IASbaba Prelims 60 Days Plan, Rapid Revision Series (RaRe)
Archives
Hello Friends
The 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series is IASbaba’s Flagship Initiative recommended by Toppers and loved by the aspirants’ community every year.
It is the most comprehensive program which will help you complete the syllabus, revise and practice tests on a daily basis. The Programme on a daily basis includes
1. Daily RaRe Series (RRS) Videos on High Probable Topics (Monday – Saturday)
- In video discussions, special focus is given to topics which have high probability to appear in UPSC Prelims Question Paper.
- Each session will be of 20 mins to 30 mins, which would cover rapid revision of 15 high probable topics (both static and current affairs) important for Prelims Exam this year according to the schedule.
Note – The Videos will be available only in English.
2. Rapid Revision (RaRe) Notes
- Right material plays important role in clearing the exam and Rapid Revision (RaRe) Notes will have Prelims specific subject-wise refined notes.
- The main objective is to help students revise most important topics and that too within a very short limited time frame.
Note – PDFs of Daily Tests & Solution and ‘Daily Notes’ will be updated in PDF Format which are downloadable in both English & हिंदी.
3. Daily Prelims MCQs from Static (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily Static Quiz will cover all the topics of static subjects – Polity, History, Geography, Economics, Environment and Science and technology.
- 20 questions will be posted daily and these questions are framed from the topics mentioned in the schedule and in the RaRe videos.
- It will ensure timely and streamlined revision of your static subjects.
4. Daily Current Affairs MCQs (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily 5 Current Affairs questions, based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, would be published from Monday to Saturday according to the schedule.
5. Daily CSAT Quiz (Monday – Saturday)
- CSAT has been an achilles heel for many aspirants.
- Daily 5 CSAT Questions will be published.
Note – Daily Test of 20 static questions, 5 current affairs, and 5 CSAT questions. (30 Prelims Questions) in QUIZ FORMAT will be updated on a daily basis in Both English and हिंदी.
To Know More about 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series – CLICK HERE
Download 60 Day Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series Schedule – CLICK HERE
Download 60 Day Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series Notes & Solutions DAY 58– CLICK HERE
Note –
- Comment your Scores in the Comment Section. This will keep you accountable, responsible and sincere in days to come.
- It will help us come out with the Cut-Off on a Daily Basis.
Important Note
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- You can post your comments in the given format
- (1) Your Score
- (2) Matrix Meter
- (3) New Learning from the Test
Test-summary
0 of 30 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Information
The following Test is based on the syllabus of 60 Days Plan-2022 for UPSC IAS Prelims 2022.
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 30 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 30
1. Question
Consider the following statements regarding National Disposable Income (NDI):
- It gives an idea of what is the maximum amount of goods and services the domestic economy has at its disposal.
- NDI includes both factor incomes and current transfers, whereas National Income includes only factor incomes.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
Apart from the categories of aggregate macroeconomic variables such as National Income, Personal Income, Personal Disposable Income, another aggregate income categories used in National Income accounting is National Disposable Income.National Disposable Income = Net National Product at market prices + Net current transfers from the rest of the world
The significance of the National Disposable Income is that it gives an idea of what is the maximum amount of goods and services the domestic economy has at its disposal.
National income includes only factor incomes whereas NDI includes both factor incomes and current transfers.
Current transfers from the rest of the world include items such as gifts, aids, etc.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
Apart from the categories of aggregate macroeconomic variables such as National Income, Personal Income, Personal Disposable Income, another aggregate income categories used in National Income accounting is National Disposable Income.National Disposable Income = Net National Product at market prices + Net current transfers from the rest of the world
The significance of the National Disposable Income is that it gives an idea of what is the maximum amount of goods and services the domestic economy has at its disposal.
National income includes only factor incomes whereas NDI includes both factor incomes and current transfers.
Current transfers from the rest of the world include items such as gifts, aids, etc.
-
Question 2 of 30
2. Question
With reference to Viability Gap Funding, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It refers to the one-time grants provided to support infrastructure projects that are economically justified but fall short of financial viability.
- It is administered by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Funding is subject to a maximum of 30% of the total project cost.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Viability Gap Funding (VGF) means a grant one-time or deferred, provided to support infrastructure projects that are economically justified but fall short of financial viability.
The lack of financial viability usually arises from long gestation periods and the inability to increase user charges to commercial levels. Infrastructure projects also involve externalities that are not adequately captured in the direct financial returns to the project sponsor.
Viability Gap Funding is provided to infrastructure projects that are to be undertaken through
Public-Private Partnerships.It is administered by the Ministry of Finance with suitable budgetary provisions.
The quantum of VGF provided under this scheme is in the form of a capital grant at the stage of project construction. The amount of VGF will be equivalent to the lowest bid for a capital subsidy, but subject to a maximum of 20% of the total project cost.
In case the sponsoring Ministry/State Government/ statutory entity proposes to provide any assistance over and above the said VGF, it will be restricted to a further 20% of the total project cost.
Social infrastructure projects suffer from poor viability and that the government will enhance the quantum of VGF up to 30 percent each of the total project cost.
Support under this scheme is available only for infrastructure projects where private sector sponsors are selected through a process of competitive bidding.
The lead financial institution for the project is responsible for regular monitoring and periodic evaluation of project compliance with agreed milestones and performance levels, particularly for the purpose of grant disbursement.
VGF is disbursed only after the private sector company has subscribed and expended the equity
contribution required for the project.Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Viability Gap Funding (VGF) means a grant one-time or deferred, provided to support infrastructure projects that are economically justified but fall short of financial viability.
The lack of financial viability usually arises from long gestation periods and the inability to increase user charges to commercial levels. Infrastructure projects also involve externalities that are not adequately captured in the direct financial returns to the project sponsor.
Viability Gap Funding is provided to infrastructure projects that are to be undertaken through
Public-Private Partnerships.It is administered by the Ministry of Finance with suitable budgetary provisions.
The quantum of VGF provided under this scheme is in the form of a capital grant at the stage of project construction. The amount of VGF will be equivalent to the lowest bid for a capital subsidy, but subject to a maximum of 20% of the total project cost.
In case the sponsoring Ministry/State Government/ statutory entity proposes to provide any assistance over and above the said VGF, it will be restricted to a further 20% of the total project cost.
Social infrastructure projects suffer from poor viability and that the government will enhance the quantum of VGF up to 30 percent each of the total project cost.
Support under this scheme is available only for infrastructure projects where private sector sponsors are selected through a process of competitive bidding.
The lead financial institution for the project is responsible for regular monitoring and periodic evaluation of project compliance with agreed milestones and performance levels, particularly for the purpose of grant disbursement.
VGF is disbursed only after the private sector company has subscribed and expended the equity
contribution required for the project. -
Question 3 of 30
3. Question
Gross National Product is obtained from adjusting the following:
- Depreciation
- Net Indirect taxes
- Net factor income from abroad
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Gross National Product (GNP) is the total value of all finished goods and services produced by a country’s citizens in a given financial year, irrespective of their location.
It is defined as follows:
GNP = GDP + Factor income earned by the domestic factors of production employed in the rest of the world – Factor income earned by the factors of production of the rest of the world employed in the domestic economy
Hence, GNP = GDP + Net factor income from abroad
(Net factor income from abroad = Factor income earned by the domestic factors of production employed in the rest of the world – Factor income earned by the factors of production of the rest of the world employed in the domestic economy).Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Gross National Product (GNP) is the total value of all finished goods and services produced by a country’s citizens in a given financial year, irrespective of their location.
It is defined as follows:
GNP = GDP + Factor income earned by the domestic factors of production employed in the rest of the world – Factor income earned by the factors of production of the rest of the world employed in the domestic economy
Hence, GNP = GDP + Net factor income from abroad
(Net factor income from abroad = Factor income earned by the domestic factors of production employed in the rest of the world – Factor income earned by the factors of production of the rest of the world employed in the domestic economy). -
Question 4 of 30
4. Question
Consider the following:
- Gold reserves
- Loan to Commercial Banks
- Currency notes held by Public
- Foreign Exchange Reserves
- Deposits of Central Government with RBI
Which of the following can be considered as liabilities for the Reserve Bank of India?
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Balance Sheet of RBI shows the assets and liabilities of RBI. Asset and liabilities are equal for the central bank.
Assets:
- Gold Reserves
- Foreign Exchange Reserves
- Investment in Government Securities (Loan to GoI)
- Investment in Foreign Securities
- Loan to Banks
- Loan to Central Government, State Governments, NABARD etc.
Liabilities:
- Currency notes held in Banking Department
- Currency notes held by Public
- Vault Cash held by Commercial Banks
- Deposits of Commercial Banks, Scheduled State Co-operative Banks & Other Banks with RBI
- Deposits of Central Government & State Governments with RBI
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Balance Sheet of RBI shows the assets and liabilities of RBI. Asset and liabilities are equal for the central bank.
Assets:
- Gold Reserves
- Foreign Exchange Reserves
- Investment in Government Securities (Loan to GoI)
- Investment in Foreign Securities
- Loan to Banks
- Loan to Central Government, State Governments, NABARD etc.
Liabilities:
- Currency notes held in Banking Department
- Currency notes held by Public
- Vault Cash held by Commercial Banks
- Deposits of Commercial Banks, Scheduled State Co-operative Banks & Other Banks with RBI
- Deposits of Central Government & State Governments with RBI
-
Question 5 of 30
5. Question
Consider the following statements:
- Deflation refers to the direction of prices, whereas disinflation refers to the rate of change in the rate of inflation.
- Deflation decreases the value of money whereas disinflation increases the value of money.
Which of the following statements given above is/are incorrect?
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Deflation is a decline in general price levels throughout an economy, typically associated with a
contraction in the supply of money and credit in the economy. Deflation is the opposite of inflation, which represents widespread price increases of goods and services in an economy.Disinflation is a temporary slowing of the pace of price inflation. Unlike deflation, which refers to the direction of prices, disinflation refers to the rate of change in the rate of inflation.
Deflation is mainly caused by shifts in supply and demand. Disinflation, on the other hand, shows the rate of change of inflation over time. The inflation rate is declining over time, but it remains positive.
During times of deflation, since the money supply is tightened, there is an increase in the value of money, which increases the real value of debt. Inflation increases the price of goods and services over time, effectively decreasing the number of goods and services one can buy with a dollar in the future as opposed to a dollar today. This effectively decreases the time value of money. Since inflation is positive during disinflation, the value of money declines.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Deflation is a decline in general price levels throughout an economy, typically associated with a
contraction in the supply of money and credit in the economy. Deflation is the opposite of inflation, which represents widespread price increases of goods and services in an economy.Disinflation is a temporary slowing of the pace of price inflation. Unlike deflation, which refers to the direction of prices, disinflation refers to the rate of change in the rate of inflation.
Deflation is mainly caused by shifts in supply and demand. Disinflation, on the other hand, shows the rate of change of inflation over time. The inflation rate is declining over time, but it remains positive.
During times of deflation, since the money supply is tightened, there is an increase in the value of money, which increases the real value of debt. Inflation increases the price of goods and services over time, effectively decreasing the number of goods and services one can buy with a dollar in the future as opposed to a dollar today. This effectively decreases the time value of money. Since inflation is positive during disinflation, the value of money declines.
-
Question 6 of 30
6. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Gadgil-Mukherjee Formula:
- It was introduced in the context of estimation of poverty in rural areas post-independence.
- It was first adopted during the Third Five Year Plan.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
It was introduced in the context of estimation of devolution of funds between different
Indian states.Up to 3rd Five Year Plan (FYP) [1961-66] and during Plan Holiday (1966-69), allocation of Central Plan Assistance to states was schematic and no formula was in use.
The Gadgil Formula was adopted during 4th FYP (1969-74) and used in 5th FYP (1974-78).
It comprised of (i) Population [60%] (ii) Per Capita Income (PCI) [10%] (iii) Tax Effort [10%] (iv) Ongoing Irrigation & Power Projects [10%] and (v) Special Problems [10%]
However, item (iv) was perceived as being weighted in favour of rich states, the formula was modified by raising the weightage of PCI to 20%.
The National Development Council (NDC) approved the modified Gadgil formula in August 1980. It formed the basis of allocation during 6th FYP (1980-85), 7th FYP (1985-90) and Annual Plan (AP) 1990- 91.
Following suggestions from State Governments, the modified Gadgil Formula was revised to Population (55%), PCI [25% {20% by deviation method and 5% by distance method}], Fiscal Management (5%) and Special Development Problems (15%). However, it was used only during Annual Plan 1991-92.
Due to reservations of State Governments on revision, a Committee under Shri Pranab Mukherjee, then Deputy Chairman, Planning Commission was constituted to evolve a suitable formula. The suggestions made by the Committee were considered by NDC in December 1991, where following a consensus, the Gadgil-Mukherjee Formula was adopted. It was made the basis for allocation during 8th FYP (1992-97) and it has since been in used in five-year plans.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
It was introduced in the context of estimation of devolution of funds between different
Indian states.Up to 3rd Five Year Plan (FYP) [1961-66] and during Plan Holiday (1966-69), allocation of Central Plan Assistance to states was schematic and no formula was in use.
The Gadgil Formula was adopted during 4th FYP (1969-74) and used in 5th FYP (1974-78).
It comprised of (i) Population [60%] (ii) Per Capita Income (PCI) [10%] (iii) Tax Effort [10%] (iv) Ongoing Irrigation & Power Projects [10%] and (v) Special Problems [10%]
However, item (iv) was perceived as being weighted in favour of rich states, the formula was modified by raising the weightage of PCI to 20%.
The National Development Council (NDC) approved the modified Gadgil formula in August 1980. It formed the basis of allocation during 6th FYP (1980-85), 7th FYP (1985-90) and Annual Plan (AP) 1990- 91.
Following suggestions from State Governments, the modified Gadgil Formula was revised to Population (55%), PCI [25% {20% by deviation method and 5% by distance method}], Fiscal Management (5%) and Special Development Problems (15%). However, it was used only during Annual Plan 1991-92.
Due to reservations of State Governments on revision, a Committee under Shri Pranab Mukherjee, then Deputy Chairman, Planning Commission was constituted to evolve a suitable formula. The suggestions made by the Committee were considered by NDC in December 1991, where following a consensus, the Gadgil-Mukherjee Formula was adopted. It was made the basis for allocation during 8th FYP (1992-97) and it has since been in used in five-year plans.
-
Question 7 of 30
7. Question
With reference to National Investment Fund, consider the following statements:
- The objective of this fund is to maximize economic impact mainly through investment in commercially viable projects, both greenfield and brownfield.
- It is funded by the disinvestment proceeds of central public sector enterprises.
- This fund was kept outside the Consolidated fund of India.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
National Investment Fund (NIF) was established to receive disinvestment proceeds of central public sector enterprises and to invest the same to generate earnings without depleting the corpus.
The earnings of the Fund were to be used for selected Central social welfare Schemes & capital investment requirements of profitable and revivable PSUs. This fund was kept outside the consolidated fund of India.
The fund became operational in 2005.
Entire disinvestment proceeds are to be credited to the existing ‘Public Account’ under the head NIF and they would remain there until withdrawn/invested for the approved purpose. The allocations out of the NIF will be decided in the annual Government Budget.
National Investment and Infrastructure Fund:
It is India’s first infrastructure specific investment fund. This is different from the National Investment Fund. The objective of NIIF would be to maximize economic impact mainly through infrastructure development in commercially viable projects, both greenfield and brownfield, including stalled projects.
The corpus of NIIF is Rs. 40,000 Crores. The government can provide up to 20000 crores per annum into these funds. Government’s contribution/share in the corpus will be 49% in each entity set up as an alternate Investment Fund (AIF) and will neither be increased beyond nor allowed to fall below, 49%. The whole of 49% would be contributed by the Government directly. Rest is open for contribution from others.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
National Investment Fund (NIF) was established to receive disinvestment proceeds of central public sector enterprises and to invest the same to generate earnings without depleting the corpus.
The earnings of the Fund were to be used for selected Central social welfare Schemes & capital investment requirements of profitable and revivable PSUs. This fund was kept outside the consolidated fund of India.
The fund became operational in 2005.
Entire disinvestment proceeds are to be credited to the existing ‘Public Account’ under the head NIF and they would remain there until withdrawn/invested for the approved purpose. The allocations out of the NIF will be decided in the annual Government Budget.
National Investment and Infrastructure Fund:
It is India’s first infrastructure specific investment fund. This is different from the National Investment Fund. The objective of NIIF would be to maximize economic impact mainly through infrastructure development in commercially viable projects, both greenfield and brownfield, including stalled projects.
The corpus of NIIF is Rs. 40,000 Crores. The government can provide up to 20000 crores per annum into these funds. Government’s contribution/share in the corpus will be 49% in each entity set up as an alternate Investment Fund (AIF) and will neither be increased beyond nor allowed to fall below, 49%. The whole of 49% would be contributed by the Government directly. Rest is open for contribution from others.
-
Question 8 of 30
8. Question
Consider the following statements regarding SWADES initiative:
- It was launched to harness the skills of Indians returning home from abroad under the Vande Bharat Mission.
- The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) is supporting the implementation of the project.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
The Government of India launched SWADES (Skilled Workers Arrival Database for Employment Support) to harness the skills of Indians returning home from abroad under the Vande Bharat Mission.
About initiative:
- It is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship, the Ministry of Civil Aviation and the Ministry of External Affairs.
- The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC)is supporting the implementation of the project.
- It aims to create a database of qualified citizens based on their skill sets (skill mapping) and experience to tap into and fulfil demand of Indian and foreign companies.
- The collected information will be shared with the companies for suitable placement opportunities in the country.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
The Government of India launched SWADES (Skilled Workers Arrival Database for Employment Support) to harness the skills of Indians returning home from abroad under the Vande Bharat Mission.
About initiative:
- It is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship, the Ministry of Civil Aviation and the Ministry of External Affairs.
- The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC)is supporting the implementation of the project.
- It aims to create a database of qualified citizens based on their skill sets (skill mapping) and experience to tap into and fulfil demand of Indian and foreign companies.
- The collected information will be shared with the companies for suitable placement opportunities in the country.
-
Question 9 of 30
9. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR) of a firm:
- A DSCR of more than 1 means that the borrower will be unable to cover or pay current debt obligations.
- It is applied to corporate, government, and personal finance.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR) is a measure of the cash flow available to pay current debt obligations. The debt-service coverage ratio applies to corporate, government, and personal finance.
In the context of corporate finance, the debt-service coverage ratio (DSCR) is a measurement of a firm’s available cash flow to pay current debt obligations.
The DSCR shows investors whether a company has enough income to pay its debts. The formula for the debt-service coverage ratio is the ratio of net operating income and the total debt servicing for the entity.
Lenders will routinely assess a borrower’s DSCR before making a loan. A DSCR of less than 1 means negative cash flow, which means that the borrower will be unable to cover or pay current debt obligations without drawing on outside sources – in essence, borrowing more.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR) is a measure of the cash flow available to pay current debt obligations. The debt-service coverage ratio applies to corporate, government, and personal finance.
In the context of corporate finance, the debt-service coverage ratio (DSCR) is a measurement of a firm’s available cash flow to pay current debt obligations.
The DSCR shows investors whether a company has enough income to pay its debts. The formula for the debt-service coverage ratio is the ratio of net operating income and the total debt servicing for the entity.
Lenders will routinely assess a borrower’s DSCR before making a loan. A DSCR of less than 1 means negative cash flow, which means that the borrower will be unable to cover or pay current debt obligations without drawing on outside sources – in essence, borrowing more.
-
Question 10 of 30
10. Question
Consider the following statements regarding National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NBFID):
- It is a statutory body enacted under the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development Act, 2021.
- It can lend or invest, directly or indirectly in infrastructure projects located entirely or partly in India.
- It can raise money in the form of loans in Indian rupees only.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Recently Parliament enacted the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) Act, 2021 which laid down the foundation for the establishment of a statutory institution, National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NBFID) which was announced in the Budget speech by Finance Minister as the principal development financial institution (DFIs) for infrastructure financing.
It will have both developmental as well as financial objectives.
Developmental objectives include facilitating the development of the market for bonds, loans, and derivatives for long-term infrastructure financing.
Functions of NBFID include:
- extending loans and advances for infrastructure projects,
- taking over or refinancing such existing loans,
- attracting investment from private sector investors and institutional investors for infrastructure projects,
- organising and facilitating foreign participation in infrastructure projects as the principal development financial institution (DFIs) for long-term infrastructure financing.
Financial objectives will be to directly or indirectly lend, invest, or attract investments for infrastructure projects located entirely or partly in India. The central government will prescribe the sectors to be covered under the infrastructure domain.
NBFID may raise money in the form of loans or otherwise both in Indian rupees and foreign currencies, or secure money by the issue and sale of various financial instruments including bonds and debentures.
NBFID may borrow money from: (i) central government, (ii) Reserve Bank of India (RBI), (iii) scheduled commercial banks, (iii) mutual funds, and (iv) multilateral institutions such as World Bank and Asian Development Bank.
Shares of NBFID may be held by: (i) central government, (ii) multilateral institutions, (iii) sovereign wealth funds, (iv) pension funds, (v) insurers, (vi) financial institutions, (vii) banks, and (viii) any other institution prescribed by the central government.
Initially, the central government will own 100% shares of the institution which may subsequently be reduced up to 26%.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Recently Parliament enacted the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) Act, 2021 which laid down the foundation for the establishment of a statutory institution, National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NBFID) which was announced in the Budget speech by Finance Minister as the principal development financial institution (DFIs) for infrastructure financing.
It will have both developmental as well as financial objectives.
Developmental objectives include facilitating the development of the market for bonds, loans, and derivatives for long-term infrastructure financing.
Functions of NBFID include:
- extending loans and advances for infrastructure projects,
- taking over or refinancing such existing loans,
- attracting investment from private sector investors and institutional investors for infrastructure projects,
- organising and facilitating foreign participation in infrastructure projects as the principal development financial institution (DFIs) for long-term infrastructure financing.
Financial objectives will be to directly or indirectly lend, invest, or attract investments for infrastructure projects located entirely or partly in India. The central government will prescribe the sectors to be covered under the infrastructure domain.
NBFID may raise money in the form of loans or otherwise both in Indian rupees and foreign currencies, or secure money by the issue and sale of various financial instruments including bonds and debentures.
NBFID may borrow money from: (i) central government, (ii) Reserve Bank of India (RBI), (iii) scheduled commercial banks, (iii) mutual funds, and (iv) multilateral institutions such as World Bank and Asian Development Bank.
Shares of NBFID may be held by: (i) central government, (ii) multilateral institutions, (iii) sovereign wealth funds, (iv) pension funds, (v) insurers, (vi) financial institutions, (vii) banks, and (viii) any other institution prescribed by the central government.
Initially, the central government will own 100% shares of the institution which may subsequently be reduced up to 26%.
-
Question 11 of 30
11. Question
Which of the following are prohibited to receive foreign contribution under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act, 2010?
- Member of any legislature
- Candidate for election
- Political party
- Government servant or employee of any corporation
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has notified new rules under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), 2010.
As per Section 1(2) of FCRA, 2010, the provisions of the act shall apply to:
- Whole of India
- Citizens of India outside India; and
- Associate Branches or subsidiaries, outside India, of companies or bodies corporate, registered or incorporated in India.
Any “Person” can receive foreign contribution subject to the following conditions:
- It must have a definite cultural, economic, educational, religious or social program.
- It must obtain the FCRA registration/prior permission from the Central Government
- It must not be prohibited under Section 3 of FCRA, 2010.
As defined in Section 3(1) of FCRA, 2010, the following are prohibited to receive foreign contribution:
- candidate for election;
- correspondent, columnist, cartoonist, editor, owner, printer, or publisher of a registered newspaper;
- Public Servant, Judge, Government servant or employee of any corporation or any other body controlled or owned by the Government;
- member of any legislature;
- a political party or office bearer thereof;
- organization of a political nature as may be specified under sub-section (1) of Section 5 by the central government.
- association or company engaged in the production or broadcast of audio news or audio-visual news or current affairs programs through any electronic mode, or any other electronic form as defined in clause (r) of sub-section (1) of Section 2 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 or any other mode of mass communication;
- correspondent or columnist, cartoonist, editor, owner of the association or company referred to in point (g).
- Individuals or associations who have been prohibited from receiving foreign contributions.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has notified new rules under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), 2010.
As per Section 1(2) of FCRA, 2010, the provisions of the act shall apply to:
- Whole of India
- Citizens of India outside India; and
- Associate Branches or subsidiaries, outside India, of companies or bodies corporate, registered or incorporated in India.
Any “Person” can receive foreign contribution subject to the following conditions:
- It must have a definite cultural, economic, educational, religious or social program.
- It must obtain the FCRA registration/prior permission from the Central Government
- It must not be prohibited under Section 3 of FCRA, 2010.
As defined in Section 3(1) of FCRA, 2010, the following are prohibited to receive foreign contribution:
- candidate for election;
- correspondent, columnist, cartoonist, editor, owner, printer, or publisher of a registered newspaper;
- Public Servant, Judge, Government servant or employee of any corporation or any other body controlled or owned by the Government;
- member of any legislature;
- a political party or office bearer thereof;
- organization of a political nature as may be specified under sub-section (1) of Section 5 by the central government.
- association or company engaged in the production or broadcast of audio news or audio-visual news or current affairs programs through any electronic mode, or any other electronic form as defined in clause (r) of sub-section (1) of Section 2 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 or any other mode of mass communication;
- correspondent or columnist, cartoonist, editor, owner of the association or company referred to in point (g).
- Individuals or associations who have been prohibited from receiving foreign contributions.
-
Question 12 of 30
12. Question
With reference to Real Estate Regulation and Development Act 2016, consider the following statements:
- The Act establishes Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA) in each state for regulation of the real estate sector.
- It mandates promoters to park 50% of all project receivables into a separate reserve account.
- The Act is applicable to all the States and Union Territories except Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
Which of the following statements given above is/are NOT correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 (RERA) was passed by the Parliament in March, 2016 heralding a new era of transformation in the real estate sector.
The core objective of this transformative legislation is to ensure regulation and promotion of real estate sector in an efficient manner and to protect the interest of home buyers.
The Act is applicable to all the states/UTs.
In August 2020, Jammu and Kashmir notified its RERA rules and the UT is now bound by the central rules, although it does have the authority to draft and implement specific rules with respect to local land laws. Ladakh too notified its RERA rules on October 8, 2020.
Key Provisions of Real Estate Regulation Act:
The Act establishes Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA) in each state for regulation of the real estate sector and also acts as an adjudicating body for speedy dispute resolution.
Establishment of Real Estate Appellate Tribunal- Decisions of RERAs can be appealed in these tribunals.
Mandatory Registration: All projects with a plot size of a minimum of 500 sq. mt need to be registered with Regulatory Authorities.
Under the RERA act, a minimum of 70% of the buyers’ and investors’ money will be kept in a separate reserve account. This money will then be allotted to the builders only for construction and land-related costs.
Liability: Developer’s liability to repair structural defects for five years.
Both promoter and buyer are liable to pay an equal rate of interest in case of any default from either side.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 (RERA) was passed by the Parliament in March, 2016 heralding a new era of transformation in the real estate sector.
The core objective of this transformative legislation is to ensure regulation and promotion of real estate sector in an efficient manner and to protect the interest of home buyers.
The Act is applicable to all the states/UTs.
In August 2020, Jammu and Kashmir notified its RERA rules and the UT is now bound by the central rules, although it does have the authority to draft and implement specific rules with respect to local land laws. Ladakh too notified its RERA rules on October 8, 2020.
Key Provisions of Real Estate Regulation Act:
The Act establishes Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA) in each state for regulation of the real estate sector and also acts as an adjudicating body for speedy dispute resolution.
Establishment of Real Estate Appellate Tribunal- Decisions of RERAs can be appealed in these tribunals.
Mandatory Registration: All projects with a plot size of a minimum of 500 sq. mt need to be registered with Regulatory Authorities.
Under the RERA act, a minimum of 70% of the buyers’ and investors’ money will be kept in a separate reserve account. This money will then be allotted to the builders only for construction and land-related costs.
Liability: Developer’s liability to repair structural defects for five years.
Both promoter and buyer are liable to pay an equal rate of interest in case of any default from either side.
-
Question 13 of 30
13. Question
Which of the following body compiles the Consumer Price Index for Rural Labourers?
Correct
Solution (a)
Basic Info:
Consumer Price Index, CPI:
It measures price changes from the perspective of a retail buyer.
It measures changes over time in the level of retail prices of selected goods and services on which consumers of a defined group spend their incomes.
Four types of CPI are as follows:
- CPI for Industrial Workers (IW).
- CPI for Agricultural Labourer (AL).
iii. CPI for Rural Labourer (RL).
- CPI (Rural/Urban/Combined).
Of these, the first three are compiled by the Labour Bureau in the Ministry of Labour and Employment. Fourth is compiled by the Central Statistical Organisation (CSO) in the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Basic Info:
Consumer Price Index, CPI:
It measures price changes from the perspective of a retail buyer.
It measures changes over time in the level of retail prices of selected goods and services on which consumers of a defined group spend their incomes.
Four types of CPI are as follows:
- CPI for Industrial Workers (IW).
- CPI for Agricultural Labourer (AL).
iii. CPI for Rural Labourer (RL).
- CPI (Rural/Urban/Combined).
Of these, the first three are compiled by the Labour Bureau in the Ministry of Labour and Employment. Fourth is compiled by the Central Statistical Organisation (CSO) in the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
-
Question 14 of 30
14. Question
The Committee on Virtual Currencies was headed by?
Correct
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
Inter-Ministerial Committee on Virtual Currencies was headed by Subhash Chandra Garg.
Key recommendations:
- Ban on all forms of private crypto-currencies.
- Look into the introduction of an official digital currency in the country.
- Data localisation requirements proposed in the draft Data Protection Bill may need to be applied carefully.
The committee set up by Centre has also proposed a draft bill ‘Banning of Crypto-currency & Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 2019’.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
Inter-Ministerial Committee on Virtual Currencies was headed by Subhash Chandra Garg.
Key recommendations:
- Ban on all forms of private crypto-currencies.
- Look into the introduction of an official digital currency in the country.
- Data localisation requirements proposed in the draft Data Protection Bill may need to be applied carefully.
The committee set up by Centre has also proposed a draft bill ‘Banning of Crypto-currency & Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 2019’.
-
Question 15 of 30
15. Question
Which of the following are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)?
- Credit rating agencies
- Commodity spot markets
- Alternative Investment Funds
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
SEBI is a statutory regulatory body established on the 12th of April, 1992. It monitors and regulates the Indian capital and securities market while ensuring to protect the interests of the investors, formulating regulations and guidelines. The head office of SEBI is in Mumbai.
The spot market is where financial instruments, such as commodities, currencies, and securities, are traded for immediate delivery whereas Commodity futures pertain to a specific settlement date in the future. In the Spot market, a party to party contract (buyer and seller may be known to each other) takes place. In a Commodity market, trade takes place anonymously between two parties on the Stock Exchange platform.
While the SEBI regulates the commodity futures business in India, the commodity spot markets are not regulated by SEBI. They come under the direct purview of respective state governments.
A credit rating agency is an entity that assesses the ability and willingness of the issuer company for timely payment of interest and principal on a debt instrument. Credit rating agencies are regulated by SEBI. The SEBI (Credit Rating Agencies) Regulations, 1999 govern the credit rating agencies and provide for eligibility criteria for registration of credit rating agencies, monitoring and review of ratings.
Alternative Investment Fund or AIF means any fund established or incorporated in India which is a privately pooled investment vehicle that collects funds from sophisticated investors, whether Indian or foreign, for investing it in accordance with a defined investment policy for the benefit of its investors. They are regulated as per SEBI (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
SEBI is a statutory regulatory body established on the 12th of April, 1992. It monitors and regulates the Indian capital and securities market while ensuring to protect the interests of the investors, formulating regulations and guidelines. The head office of SEBI is in Mumbai.
The spot market is where financial instruments, such as commodities, currencies, and securities, are traded for immediate delivery whereas Commodity futures pertain to a specific settlement date in the future. In the Spot market, a party to party contract (buyer and seller may be known to each other) takes place. In a Commodity market, trade takes place anonymously between two parties on the Stock Exchange platform.
While the SEBI regulates the commodity futures business in India, the commodity spot markets are not regulated by SEBI. They come under the direct purview of respective state governments.
A credit rating agency is an entity that assesses the ability and willingness of the issuer company for timely payment of interest and principal on a debt instrument. Credit rating agencies are regulated by SEBI. The SEBI (Credit Rating Agencies) Regulations, 1999 govern the credit rating agencies and provide for eligibility criteria for registration of credit rating agencies, monitoring and review of ratings.
Alternative Investment Fund or AIF means any fund established or incorporated in India which is a privately pooled investment vehicle that collects funds from sophisticated investors, whether Indian or foreign, for investing it in accordance with a defined investment policy for the benefit of its investors. They are regulated as per SEBI (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012.
-
Question 16 of 30
16. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Priority Sector Lending:
- The provisions of Priority Sector Lending apply to every Commercial Bank.
- According to the new guidelines loan limits for renewable energy have been doubled.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
The concept of ‘Priority sector lending’ focuses on the idea of increasing the lending of the banks towards few specified sectors and activities in the economy. The provisions of PSL apply to every Commercial Bank [including Regional Rural Bank (RRB), Small Finance Bank (SFB), Local Area Bank] and Primary (Urban) Co- operative Bank (UCB).
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) revised priority sector lending (PSL) guidelines to include entrepreneurship and renewable resources, in line with emerging national priorities. RBI considered the recommendations made by the UK Sinha-led expert committee on Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises and the MK Jain led Internal Working Group to Review Agriculture Credit apart from discussions with all stakeholders.
Some of the salient features of revised PSL guidelines are:
Fresh categories included in the PSL category:
- bank finance of up to ₹50 crores to start-ups.
- loans to farmers both for installation of solar power plants for solarisation of grid-connected agriculture pumps.
- for setting up compressed biogas (CBG) plants.
Higher weightage has been assigned to incremental priority sector credit in ‘identified districts’ where priority sector credit flow is comparatively low.
Loan limits for renewable energy have been doubled.
For the improvement of health infrastructure, the credit limit for health infrastructure (including those under ‘Ayushman Bharat’) has been doubled.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
The concept of ‘Priority sector lending’ focuses on the idea of increasing the lending of the banks towards few specified sectors and activities in the economy. The provisions of PSL apply to every Commercial Bank [including Regional Rural Bank (RRB), Small Finance Bank (SFB), Local Area Bank] and Primary (Urban) Co- operative Bank (UCB).
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) revised priority sector lending (PSL) guidelines to include entrepreneurship and renewable resources, in line with emerging national priorities. RBI considered the recommendations made by the UK Sinha-led expert committee on Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises and the MK Jain led Internal Working Group to Review Agriculture Credit apart from discussions with all stakeholders.
Some of the salient features of revised PSL guidelines are:
Fresh categories included in the PSL category:
- bank finance of up to ₹50 crores to start-ups.
- loans to farmers both for installation of solar power plants for solarisation of grid-connected agriculture pumps.
- for setting up compressed biogas (CBG) plants.
Higher weightage has been assigned to incremental priority sector credit in ‘identified districts’ where priority sector credit flow is comparatively low.
Loan limits for renewable energy have been doubled.
For the improvement of health infrastructure, the credit limit for health infrastructure (including those under ‘Ayushman Bharat’) has been doubled.
-
Question 17 of 30
17. Question
Consider the following statements:
- Under Ways and Means Advance (WMA) mechanism, both the Central Government and State Government are allowed to borrow from RBI.
- Commercial bills are unsecured, long- term debt issued by a corporation for the financing of long-term liabilities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Basic Info:
Money market refers to a section of the financial market where financial instruments with high liquidity and short-term maturities are traded. The money market primarily facilitates lending and borrowing of funds between banks and entities like Primary Dealers (PDs).
Banks and PDs borrow and lend overnight or for the short period to meet their short term mismatches in fund positions. This borrowing and lending is on unsecured basis.
- Call Money is the borrowing or lending of funds for 1day.
- If money is borrowed or lend for period between 2 days and 14 days it is known as Notice Money.
- Term Money refers to borrowing/lending of funds for period between 15 days and one year.
Ways and Means Advances (WMA) is a facility for both the Centre and states to borrow from the RBI. These borrowings are meant purely to help them to tide over temporary mismatches in cash flows of their receipts and expenditures. Section 17(5) of the RBI Act, 1934 authorises the central bank to lend to the Centre and state governments subject to their being repayable “not later than three months from the date of the making of the advance”.
Commercial bills are unsecured, short-term debt issued by a corporation, often times for the financing of short-term liabilities and inventory.
Bills of exchange are negotiable instruments drawn by the seller (drawer) of the goods or services on the buyer (drawee) of the goods for the value of the goods delivered.
These bills are called trade bills. These trade bills are called commercial bills when they are accepted by commercial banks for discounting. If the bill is payable at a future date and the seller needs money immediately, he may approach his bank for discounting the bill. The bank or any other discounting body takes a commission for it.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Basic Info:
Money market refers to a section of the financial market where financial instruments with high liquidity and short-term maturities are traded. The money market primarily facilitates lending and borrowing of funds between banks and entities like Primary Dealers (PDs).
Banks and PDs borrow and lend overnight or for the short period to meet their short term mismatches in fund positions. This borrowing and lending is on unsecured basis.
- Call Money is the borrowing or lending of funds for 1day.
- If money is borrowed or lend for period between 2 days and 14 days it is known as Notice Money.
- Term Money refers to borrowing/lending of funds for period between 15 days and one year.
Ways and Means Advances (WMA) is a facility for both the Centre and states to borrow from the RBI. These borrowings are meant purely to help them to tide over temporary mismatches in cash flows of their receipts and expenditures. Section 17(5) of the RBI Act, 1934 authorises the central bank to lend to the Centre and state governments subject to their being repayable “not later than three months from the date of the making of the advance”.
Commercial bills are unsecured, short-term debt issued by a corporation, often times for the financing of short-term liabilities and inventory.
Bills of exchange are negotiable instruments drawn by the seller (drawer) of the goods or services on the buyer (drawee) of the goods for the value of the goods delivered.
These bills are called trade bills. These trade bills are called commercial bills when they are accepted by commercial banks for discounting. If the bill is payable at a future date and the seller needs money immediately, he may approach his bank for discounting the bill. The bank or any other discounting body takes a commission for it.
-
Question 18 of 30
18. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Small Saving Schemes in India:
- Money collected through these schemes can be used as a source of financing the government deficit.
- Collections from all small savings instruments are credited to the National Small Savings Fund.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
They are the major source of household savings in India and comprise 12 instruments. The depositors get an assured interest on their money.
Collections from all small savings instruments are credited to the National Small Savings Fund.
Small savings have emerged as a key source of financing the government deficit, especially after the Covid-19 pandemic led to a ballooning of the government deficit, necessitating higher need for borrowings.
The National Small Savings Fund is administered by the Government of India, Ministry of Finance (Department of Economic Affairs) under National Small Savings Fund (Custody and Investment) Rules, 2001, framed by the President under Article 283(1) of the Constitution.
The objective of NSSF is to de-link small savings transactions from the Consolidated Fund of India and ensure their operation in a transparent and self-sustaining manner.
The Shyamala Gopinath panel (2010) constituted on the Small Saving Scheme had suggested a market-linked interest rate system for small savings schemes.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
They are the major source of household savings in India and comprise 12 instruments. The depositors get an assured interest on their money.
Collections from all small savings instruments are credited to the National Small Savings Fund.
Small savings have emerged as a key source of financing the government deficit, especially after the Covid-19 pandemic led to a ballooning of the government deficit, necessitating higher need for borrowings.
The National Small Savings Fund is administered by the Government of India, Ministry of Finance (Department of Economic Affairs) under National Small Savings Fund (Custody and Investment) Rules, 2001, framed by the President under Article 283(1) of the Constitution.
The objective of NSSF is to de-link small savings transactions from the Consolidated Fund of India and ensure their operation in a transparent and self-sustaining manner.
The Shyamala Gopinath panel (2010) constituted on the Small Saving Scheme had suggested a market-linked interest rate system for small savings schemes.
-
Question 19 of 30
19. Question
With reference to E-commerce sector in India, consider the following statements:
- 100% FDI under automatic route is permitted in marketplace model of e-commerce.
- Provisions of the Consumer Protection Act, 2019 are not applicable to e-commerce companies.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Basic Info:
E-commerce means buying and selling of goods and services including digital products over digital & electronic network.
There are two Types of e-commerce business models:
- Inventory based model- an e-commerce activity where inventory of goods and services is owned by e-commerce entity and is sold to the consumers directly. E.g.- Grofers
- Marketplace based model – means providing of an information technology platform by an ecommerce entity on a digital & electronic network to act as a facilitator between buyer and seller. E.g.- Amazon, Flipkart etc.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Provisions for e-commerce:
- 100% FDI under automatic route is permitted in marketplace model of e-commerce.
- FDI is not permitted in inventory-based model of e-commerce.
As per the e-commerce policy, E-commerce entity providing a marketplace will not exercise ownership or control over the inventory i.e. goods purported to be sold. Such an ownership or control over the inventory will render the business into inventory-based model
An e-commerce entity will not permit more than 25% of the sales value on financial year basis affected through its marketplace from one vendor or their group companies.
As per the recently passed Consumer Protection Act, 2019:
- No e-commerce entity shall impose cancellation charges on consumers cancelling after confirming purchase unless similar charges are also borne by the e- commerce entity, if they cancel the purchase order unilaterally for any reason.
- Every e-commerce entity shall ensure that the grievance officer acknowledges the receipt of any consumer complaint within forty-eight hours and redresses the complaint within one month from the date of receipt of the complaint.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Basic Info:
E-commerce means buying and selling of goods and services including digital products over digital & electronic network.
There are two Types of e-commerce business models:
- Inventory based model- an e-commerce activity where inventory of goods and services is owned by e-commerce entity and is sold to the consumers directly. E.g.- Grofers
- Marketplace based model – means providing of an information technology platform by an ecommerce entity on a digital & electronic network to act as a facilitator between buyer and seller. E.g.- Amazon, Flipkart etc.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Provisions for e-commerce:
- 100% FDI under automatic route is permitted in marketplace model of e-commerce.
- FDI is not permitted in inventory-based model of e-commerce.
As per the e-commerce policy, E-commerce entity providing a marketplace will not exercise ownership or control over the inventory i.e. goods purported to be sold. Such an ownership or control over the inventory will render the business into inventory-based model
An e-commerce entity will not permit more than 25% of the sales value on financial year basis affected through its marketplace from one vendor or their group companies.
As per the recently passed Consumer Protection Act, 2019:
- No e-commerce entity shall impose cancellation charges on consumers cancelling after confirming purchase unless similar charges are also borne by the e- commerce entity, if they cancel the purchase order unilaterally for any reason.
- Every e-commerce entity shall ensure that the grievance officer acknowledges the receipt of any consumer complaint within forty-eight hours and redresses the complaint within one month from the date of receipt of the complaint.
-
Question 20 of 30
20. Question
The Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) Synthesis Report is published by?
Correct
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) recently in its report Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) synthesis report, called for more ambitious climate action plans by the countries in order to achieve the Paris Agreement target of containing global temperature rise to two degrees Celsius (ideally 1.5°C) by the end of the century.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) recently in its report Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) synthesis report, called for more ambitious climate action plans by the countries in order to achieve the Paris Agreement target of containing global temperature rise to two degrees Celsius (ideally 1.5°C) by the end of the century.
-
Question 21 of 30
21. Question
Consider the following statements regarding ‘Open RAN (Radio Access Network) architecture’
- Open RAN will create a multi-supplier RAN solution that allows for the separation between hardware and software with open interfaces.
- Open-RAN is a technology that allows networks to be built using subcomponents from a variety of vendors
Select the correct statement(s)
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Open RAN will create a multi-supplier RAN solution that allows for the separation between hardware and software with open interfaces. Idea of Open RAN is to enable operators to mix and match components from different vendors Open-RAN is not a technology, but rather an ongoing shift in mobile network architecture that allows networks to be built using subcomponents from a variety of vendors. O-RAN has an open, multi-vendor architecture for deploying mobile networks, as opposed to the single-vendor proprietary architecture. Context – The Ministry of Communications has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with M/s VVDN Technologies Private Limited to facilitate registered startups, innovators and MSMEs working in the field of Open RAN (Radio Access Network) to get their product tested at the existing lab of M/s VVDN
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Open RAN will create a multi-supplier RAN solution that allows for the separation between hardware and software with open interfaces. Idea of Open RAN is to enable operators to mix and match components from different vendors Open-RAN is not a technology, but rather an ongoing shift in mobile network architecture that allows networks to be built using subcomponents from a variety of vendors. O-RAN has an open, multi-vendor architecture for deploying mobile networks, as opposed to the single-vendor proprietary architecture. Context – The Ministry of Communications has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with M/s VVDN Technologies Private Limited to facilitate registered startups, innovators and MSMEs working in the field of Open RAN (Radio Access Network) to get their product tested at the existing lab of M/s VVDN
-
Question 22 of 30
22. Question
With reference to ‘United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD)’, consider the following statements
- It is the sole legally binding international agreement linking environment and development to sustainable land management
- Global Land Outlook (GLO) is a UNCCD flagship publication that underscores land system challenges
- The theme of COP 15 which took place recently was ‘Restore Land to Sustain Life’
Choose the correct answer using the code given below
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Incorrect UNCCD was established in 1994, the sole legally binding international agreement linking environment and development to sustainable land management. The Global Land Outlook (GLO), the UNCCD flagship publication, underscores land system challenges, showcases transformative policies and practices, and points to cost-effective pathways to scale up sustainable land and water management. The Theme of COP 15 of the UNCCD was ‘Land. Life. Legacy: From scarcity to prosperity’ Context – The Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change addressed the fifteenth session of the Conference of the Parties (COP15) of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) in Cote d’Ivoire (Western Africa).
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Incorrect UNCCD was established in 1994, the sole legally binding international agreement linking environment and development to sustainable land management. The Global Land Outlook (GLO), the UNCCD flagship publication, underscores land system challenges, showcases transformative policies and practices, and points to cost-effective pathways to scale up sustainable land and water management. The Theme of COP 15 of the UNCCD was ‘Land. Life. Legacy: From scarcity to prosperity’ Context – The Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change addressed the fifteenth session of the Conference of the Parties (COP15) of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) in Cote d’Ivoire (Western Africa).
-
Question 23 of 30
23. Question
Consider the following statements regarding ‘AIM-PRIME (Program for Researchers in Innovation, Market Readiness, and Entrepreneurship) Playbook’
- It aims to promote science-based, deep technology ideas to market through training and guidance over a period of 6 months
- AIM has collaborated with World Bank to launch this nationwide programme
Select the correct statement(s)
Correct
Solution (d)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Incorrect The programme aims to promote science-based, deep technology ideas to market through training and guidance over a period of 12 months. It focuses on science-based, knowledge-intensive, deep technology entrepreneurship. AIM has collaborated with Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) to launch this nationwide programme which will be implemented by Venture Centre – a non-profit technology business incubator hosted by Council Of Scientific And Industrial Research–National Chemical Laboratory (CSIR-NCL). Context – AIM, NITI Aayog launched the AIM-PRIME Playbook to help academicians launch deep-tech spin-offs
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Incorrect The programme aims to promote science-based, deep technology ideas to market through training and guidance over a period of 12 months. It focuses on science-based, knowledge-intensive, deep technology entrepreneurship. AIM has collaborated with Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) to launch this nationwide programme which will be implemented by Venture Centre – a non-profit technology business incubator hosted by Council Of Scientific And Industrial Research–National Chemical Laboratory (CSIR-NCL). Context – AIM, NITI Aayog launched the AIM-PRIME Playbook to help academicians launch deep-tech spin-offs
-
Question 24 of 30
24. Question
‘PRAAPTI’, a portal seen in news is related to
Correct
Solution (b)
The Union Ministry of Power has launched web portal and app namely PRAAPTI (Payment Ratification And Analysis in Power procurement for bringing Transparency in Invoicing of generators). The webportal and app aims to bring transparency in power purchase transactions between Generators and Discoms. The PRAAPTI app and web Portal will capture invoicing and payment data for various long term Power Purchasing Agreements (PPAs) from power generation companies (generators).
Context – The portal was in news
Incorrect
Solution (b)
The Union Ministry of Power has launched web portal and app namely PRAAPTI (Payment Ratification And Analysis in Power procurement for bringing Transparency in Invoicing of generators). The webportal and app aims to bring transparency in power purchase transactions between Generators and Discoms. The PRAAPTI app and web Portal will capture invoicing and payment data for various long term Power Purchasing Agreements (PPAs) from power generation companies (generators).
Context – The portal was in news
-
Question 25 of 30
25. Question
Consider the following statements regarding ‘Coastal Regulation Zones’
- The coastal regulation zones have been declared by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate change under the Biodiversity Act of 2002
- CRZ Rules are made by the Union environment ministry but it is implemented by state governments through their Coastal Zone Management Authorities
- National Coastal Zone Management Authority (NCZMA) has recommended that gas-based power plants be permitted within the Island Coastal Regulation Zone area only on islands with geographical areas greater than 1000 sq. km.
Select the correct answer using the code given below
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Correct Incorrect The coastal regulation zones have been declared by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate change under the Environment Protection Act 1986. While the CRZ Rules are made by the Union environment ministry, implementation is to be ensured by state governments through their Coastal Zone Management Authorities. The National Coastal Zone Management Authority (NCZMA) has recommended that gas-based power plants be permitted within the Island Coastal Regulation Zone area only on islands with geographical areas greater than 100 sq. km. Context – Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has approved an exemption to the laws governing the regulation of coastal zones and has paved the way for gas-powered plants to be set up at Andaman and Nicobar islands.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Correct Incorrect The coastal regulation zones have been declared by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate change under the Environment Protection Act 1986. While the CRZ Rules are made by the Union environment ministry, implementation is to be ensured by state governments through their Coastal Zone Management Authorities. The National Coastal Zone Management Authority (NCZMA) has recommended that gas-based power plants be permitted within the Island Coastal Regulation Zone area only on islands with geographical areas greater than 100 sq. km. Context – Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has approved an exemption to the laws governing the regulation of coastal zones and has paved the way for gas-powered plants to be set up at Andaman and Nicobar islands.
-
Question 26 of 30
26. Question
Six girls are sitting in a circle facing to the centre of the circle. They are P, Q, R, S, T and V. T is not between Q and S but some other one. P is next to the left of V. R is 4th to the right of P. What is the position of T?
Correct
Solution (d)

Hence, Option(d) is the right answer.
Incorrect
Solution (d)

Hence, Option(d) is the right answer.
-
Question 27 of 30
27. Question
In a class there are seven students (including boys and girls) A, B, C, D, E, F and G. They sit on three benches I, II and III. Such that at least two students on each bench and at least one girl on each bench. C who is a girl student, does not sit with A, E and D. F the boy student sits with only B. A sits on the bench I with his best friends. G sits on the bench III. E is the brother of C. Which of the following is the group of girls ?
Correct
Solution (c)

BCD are the group of girls.
Incorrect
Solution (c)

BCD are the group of girls.
-
Question 28 of 30
28. Question
A, B, C, D, E, F and G are sitting in a row facing North. F is to the immediate right of E. E is 4th to the right of G. C is the neighbour of B and D. Person who is third to the left of D is at one of ends. Who are the neighbors of B?
Correct
Solution (b)
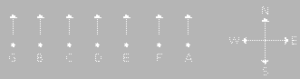
C and G are the neighbours of B.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
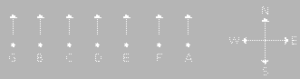
C and G are the neighbours of B.
-
Question 29 of 30
29. Question
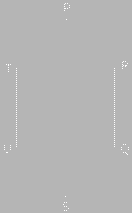
Six friends P, Q, R, S, T and U are sitting around the hexagonal table each at one corner and are facing the centre of the hexagonal. P is second to the left of U. Q is neighbour of R and S. T is second to the left of S. Who is the fourth person to the left of Q ?
Correct
Solution (a)
P is the fourth person to the left of Q.
Incorrect
Solution (a)

P is the fourth person to the left of Q.
-
Question 30 of 30
30. Question
Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow each passage. Your answer to these questions should be based on passage only.
The origin of water on Earth is linked to the formation of Earth. According to some currently accepted theories Earth began as a waterless mass of rock surrounded by cloud of gas. Radioactive materials in the rock and increasing pressure in the Earth‘s interior gradually produced enough heat to melt the interior of the Earth. The heavy materials, such as iron ores, then sank. The light silicates (rocks made up of silicon and oxygen) rose to the Earth‘s surface and formed the earliest crust.
Many silicate rocks have water molecules integrated into their atomic arrangement – water can be driven out of such rocks by the action of heat. Thus the heating of the Earth‘s interior caused release of water contained in such rocks to the surface. Over millions of years, water thus released collected slowly in low places of the crust and formed the oceans. Whatsoever might have been the origin of water, earth‘s original supply of water is still in use and very little, if any, has been added during the past billion years or so. The same water has been pumped time and again from the oceans into the air, dropped down upon the lands and transferred back to sea. A single drop of water spends 8 to 10 days passing through air, 2 to 3 weeks in a river, as long as 100 years in a Himalayan Glacier or from 100 to 40,000 year underground.
Q.30) Consider the following statements with respect to the passage:
- Earth’s original supply of water has ended and most of the water which is in current use has been added during the past billion years
- The heating of the Earth‘s interior caused release of water contained radioactive materials in the rock
Choose the correct code
Correct
Solution (d)
The second paragraph of the passage tells that “Whatsoever might have been the origin of water, earth‘s original supply of water is still in use and very little, if any, has been added during the past billion years or so.” And it also says that “the heating of the Earth‘s interior caused release of water contained in such rocks to the surface” here such rocks means silicate rocks.
Hence, both the statements are incorrect.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
The second paragraph of the passage tells that “Whatsoever might have been the origin of water, earth‘s original supply of water is still in use and very little, if any, has been added during the past billion years or so.” And it also says that “the heating of the Earth‘s interior caused release of water contained in such rocks to the surface” here such rocks means silicate rocks.
Hence, both the statements are incorrect.
All the Best
IASbaba











