Science and Technology
Syllabus
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Context: The era of 5G is here! A technology that’s been talked about over the past couple of years is finally rolling out across different countries like China, US, Japan, and even South Korea.
- In India, Union Cabinet has given approval of the 5G spectrum auction, scheduled to begin on 26 July, 2022.
- 5G is the fifth generation cellular technology that apart from increasing the downloading and uploading speeds(speed of 1 Gbps) over the mobile network, also reduces the latencye. the time taken by a network to respond.
- It also increases energy efficiencyand offers more stable network connections.
- 5G is also designed to deliver signals more reliablythan earlier cellular networks
- 5G will have a wider area in the frequency spectrum(range of frequencies) that will ensure no network congestion.
- In addition, it will also ensure connectivity to a full circlee. everything is connected to every other thing.
- 5G will help facilitate the ecosystem for the Internet of Things (IoT)and to incorporate Artificial Intelligence (AI) in our daily lives and
- To get the benefits of 5G, users will have to buy new phones, while carriers will need to install new transmission equipment to offer the faster service.
- 5G mainly works in 3 bands, namely low, mid and high-frequency spectrum — all of which have their uses and limitations.
- While the low band spectrum has shown great promise in terms of coverage but the maximum speed is limited to 100 Mbps. This means that while telcos can use and install it for commercial cellphone users who may not have specific demands for very high speed internet, the low band spectrum may not be optimal for specialised needs of the industry.
- The mid-band spectrum, on the other hand, offers higher speeds compared to the low band, but has limitations in terms of coverage area and penetration of signals. Telcos and companies, which have taken the lead on 5G, have indicated that this band may be used by industries and specialised factory units for building captive networks that can be moulded into the needs of that particular industry.
- The high-band spectrum offers the highest speed of all the three bands, but has extremely limited coverage and signal penetration strength. Internet speeds in the high-band spectrum of 5G has been tested to be as high as 20 Gbps (giga bits per second), while, in most cases, the maximum internet data speed in 4G has been recorded at 1 Gbps.
It is said there are five technologies that make up the foundation of 5G technology:
- Millimeter-wave:
- Millimeter-wave 5G acquires huge chunks of data which allows it to data transfer speeds in excess of 1Gbps.
- This form of technology is currently being used in the US by telecom operators like Verizon and AT&T.
- Small cells
- Since mmWave cannot travel through obstacles, mini cell towers are deployed in large numbers across an area to relay the signal from the main cell tower.
- These small cells have to be placed in close proximity compared to traditional towers to make sure the users get uninterrupted 5G signals.
- Massive MIMO (Multiple-inputs & multiple-output)
- This technology is used on large cell towers to manage heavy traffic. A regular cell tower that distributes 4G comes with 12 antennas that handle all of the cellular traffic in the area.
- MIMO can support 100 antennas at the same time which increases the overall capacity of the tower to handle more traffic.
- This technology helps make the delivery of 5G signals smoother.
- Beamforming
- Beamforming is a technology that can regularly monitor multiple sources of frequencies and then switch to a stronger and faster tower if one signal is blocked.
- This ensures that specific data is sent only in a specific direction. Something like a traffic light for data.
- Full duplex
- Full-duplex is a technology that allows a node to transmit and receive data simultaneously in the same frequency band.
- Landline telephones and short-wave radio use this kind of technology.
- It’s like a two-way street that allows equal traffic both ways
- High Speeds: Imagine downloading a full HD movie in under 3 seconds. That’s how fast downloads are with 5G. 5G is capable of delivering speeds up to 20Gbps with a 100x increase in traffic capacity and network efficiency.
- Reduced Latency: Also, with mmWave, you can even achieve latency of just 1ms which helps with immediate connection establishment and that subsequently reduces network traffic.
- Foundation for latest technologies: It is believed that at its full potential 5G will be able to offer speeds that can render augmented reality in real-time. This will further lead to the development of more hardware that works on augmented reality. This tech is also going to be the foundation for virtual reality, autonomous driving and the internet of things.
- Ripple Effect: The advantages of 5g will not only make your smartphone experience better but will also open up avenues for advancements in other fields like medical, infrastructure and even manufacturing.
In Summary, we can that 5G entails the following advantages:
- Improved data transfer speed
- Reduce latency time
- Will shape the Fourth Industrial Revolution by enabling Internet of Things
- Leads to more data-intensive, digital economy.
- Capital intensive: Deploying 5G technology is costly which means that network operators will have to tear down their current ecosystem because it needs a frequency beyond 3.5Ghz which is a bigger bandwidth than what 3G or 4G use.
- Limited Bandwidth: Sub-6 GHz spectrum has limited bandwidth and therefore its speeds could potentially be slower than what mmWave has to offer.
- Need for Hardware deployment: Also, mmWave is only effective in shorter distances and cannot travel through obstacles. It also tends to get absorbed by trees and even rainfall which means you’ll need a lot of hardware deployment in order to make 5G work effectively.
- Unknown safety issues: There could also be security and privacy issues with 5G technology which will only surface when the technology is more accessible.
- Scepticism over growth: 5G is growing but not at the rate people expected. Even at its present rate, 5G will not overtake 4G and 3G by 2025, as per several reports.
- However, Qualcomm believes that by 2022, the number of shipped 5G smartphones will be over 750 million, and 5G connections should be at 1 billion by 2023, two years faster than 4G hit that number
- Domestic Industrial Stress: India’s Telecom sector is under stress in recent times due to intense competition unleashed by Jio’s entry. Unless, there is some sort of support by the government (bank loans or low spectrum charges), companies will find it hard to roll out 5G in the foreseeable future.
- 5G is said to work best in a particular frequency of the spectrum which is mostly above 6Ghz. Even old technologies like 2G, 3G, and 4G operate on wireless bands which are mostly between 3.5Ghz to 6Ghz.
- Reports have shown that 5G can co-exist with 4G, but since 3Ghz-6Ghz spectrum is overpopulated researchers are looking to experiment beyond 6Ghz in shorter mmWave which is between 30-300Ghz.
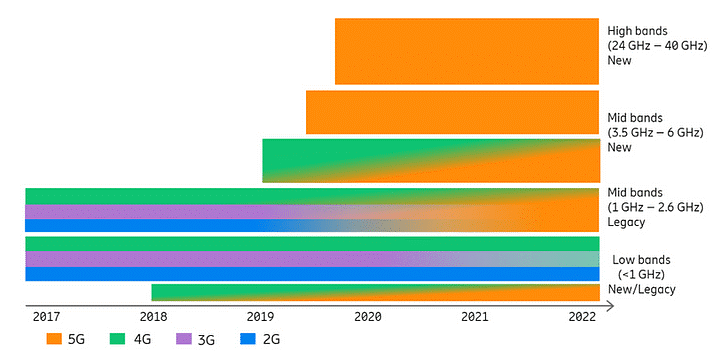
- This section of the spectrum was earlier used for over the air television but never for mobile devices. Opening it up means more bandwidth for mobile devices.
- Some of the technologies like 5G NR (New Radio) and even 5Ge (AT&T proprietary LTE advanced network) work on the 4G network, but aren’t as fast as mmWave which means the only way to have access to speeds over 1Gbps is by deploying new hardware.
A standing committee of Lok Sabha on Information Technology had submitted its report on 5G in Feb 2021 and said that India will miss the 5G bus. Key takeaways of the report were:
- Little Progress on ground: Despite the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) having submitted a report on the steps to make India 5G ready as early as August 2018, there was very little progress on the ground.
- High Spectrum Prices: the reserve price for auction of 5G was one of the highest in the world. It needed to be rationalised, taking into account the per capita income of the country and also by comparing it with reserve price mandated by other countries.
- Inadequate and poor development of test cases: Globally, as many as 118 telecom service providers across 59 countries have started deploying 5G networks. India is yet to give formal approvals for 5G testing despite all the three major private telecom players having submitted their applications as early as January 2020.
- Delayed rollout of 5G: Comparing it to the deployment of other older technologies such as 2G, on which it was late by four years, 3G on which India was as much as a decade late, and 4G on which India missed by the bus by 7 years, the committee concluded that “sufficient preparatory work had not been undertaken for launching of 5G services in India.”
- Low reach of optical fibre across India, and deficient back-haul capacity are other factors which is delaying the deployment of 5G in India.
- In the initial phase, these trials will be for 6 months, including a 2 month period for procurement and setting up of the equipment.
- In these 6 months, telcos will be required to test their set up in urban areas, semi-urban areas as well as rural areas.
- During this period, the telcos will be provided with experimental spectrum in various bands, such as the mid-band of 3.2 GHz to 3.67 GHz, the millimeter wave band of 24.25 GHz to 28.5 GHz, and others.
- Identification of basic ingredients: The immediate priority for India will be in identifying end users and population to be covered, identification of cities for the 5G roll out, working out an investment model for 5G deployment.
- Creating a level-playing field through market mechanism such as facilitating, simulating, auctioning, ensuring competition, functioning markets, etc.
- Spectrum Roadmap: TRAI should prepare a foolproof spectrum road map with a predictable renewal process which will compensate the huge investment required for deployment and ensure coverage.
- Spectrum Sharing: Global trial runs show that the key areas for 5G deployment are harmonisation of 5G spectrum bands, pricing and sharing of the spectrum. In this light, sharing of available spectrum needs to be promoted.
- Government Financial Incentive: As the deployment of 5G network is expensive, both the Central and State governments need to consider measures which stimulate fibre investment, attract investment through PPPs and facilitate investment funds on a nominal interest basis.
- Allowing 100% foreign direct investment in the telecom sector under the automatic route along with these policy reforms augurs well for the sector to attract investment.
- Conscious of Digital Divide: The negative implication of 5G is furthering the ‘digital divide’. Therefore, Government policies should also focus on affordable coverage through synchronisation of bandwidth.
Conclusion
As India has already witnessed digital revolution even in its remotest areas due to cost-effective 4G technology, the use of 5G can play a vital role in enhancing this sector and also facilitating India’s goal to emerge as a manufacturing and innovation hub.
Mains Practice Question – It is said that 5G will be the base for upcoming fourth industrial revolution. Elaborating on the statement, comment if India is doing enough to be a frontrunner in this field.
Note: Write answers to this question in the comment section.












