues ‘job stamps’ and distributes them to approved institutions – schools, colleges, government departments, health centres, municipalities, neighbourhood associations, urban local bodies, etc
- Each job stamp can be converted into one person-day of work within a specified period, with the approved institution arranging the work
- Wages, paid by the government, would go directly to the workers’ accounts against job stamps certified by the employer.
- Employees are to be selected from a pool of registered workers by the approved employer, or, by an independent ‘placement agency’ (to avoid collusion)
What is the role of the placement agency?
- The primary role of the placement agency is to assign registered workers to approved employers as and when required. But it could also serve other purposes, for example, certifying workers’skills, protecting workers from exploitation and arranging social benefits for them.
- Various options could be considered for the placement agency, such as: (1) a single agency for the municipality, run by the local government; (2) a worker cooperative; (3) multiple placement agencies, run as non-profit organisations or cooperatives.
Precedents
- Some countries have employment-subsidy schemes of similar inspiration, e.g. “service voucher schemes” (SVS) in several European countries.
- Belgium has a very popular SVS for domestic services such as cleaning and ironing. It was used by 1 out of 5 households in 2016.
- The service vouchers are much like job stamps, except that they are used by households instead of public institutions, for the purpose of securing domestic services such as cooking and cleaning.
- The service vouchers are not free, but they are highly subsidised, and households have an incentive to use them since that is a way of buying domestic services very cheap.
- In the DUET scheme, the use of job stamps relies on a sense of responsibility among the heads of public institutions, not their self-interest.
How is DUET different from MGNREGA?
- It is meant to create a lasting institution as an antidote to urban unemployment and urban decay.
- The motivation for DUET is quite different from that for MNREGA. MNREGA offers insurance to rural workers in a slack season or in a drought year when agricultural jobs disappear. That is not the case of urban production.
What is the rationale/merits of DUET?
- Job Creation: Activating a multiplicity of approved employers will help to generate a lot of employment.
- Activating a multiplicity of potential employers: The approved employers will have a stake in ensuring that the work is productive.
- Efficient: The scheme requires little staff of its own since existing institutions are the employers. The Scheme thus avoids the need for special staff, facilitating productive work.
- Avoids Leakages: Workers are assured of timely payment at the minimum wage as it involves direct payment of wages using JAM trinity.
- Towards employment guarantee: It would be relatively easy to move from DUET towards demand-driven ’employment guarantee’. That would require the municipality to act as a last-resort employer, committed to providing work to all those who are demanding work
- Urban Infrastructure Creation: Urban areas could use some infrastructure and there is under utilised labour but there are no resources to use this labour to build the infrastructure. DUET may be one way to solve this problem
What are the precautions that one needs to take to make DUET a success?
- Permissible List of Works: To avoid abuse, the use of job stamps could be restricted to a list of permissible works. But the list should be fairly comprehensive, and not restricted to maintenance.
- Avoid Displacement of Existing Jobs: The list of works should not be so broad as to displace existing jobs in public institutions.
- Ensure Worker Safety: All DUET employment should be subject to worker safety and welfare norms specified in the scheme and existing labour laws.
- Equity in worker registration: All urban residents above the age of 18 should be eligible to register under DUET, but special registration drives or placement agencies could be located in low-income neighbourhoods.
- Integrate Skilling: The scheme would cover both skilled and unskilled workers. Whenever a skilled worker is employed, an assistant (unskilled) worker could be mandatorily employed as well, to impart an element of training and skill formation to the scheme.
- Giving priority to women would have two further merits. First, it would reinforce the self-targeting feature of DUET, because women in relatively well-off households are unlikely to go (or be allowed to go) for casual labour at the minimum wage. Second, it would promote women’s general participation in the labour force.
- Needs Independent Monitoring: An independent authority could be appointed or designated at the municipal level to monitor, inspect, audit and evaluate the works.
Conclusion
The scheme should be given a chance by way of a pilot scheme in select districts or even municipalities.
INTERNATIONAL /SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Important International Events.
- Security and its challenges
France’s New Security Law
Context: For the second weekend in a row, Paris has been rocked by street protests after the government introduced a controversial security bill in parliament that seeks to provide greater powers and protections for police officers.
What does the proposed law seek to do?
- Ground and air mass surveillance: The proposed “global security” law allow the police and the paramilitary forces to use body cameras and drones to film citizens, and allow the recorded footage to be livestreamed to the command post
- Restricting the filming of police officers: Another provision penalises publishing “the image of the face or any other element of identification” of a police or paramilitary official who is acting in “a police operation”, if the dissemination is done with “the intent of harming their physical or mental integrity”.
What are the opponents of the new law saying?
- Accountability of Police action weakened: Journalists and human rights groups have expressed concern that new law would make it harder to cover public events and record instances of police violence, thus making it more difficult to hold officers accountable.
- Police Excesses will go undetected: Critics have highlighted two instances of police excesses within one week at the end of November that grabbed national attention, which they argue would have been left unreported had the proposed law been in place
- Authoritarian Law: Civil liberties groups and left-wing parties have called the bill authoritarian and unnecessary, insisting that existing laws are sufficient to protect police officers.
- Draconian in character: Its wording has also been criticised as being open-ended, and reporters have worried how the courts would interpret the term “intent of harming”.
- Freedom of Press: The provisions in bill intend to target press freedoms by restricting the coverage of police officers during protests/ clashes.
What have the bill’s supporters said?
- Protecting Police Officers: The new law is aimed at protecting police officers and their families from online trolling and harassment when off duty.
- Support by Citizens: As per a Bloomberg report, a government-commissioned survey found that 58 per cent of respondents backed the new security law.
- Rise of Conservatives as reaction to rising terrorism: Notably, analysts have pointed to a rightward shift of the French electorate supporting such laws that empower police. This shift from liberalism is more pronounced in the aftermath of a spate of recent terror attacks including the October beheading of schoolteacher Samuel Paty, and the Nice stabbing attack.
- Domestic Politics: President Macron has been increasingly trying to appeal to right-wing voters, especially before the Presidential election of early 2022. Laws like these which have tinge of majoritarianism is useful in attracting such voters
Value Addition
- Another controversial legal measure, the so-called “anti-separatism” bill is being proposed by the French Government.
- The bill, which aims to crack down on Islamic radicalism, is to be introduced in Parliament in December, and envisages a range of measures, including school education reforms to ensure Muslim children do not drop out, stricter controls on mosques and preachers, and has caused concern among Muslims in France.
Connecting the dots:
- George Floyd Incident of US
- Thoothukudi violence and Judicial Deaths in India
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 The largest planet in solar system is the:
- Mars
- Jupiter
- Saturn
- Venus
Q.2 Where are the stone chariots in India located?
- Karnataka
- Odisha
- Tamil Nadu
- Madhya Pradesh
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.3 Consider the following statements:
- Karsog Kulth is a legume grown as a kharif crop in Himachal Pradesh
- Pangi ki Thangi is a type of hazelnut which grows in Pangi valley, Uttarakhand.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 7th December 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
About Predicting Protein Structures using Artificial Intelligence:
About need for transparency in authorisation of Vaccines:
About farmer protest against new farm bills:












