IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
- Mains – GS 3 (Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development and Employment)
In News: the Union government announced a reduction in the excise duty on petrol and diesel by Rs 8 per litre and Rs 6 per litre respectively.
- Alongside, the government also reduced the customs duty on raw materials and intermediaries for plastic products and iron and steel.
Reason for reduction
- These decisions are driven by the desire to cool the surge in inflation — recent data showed that retail inflation had risen to an eight-year high of 7.9 per cent in April, while wholesale inflation has been in double digits for 13 consecutive months.
- As per some analysts the cut in fuel taxes could help reduce inflation directly by around 20 basis points in June
- This is the second time in the recent past that the Centre has cut fuel taxes. In November last year, the Centre had lowered the excise duty on petrol by Rs 5 and by Rs 10 on diesel.
The entire burden of the tax cuts will be borne by the Centre
- Union Finance Minister said that the entire duty reduction in petrol and diesel announced has been done out of the Road & Infrastructure Cess (RIC) component of the taxes levied on petroleum products so the entire burden of the tax cuts will be borne by the Centre,
- Allaying concerns that the duty cuts will lower the devolution of taxes to States, Finance Minister said that the basic excise duty on petro products, which is sharable with States, has not been touched.
Taxes levied on petrol and diesel
- The total taxes levied on petrol and diesel include a Basic Excise Duty (BED), a Special Additional Excise duty (SAED), the Road & Infrastructure Cess (RIC) and the Agriculture & Infrastructure Development Cess (AIDC), of which only the BED is sharable with States
- The two cuts announced (November and the present one) is from Road & Infrastructure Cess (RIC) component of the taxes levied on petroleum products
Excise duty and Custom duty
- Excise duty is a form of tax imposed on goods for their production, licensing and sale.
- It is the opposite of Customs duty in sense that it applies to goods manufactured domestically in the country, while Customs is levied on those coming from outside of the country.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) With reference to India’s decision to levy an equalization tax of 6% on online advertisement services offered by non-resident entities, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2018)
- It is introduced as a part of the Income Tax Act.
- Non-resident entities that offer advertisement services in India can claim a tax credit in their home country under the “Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements”.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Source: Indian Express & The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – History
- Mains – GS 1 (Modern Indian History from about the middle of the eighteenth century until the present- significant events, personalities, issues)
In News: Celebrating the 250th birth anniversary of Raja Ram Mohan Roy
- In West Bengal, the unveiling of a statue at Raja Ram mohan Roy Library Foundation, Salt Lake, by Minister of Culture, will mark the inauguration of the Centre’s celebration plans.
About Raja Ram Mohan Roy
- Raja Ram Mohan Roy was the father of Modern India’s Renaissance and a tireless social reformer who inaugurated the age of enlightenment and liberal reformist modernization in India
His Life
- Raja Ram Mohan Roy was born on 22 May 1772 in an orthodox Brahman family at Radhanagar in Bengal.
- Ram Mohan Roy’s early education included the study of Persian and Arabic at Patna where he read the Quran, the works of Sufi mystic poets and the Arabic translation of the works of Plato and Aristotle. In Benaras, he studied Sanskrit and read Vedas and Upanishads.
- Returning to his village, at the age of sixteen, he wrote a rational critique of Hindu idol worship.
- From 1803 to 1814, he worked for East India Company as the personal diwan first of Woodforde and then of Digby.
- In 1814, he resigned from his job and moved to Calcutta in order to devote his life to religious, social and political reforms.
- In November 1830, he sailed for England to be present there to counteract the possible nullification of the Act banning Sati.
- Ram Mohan Roy was given the title of ‘Raja’ by the titular Mughal Emperor of Delhi, Akbar II whose grievances the former was to present before the British king.
Ideology
- Ram Mohan Roy was greatly influenced by western modern thought and stressed on rationalism and modern scientific approach.
- He believed that religious orthodoxies have become causes of injury and detrimental to social life and sources of trouble and bewilderment to the people, instead of tending to the amelioration of the condition of society.
- Raja Ram Mohan Roy concluded that religious reform is both social reform and political modernisation.
- Ram Mohan was attracted to Islamic monotheism. He said that monotheism is also the fundamental message of Vedanta.
- His idea of single, unitarian god was a corrective to the polytheism of orthodox Hinduism and to Christian trinitarianism. He believed that monotheism supported one universal model for humanity.
- He believed in social equality of all human beings and thus was a strong opposer of the caste system.
Brahmo Samaj
- Raja Ram Mohan Roy founded Brahmo Sabha in 1828, which was later renamed as Brahmo Samaj.
- Its chief aim was the worship of the eternal God. It was against priesthood, rituals and sacrifices.
- It focused on prayers, meditation and reading of the scriptures. It believed in the unity of all religions.
- It was the first intellectual reform movement in modern India. It led to the emergence of rationalism and enlightenment in India which indirectly contributed to the nationalist movement.
- It was the forerunner of all social, religious and political movements of modern India.
Contributions
Social reforms:
- He founded the Atmiya Sabha in 1814, the Calcutta Unitarian Association in 1821, and the Brahmo Sabha in 1828 which later became the Brahmo Samaj
- He campaigned against the caste system, untouchability, superstitions and use of intoxicants.
- He was well known for his pioneering thought and action on the emancipation of women and especially on the abolition of sati and widow remarriage.
- He attacked child marriage, illiteracy of women and the degraded state of widows and demanded the right of inheritance and property for women.
- It was his relentless advocacy alongside contemporaries such as Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar that finally led to the abolition of Sati under the governor generalship of William Bentinck in 1829.
Educational reforms:
- He supported David Hare’s efforts to find the Hindu College in 1817, while Roy’s English school taught mechanics and Voltaire’s philosophy.
- He followed it up with the Anglo-Hindu School in 1822 and, in 1830, assisted Alexander Duff to set up the General Assembly’s Institution, which later became the Scottish Church College.
- In 1825, he established Vedanta College where courses in both Indian learning and Western social and physical sciences were offered.
Literary Works of Raja Ram Mohan Roy
- Tuhfat-ul-Muwahhidin (1804)
- Vedanta Gantha (1815)
- Translation of an abridgement of the Vedanta Sara (1816)
- Kenopanishads (1816)
- Ishopanishad (1816)
- Kathopanishad (1817)
- A Conference between the Advocate for, and an Opponent of Practice of Burning Widows Alive (Bengali and English) (1818)
- Mundaka Upanishad (1819)
- A Defence of Hindu Theism (1820)
- The Precepts of Jesus- The Guide to Peace and Happiness (1820)
- Bengali Grammar (1826)
- The Universal Religion (1829)
- History of Indian Philosophy (1829)
- Gaudiya Vyakaran (1833)
Religious reforms:
- Raja Ram Mohan Roy’s first published work Tuhfat-ul-Muwahhiddin (a gift to deists) published in 1803 exposed irrational religious beliefs and corrupt practices of the Hindus as the belief in revelations, prophets, miracles etc.
- In 1814, he founded Atmiya Sabha in Calcutta to campaign against idolatry, caste rigidities, meaningless rituals and other social ills.
- He criticized the ritualism of Christianity and rejected Christ as the incarnation of God. In Precepts of Jesus (1820), he tried to separate the moral and philosophical message of the New Testament.
- Rabindranath Tagore called him a ‘Bharatpathik’ by which he meant to say that Rammohun combined in his person the underlying spirit of Indic civilisation, its spirit of pluralism, tolerance and a cosmic respect for all forms of life
Political and Economical Reforms
- Through his writings and activities, he supported the movement for free press in India.
- When press censorship was relaxed by Lord Hastings in 1819, Ram Mohan found three journals- The Brahmanical Magazine (1821); The Bengali weekly, Samvad Kaumudi (1821); and the Persian weekly, Mirat-ul-Akbar.
- Administrative reforms: He demanded the Indianisation of superior services and separation of the executive from judiciary. He demanded equality between Indians and Europeans.
- Roy condemned oppressive practices of Bengali zamindars and demanded fixation of minimum rents. He also demanded the abolition of taxes on tax-free lands.
- He called for a reduction of export duties on Indian goods abroad.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding Brahmo Samaj? (2012)
- It opposed idolatry.
- It denied the need for a priestly class for interpreting the religious texts.
- It popularized the doctrine that the Vedas are infallible
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
- Mains – GS 3 (Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, Robotics, Nano-technology, Bio-technology and issues relating to Intellectual Property Rights)
In News: The adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) chips has risen, with chipmakers designing different types of these chips to power AI applications
What are AI chips?
- AI chips are built with specific architecture and have integrated AI acceleration to support deep learning-based applications.
- These chips, with their hardware architectures and complementary packaging, memory, storage and interconnect technologies, make it possible to infuse AI into a broad spectrum of applications to help turn data into information and then into knowledge
- There are different types of AI chips such as application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), central processing units (CPUs) and GPUs, designed for diverse AI applications.
How are they different from traditional chips?
- When traditional chips, containing processor cores and memory, perform computational tasks, they continuously move commands and data between the two hardware components
- These chips, however, are not ideal for AI applications as they would not be able to handle higher computational necessities of AI workloads which have huge volumes of data.
- Although, some of the higher-end traditional chips may be able to process certain AI applications
- In comparison, AI chips generally contain processor cores as well as several AI-optimised cores (depending on the scale of the chip) that are designed to work in harmony when performing computational tasks.
- The AI cores are optimised for the demands of heterogeneous enterprise-class AI workloads with low-latency inferencing, due to close integration with the other processor cores, which are designed to handle non-AI applications.
What are their applications?
- AI chips are used for a multitude of smart machines and devices, including ones that are said to deliver the performance of a data centre-class computer to edge devices.
- Some of these chips support in-vehicle computers to run state-of-the-art AI applications more efficiently.
- AI chips are also powering applications of computational imaging in wearable electronics, drones, and robots.
- The use of AI chips for NLP (Natural Language Processing) applications has increased due to the rise in demand for chatbots and online channels such as Messenger, Slack, and others.
- They use NLP to analyse user messages and conversational logic.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Government Schemes
- Mains – GS 2 (Government Policies and Interventions for Development in various sectors and Issues arising out of their Design and Implementation); GS 3 (Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc)
In News: The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) stated that all logistics and connectivity infrastructure projects, entailing an investment of over ₹500 crore will route through the network planning group (NPG) constituted under the PM GatiShakti initiative.
- The DPIIT said that the move will bring down the logistic cost and promote effective and efficient planning of infrastructure projects.
- The DPIIT said that all the departments will approach the NPG first for approval before making a DPR (detailed project reports) at the planning stage, adding after the NPG’s clearance, the project would follow the normal procedure of approval by the finance ministry and the Cabinet, depending upon the projects
PM GatiShakti initiative
- The government of India has launched the ambitious Gati Shakti scheme or National Master Plan for multi-modal connectivity plan, with the aim of coordinated planning and execution of infrastructure projects to bring down logistics costs.
- The Gati Shakti scheme subsumed the Rs 110 lakh crore National Infrastructure Pipeline that was launched in 2019.
- Besides cutting logistics costs, the scheme is also aimed at increasing cargo handling capacity and reducing the turnaround time at ports to boost trade.
- It also aims to have 11 industrial corridors and two new defence corridors – one in Tamil Nadu and other in Uttar Pradesh.
- Integrated Approach: It intends to bring together 16 infrastructure related Ministries.

- Implementation framework includes Empowered Group of Secretaries (EGOS), Network Planning Group (NPG) and Technical Support Unit (TSU) with required technical competencies.
- NPG consists of heads of the network planning wing of respective infrastructure ministries and it will assist the empowered group of secretaries (EGOS), which is headed by the cabinet secretary.
- EGOS consist of secretaries of 18 ministries as members and Head of Logistics Division, under the DPIIT, as member convenor.
- Further, in view of the complexities involved in overall integration of networks, enhancing optimization to avoid duplication of works for holistic development of any region as well as reducing logistics costs through micro-plan detailing, the Technical Support Unit (TSU) is approved
- TSU shall have domain experts from various infrastructure sectors as Aviation, Maritime, Public Transport, Rail, Roads & Highways, Ports, etc. and Subject Matter Experts (SMEs)
The PM GatiShakti NMP is intended to break Departmental Silos and bring in more holistic and integrated planning and execution of projects with a view to address the issues of Multi Modal connectivity and last mile connectivity. This will help in bringing down the logistics cost. This will translate into enormous economic gains to consumers, farmers, youth as well as those engaged in businesses.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements: (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, and financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 3
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy – Agriculture
- Mains – GS 3 (Transport and Marketing of Agricultural Produce and Issues and Related Constraints)
Stats
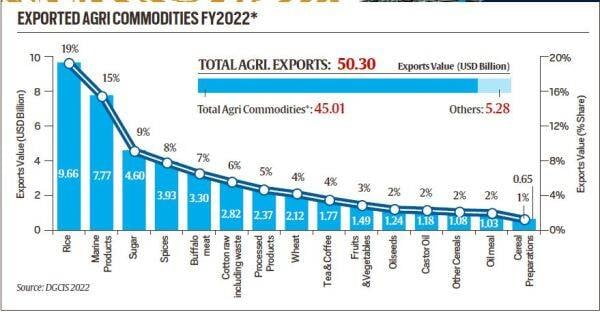
- In the fiscal year 2021-22 (FY22), agri-exports scaled an all-time high of $50.3 billion, registering a growth of 20 per cent over the preceding year.
- This was made possible largely by rising global commodity prices, but also by the favourable and aggressive export policy of the Ministry of Commerce and its various export promotion agencies like APEDA, MPEDA, and commodity boards.
- Among the several agri-commodities exported in FY22, rice ranks first with exports of $9.6 billion in value (with 21.2 million metric tonnes (MMT) in quantity). It is followed by marine products worth $7.7 billion (1.4 MMT), sugar worth $4.6 billion (10.4 MMT), spices worth $3.9 billion (1.4 MMT) and bovine (buffalo) meat worth $3.3 billion (1.18 MMT).
Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA)
- The APEDA was established by the Government of India under the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority Act, 1985.
- It functions under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. The Authority has its headquarters in New Delhi.
Composition
- A Chairman appointed by the Central Government
- The Agricultural Marketing Advisor to the Government of India, ex-official member
- Three members of Parliament of whom two are elected by the House of People and one by the Council of States
- Eight members appointed by the Central Government representing respectively…many more from agriculture and allied sectors
Functions
- APEDA is mandated with the responsibility of export promotion and development of the scheduled products fruits, vegetables and their products; meat and meat products; poultry and poultry products; dairy products etc
- APEDA has been entrusted with the responsibility to monitor import of sugar.
- It looks after the development of industries relating to the scheduled products for export by way of providing financial assistance or otherwise for undertaking surveys and feasibility studies, participating through subsidy schemes.
- Registration of persons as exporters of the scheduled products and fixing of standards and specifications for the scheduled products for the purpose of exports
- Carrying out inspection of meat and meat products in slaughterhouses, processing plants, storage premises and improving packaging of the scheduled products
Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA)
- Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA) is a nodal coordinating, state-owned agency engaged in fishery production and allied activities.
- It was established in 1972 under the Marine Products Export Development Authority Act (MPEDA), 1972.
- It functions under the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- It is headquartered in Kochi, Kerala.
- Its mandate is to increase exports of seafood including fisheries of all kinds, specifying standards, marketing, processing, extension, and training in various aspects.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) Among the following, which one is the largest exporter of rice in the world in the last five years? (2019)
- China
- India
- Myanmar
- Vietnam
Source: Indian Express
Baba’s Explainer – National Education Policy (NEP) 2020
Syllabus
- GS-2: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Education, Human Resources
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in News: Since the introduction of the National Education Policy, 2020 (NEP), Kerala has viewed the policy document with serious disagreements.
- However, two years down the line, the State has begun to warm up to some of the provisions, but with considerable hesitance. The government has hinted that the reforms might be introduced only during the 2023-24 academic year.
- The last NEP was that of 1986 and modified in 1992.
- NEP 2020 is based on the report filed by the committee headed by eminent space scientist Kasturirangan.
Read Complete Details on National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 – CLICK HERE
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Arrange the following events associated with Raja Ram Mohan Roy in chronological order.
- Vedanta College
- Atmiya Sabha
- Literary work – Tuhfat-ul-Muwahhiddin
- Brahmo Sabha
Choose the correct code:
- 1-4-2-3
- 1-3-2-4
- 2-1-3-4
- 3-2-1-4
Q.2) Consider the following statements
- PM GatiShakti’s initiative subsumed National Infrastructure Pipeline scheme
- Besides cutting logistics costs, the scheme also aims at increasing cargo handling capacity
- Empowered Group of Secretaries (EGOS) under PM GatiShakti is headed by Finance secretary of India
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.3) Consider the following agri commodities exported from India in the Financial Year 2022.
- Marine Products
- Wheat
- Sugar
- Oil Meal
- Rice
Which of the above-mentioned items were among the top three agri export commodities?
- 1, 2 and 5
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 3 and 5
- 1, 4 and 5
ANSWERS FOR 23rd MAY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d Q.2) – a Q.3) – c













