IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography & Environment
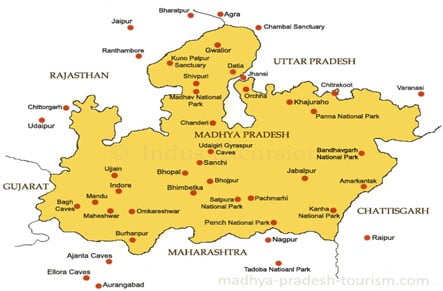
In News: Cheetahs likely to arrive in Madhya Pradesh’s Kuno National Park before August 15.
- India is one step closer to bringing back the world’s fastest animal, which has been extinct in the country since 1952, with an agreement that was signed between the government and the visiting Namibian Deputy Prime Minister.
- The agreement, which has been negotiated for some years, will prepare the ground for the relocation of the first batch of cheetahs from southern Africa to Madhya Pradesh’s Kuno National Park, with officials trying to complete the first transfer before August 15.
- The MoU focused on biodiversity conservation, and the sharing of expertise between the two countries, technological applications, collaborations on climate change, pollution and waste management, and the exchange of personnel for training and education in wildlife management.
- While the current carrying capacity for the Kuno National Park is a maximum of 21 cheetahs, once restored the larger landscape can hold about 36 cheetahs.
Kuno National Park
- Kuno National Park is a national park in Madhya Pradesh, India, established in 1981 as a wildlife sanctuary.
- State government changed the status of the wildlife sanctuary to Kuno National Park in 2018
- It is part of the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forests ecoregion.
Flora
- The vegetation of the protected area includes dry savanna forest and grassland and tropical riverine forest.
Fauna
- The main predators occurring in the protected area are Indian leopard, jungle cat, sloth bear, dhole, Indian wolf, golden jackal, striped hyena and Bengal fox.
Cheetah
- The cheetah is one of the oldest of the big cat species, with ancestors that can be traced back more than five million years to the Miocene era.
- The cheetah is also the world’s fastest land mammal that lives in Africa and Asia
| Features | Asiatic Cheetah | African Cheetah |
| Physical Characteristics | Smaller and paler than the African cheetah. Has smaller head and a longer neck. Usually have red eyes and they have a more cat-like appearance. | Bigger in size as compared to Asiatic Cheetah.
|
| Image |  |
 |
| Distribution | Around 40-50 found only in Iran. | Around 6,500-7,000 African cheetahs present in the wild. |
| Status | IUCN: Critically Endangered
CITES: Appendix-I of the List |
IUCN: Vulnerable
CITES: Appendix-I of the List |
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the following protected areas is well-known for the conservation of a sub-species of the Indian swamp deer (Barasingha) that thrives well on hard ground and is exclusively graminivorous? (2020)
- Kanha National Park
- Manas National Park
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Tal Chhaper Wildlife Sanctuary
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
- Mains – GS 1 (Society); GS 2 (Governance)
In News: A 25-year-old pregnant woman moved the Supreme Court seeking an abortion after the Delhi High Court declined her plea.
- The woman has also challenged Rule 3B of the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Rules, 2003, which allows only some categories of women to seek termination of pregnancy between 20 and 24 weeks.
- The case has raised very important questions about the framework of reproductive rights, and recognising female autonomy and agency in India.
What is India’s law on abortion?
- In 1971, The Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act (MTP Act) was introduced to “liberalise” access to abortion.
- The MTP Act allowed termination of pregnancy by a medical practitioner in two stages.
- For termination of pregnancy up to 12 weeks from conception, the opinion of one doctor was required.
- For pregnancies between 12 and 20 weeks old, the opinion of two doctors was required.
- In 2021, Parliament amended the law and allowed for a termination under the opinion of one doctor for pregnancies up to 20 weeks. For pregnancies between 20 and 24 weeks, the amended law requires the opinion of two doctors.
- For the second category, the Rules specified seven categories of women who would be eligible for seeking termination.
- Section 3B of Rules prescribed under the MTP Act reads: “The following categories of women shall be considered eligible for termination of pregnancy under clause (b) of subsection (2) Section 3 of the Act, for a period of up to twenty-four weeks, namely:
- survivors of sexual assault or rape or incest;
- minors;
- change of marital status during the ongoing pregnancy (widowhood and divorce);
- women with physical disabilities [major disability as per criteria laid down under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016
- mentally ill women including mental retardation;
- the foetal malformation that has substantial risk of being incompatible with life or if the child is born it may suffer from such physical or mental abnormalities to be seriously handicapped; and
- women with pregnancy in humanitarian settings or disaster or emergency situations as may be declared by the Government.”
- While the law recognises change in circumstances of the relationship status between a pregnant woman and her spouse — in the case of divorce and widowhood — it does not envisage the situation for unmarried women.
- This is the gap in the law that the petitioner before the Supreme Court falls in.
- The MTP Act is a provider protection law, that seeks to shield the Registered Medical Practitioner (RMP) from criminal liability, and as such it does not centre the pregnant woman’s needs and reproductive autonomy
- Access to abortion is not at the will of the pregnant woman.
- It is a highly regulated procedure whereby the law transfers the decision-making power from the pregnant woman to the RMP and provides great discretion to the RMP to determine whether abortion should be provided or not.
It is time that the legislature identifies this loophole in the present law and take the appropriate steps to uphold the reproductive rights of the women.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to the ‘Prohibition of Benami Property Transactions Act, 1988 (PBPT Act), consider the following statements: (2017)
- A property transaction is not treated as a benami transaction if the owner of the property is not aware of the transaction.
- Properties held benami are liable for confiscation by the Government.
- The Act provides for three authorities for investigations but does not provide for any appellate mechanism.
Which of the statements .given above is/are correct?
- 1only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
- Mains – GS 3 (Growth & Development)
In News: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is in the process of implementing the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) in a phased manner for wholesale and retail segments
- The introduction of CBDC was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23, by Finance Minister and necessary amendments to the relevant section of the RBI Act, 1934 have been made with the passage of the Finance Bill 2022
- India’s official digital currency is likely to debut by early 2023, which will mirror any of the currently available private company-operated electronic wallets.
- The CBDC will be a sovereign-backed digital currency.
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
- CBDCs are a digital form of a paper currency and unlike cryptocurrencies that operate in a regulatory vacuum, these are legal tender issued and backed by a central bank.
- Budget 2022-23, the Government of India announced that its central bank will issue a digital currency as early as 2022-23.
- The main objective is to mitigate the risks and trim costs in handling physical currency, costs of phasing out soiled notes, transportation, insurance and logistics.
- It will also wean people away from cryptocurrencies as a means for money transfer.
Merits
A Combination of Traditional and Innovative:
- CBDC can gradually bring a cultural shift towards virtual currency by reducing currency handling costs.
Easier Cross-Border Payments:
- CBDC can provide an easy means to speed up a reliable sovereign backed domestic payment and settlement system partly replacing paper currency.
- It could also be used for cross-border payments; it could eliminate the need for an expensive network of correspondent banks to settle cross-border payments.
Financial Inclusion:
- The increased use of CBDC could be explored for many other financial activities to push the informal economy into the formal zone to ensure better tax and regulatory compliance.
- It can also pave the way for furthering financial inclusion.
Risks
Privacy Concerns:
- The first issue to tackle is the heightened risk to the privacy of users—given that the central bank could potentially end up handling an enormous amount of data regarding user transactions.
- This has serious implications given that digital currencies will not offer users the level of privacy and anonymity offered by transacting in cash.
Disintermediation of Banks:
- The shift to CBDC can impinge upon the bank’s ability to plough back funds into credit intermediation.
Other risks are:
- Faster obsolescence of technology could pose a threat to the CBDC ecosystem calling for higher costs of upgradation.
- Operational risks of intermediaries as the staff will have to be retrained and groomed to work in the CBDC environment.
- Elevated cyber security risks, vulnerability testing and costs of protecting the firewalls
- Operational burden and costs for the central bank in managing CBDC.
Way forward
- Robust data security systems will have to be set up to prevent data breaches. Thus, it is important to employ the right technology that will back the issue of CBDCs.
- The financial data collected on digital currency transactions will be sensitive in nature, and the government will have to carefully think through the regulatory design. This would require close interaction between the banking and data protection regulators.
- Also, the institutional mechanisms would need to ensure that there is no overlap between different regulators and chart out a clear course of action in case there is a data breach of digital currencies.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to ‘Bitcoins’, sometimes seen in the news which of the following statements is/are correct (2016)
- Bitcoins are tracked by the Central Banks of the countries.
- Anyone with a Bitcoin address can send and receive Bitcoins from anyone else with a Bitcoin address.
- Online payments can be sent without either side knowing the identity of the other.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
In News: Recently, NITI Aayog has released a Report titled- ‘Digital Banks: A Proposal for Licensing & Regulatory Regime for India’.
- It suggested setting up Digital Banks and a licensing and regulatory framework for such Banks.
Digital Bank:
- It will be defined in the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, and shall have its own balance sheet and legal existence.
- It will be different from the 75 Digital Banking Units (DBUs) — announced by Finance Minister in Union Budget 2022-23 – which are being set up to push digital payments, banking and fintech innovations in underserved areas
- Digital banks will be subject to prudential and liquidity norms on a par with existing commercial banks.
Findings
- In recent years, India has made rapid strides in furthering Financial Inclusion (FI), catalysed by the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) and India Stack.
- The FI has been furthered by the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), which has witnessed extraordinary adoption.
- The FI also resulted in Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) through apps such as PM-KISAN and extending microcredit facilities to street vendors through PM-SVANIDHI.
- India is at the cusp of operationalizing its own open banking framework.
- Creating a blueprint for digital banking regulatory framework and policy offers India the opportunity to cement her position as the global leader in Fintech at the same time as solving the several public policy challenges she faces.
Recommendations
- Issue of a restricted digital bank licence, the license would be restricted in terms of volume/value of customers serviced and the like.
- Enlistment of the licensee in a regulatory sandbox framework enacted by the Reserve Bank of India
Source: Pib.Gov
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
In News: Recently, Ministry of Tribal Affairs and Meta have launched the second phase of the GOAL Programme (GOAL 2.0).
GOAL Programme
- GOAL (Going Online as Leaders) was launched as a pilot project in May 2020 and it was completed by December 2021.
- It aimed at digital empowerment of tribal youth and women through the concept of mentor and mentee.
- The programme is fully funded by Meta.
Trainings were provided for three pillars:
- Communication & Life Skills
- Enabling Digital Presence
- Leadership & Entrepreneurship
GOAL 2.0
- Goal 2 program will be open to all people from tribal communities.
- In Phase-I, the digital mentorship was provided online by attaching one mentor to 2 mentees.
Objective:
- The program aims to upskill and digitally enable tribal youth via Facebook live sessions and Meta Business Coach, a digital learning tool.
- There will be special focus on more than 10 lakh members of 50000 Vandhan Self Help Groups.
- They will be digitally trained with regard to market demand, packaging, branding and marketing of their products.
- The GOAL 2 will enable maximum participation and percolation of benefits of the training within the tribal youth with provision of Chatbot, need based on line sessions from Industry experts in different fields as per requirements from the mentees.
Agencies Involved:
- The Ministry of Tribal Affairs in coordination with the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, will be providing 6 digital classes in each of the 175 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) selected under the program.
- The project is being implemented by The Education and Research Network, which is an autonomous organization under the MeITY.
Source: Pib.Gov
Previous Year Question
Q.1) What is the aim of the programme ‘Unnat Bharat Abhiyan’? (2017)
- Achieving 100% literacy by promoting collaboration between voluntary organizations and government’s education system and local communities.
- Connecting institutions of higher education with local communities to address development challenges through appropriate technologies.
- Strengthening India’s scientific research institutions in order to make India a scientific and technological power.
- Developing human capital by allocating special funds for health care and education of rural and urban poor, and organizing skill development programmes and vocational training for them.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
In News: Residents of two buildings on Marine Drive, the iconic 3-km promenade in south Mumbai, complained of “unusual vibrations” during high tide over the past weekend.
- They wrote to say that the unusual vibrations, coinciding with high-tide times, were the result of the relocation of tetrapods as part of the ongoing Coastal Road Project (MCRP).
What are tetrapods?
- Tetra pod in Greek means four-legged.
- These are four-legged concrete structures that are placed along coastlines to prevent erosion and water damage.
- Tetrapods were first used in France in the late 1940s to protect the shore from the sea.
- They are typically placed together to form an interlocking but porous barrier that dissipates the power of waves and currents.
- These are large structures, sometimes weighing up to 10 tonnes, and interlocked tetra pods act as a barrier that remains stable against the rocks when buffeted by waves.
- Tetrapods, each weighing about 2 tonnes, were placed along Marine Drive in the late 1990s to break and dissipate waves and maintain the reclaimed shoreline in South Mumbai.
Why were the tetrapods removed from the Marine Drive area?
- They were temporarily removed to help carry out reclamation for the ongoing Coastal Road Project.
- The corporation as agreed to re-install the structures.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
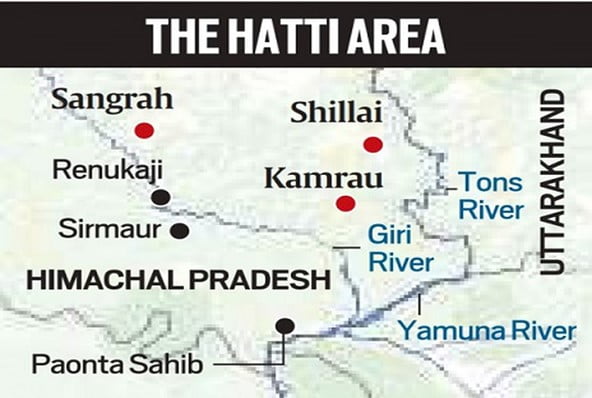
In News: The Centre is reported to be considering granting “tribal” status to the Trans-Giri region of Himachal Pradesh’s Sirmaur district.
- The demand to declare Trans-Giri a tribal area is old — and is tied up with the demand for Scheduled Tribe (ST) status for the Hatti community which lives in the area.
The community and the land
- The Hattis are a close-knit community who take their name from their traditional occupation of selling home-grown crops, vegetables, meat, and wool at small-town markets known as ‘haats’.
- Hatti men traditionally don a distinctive white headgear on ceremonial occasions.
- The present population of the Hattis is estimated at around 3 lakh.
- The Hatti homeland straddles the Himachal-Uttarakhand border in the basin of the Giri and Tons rivers, both tributaries of the Yamuna.
- The Tons marks the border between the two states.
- The Hattis are governed by a traditional council called ‘khumbli’ which, like the ‘khaps’ of Haryana, decide community matters.
Requirement of ‘tribal’ area
- In its reply in Parliament, the government laid down the requirements for such designation, and the reason why Himachal Pradesh’s claim could not be considered
- It said that the Constitution provides for two types of areas: “Scheduled Areas” in terms of the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution, and “Tribal Areas” in terms of Sixth Schedule.
- Himachal Pradesh submitted a proposal for notifying entire Trans-Giri area of Sirmour district, Dodra Kwar Sub-Division of Shimla district, 15/20 areas of Shimla and Kullu districts as Scheduled Areas in Himachal Pradesh.
- The government said, for declaration of Scheduled Areas the criteria followed are: preponderance of tribal population, compactness and reasonable size of the area, a viable administrative entity such as a district, block or taluk, and economic backwardness of the area as compared to neighbouring areas.
- The proposal was examined in the Ministry and could not be considered due to want of requisite criteria, as mentioned above.
Source: Indian Express
Baba’s Explainer – Financial Services Institutions Bureau (FSIB)
Syllabus
- GS-2: Statutory, regulatory and various quasi-judicial bodies.
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development
Context: The government has transformed Banks Board Bureau (BBB), the headhunter for directors of state-owned banks and financial institutions, into Financial Services Institutions Bureau (FSIB) by making some amendments.
- The Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC) has asked the Department of Financial Services to carry out necessary modifications in the Nationalized Banks (Management and Miscellaneous Provisions) Scheme of 1970/1980 with the approval of Finance Minister, and then notify the government resolution for establishing FSIB.
Read Complete Details on Financial Services Institutions Bureau (FSIB)
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Hatti Community recently in news is residents of?
- Mizoram
- Himachal Pradesh
- Karnataka
- Manipur
Q.2) Consider the following statements about GOAL program
- It is an initiative of NITI Aayog and Ministry of electronics and Information Technology
- It aims at digital empowerment of tribal youth and women through the concept of mentor and mentee
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Which among the following National Park is chosen by the GoI for Cheetah reintroduction?
- Anshi National Park
- Campbell Bay National Park
- Clouded Leopard National Park
- Kuno National Park
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’21st JULY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 20th JULY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – c











