IASbaba's Press Information Bureau, UPSC Articles
GS-1
Heat Waves in the country
(Topic: Geophysical phenomena)
A Heat Wave is a period of abnormally high temperatures, more than the normal maximum temperature that occurs during the summer season in the North-Western parts of India. Heat Waves typically occur between March and June, and in some rare cases even extend till July.
If the average global temperature rose by more than one degree Celsius from the present, India could “annually” expect conditions like the 2015 heat wave that killed at least 2,000, according to the ‘Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5°C,’ commissioned by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
Heat wave is not notified in the list of twelve disasters eligible for relief under National/ State Disaster Response Fund norms. However, a State Government may use up to 10 per cent of the funds available under the SDRF for providing immediate relief to the victims of natural disasters that they consider to be “disasters” within the local context in the State.
Heat wave is declared under these circumstances:
- An increase of 5°C to 6°C when the normal maximum temperature is less than or equal to 40°C.
- An increase of 7°C or more from the normal temperature is considered as severe heat wave condition.
- An increase of 4°C to 5°C when the normal maximum temperature of a station is more than 40°C.
- An increase of 6°C or more is considered as severe heat wave condition.
- If the actual maximum temperature remains 45°C or more irrespective of normal maximum temperature.
Threat posed by heat waves:
- The health impacts of Heat Waves typically involve dehydration, heat cramps, heat exhaustion and/or heat stroke.
- The Lancet Countdown 2018 report sounds a warning that rising temperatures will enable the dengue virus and malaria to spread farther and faster.
- Lancet Countdown 2018 report also mentions that India lost nearly 75 billion hours of labour due to heat waves in 2017.
- The agriculture sector is more vulnerable compared to the industrial and service sectors because workers there are more likely to be exposed to heat. This has worrying implications for rural employment and the well-being of a large section of the population (nearly 49%) that depends on farming.
- Food insecurity due to lowering of productivity due to extreme temperatures.
- It may further intensify the water scarcity and could lead to increased water disputes.
First Aid for heat stroke:
While waiting for the paramedics to arrive, initiate first aid with the aim to lower the body temperature.
- Move the person to an air-conditioned environment or at least a cool, shady area and remove any unnecessary clothing.
- Fan air over the patient while wetting his or her skin with water from a sponge or garden hose.
- Apply ice packs to the patient’s armpits, groin, neck, and back because these areas are rich with blood vessels close to the skin, cooling them may reduce body temperature.
- Do not use ice for older patients, young children, patients with chronic illness, or anyone whose heat stroke occurred without vigorous exercise.
Way Forward
Increased exposure to heatwaves needs a policy response, nationally and globally. Long term measures should be taken to address the issue in the wake of global warming and climate change:
- Establish Early Warning System and Inter-Agency Coordination to alert residents on predicted high and extreme temperatures
- Capacity building / training programme for health care professionals at local level
- Public Awareness and community outreach to protect against the extreme heat-wave through print, electronic and social media and Information, Education and Communication (IEC) materials.
- Collaboration with non-government and civil society
- Afforestation drives to increase green cover.
- A further reduction in the share of coal in the energy mix through sustained support for renewable energy, particularly solar photovoltaic, must form the cornerstone of national policy
- It is vital that India gets more ambitious about cutting back on carbon emissions, even as it presses for the fulfillment of the climate finance obligations of developed countries under the Paris Agreement of the UNFCCC. This must be matched by a shift away from use of fossil fuels for transport, and the induction of more electric vehicles.
Must Read: Heat Stroke (Hyperthermia)
Non-uniformity of Himalayas foresees significantly large earthquake events
(Topic: Geophysical phenomena)
Scientists have found that the Himalayas are not uniform and assume different physical and mechanical properties in different directions – a property present in crystals called anisotropy which could result in significantly large earthquake events in the Himalayas.
The NW region of India, an area covering Garhwal and Himachal Pradesh, has been hit by four destructive moderate to great earthquakes since the beginning of the 20th century — the Kangra earthquake of 1905, the Kinnaur earthquake of 1975, the Uttarkashi earthquake of 1991, and the Chamoli earthquake of 1999. These seismic activities manifest large-scale subsurface deformation and weak zones, underlining the need for deeper insights into the ongoing deformation beneath these tectonically unstable zones.
- The major contribution of the anisotropy is mainly because the strain induced by the Indo-Eurasia collision (going on since 50 million years) and deformation due to the collision is found to be larger in the crust than in the upper mantle.
- The inhomogeneity along the Himalayas influences the stressing rate is because of variation in the geometry of the Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT) system, and it controls the rupture size during the earthquake. This lack of homogenous physical and mechanical properties of the Himalayas could help explore new perspectives about deformations taking place at the Himalaya-Tibet crustal belt involved in the formation of the Himalayan Mountains.
GS-2
Launch of Integrated Health Information Platform (IHIP), the revised next generation Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP) digital platform
(Topic: Health)
Considered to be a new chapter in India’s public health trajectory, with the launch of IHIP, India is the first country in the world to adopt such an advanced disease surveillance system.
IHIP will provide health information system developed for real time, case-based information, integrated analytics, advanced visualization capability. It will provide analyzed reports on mobile or other electronic devices. In addition, outbreak investigation activities can be initiated and monitored electronically. It can easily be integrated with other ongoing surveillance program, while having the feature of addition of special surveillance modules.
- The new version of IHIP will house the data entry and management for India’s disease surveillance program. In addition to tracking 33 diseases now as compared to the earlier 18 diseases, it shall ensure near-real-time data in digital mode, having done away with the paper-mode of working
- The world’s biggest online disease surveillance platform, is in sync with the National Digital Health Mission and fully compatible with the other digital information systems presently being used in India.
- The refined IHIP with automated -data will help in a big way in real time data collection, aggregation & further analysis of data that will aid and enable evidence-based policy making.
India’s information system for precision public health is essential for delivering the right intervention at the right time, every time to the right population.
National Policy for Rare Diseases, 2021
(Topic: Health)
By Ministry: Ministry of Health
Aim:
- To lower the high cost of treatment for rare diseases with increased focus on indigenous research;
- To strengthen tertiary health care facilities for prevention and treatment of rare diseases through designating 8 health facilities as Centre of Excellence (CoEs).
Vision: Creation of a national hospital based registry of rare diseases so that adequate data about rare diseases is available.
Focus: Early screening and prevention through primary and secondary health care infrastructure such as Health and Wellness Centres and District Early Intervention Centres (DEICs) and through counselling for the high-risk patients.
Key Pointers:
- National Consortium shall be set up to provide the required help
- Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare will be its convenor.
- Screening will also be supported by Nidan Kendras set up by Department of Biotechnology.
- CoEs will also be provided one-time financial support of up to Rs 5 crores for upgradation of diagnostics facilities.
- A provision for financial support up to Rs. 20 lakhs under the Umbrella Scheme of Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi is proposed for treatment of those rare diseases that require a one-time treatment (diseases listed under Group 1 in the rare disease policy).
- Envisages a crowdfunding mechanism in which corporates and individuals will be encouraged to extend financial support through a robust IT platform for treatment of rare diseases. Funds so collected will be utilized by Centres of Excellence for treatment of all three categories of rare diseases as a first charge and the balance financial resources can also be used for research.
Do you know?
- In India, Haemophilia, Thalassemia, Sickle cell anaemia and Primary Immuno Deficiency in children, auto-immune diseases, Lysosomal storage disorders such as Pompe disease and Gaucher’s disease are in the rare diseases list.
Spices Board India and UNDP India’s Accelerator Lab sign MoU
(Topic: Collaboration with International organisations)
Aim: To develop blockchain-powered traceability Interface for Indian spices to enhance transparency in supply chain and trade
- UNDP and Spices Board India are working towards integrating the Blockchain Traceability Interface with the e-Spice Bazaar portal developed by Spices Board India for connecting spices farmers with markets.
- The project will be piloted with over 3,000 farmers engaged in chilli and turmeric farming in select Districts of Andhra Pradesh.
Blockchain is a decentralized process of recording transactions on an open and shared electronic ledger. This allows for ease and transparency in data management across a complex network, including, farmers, brokers, distributors, processors, retailers, regulators, and consumers, thus simplifying the supply chain.
- It will allow farmers just as all other members of the supply chain to access the information which further makes the entire supply chain more efficient and equitable.
- Enhance consumer confidence and facilitate sourcing of spices for exports as well as for local value addition and use.
Spices in India
- India is the largest exporter, producer and consumer of spices in the world. India’s spices export crossed a milestone of 3 Bn USD during 2019-20.
- Spices Board is the agency responsible for export promotion of Indian spices in the world markets
About Spices Board: Spices Board is one of the five Commodity Boards functioning under the Ministry of Commerce &Industry. It is an autonomous body responsible for the export promotion of the 52 scheduled spices and development of Cardamom (Small & Large). The main functions of the Spices Board are the following:
(i) Research, Development and Regulation of domestic marketing of Small & Large Cardamom;
(ii) Post-harvest improvement of all spices;
(iii) Export promotion of all spices and assisting exporters in technology upgradation, quality management, brand promotion, research & product development;
(iv) Development of spices in the North East;
(v) Regulation of quality of spices for exports through its quality evaluation services; etc.
About UNDP: UNDP works across 170 countries and territories to eradicate poverty while protecting the planet. We help countries develop strong policies, skills, partnerships, and institutions so they can sustain their progress. UNDP has worked in India since 1951 in almost all areas of human development, from systems strengthening to inclusive growth and sustainable livelihoods, as well as sustainable energy, environment, and resilience. UNDP’s programmes continue to integrate a global vision for catalytic change with India’s national priorities. With over 30 projects on the ground in almost every state, today, it works to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals by transforming traditional models to do development differently.
Atal Innovation Mission joins hands with CIPS for innovations in public systems
(Topic: Government policies in skill development and entrepreneurship)
Aim: To reinforce the innovation and entrepreneurship ecosystem in India by developing a database of innovations in public systems for improving public services
- Will help startups to access and promote their innovations to grassroot levels by synergizing with the local administration. The challenges faced by the local administration in delivering the services to the citizens can be addressed through the start-ups by drafting a plan of action with the support of CIPS mentors.
- AIM and CIPS will jointly organize round tables involving the district and local level administration officials tocreate awareness about innovative products and solutions and help them understand standard processes and policies around procurement so that procurement and implementation of relevant innovative solutions can be expedited.
- The need of the hour is to ensure capacity building of teachers/mentors at grassroot levels to promote innovative learning among the students. This can be achieved by jointly creating an Innovation Learning Management System (iLMS).
- The partnership will also help promote the programs launched by AIM at state and district level and liaison with the states. It will strengthen the AIM Mentor of Change program through larger participation of government officers at district level.
There is growing evidence that multi-actor collaboration in networks, partnerships and inter-organisational teams can spur public innovation. The involvement of different public and private actors in public innovation processes may improve the understanding of the problem or challenge at hand, bring forth new ideas and proposals, and build joint ownership of new and bold solutions.
MoU between India and Japan for Academic and Research Cooperation and Exchange
(Topic: India and Japan)
The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi, is apprised of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed between National Atmospheric Research Laboratory (NARL), Dept of Space, Government of India and Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere (RISH), Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan for Academic and Research Cooperation and Exchange
Objectives
- This MoU shall enable NARL and RISH to continue their cooperation in areas of atmospheric science and technology, collaborative scientific experiments/campaigns and related modelling studies utilising the research facilities of RISH and NARL, exchange of scientific materials, publications and information, joint research meetings and workshops, exchange of faculty members, students and researchers.
- This MoU would lead to mutual utilization of facilities such as the Middle and Upper atmosphere (MU) radar in Shigaraki, Japan, the Equatorial Atmosphere Radar (EAR) in Kototabang, Indonesia and complementary instruments available from RISH, and the Mesosphere-Stratosphere-Troposphere (MST) radar and complementary instruments available at NARL.
Background
NARL and RISH have been collaborating in the area of atmospheric science and technology as well as exchange of scientists. This arrangement was formalised in 2008 through an MoU. The above MoU was renewed in the year 2013. A fresh MOU to promote collaborative research, as per the new guidelines, was signed in November 2020 by both sides and exchanged.
NARL scientists worked as resource persons in the international school on atmospheric radar conducted by RISH. A team of Professors and Researchers of Kyoto University visited NARL and conducted focused workshop to strengthen cooperative research being carried out by the two institutes.
Cabinet approves Production Linked Incentive scheme ‘National Programme on High Efficiency Solar PV Modules’
The Cabinet has approved the Ministry of New & Renewable Energy’s proposal for implementation of the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme ‘National Programme on High Efficiency Solar PV (Photo Voltic) Modules’ for achieving manufacturing capacity of Giga Watt (GW) scale in high efficiency solar PV modules with an outlay of Rs.4,500 crore.
Solar capacity addition presently depends largely upon imported solar PV cells and modules as the domestic manufacturing industry has limited operational capacities of solar PV cells and modules. The National Programme on High Efficiency Solar PV Modules will reduce import dependence in a strategic sector like electricity. It will also support the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
Solar PV manufacturers will be selected through a transparent competitive bidding process. PLI will be disbursed for 5 years post commissioning of solar PV manufacturing plants, on sales of high efficiency solar PV modules. Manufacturers will be rewarded for higher efficiencies of solar PV modules and also for sourcing their material from the domestic market. Thus, the PLI amount will increase with increased module efficiency and increased local value addition.
The outcomes/ benefits expected from the scheme are as follows:
- Additional 10,000 MW capacity of integrated solar PV manufacturing plants,
- Direct investment of around Rs.17,200 crore in solar PV manufacturingprojects
- Demand of Rs.17,500 crore over 5 years for ‘Balance of Materials’,
- Direct employment of about 30,000 and Indirect employment of about1,20,000 persons,
- Import substitution of around Rs.17,500 crore every year, and
- Impetus to Research & Development to achieve higher efficiency in solar PV modules.
GS-3
MoU Signed between Ministry of AYUSH and Department of Animal Husbandry for research on new formulations in quality drugs for veterinary science
(Topic: Animal Husbandry)
An Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the National Medicinal Plants Board (NMPB), Ministry of AYUSH and Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying for research on new formulations in quality drugs for veterinary science through medicinal herbs. The initiative involves capacity building in related areas through training, exploring marketing possibilities for herbal veterinary medicines on a sustainable basis and providing for services including cultivation, preservation and conservation of medicinal plants.
The Ministry of AYUSH will support Department of Animal Husbandry for
- Developing curriculum and courses for AYUSH herbal veterinary education programs,
- Identifying potential medicinal plant species used in veterinary medicine and provide their standards, training and awareness program on Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs)& Good Field Collection Practices (GFCPs) etc.,
- Development of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) for manufacturing of AYUSH/herbal veterinary medicines,
- Skill development and capacity building,
- Facilitate and render financial assistance for plantations and nursery development for medicinal plants,
- Facilitate standardizing norms for medicinal plants,
- Assist establishing research and testing centers as per scope of the Scheme.
The Department of Animal Husbandry will support Ministry of AYUSH for its expert technical opinion for essentiality, desirability and feasibility with respect to Ayurvedic medicines.
- The Department will create awareness with support of NDDB among dairy farmers and agro-farmers about utilization and importance of herbal veterinary medicine and cultivation of medicinal herbs,
- Develop course curriculum for Ayurveda and its allied subjects in veterinary medicine,
- Identify list of priority livestock and poultry diseases of economic importance with respect to research activity or application of veterinary Ayurveda and allied streams,
- Support farmers for undertaking cultivation and conservation of medicinal plants and related activities,
- Support identify opportunities for scientific and technological collaboration to research institute (Veterinary Colleges and ICAR research institutes).
Union Cabinet approves Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for White Goods (Air Conditioners and LED Lights)
(Topic: Indian Economy)
The prime objective of the PLI scheme is to make manufacturing in India globally competitive by removing sectoral disabilities, creating economies of scale and ensuring efficiencies. It is designed to create complete component ecosystem in India and make India an integral part of the global supply chains. The scheme is expected to attract global investments, generate large scale employment opportunities and enhance exports substantially.
The PLI Scheme for White Goods shall extend an incentive of 4% to 6% on incremental sales of goods manufactured in India for a period of five years to companies engaged in manufacturing of Air Conditioners and LED Lights. Selection of companies for the Scheme shall be done so as to incentivize manufacturing of components or sub-assemblies which are not manufactured in India presently with sufficient capacity. Mere assembly of finished goods shall not be incentivized.
Companies meeting the pre-qualification criteria for different target segments will be eligible to participate in the Scheme. Incentives shall be open to companies making brown field or green field Investments. Thresholds of cumulative incremental investment and incremental sales of manufactured goods over the base year would have to be met for claiming incentives.
The Scheme is expected to be instrumental in achieving growth rates that are much higher than existing ones for AC and LED industries, develop complete component eco-systems in India and create global champions manufacturing in India. They will have to meet the compulsory BIS and BEE Quality standards for sales into domestic market and applicable standards for global markets. It will also lead to investments in innovation and research and development and upgradation of technology.
Copyright (Amendment) Rules, 2021
(Topic: Economy)
In India, the copyright regime is governed by the Copyright Act, 1957 and the Copyright Rules, 2013. The Copyright Rules, 2013 were last amended in the year 2016.
The amendments have been introduced with the objective of bringing the existing rules in parity with other relevant legislations. It aims to ensure smooth and flawless compliance in the light of the technological advancement in digital era by adopting electronic means as primary mode of communication and working in the Copyright Office. A new provision regarding publication of a copyrights journal has been incorporated, thereby eliminating the requirement of publication in the Official Gazette. The said journal would be available at the website of the Copyright Office.
In order to encourage accountability and transparency, new provisions have been introduced, to deal with the undistributed royalty amounts and use of electronic and traceable payment methods while collection and distribution of royalties. To reinforce transparency in working of copyright societies a new rule has been introduced, whereby the copyright societies will be required to draw up and make public an Annual Transparency Report for each financial year.
The amendments have harmonised the Copyright Rules with the provisions of Finance Act, 2017 whereby the Copyright Board has been merged with Appellate Board.
The compliance requirements for registration of software works have been largely reduced, as now the applicant has the liberty to file the first 10 and last 10 pages of source code, or the entire source code if less than 20 pages, with no blocked out or redacted portions.
The time limit for the Central Government to respond to an application made before it for registration as a copyright society is extended to one hundred and eighty days, so that the application can be more comprehensively examined.
Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Pre-packaged Insolvency Resolution Process) Regulations, 2021
(Topic: Economy)
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Ordinance, 2021 promulgated on 4th April, 2021 provides for pre-packaged insolvency resolution process (PPIRP) for corporate debtors classified as micro, small and medium enterprises. The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India notified the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Pre-packaged Insolvency Resolution Process) Regulations, 2021 (PPIRP Regulations) today to enable operationalisation of PPIRP.
The PPIRP Regulations detail the Forms that stakeholders are required to use, and the manner of carrying out various tasks by them as part of the PPIRP. These provide details and manner relating to:
- Eligibility to act as resolution professional, and his terms of appointment;
- Eligibility of registered valuers and other professionals;
- Identification and selection of authorised representative;
- Public announcement and claims of stakeholders;
- Information memorandum;
- Meetings of the creditors and committee of creditors;
- Invitation for resolution plans;
- Competition between the base resolution plan and the best resolution plan;
- Evaluation and consideration of resolution plans;
- Vesting management of corporate debtor with resolution professional;
- Termination of PPIRP.
India emerging a leader in supercomputing
(Topic: Science and Technology)
India is fast emerging a leader in high power computing with the National Super Computing Mission (NSM) boosting it to meet the increasing computational demands of academia, researchers, MSMEs, and startups in areas like oil exploration, flood prediction as well as genomics and drug discovery.
Computing infrastructure has already been installed in four premier institutions and installation work is in rapid progress in 9 more. Completion in of Phase II of NSM in September 2021 will take the country’s computing power to 16 Petaflops (PF). MoUs have been signed with a total of 14 premier institutions of India for establishing Supercomputing Infrastructure with Assembly and Manufacturing in India. These include IITs, NITs, National Labs, and IISERs.
The National Supercomputing Mission was launched to enhance the research capacities and capabilities in the country by connecting them to form a Supercomputing grid, with National Knowledge Network (NKN) as the backbone.
- The NSM is setting up a grid of supercomputing facilities in academic and research institutions across the country. Part of this is being imported from abroad and part built indigenously.
- The Mission is being jointly steered by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and implemented by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Pune, and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru.
- PARAM Shivay, the first supercomputer assembled indigenously, was installed in IIT (BHU), followed by PARAM Shakti, PARAM Brahma, PARAM Yukti, PARAM Sanganak at IIT-Kharagpur IISER, Pune, JNCASR, Bengaluru and IIT Kanpur respectively.
Supernova explosion traced to one of the hottest kind of stars
(Topic: Space)
Indian astronomers have tracked a rare supernova explosion and traced it to one of the hottest kind of stars called Wolf–Rayet stars or WR stars.
The rare Wolf–Rayet stars are highly luminous objects a thousand times that of the Sun and have intrigued astronomers for long. They are massive stars and strip their outer hydrogen envelope which is associated with the fusion of Helium and other elements in the massive core. Tracking of certain types of massive luminous supernovae explosion can help probe these stars that remain an enigma for scientists.
A team of astronomers from Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES), Nainital an autonomous institute under the Department of Science & Technology, Govt. of India with international collaborators have conducted the optical monitoring of one such stripped-envelope supernova called SN 2015dj hosted in the galaxy NGC 7371 which was spotted in 2015. They calculated the mass of the star that collapsed to form the supernovae as well as the geometry of its ejection.
The scientists also found that the original star was a combination of two stars – one of them is a massive WR star and another is a star much less in mass than the Sun. Supernovae (SNe) are highly energetic explosions in the Universe releasing an enormous amount of energy. Long-term monitoring of these transients opens the door to understand the nature of the exploding star as well as the explosion properties. It can also help enumerate the number of massive stars.
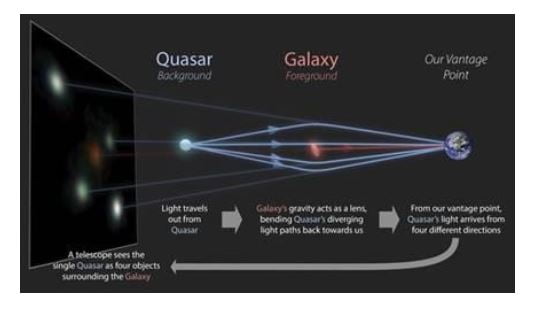
Dozen rare quadruply imaged quasars discovered can help determine expansion rate of the universe
(Topic: Space)
A group of astronomers have discovered a dozen quasars that have been warped by a naturally occurring cosmic “lens” and split into four similar images. This rare discovery increases the number of known quasars or quads by about 25 percent and can help determine the expansion rate of the universe and help address other mysteries.
Quasars are extremely luminous cores of distant galaxies that are powered by supermassive black holes. Quadruply imaged quasars are rare, and the first quadruple image was discovered in 1985. Over the past four decades, astronomers had found about fifty of these “quadruply imaged quasars” or quads for short, which occur when the gravity of a massive galaxy that happens to sit in front of a quasar splits its single image into four.
The study by Gaia Gravitational Lenses Working Group (GraL) of astronomers, which included scientists from Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES), Nainital, an autonomous institute of Department of Science and Technology, spanning only a year and a half, demonstrates the power of machine-learning to assist astronomers in their search for these cosmic jewels.
Cosmological Dilemma
In recent years, a discrepancy has emerged over the precise value of the universe’s expansion rate, also known as Hubble-Lemaître’s constant. Two primary means can be used to determine this number: one relies on measurements of the distance and speed of objects in our local universe, and the other extrapolates the rate from models based on distant radiation left over from the birth of our universe called the cosmic microwave background. The problem is that the numbers do not match. The quasars lie in between the local and distant targets used for the previous calculations. The new quasar quads, which the team gave nicknames such as “Wolf’s Paw” and “Dragon Kite,” will help in future calculations of Hubble-Lemaître’s constant and may illuminate why the two primary measurements are not in alignment.
Prelims-oriented News
World Health Day: 6th April
World’s highest Railway Bridge: Chenab Bridge in Jammu & Kashmir by Indian Railways
Exercise La Perouse: Led by French Navy
World Homoeopathy Day: 10th April – observed to commemorate the birth anniversary of the founder of Homoeopathy, Dr. Christian Fredrich Samuel Hahnemann.
FDI inflows in India
- India Attracts total FDI inflow of US$ 72.12 billion during April, 2020 to January, 2021;
- Computer Software & Hardware emerged as top sector with 45.81% of total FDI Equity inflow
- Japan leads the list of Investor countries with 29.09% of the total FDI Equity inflows during January, 2021
Launch of NanoSniffer, a Microsensor based Explosive Trace Detector
- World’s first Explosive Trace Detector using microsensor technology
- NanoSniffer is a 100% Made in India product in terms of research, development & manufacturing
- Will reduce our dependency on imported explosive trace detector devices
- Home-grown Explosive trace detector device (ETD) – NanoSniffer can detect explosives in less than 10 seconds
Launch of ‘मधुक्रान्तिपोर्टल‘ & ‘Honey Corners’
- An initiative of National Bee Board (NBB), Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare under National Beekeeping & Honey Mission (NBHM)
- This portal is being developed for online registration to achieve traceability source of Honey and other beehive products on a digital platform. The portal enables consumers to know the source of honey and assure quality of the products
- Honey Mission will lead to increase in income of farmers, employment generation and increase in exports
National Beekeeping & Honey Mission (NBHM) was approved by Government of India for Rs. 500.00 crores allotted under Aatma Nirbhar Bharat Announcement for overall promotion and development of scientific beekeeping & to achieve the goal of “Sweet Revolution”.
NBHM is implemented through National Bee Board (NBB). The scheme has three Mini Missions (MM-I, II & III) under which main thrust is given on awareness, capacity building/trainings, focus on women empowerment through beekeeping, setting up of requisite infrastructural facilities, viz.; Integrated Beekeeping Development Centres (IBDCs), Honeybees Disease Diagnostic Labs, Setting up of/upgradation of Honey Testing labs, Beekeeping Equipment Manufacturing Units, Custom Hiring Centres, Api therapy Centres, Development of Quality Nucleus Stock Centres & Bee Breeders, etc., Digitization/online registration, etc. under MM-I, processing, value addition, market support, etc. under MM-II and R&D under MM-III.
Minister of State for Education to attend consultation meeting of Education Ministers of E9 countries
E9 initiative: Scaling up digital learning to accelerate progress towards SDG4
The initiative aims to accelerate recovery and advance the Sustainable Development Goal 4 agenda by driving rapid change in education systems in three of the 2020 Global Education Meeting priorities:
(i) Support to teachers;
(ii) Investment in skills; and
(iii) Narrowing of the digital divide
E9 Countries: Bangladesh, Brazil, China, Egypt, India, Indonesia, Mexico, Nigeria, and Pakistan
India –
- Spoke about the One Nation-One Digital Platform -DIKSHA, One Nation-One Channel programme of -SWAYAM PRABHA, SWAYAM MOOCS and radio broadcasting were used to take education to the remotest part of the country. The online education was imparted to differently-abled children, and launched PM e-VIDYA to provide multi-modal access to education which benefitted nearly 250 million school-going children across India.
- The pandemic has demonstrated amply that digital and multi-modal education is a must to ensure affordable education for all. This requires strengthening digital infrastructure, developing tools and digital skills. It also requires teacher training, data security and privacy, funding, and assessment tools.
- Government is setting up National Digital Education Architecture to deliver a ‘digital first’ approach to support teaching and learning.
India-Sri Lanka Police Chiefs’ Dialogue (PCD): While appreciating each other’s ongoing action against the drug traffickers and other organised criminals exploiting the narrow sea route between the two countries, the two sides emphasized the need for sharing of real time intelligence and feedback. Both sides also agreed to work jointly against the terrorist entities including the Global Terrorist Groups and fugitives, wherever they are present and active. As the way forward, it was decided to strengthen the existing cooperation mechanisms, as also designate ‘nodal points’ for timely and effective handling of existing as well as emerging security challenges.
India-Netherlands Virtual Summit
- It was the first high level Summit attended by Netherlands’ PM Mark Rutte after the general elections held in March 2021.
- During the Summit, the two leaders exchanged views on further expanding the relationship in trade and economy, water management, agriculture sector, smart cities, science & technology, healthcare and space.
- The two Prime Ministers also agreed on instituting a ‘Strategic Partnership on Water’ to further deepen the Indo-Dutch cooperation in the water related sector, and upgrading the Joint Working Group on water to Ministerial-level.
- Netherlands’ Indo-Pacific Policy was also welcomed.
92% target achieved in the 1st phase of Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana – Gramin
Under PMAY-G with the introduction of certain implementation reforms, the Government has aimed at improving the speed and quality of houses construction, ensuring timely release of funds to beneficiaries, direct transfer of funds to beneficiaries’ account, technical assistance to beneficiaries, stringent monitoring through MIS-AwaasSoft and AwaasApp.
- The Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana – Gramin (PMAY-G) is one of the flagship programmes of the Government of India which is driven by the noble objective of providing “Housing for All” by the year 2022.
- It is a social welfare program through which the Government provides financial assistance to houseless beneficiaries identified using SECC 2011 data to help them construct a house of respectable quality for their personal living.
- The Scheme envisaged constructing 2.95 crore PMAY-G houses with all basic amenities by the year 2021-22.
- The scheme envisioned providing other facilities to make it an aspirational home for the beneficiaries through convergence with other schemes like Swachh Bharat Mission, PM Ujjwala Yojana for providing LPG connection and unskilled wage component of 90-95 days under MGNREGS.
Significant progress has been made in this direction since the launch of the scheme by the Prime Minister in November 2016.
Babu Jagjivan Ram
Babu Jagjivan Ram, who was affectionately known as Babuji, was born on the 5th of April, 1908. He was much more than a politician where he dedicated his life fighting for the freedom of the country and bringing the voices of the oppressed communities of the country.
Crusader of Social Justice
- Being a Dalit leader himself, his contributions as a social reformer were immense apart from his other influences.
- He was a member of the First Cabinet of Jawaharlal Nehru’s interim Government where he was the youngest Minister and a member of the Constituent Assembly of India.
- Babu Jagivan Ram was among the few who gave a very strong emphasis on the importance of the principles of social justice that was cherished in the Indian Constitution.
- Babu Jagjivan Ram as a crusader of social justice was instrumental in the establishment of the All Indian Depressed Classes League in the year 1935. This organization primarily sought to provide welfare and equality for the untouchables in the caste ridden societies.
He is also well known for the mass organization of movements that were dedicated for the welfare of the rural labour after he became a member of the Legislative Assembly of Bihar in the year 1937.
Babu Jagjivan Ram went on to be a prominent member of the Indian National Congress where he worked whole heartedly for the party for over forty years in a wide range of port folios after which he also became the Deputy Prime Minister of India from 1977 to 1979.
He was the Defence Minister of India during the Indo-Pak war of 1971, which resulted in the creation of Bangladesh.
His contribution to the Green Revolution in India and modernising Indian agriculture, during his two tenures as Union Agriculture Minister are still remembered, especially during 1974 drought when he was asked to hold the additional portfolio to tide over the food crisis.
Babu Jagjivan Ram went to convince Mahatma Gandhi to join Constituent Assembly as his guidance was required. This was when Gandhi ji gave him what is popularly known as Gandhi ji’s Talisman.
Dandi March
The salt movement led by Gandhi started on March 12 in 1930, from Sabarmati Ashram to the coastal village of Dandi (240 miles). The Salt March is also known as the Dandi March and the Dandi Satyagraha.
Objective:
- To produce salt from the seawater in the coastal village of Dandi, as was the practice of the local populace until British officials introduced taxation on salt production and deemed their sea-salt reclamation activities illegal.
- It was a direct-action campaign of tax resistance and nonviolent protest against the British salt monopoly under the 1882 British Salt Act.
The march directly followed the Poorna Swaraj declaration of sovereignty and self-rule by the Indian National Congress on 26 January 1930. The then Viceroy, Lord Irwin was hardly perturbed by the threat of a salt protest and the government did nothing to prevent the salt march from taking place.
The salt tax accounted for 8.2% of the British Raj revenue from tax. When Gandhi broke the salt laws on 6 April 1930, it sparked large scale acts of civil disobedience against the British Raj salt laws by millions of Indians.
As per the Gandhi-Irwin Pact Indians were allowed to make salt for domestic use.
National Salt Satyagraha Memorial: In Dandi, Gujarat; Dandi memorial encapsulates the ideals of Mahatma Gandhi- Agrah for Swadeshi, Swatchagrah and Satyagraha
- One can view statues of Mahatma Gandhi and 80 Satyagrahis who had marched with him during the historic Dandi Salt March in 1930 to make salt from sea water against the British law.
- The memorial also has 24-narrative murals depicting various events and stories from the historic 1930 Salt March.
- Solar trees are installed to meet the energy requirements of the memorial complex.
Guru Tegh Bahadur (1621–1675) – 400th Birth Anniversary (Prakash Purab)
The period of history in India in the last four centuries cannot be imagined without the influence of Guru Tegh Bahadur, the ninth Sikh Guru.
- Guru Tegh Bahadur was the ninth of ten Gurus of the Sikh religion. Born at Amritsar in 1621, was the youngest son of Guru Hargobind.
- One hundred and fifteen of his hymns are in Guru Granth Sahib.
- There are several accounts explaining the motive behind the assassination of Guru Tegh Bahadur on Aurangzeb’s orders. He stood up for the rights of Kashmiri Pandits who approached him against religious persecution by Aurangzeb.
- He was publicly killed in 1675 on the orders of Mughal emperor Aurangzeb in Delhi for himself refusing Mughal rulers and defying them.
- Gurudwara Sis Ganj Sahib and Gurdwara Rakab Ganj Sahib in Delhi mark the places of execution and cremation of his body.
Impact of his martyrdom: The execution hardened the resolve of Sikhs against religious oppression and persecution. His martyrdom helped all Sikh Panths consolidate to make the protection of human rights central to its Sikh identity. Inspired by him, his nine-year-old son, Guru Gobind Singh Ji, eventually organized the Sikh group into a distinct, formal, symbol-patterned community came to be known as Khalsa (Martial) identity.
Sri Sri Harichand Thakur
- Harichand Thakur, sometimes known as Shri Shri Harichand Thakur worked among the untouchable people of Bengal Presidency. He formed the Matua sect of Hindus.
- According to historian Sekhar Bandyopadhyay, Thakur “experienced atma darshan or self revelation, through which he realized that he was the incarnation of God himself, born in this world to bring salvation to the downtrodden”.
- Thakur, whose family were Vaishnavite Hindus, founded a sect of Vaishnavite Hinduism called Matua. This was adopted by members of the Namasudra community, who were then also known by the pejorative name of Chandalas and considered to be untouchable.
- The sect was opposed to caste oppression and, according to Sipra Mukherjee “[inspired] the community towards education and social upliftment”. It has subsequently attracted adherents from other caste communities that were marginalised by the upper castes, including the Chamars, Malis, and Telis.
Mahatma Jyotiba Phule
- Given the title of Mahatma on May 11, 1888
- Work: eradication of untouchability and caste system, emancipation and empowerment of women, reform of Hindu family life
- Along with his wife, Savitribai Phule, he is regarded as pioneers of women’s education in India. Both Savitribai Phule & her husband Jyotirao Phule went on to found India’s first school for girls called Bhide Wada in Pune in 1848. Later started schools for children from the then untouchable castes such as Mahar and Mang.
- The Phules started the Satyashodhak Samaj (Society for Truth-Seeking), through which they wanted to initiate the practice of Satyashodhak marriage, in which no dowry was taken.
- The Phules also started the Literacy Mission in India between 1854-55
- In 1863, he opened a home for pregnant Brahmin widows to give birth in a safe and secure place.
- Opened an orphanage home to avoid infanticide. In this regard, he is believed to be the first Hindu to start an orphanage for the unfortunate children.
Savitribai Phule: Savitribai Phule, the social reformer who is considered to be one of India’s first modern feminists, was born on January 3, 1831
- A crusader for women empowerment, she broke all stereotypes and spent her life promoting the noble cause of women’s education
- Savitribai was married at a very young age of 9 to social reformer Jyotirao Phule. Jyotirao was 12 years old at the time of marriage. It was Jyotirao who helped her learn how to read and write. He helped her attain high levels of education and live her life with her head held high.
- Savitribai set up India’s first women’s school from different castes in Bhidewada, Pune and became first woman teacher in the country. In her lifetime she built 18 such schools in the region.
- She also worked towards preventing female infanticide and set up a home, Balhatya Pratibandhak Griha, to prevent the killing of widows. She also campaigned against child marriage and sati pratha, which undermined the existence of women. As part of the Satyashodhak Samaj, the Phule couple organised marriages without a priest, without dowry, and at a minimum cost. The wedding vows in these marriages were the pledges taken by both the bride and the bridegroom.
- In 2014, the Maharashtra government in a tribute to Savitribai Phule renamed Pune University in her name.













