UPSC Articles
Findings of Chandrayaan-2
Part of: Prelims and GS III – Awareness in space.
Context The Orbiter and other instruments of Chandrayaan-2 mission have, in two years, gathered a wealth of new information that has added to our knowledge about the Moon and its environment.
What happened to Chandrayaan-2?
- Chandrayaan-2, India’s second mission to the Moon, had failed to make a soft-landing on the lunar surface.
- The lander and rover malfunctioned in the final moments and crash-landed, getting destroyed in the process.
Why is this mission still relevant?
- Despite the failure, the mission’s orbiter and other parts have been functioning normally, gathering information.
- Recently, the ISRO released the information gathered by the scientific payloads till now, some of which were still to be analysed and assessed.
Key information gathered from Chandrayaan-2
- Presence of water molecules on moon which is the most precise information about water till date.
- Presence of Minor elements: Chromium, manganese and Sodium have been detected for the first time through remote sensing.
- Information about solar flares: A large number of microflares outside the active region have been observed for the first time. It shall help in understanding the mechanism behind heating of the solar corona.
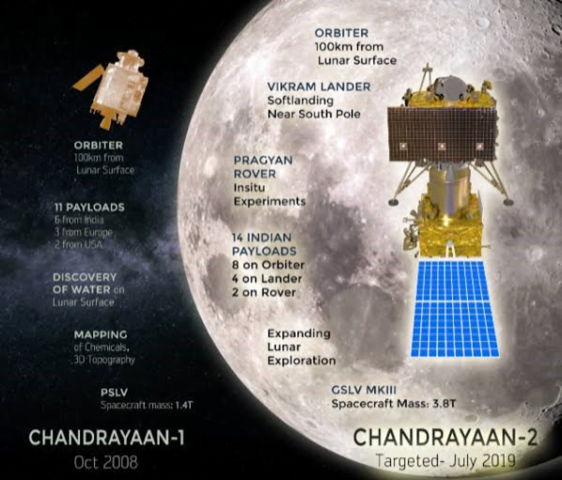
More about the Chandrayaan-2 Mission
- Scientists used the Solar X-ray Monitor (XSM) onboard Chandrayaan-2 in September 2019 to study the Sun.
- Primary objective of Chandrayaan 2: To demonstrate the ability to soft-land on the lunar surface and operate a robotic rover on the surface.
- The mission consisted of an Orbiter of the Moon, Vikram (after Vikram Sarabhai) – the lander and Pragyan (wisdom) – the rover, all equipped with scientific instruments to study the moon.