UPSC Articles
Baikal-GVD: Underwater neutrino telescope
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Sci and Tech
In news
- Russian scientists launched one of the world’s biggest underwater neutrino telescopes called the Baikal-GVD (Gigaton Volume Detector) in the waters of Lake Baikail.
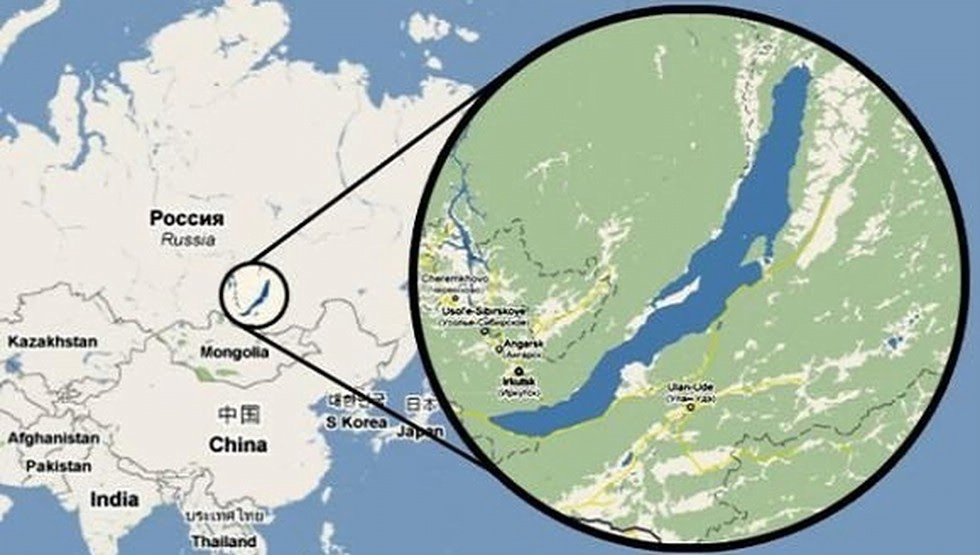
- Lake Baikal is the world’s deepest lake situated in Siberia.
Key takeaways
- Mission: To study in detail the fundamental particles called neutrinos and to possibly determine their sources.
- It is one of the three largest neutrino detectors in the world along with the IceCube at the South Pole and ANTARES in the Mediterranean Sea.
Important value additions
Lake Baikal
- Lake Baikal is a rift lake located in southern Siberia, Russia.
- It is the largest freshwater lake by volume in the world, containing 22 to 23% of the world’s fresh surface water.
- It is the seventh-largest lake in the world by surface area.
- Maximum depth: 1,642 m (5,387 ft)
- It is the world’s oldest (25–30 million years) and deepest lake.
- It has a long, crescent shape.
- The region to the east of Lake Baikal is referred to as Transbaikalia or as the Trans baikal.
- The loosely defined region around the lake itself is sometimes known as Baikalia.
- UNESCO declared Lake Baikal a World Heritage Site in 1996.











