IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
RBI to Issue CyberSecurity Norms for Payment services
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy
In news
- The RBI will soon issue cybersecurity norms for payment service providers (PSPs), following a series of data breaches faced by operators.
Key takeaways
- The standards for fintech-driven payment services providers will be similar to cyber hygiene norms issued recently for banks and non-banking finance companies (NBFCs).
- The firms will also have to do more than observe the minimum standards to ensure safety as digital transactions gain further traction.
- The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) had laid down a framework for a more even distribution of share of third-party app providers in the UPI system.
Important value additions
The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI)
- It is an umbrella organisation for operating retail payments and settlement systems under the ownership of Reserve Bank of India in India.
- Founded in: 2008.
- Headquarters: Mumbai
Related articles:
- RBI introduces risk-based internal audit norms for NBFCs, UCBs
- Structured Finance and Partial Guarantee Programme to NBFC-MFIs launched
- Special liquidity scheme for NBFCs/HFCs approved
Virafin receives emergency use approval
Part of: GS Prelims and GS –II – Health & GS-III – Sci & tech
In news
- Drug Controller General Of India (DCGI) gave a restricted emergency use approval to the Zydus Cadila’s ‘Virafin’ for treating the patients showing moderate COVID-19 symptoms.
Key takeaways
- Virafin is a pegylated interferon alpha-2b(PegIFN), which when subcutaneously injected to the patient in the early stages of infection, resulted in their faster recovery.
- The clinical trials have confirmed the safety, tolerability and efficacy of Virafin.
- The studies also reported that Viarfin reduces viral load and aid in managing the disease in a better way, such as reduction in the need for supplemental oxygen.
Ways and Means Advances scheme of State Governments/ UTs
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy
In news
- The RBI decided to continue with the existing interim Ways and Means Advances (WMA) scheme limit of ₹51,560 crore for all States/ UTs shall for six months i.e., up to September 30, given the prevalence of COVID-19.
Key takeaways
- Ways and means advances (WMA) is a mechanism used by RBI under its credit policy to provide to States, banking with it, to help them tide over temporary mismatches in the cash flow of their receipts and payments.
- This is guided under Section 17(5) of RBI Act, 1934.
- Based on the recommendations of the Advisory Committee on WMA to State Governments, 2021 (chaired by Sudhir Shrivastava), the RBI had revised the WMA Scheme of States and Union Territories (UTs)
- The WMA limit arrived at by the Committee based on total expenditure of States/ UTs, works out to be ₹47,010 crore.
- The RBI said it would review the WMA limit thereafter, depending on the course of the pandemic and its impact on the economy.
Draft Standards for Road-Trains
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III Infrastructure
In news
- Ministry of Road Transport & Highways has published Draft Standards for Road-Trains.
Key takeaways
- To revolutionize the transport of goods and reduce the overall logistic costs, the Automotive Industry Standards Committee has amended its AIS-113 Standard to include the safety requirements of Road-Trains.
- The standards have been prepared after examining European benchmarks, keeping in mind Indian operating conditions.
Important value additions
- Road-Train is a motor vehicle wherein the traction is provided by the puller, which is connected to a serial combination of trailers or semi- trailers.
- These shall ply on select stretches to reduce congestion, save fuel and reduce noise & air-pollution.
- The Automotive Industry Standards Committee has representatives from the relevant Ministries, Testing Agencies, Industry stakeholders, BIS etc.
Miscellaneous
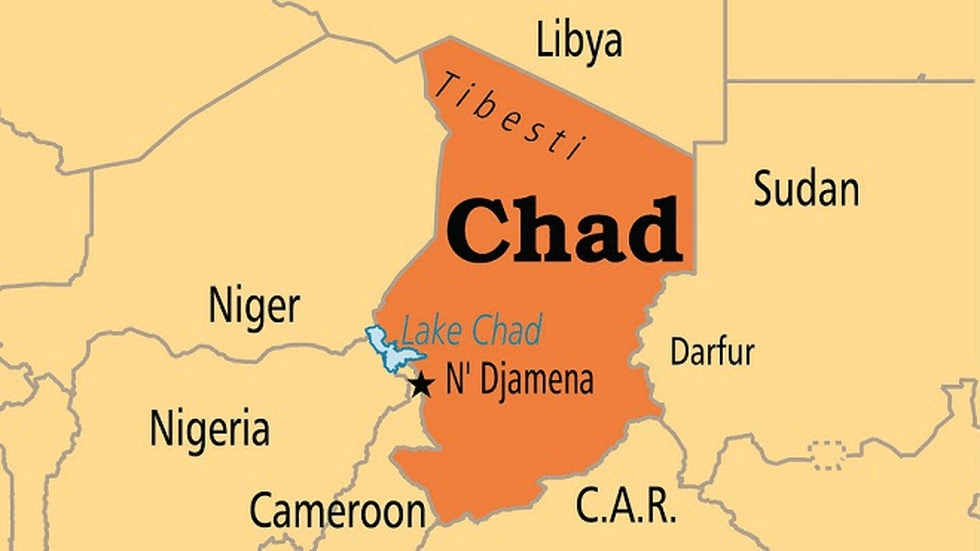
Chad
-
Chad’s President Idriss Deby Itno died recently.
- Chad is a landlocked country in north-central Africa.
- It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon to the south-west, Nigeria to the southwest (at Lake Chad), and Niger to the west.
- Lake Chad, after which the country is named, is the second-largest wetland in Africa.
- The capital N’Djamena is the largest city.
(Mains Focus)
GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
Topic:
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources
National Pension System: Government Tweaks & its impact
Context: Given the dominance of informal employment in India, the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation, which is contingent on a formal employer-employee relationship, only covers a fraction of the workforce.
About New Pension Scheme
- Started as the New Pension Scheme for government employees in 2004 under a new regulator called the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA), the National Pension System (NPS) has been open for individuals from all walks of life to participate and build a retirement nest-egg
- The NPS has been gradually growing in size and now manages ₹5.78 lakh crore of savings and 4.24 crore accounts in multiple savings schemes.
- Of these, over 3.02 crore accounts are part of the Atal Pension Yojana (APY), a government-backed scheme for workers in the unorganised sector that assures a fixed pension payout after retirement.
- The rest constitute voluntary savings from private sector employees and self-employed individuals, for whom some significant changes are on the anvil.
What overhaul is the PFRDA planning?
- Annuitisation of Savings: The law regulating the NPS allows members to withdraw just 60% of their accumulated savings at the time of retirement. With the remaining 40%, it is mandatory to buy an annuity product that provides a fixed monthly income to retirees till their demise.
- Exemption to annuitisation: Members who accumulate up to ₹2 lakh in their NPS account at the time of retirement are exempted from the mandatory annuitisation, and can withdraw the full amount.
- Proposal for New Exemption Limit: Recently, PFRDA chairman said this limit will soon be revised to ₹5 lakh.
- Suppose somebody reached ₹2.1 lakh at retirement, he will get an annuity component of ₹84,000 (40% of corpus), which, today, will give an income of ₹400 or ₹450 a month. So, now, PFRDA will allow those with savings up to ₹5 lakh to take the entire corpus out if they choose
- More Flexibility: PFRDA has now proposed to give members a choice to retain 40% of their corpus with the NPS fund managers even after retirement. This, the PFRDA chief believes, will allow them to get better returns, and these savings can be paid out to members over 15 years through something like the systematic withdrawal plan offered by mutual funds.
- Relaxation in age norms: Age restrictions to join the NPS are also being eased to allow people to join the scheme up to the age of 70 years, from 65 years earlier.
- Additional Fund Managers: At least three more fund managers are expected to be appointed soon, which will take the total managers to ten.
- While this change shall need Parliament’s nod, the expansion of the annuity-free withdrawal limit from ₹2 lakh to ₹5 lakh is being done immediately
What prompted this rethink?
- Complaints from NPS Subscribers: Falling interest rates and poor returns offered by annuity products had triggered complaints from some members and experts about the compulsory annuitisation clause.
- Poor returns: Since annuities are taxable, deducting the tax and factoring in the inflation means annuities are yielding negative returns. With retail inflation running at about 5%-6% over the past year, the returns on annuities are, in fact, negative, even if one does not factor in the tax.
What is the impact of changes being made?
- To avoid forcing people into such an unattractive investment, the regulator has tweaked its rules so as to allow better returns to its pension subscribers.
- The flexibility of the pension system will enable more people to invest in NPS as it will be considered as safe & risk free return on their savings.
- Appointment of additional fund managers shows that government is serious about expanding the user base of NPS and make it more attractive to them through efficient utilization of funds.
SCIENCE & TECH/ INTERNATIONAL
Topic:
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
- GS-2: Significant international events, international agencies etc
Russia’s withdrawal from International Space Station
Context: After more than two decades of international cooperation in space research, Russia announced that it would be withdrawing from the International Space Station in 2025.
What does the International Space Station do?
- A space station is essentially a large spacecraft that remains in low-earth orbit for extended periods of time.
- It is like a large laboratory in space, and allows astronauts to come aboard and stay for weeks or months to carry out experiments in microgravity.
- The ISS has been in space since 1998, and has been known for the exemplary cooperation between the five participating space agencies that have been running it: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada).
- As per NASA, 243 people from 19 countries have so far visited the ISS, and the floating laboratory has hosted more than 3,000 research and educational investigations in various disciplines, including biology, human physiology, and physical, material and space science.
The recent US-Russia space rivalry
- Russia has been a crucial player in making the ISS a success, with other space agencies relying on advanced Russian modular space station construction technology to build the space station in the initial years.
- Russia was also indispensable because of its Soyuz passenger vehicle, which served as the only way for transporting astronauts to the ISS ever since the US retired its Space Shuttle Program in 2011
- This reliance on Russia ended last year, however, when the US started to use the SpaceX system developed by Elon Musk.
- This was a major blow for Roscosmos, as this meant an end to the funding it received from NASA for carrying astronauts to the space station. Between 2011 and 2019, NASA had spent $3.9 billion on the Soyuz flights.
- Next year, the US is also expected to have another domestic option apart from SpaceX, as Boeing’s delayed Starliner capsule is expected to become operational.
- Last year, Russia rejected a US offer to be a part of the Artemis program (NASA’s program to return astronauts to the lunar surface), but in March 2021 signed an agreement with China to jointly develop a lunar base.
Growing US-Russia Tensions
- The development also comes at a time when relations between the West and Russia have been going from bad to worse.
- The US has blamed the Kremlin for carrying out the “SolarWinds” hack and interfering in the 2020 election.
- Recently, Russia received flak from the NATO alliance after it was accused by the Czech Republic of being involved in a 2014 explosion at an arms depot.
- Last year, the US accused Russia of carrying out a weapons test after a projectile was said to have been fired from a Russian satellite. Russia, in return, blamed the US for treating space as a “military theatre”.
So, what does Russia plan to do now?
- Russia now plans to build and manage its own space station, which it aims to launch into orbit by 2030. Its space module is being assembled by the Energia corporation, and is set to cost at least $5 billion.
- The station will reportedly orbit the Earth at a higher latitude, enabling it to better observe the polar regions, especially since Russia plans to develop the Arctic sea route as the ice melts.
- Building a new station would also help Russia tide over challenges that its cosmonauts currently face on the ageing ISS, such as conducting experiments and adapting the latest technology to a hardware architecture that is over two decades old.
- However, leaving the ISS would also mean that Russian researchers would lose access to a laboratory that has seen over 15 years of engineering and assembly work to build it, and whose research potential is only now truly expected to take off.
- NASA has ruled out retiring the ISS until at least 2028, and may continue to use it after that by upgrading key systems.
- Russia would manage the space station itself, but has left the door open for other countries to join.
Connecting the dots :
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following is/are NPCI operated systems?
- National Automated Clearing House (NACH)
- Immediate Payment Service (IMPS),
- Aadhaar enabled Payment System (AePS)
- Bharat Bill Payment System
Select the correct code
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2,3 and 4
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Ways and means advances (WMA)?
- It is a credit policy by RBI
- It is provided to States to help them tide over temporary mismatches in the cash flow of their receipts and payments.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Where is Lake Chad located?
- Africa
- North America
- South East Asia
- Europe
ANSWERS FOR 24th April 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | C |
Must Read
On U.S.-India climate pact:
A case for judicial federalism:
On Supreme Court’s deportation order of Rohingya Refugees:











