IASbaba Daily Prelims Quiz
For Previous Daily Quiz (ARCHIVES) – CLICK HERE
The Current Affairs questions are based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, which are very important sources for UPSC Prelims Exam. The questions are focused on both the concepts and facts. The topics covered here are generally different from what is being covered under ‘Daily Current Affairs/Daily News Analysis (DNA) and Daily Static Quiz’ to avoid duplication. The questions would be published from Monday to Saturday before 2 PM. One should not spend more than 10 minutes on this initiative.
We will make sure, in the next 4 months not a single day is wasted. All your energies are channelized in the right direction. Trust us! This will make a huge difference in your results this time, provided that you follow this plan sincerely every day without fail.
Gear up and Make the Best Use of this initiative.
Do remember that, “the difference between Ordinary and EXTRA-Ordinary is PRACTICE!!”
To Know More about Ace the Prelims (ATP) 2021 – CLICK HERE
Important Note:
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- After completing the 5 questions, click on ‘View Questions’ to check your score, time taken and solutions.
Test-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
Department of Atomic Energy comes under the administrative control of:
Correct
Solution (d)
Explanation:
About The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE)
The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) came into being on August 3, 1954 under the direct charge of the Prime Minister through a Presidential Order. According to the Resolution constituting the AEC, the Secretary to the Government of India in the Department of Atomic Energy is ex-officio Chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission.
DAE has been engaged in the development of nuclear power technology, applications of radiation technologies in the fields of agriculture, medicine, industry and basic research.
DAE comprises five research centres, three industrial organizations, five public sector undertakings and three service organizations. It has under its aegis two boards for promoting and funding extra-mural research in nuclear and allied fields, mathematics and a national institute (deemed university).
It also supports eight institutes of international repute engaged in research in basic sciences, astronomy, astrophysics, cancer research and education. It also has in its fold an educational society that provides educational facilities for children of DAE employees.
Article reference: DAE plans to rope in private agencies for Nuclear Medicine
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Explanation:
About The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE)
The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) came into being on August 3, 1954 under the direct charge of the Prime Minister through a Presidential Order. According to the Resolution constituting the AEC, the Secretary to the Government of India in the Department of Atomic Energy is ex-officio Chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission.
DAE has been engaged in the development of nuclear power technology, applications of radiation technologies in the fields of agriculture, medicine, industry and basic research.
DAE comprises five research centres, three industrial organizations, five public sector undertakings and three service organizations. It has under its aegis two boards for promoting and funding extra-mural research in nuclear and allied fields, mathematics and a national institute (deemed university).
It also supports eight institutes of international repute engaged in research in basic sciences, astronomy, astrophysics, cancer research and education. It also has in its fold an educational society that provides educational facilities for children of DAE employees.
Article reference: DAE plans to rope in private agencies for Nuclear Medicine
-
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
Consider the following statements about Defence Production in India:
- Foreign Direct Investment in Defence is 100% in India.
- SRIJAN Portal is portal of patents for defence product, which will be provided freely to domestic industry.
- Chetak Helicopter is fully indigenous helicopter made by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Explanation:
Statement 1: Currently, 100 per cent overseas investments are permitted in the defence industry — 74 per cent is allowed under the automatic route but beyond that, government approval is required. (Till now 49% of FDI was allowed under automatic route). (So, Statement 1 is correct.)
Statement 2: SRIJAN portal
- Pursuant to Atmanirbhar Bharat announcement, Department of Defence Production has developed an indigenization portal, srijandefence.gov.in, as ‘opportunities for Make in India’ in Defence, which will give information on items that can be taken up for indigenization by the private sector.
- On this portal, DPSUs/OFB/SHQs can display their items which they have been importing or are going to import which the Indian Industry can design, develop and manufacture as per their capability or through joint venture with OEMs.
- The Indian Industry will be able to show their interest. The concerned DPSUs/OFB/SHQs, based on their requirement of the items and their guidelines & procedures will interact with the Indian industry for indigenization.
- So, Statement 2 is incorrect.
Statement 3: Chetak Helicopter is made under a licensing arrangement between French aircraft company Sud Aviation and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). The majority of these were acquired for military purposes with the Indian Armed Forces, who have used them to perform various mission roles, including training, transport, CASEVAC (casualty evacuation), communications and liaison roles. By 2017, the Chetak was reportedly serving as the most widely used IAF helicopter for training, light utility and light attack roles. (So, Statement 3 is incorrect)
Article reference: Indigenous Aircraft and Submarines
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Explanation:
Statement 1: Currently, 100 per cent overseas investments are permitted in the defence industry — 74 per cent is allowed under the automatic route but beyond that, government approval is required. (Till now 49% of FDI was allowed under automatic route). (So, Statement 1 is correct.)
Statement 2: SRIJAN portal
- Pursuant to Atmanirbhar Bharat announcement, Department of Defence Production has developed an indigenization portal, srijandefence.gov.in, as ‘opportunities for Make in India’ in Defence, which will give information on items that can be taken up for indigenization by the private sector.
- On this portal, DPSUs/OFB/SHQs can display their items which they have been importing or are going to import which the Indian Industry can design, develop and manufacture as per their capability or through joint venture with OEMs.
- The Indian Industry will be able to show their interest. The concerned DPSUs/OFB/SHQs, based on their requirement of the items and their guidelines & procedures will interact with the Indian industry for indigenization.
- So, Statement 2 is incorrect.
Statement 3: Chetak Helicopter is made under a licensing arrangement between French aircraft company Sud Aviation and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). The majority of these were acquired for military purposes with the Indian Armed Forces, who have used them to perform various mission roles, including training, transport, CASEVAC (casualty evacuation), communications and liaison roles. By 2017, the Chetak was reportedly serving as the most widely used IAF helicopter for training, light utility and light attack roles. (So, Statement 3 is incorrect)
Article reference: Indigenous Aircraft and Submarines
-
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
Consider the following statements regarding “Regulation of NGOs in India”:
- Foreign funding of voluntary organizations in India is regulated under Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 2010.
- Implementation agency for Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 2010 is Reserve Bank of India.
- Under this Act, to receive fund from foreign sources, NGO has to register them every year.
Which of the above statement is/are incorrect?
Correct
Solution (c)
Explanation:
Statement 1: The FCRA was enacted in 1976 in order to maintain strict control over voluntary organisations and political associations that received foreign funding. In the year 1984, an amendment was made to the act requiring all the Non-Governmental Organisations to register them with the Home Ministry. In 2010, the act was repealed and a new act with strict provisions was enacted.
Statement 2: Since the Act is internal security legislation, despite being a law related to financial legislation, it falls into the purview of Home Ministry and not the Reserve Bank of India. (Hence, Statement 2 is incorrect)
Statement 3: The Salient Features of FCRA, 2010
- A provision was made for the cancellation of registrations of NGOs if the Home Ministry believes that the organisation is political and not neutral.
- The registration certificate granted to the NGOs under the 2010 act came with five-year validity. So renewal of registration should be once in 5 years, and not in one year.
- A provision was inserted stating that the asset of the person who has become defunct needs to be disposed off in a manner stated by the government.
- A separate account needs to be maintained by the organisations to deposit the Foreign Contributions received and no other funds except for Foreign Contributions shall be deposited in that account.
- Every bank would be obligated to report to the prescribed authority, the amount of foreign remittances received and other related details such as the source, manner of receipt etc.
Article Link: NGO’S With FCRA Clearance
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Explanation:
Statement 1: The FCRA was enacted in 1976 in order to maintain strict control over voluntary organisations and political associations that received foreign funding. In the year 1984, an amendment was made to the act requiring all the Non-Governmental Organisations to register them with the Home Ministry. In 2010, the act was repealed and a new act with strict provisions was enacted.
Statement 2: Since the Act is internal security legislation, despite being a law related to financial legislation, it falls into the purview of Home Ministry and not the Reserve Bank of India. (Hence, Statement 2 is incorrect)
Statement 3: The Salient Features of FCRA, 2010
- A provision was made for the cancellation of registrations of NGOs if the Home Ministry believes that the organisation is political and not neutral.
- The registration certificate granted to the NGOs under the 2010 act came with five-year validity. So renewal of registration should be once in 5 years, and not in one year.
- A provision was inserted stating that the asset of the person who has become defunct needs to be disposed off in a manner stated by the government.
- A separate account needs to be maintained by the organisations to deposit the Foreign Contributions received and no other funds except for Foreign Contributions shall be deposited in that account.
- Every bank would be obligated to report to the prescribed authority, the amount of foreign remittances received and other related details such as the source, manner of receipt etc.
Article Link: NGO’S With FCRA Clearance
-
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
Consider the following statements regarding “Coalition of Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI)”:
- PM of India proposed it in 19th Conference of Parties of United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction, 2015.
- As for now, nearly half of the UN member countries are its member.
- It considers Economic, Social, Physical and Natural infrastructure in category of Infrastructure.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Explanation:
Statement 1: The Prime Minister of India launched CDRI during his speech at the UN Climate Action Summit on 23 September 2019. The Prime Minister had initially announced India’s intention to work with partner countries and key stakeholders to form a coalition working towards the goal of improving the disaster resilience of infrastructure at the Asian Ministerial Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction (AMCDRR) held in November 2016 in New Delhi. (So, Statement 1 is incorrect)
Statement 2: As of March, 2021, CDRI has 22 countries as its member.
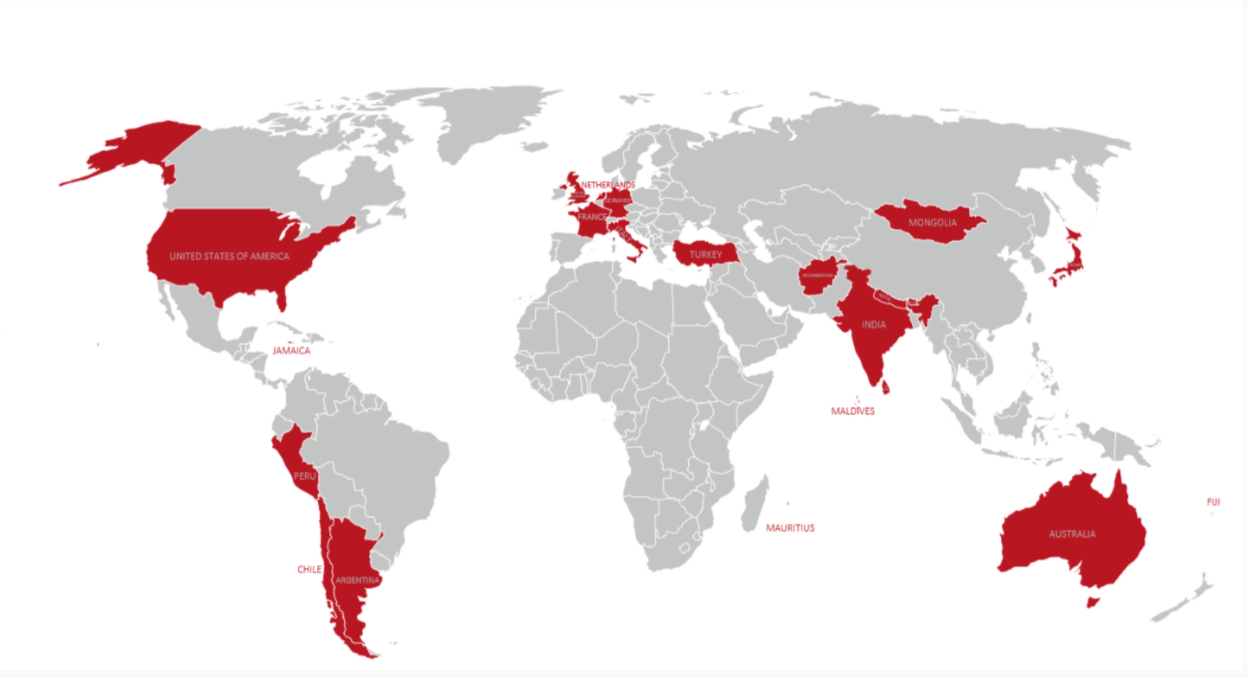
Statement 3: The term “infrastructure” is meant to include major economic, physical infrastructure (energy, telecommunication, roads, railways, airports, etc.), social infrastructure (schools, hospitals, etc.), and ecological infrastructure (natural waterways, waste management, etc.). In its initial phase, the CDRI will prioritize sectors where it can have the greatest multiplier effect.
The scope of “disasters” includes those emanating from natural hazards as well as man-made hazards. In practice, while looking at the resilience of a particular infrastructure system, the emphasis would depend on its risk exposure to different kinds of hazards, whether natural or man-made.
Basics of CDRI
- The Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) is an international coalition of countries, United Nations (UN) agencies, multilateral development banks, the private sector, and academic institutions that aims to promote disaster-resilient infrastructure.
- Its objective is to promote research and knowledge sharing in the fields of infrastructure risk management, standards, financing, and recovery mechanisms.
- CDRI’s initial focus is on developing disaster-resilience in ecological, social, and economic infrastructure.
- It aims to achieve substantial changes in member countries’ policy frameworks and future infrastructure investments, along with a major decrease in the economic losses suffered due to disasters.
Article link: Shared climate vision on visit agenda with friend PM Modi: Boris Johnson
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Explanation:
Statement 1: The Prime Minister of India launched CDRI during his speech at the UN Climate Action Summit on 23 September 2019. The Prime Minister had initially announced India’s intention to work with partner countries and key stakeholders to form a coalition working towards the goal of improving the disaster resilience of infrastructure at the Asian Ministerial Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction (AMCDRR) held in November 2016 in New Delhi. (So, Statement 1 is incorrect)
Statement 2: As of March, 2021, CDRI has 22 countries as its member.

Statement 3: The term “infrastructure” is meant to include major economic, physical infrastructure (energy, telecommunication, roads, railways, airports, etc.), social infrastructure (schools, hospitals, etc.), and ecological infrastructure (natural waterways, waste management, etc.). In its initial phase, the CDRI will prioritize sectors where it can have the greatest multiplier effect.
The scope of “disasters” includes those emanating from natural hazards as well as man-made hazards. In practice, while looking at the resilience of a particular infrastructure system, the emphasis would depend on its risk exposure to different kinds of hazards, whether natural or man-made.
Basics of CDRI
- The Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) is an international coalition of countries, United Nations (UN) agencies, multilateral development banks, the private sector, and academic institutions that aims to promote disaster-resilient infrastructure.
- Its objective is to promote research and knowledge sharing in the fields of infrastructure risk management, standards, financing, and recovery mechanisms.
- CDRI’s initial focus is on developing disaster-resilience in ecological, social, and economic infrastructure.
- It aims to achieve substantial changes in member countries’ policy frameworks and future infrastructure investments, along with a major decrease in the economic losses suffered due to disasters.
Article link: Shared climate vision on visit agenda with friend PM Modi: Boris Johnson
-
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
World Air Quality Report 2020 has been released by:
Correct
Solution (d)
Explanation
About World Air Quality Report 2020
- World Air Quality Report, 2020 has been released globally by IQAir (Swiss Organization).
- As per the report, India is the third most polluted country in the world .
- New Delhi was the world’s most polluted capital for the third straight year in 2020, based on the concentration of lung-damaging airborne particles known as PM2.5.
- India was home to 35 of the world’s 50 most polluted cities. Prolonged exposure to PM2.5 can lead to deadly diseases, including cancer and cardiac problems.
- In 2020, New Delhi’s average annual concentration of PM2.5 in a cubic meter of air was 84.1, the study said, more than double the level of Beijing, which averaged 37.5 during the year, making it the 14th most polluted city in the world.
- Air pollution caused an estimated 54,000 premature deaths in New Delhi in 2020.
Article link: New Delhi is world’s most polluted capital for third straight year: IQAir study
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Explanation
About World Air Quality Report 2020
- World Air Quality Report, 2020 has been released globally by IQAir (Swiss Organization).
- As per the report, India is the third most polluted country in the world .
- New Delhi was the world’s most polluted capital for the third straight year in 2020, based on the concentration of lung-damaging airborne particles known as PM2.5.
- India was home to 35 of the world’s 50 most polluted cities. Prolonged exposure to PM2.5 can lead to deadly diseases, including cancer and cardiac problems.
- In 2020, New Delhi’s average annual concentration of PM2.5 in a cubic meter of air was 84.1, the study said, more than double the level of Beijing, which averaged 37.5 during the year, making it the 14th most polluted city in the world.
- Air pollution caused an estimated 54,000 premature deaths in New Delhi in 2020.
Article link: New Delhi is world’s most polluted capital for third straight year: IQAir study











