IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Education Ministry approves release of Performance Grading Index
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Education
In news
- Union Education Minister has recently approved the release of the Performance Grading Index 2019-20.
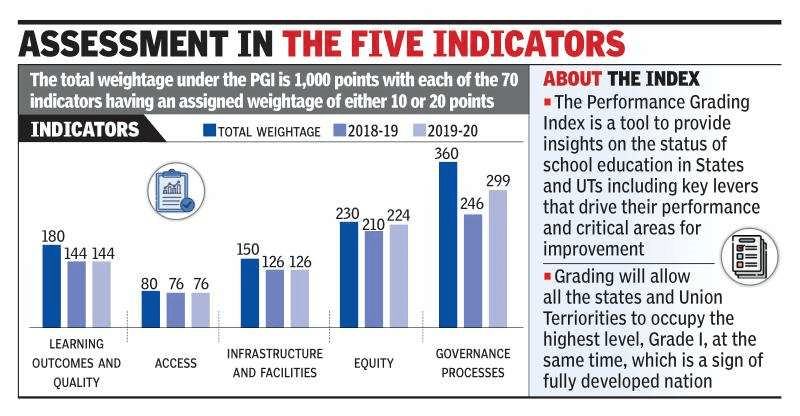
Features of the PGI
- The PGI provides grades to the states and union territories instead of ranks.
- Grading allows states and union territories to be considered at the same level.
- It eliminates the possibility of being cast as a stigma due to one’s underperformance.
- It comprises 70 indicators on aggregate classified into categories with a maximum score of 1000.
Result of the PGI
- Top performing states: Punjab, Tamilnadu, Kerala
- Lowest performing states: Meghalaya and Ladakh
Significance
- It would help them focus on the gaps and prioritise those areas for intervention to ensure that the school education system is strong at every level
Recent steps to improve quality of School Education
- National Achievement Survey conducted by the NCERT for classes 3, 5, 8 and 10.
- India shall also participate in Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) to be conducted by the OECD in 2021.
- Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA) platform for high quality e learning material.
G7 Nations agree on global minimum tax of at least 15%
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – International Relations & GS-III – Economy
In news
- A group of the world’s richest nations reached a landmark deal to close cross-border tax loopholes used by some of the world’s biggest companies.
- The Group of Seven (G7) would support a minimum global corporation tax rate of at least 15%.
- They would put in place measures to ensure taxes were paid in the countries where businesses operate.
How will it work?
- Global minimum tax rate would apply to Overseas profits.
- Governments could set whatever local corporate tax rate they want, but if companies pay lower rates in a particular country, their home governments could top-up their taxes to the minimum rate, thus eliminating the advantage of shifting profits.
- The Organisation of Economic, Cooperation and Development (OECD) has also been coordinating tax negotiations on rules for taxing cross-border Digital Services and curbing tax base erosion, including a global corporate minimum tax.
- Also, countries would lose the device used to push policies that suit them once a global minimum rate is put in place.
Impact on India
- The decision is likely to benefit India as India has wanted to keep corporate tax rate artificially lower to attract FDI in comparison to tax havens or low taxation countries.
Global food price index rises to 10- year high
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Policies and interventions and International Relations
In news
- Food and Agricultural Organisation’s (FAO) food price index (FPI) rose at their fastest monthly rate in a Decade in May.
- However, world cereal production is on its way to reach a new record.
Reasons for this inflation
- Revived demand in some countries.
- A backlog of low production
- Market and supply disruptions due to restrictions on movement due to COVID-19
Impact of the inflation
- Higher inflation will affect poor countries dependent on imports.
- Huge Multi-National Companies such as Nestlé and Coca-Cola could pass on increased prices of their raw materials to consumers.
What is inflation?
- It measures the average price change in a basket of commodities and services over time.
- However, a certain level of inflation is required in the economy to ensure that expenditure is promoted and hoarding money through savings is demotivated.
Important value additions
- FPI is released by Food and Agriculture Organisation
- It is a measure of the monthly change in international prices of a basket of food commodities.
- It consists of the average of five commodity group price indices- cereals, oilseeds, dairy products, meat and sugar.
- It is weighted with the average export shares of each of the groups
Related articles
How Food Inflation will affect Economy?
Rising Prices of Essential Commodities
New PLI scheme notified for white goods and telecom sector
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Economy
In news
- Recently, Production Linked Incentive schemes were announced for white goods and Telecom and Network Equipment
- White goods include large electrical goods used domestically such as refrigerators and washing machines, Air conditioners and LED lights, typically white in colour.
For White Goods
- Objective:
- To create complete component ecosystems in India
- To make India an integral part of the Global supply chains
- Duration and funds
- Rs. 6,238 crores
- From 2021-22 to FY 2028-29
- Features
- It will offer an incentive of 4 to 6% on incremental sales of goods manufactured in India.
- Benefits
- Increased investment, production, exports
- Create additional 4 lakh direct and indirect jobs
For Telecom sector and Network Equipment
- Objective
- To make India a global manufacturing hub for Telecom and networking products.
- Duration and funds
-
- Rs. 12, 195 crores with 1,000 crore to be allocated for MSMEs
- From Fy 2021-22 to FY 2025-26
- Features
- It is available to both MSMEs and non MSMEs companies.
- Also available to Domestic and global companies with minimum investment threshold limits for MSMEs above Rs. 10 crore and non MSMEs above Rs. 100 crore.
- Benefits
- Investment of around Rs. 3,000 crores
- Increased production and exports of Rs. 2 lakh crore over five years
- Create direct and indirect jobs
‘Ecosystem Restoration for people, nature and climate’ report by UNEP
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Conservation; Climate change
In news
- ‘Ecosystem Restoration for people, nature and climate’ report was recently published by the United Nations environment programme (UNEP).
- The report has been published in Association with Food and Agriculture Organisation for UN Decade on ecosystem Restoration 2021-2030.
- Ecosystem restoration means assisting in the recovery of ecosystems that have been degraded or destroyed, as well as conserving the ecosystems that are still intact.

Key findings of the report
- We are using the equivalent of 1.6 Earths to maintain our current way of life and the ecosystem is unable to keep up with our demands.
- Every year ecosystem services worth more than 10% of our global economic output are lost.
- Around 1/3rd of the world’s farmland is degraded.
- About 87% of Inland wetlands worldwide have disappeared since 1700.
- 1/3rd of commercial fish species are over-exploited.
- Degradation is already affecting the well-being of 40% of the world’s population.
- Countries need to deliver on their existing commitments to restore 1 billion hectares of degraded land and make similar commitments for Marine and coastal areas.
- Restoration is essential for keeping Global temperature is below 2° Celsius
Recommendations
- Restoration and avoiding degradation.
- Large scale investments in dryland agriculture
- Mangrove protection
- Water management
Miscellaneous
Asia Pacific economic cooperation (APEC)
-
APEC Leaders met online to discuss ways to build back the economy better from the pandemic.
- APEC is a regional economic forum established in 1989 to take maximum advantage of the growing interdependence of the Asia-Pacific.
- It has 21 members.
- Aim: To create greater prosperity for the region by promoting balanced, inclusive and sustainable growth.
- India is not a member of APEC.
(Mains Focus)
SCIENCE & TECH/ ECONOMY
Topic:
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
- GS-3: Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers etc.
Supersonic Flying
Context: Nearly two decades since the last supersonic passenger flight, of the British-French airliner Concorde, took off, the planes are set to return to the runways by 2029.
United Airlines of USA has recently announced it was ordering 15 planes (named Overture) with the ability to travel at Mach 1.7, faster than the speed of sound, from the Denver-based startup Boom.
What is a supersonic plane?
- Supersonic aircraft are planes that can fly faster than the speed of sound. Usually, supersonic planes can travel at the speed of around 900 kmph, twice the speed of normal aircraft

- The technology for supersonic flights is actually over 70 years old, but only recently has been used for commercial flying.
- Before 1976, when the first commercial supersonic flight took off, the planes were used entirely for military purposes.
- Concorde, the British-French turbojet-powered commercial airliner, was the first aircraft to carry passengers at supersonic speed, but eventually had to discontinue, due to cost and other concerns.
- Supersonic vehicles in the past have been flagged for their high use of jet fuels, causing extensive environmental damage.
About Boom’s Overture supersonic plane
- Long Range: The Overture aircraft would travel at the speed of Mach 1.7 or 1,805 kmph with a range of 4,250 nautical miles (7871Km). In a single flight, it could carry 65 to 88 passengers and reach an altitude of 60,000 ft. This would enable travel of passengers between busy routes like Paris-New York, Los Angeles to Sydney and San Francisco to Tokyo.
- Halves the Travel Time: Overture aircraft can reduce travel time by about half of today’s planes. Travel time from Singapore to Dubai, usually around seven hours, would be reduced to four hours.
- Commercial Operations within decade: The company has expressed confidence in getting an “experimental” jet ready by 2022, start rolling out aircraft by 2025 and eventually open them for passengers by 2029.
- No Overland Noise: The Overture will also not be noisy as supersonic planes in the past were, Boom claims, as it aims for “zero overland noise.” This essentially means that it will cruise at supersonic speeds only over water, ensuring that no sonic boom or excessive noise reaches the surfaces where people live.
- Coastal buffer zones will be created into route planning of the airline, enabling the Overture planes to travel over Mach 1 only after it reaches a “safe” distance from the shore.
- Net-Zero Emissions: Boom claims to produce an eco-friendly aircraft with “net-zero carbon emissions”, set to fly with 100 per cent sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) made from biodegradable material
- Cost cutting technologies: The company also promises to equip the airliner with advanced aerodynamics and carbon composite materials. Through this, it says, it will be able to cut significant development and maintenance costs in ways which the Concorde planes could not.
- Helps recover the sector impacted by Pandemic: The announcement of the new technology comes at the time when the global aviation industry is bearing losses due to the Covid-19 pandemic, and a third of the world’s air routes have been lost since 2020.
Challenges for Supersonic Overture Flights
- High Production Costs: The costs of making “sustainable” supersonic planes are extremely high. The very nature of its flying — using excessive amounts of fuel and energy — is likely to have high environmental costs.
- Noise Pollution: The very speed of the planes result in producing excessive amounts of noise pollution in the environment. The “Sonic Boom” created by these planes feels like an explosion to the human ear.
- Limitations in areas of operation: Noise pollution caused by Sonic boom limits where and when the supersonic planes can fly. They can only reach their actual speed until they are far enough from people and completely over the ocean.
- Government Approvals: Regulatory approvals to fly such planes can be unsuccessful, especially for transatlantic flights. Getting clearance from regulators around the world would be a challenging task, since the supersonic planes in the past have already been flagged for these hurdles.
- Expensive Fuel: Sustainable aviation fuel is currently very limited in its supply, and is extremely expensive. Moreover, the use of this fuel does not eliminate greenhouse gas emissions altogether.
- Safety Concerns: One of reasons for discontinuance of Concorde flights were safety. The July 2000 accident, when an Air France Concorde crashed right after takeoff, killing all 109 people on board and four on ground, brought safety of supersonic flights into limelight.
- Accessible only to rich: Lastly, it would not be economically feasible for everyone. Only the very rich can afford supersonic planes, as a ticket is likely to be way more costlier than a first class ticket of a regular plane.
Connecting the dots:
- Reforms in India Civil Aviation Sector
- Aviation Flying for all
- UDAN scheme
- National Civil Aviation Policy 2016 and National Civil Aviation programme 2018
WOMEN/ GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
Topic:
- GS-1: Society & issues related to women.
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to it
The invisible women in India’s labour market
Context: India’s female labour force participation rates have been dismal over the past two decades.
Issues
- At 24.5% in 2018-19, its current participation rate is well below the global average of 45%, and is also the lowest in South Asia.
- Despite rising GDP, increasing educational attainment, rising household incomes, and declining fertility, women’s participation in the labour market has decreased.
- The gender gap in participation is overwhelmingly large and has been widening over the last decade or so
- Women’s participation has decreased substantially across all age brackets, especially between 25 to 59 years.
- There are considerable variations in the rates of women’s labour force participation between rural and urban areas (26.4% for rural versus 20.4% for urban women).
- Available evidence suggests that finding a paid job is much harder for women than men. And once they enter the labour market, women still face limited work options, have fewer learning and career advancement opportunities.
- Women are overrepresented in the informal economy, particularly in vulnerable, low skilled and poorly paid jobs that have limited social security.
What factors influence Women to enter labour market & work?
Multiple factors influence women’s decision to enter the labour market, including
- Demand and supply-side drivers
- Prevailing socio-cultural
- Gender norms and attitudes.
Specifically, women’s ability to work is influenced by
- Their marital status
- Number of children
- Caste, religion and ethnicity
- Lack of essential education and vocational skills
- Labour market discrimination.
- Availability of women-friendly jobs.
Does lower participation rate indicate that women work less?
- The low participation rates, however, do not indicate that women are working less. Instead, women’s time and efforts are diverted to unpaid care work (such as raising children, caring for sick and elderly) and domestic work.
- Women spend disproportionately more time on unpaid care work in India than men, particularly if married. The Time-use Survey of 2019 shows that, on average, a woman spends 19.5% of her time every day in unpaid responsibilities compared to merely 2.5% by a man.
- While essential to the welfare of society and the economy, these activities are not accounted for in the System of National Accounts and employment, which means that they remain unrecorded and undervalued
- As a result, such unpaid essential work finds limited focus in policies and programmes aimed at improving labour market outcomes.
- Also, the declining labour force participation is associated with women’s limited involvement in sectors that provide jobs in white-collar services.
Way Ahead
Policymakers should take a holistic and integrated approach to improve women’s labour force participation and their overall labour market outcomes by
- Enhancing access to timely and impactful skill development
- Adequate maternity benefits and entitlements
- Access to affordable childcare facilities, household infrastructure and provision of other family-friendly policies to reduce the burden of unpaid care work
- Safe and convenient transportation and public infrastructure.
- Providing access to better-paid formal jobs
- Support for women-led entrepreneurship opportunities
- Investing in public services and women-friendly public spaces
- Addressing discriminatory employment practices.
- Imparting necessary vocational and technical skills
- Invest in robust data and evidence systems to better measure and count women’s unpaid work
- Design gender-smart policies and programmes for women’s economic empowerment and overall well-being.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding Asia Pacific economic cooperation (APEC):
- APEC is a regional economic forum.
- India is one of the members of the APEC
Which of the above is or are correct
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Food Price Index is released by which of the following?
- World bank
- Food and Agricultural Organisation
- World Economic Forum
- Organisation of Economic Cooperation and Development
Q.3 Consider the following statements Key findings of the ‘Ecosystem Restoration for people, nature and climate’ report:
- It was published by United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
- 1/3rd of commercial fish species are over-exploited.
Which of the above is or are correct
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 7th June 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
On Performance Grading Index:
On mitigating third wave:
About Environmental Crisis:











