Governance
Context: Recently the International Monetary Fund (IMF) praised India’s Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) Scheme as a “logistical marvel” that has reached hundreds of millions of people and specifically benefitted women, the elderly and farmer.
- Earlier this month, President of the World Bank Group, had also urged other nations to adopt India’s move of targeted cash transfer instead of broad subsidies noting that “India managed to provide food or cash support to a remarkable 85 per cent of rural households and 69 per cent of urban households”.
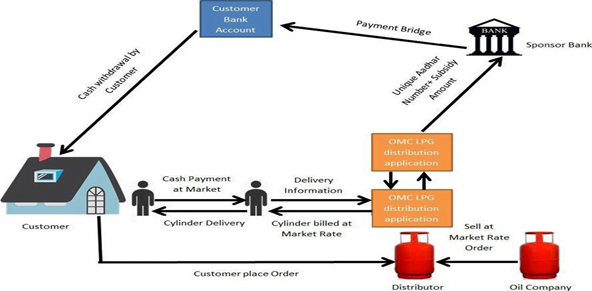
History of government’s benefit transfer:
- During mid-1980s there was leakages in India’s public welfare schemes reflected a feeling of helplessness at the highest levels in dealing with this gnawing problem.
- It led to wastage of public money and also exclusive of beneficiaries which lead to promotion of corruption.
The current era of Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT):
- India has come a long way since then, especially in the last eight years, primarily on account of the aggressive rollout of the DBT programme that transfers subsidies and cash benefits directly to beneficiaries through Aadhaar-linked bank accounts
- This has been made possible by the inclusive financial sector system where the most marginalised sections of society have been uniquely linked to the formal financial network.
The building block (Pre-requisite conditions) to adopt DBT:
- The complex and multi-layered governance machinery — its diversity, access barriers, and digital divide restrict the implementation of novel scheme unless the building blocks are effectively addressed.
- DBT alone would not have been able to address the size and scale of the problem of sub-optimal service delivery under government machinery.
- An ambitious vision, holistic approach and a multi-pronged strategy enabled the DBT ecosystem to deliver impact at a phenomenal scale — the accomplishment that has been acknowledged by the IMF and World Bank.
- In 2014, the Government of India embarked on an ambitious and well-structured financial inclusion programme with the aim of including all households within the fold of the formal financial network.
- In a mission-mode approach, it endeavoured to open bank accounts for all households, expanded Aadhaar to all, and scaled up the coverage of banking and telecom services.
- It evolved the Public Finance Management System and created the Aadhaar Payment Bridge to enable instant money transfers from the government to people’s bank accounts
- The Aadhaar-enabled Payment System and Unified Payment Interface further expanded interoperability and private-sector participation.
- This approach not only allowed all rural and urban households to be uniquely linked under varied government schemes for receiving subsidies directly into their bank accounts but also transferred money with ease.
Current status of DBT and its advantages:
- By 2022, more than 135 crore Aadhaar’s have been generated, there are 47 crore beneficiaries under Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana, 6.5 lakh Bank Mitras delivering branchless banking services and mobile subscribers number more than 120 crore.
- Riding on this network, the DBT programme has reached commanding heights towards achieving the government’s vision of “sabka Vikas”.
- Becoming the major plank of the government’s agenda of inclusive growth, it has 318 schemes of 53 central ministries spanning across sectors, welfare goals and the vast geography of the country.
- The DBT scheme that began as a pilot in 2013-14 could not have achieved the size and scale it has today without the government’s financial inclusion programme, which helped
- Eliminated leakages in welfare schemes
- Excluded fake or ghost beneficiaries and
- transfer funds to genuine beneficiaries.
- This ensured significant savings to the exchequer and enabled efficient utilisation of government funds.
DBT related scheme beneficiaries in Rural and Urban India:
- In rural Bharat, DBT has allowed the government to provide financial assistance effectively and transparently to farmers with lower transaction costs –
- be it for fertilisers or any of the other schemes including the
- PM Kisan Samman Nidhi, PM Fasal Bima Yojana, and PM Krishi Synchayee Yojana
- Thus, becoming the backbone for supporting the growth of the agricultural economy. The benefits received under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act and Public Distribution System drive the rural demand-supply chain
- In urban India, the PM Awas Yojana and LPG Pahal scheme successfully use DBT to transfer funds to eligible beneficiaries
- Various scholarship schemes and the National Social Assistance Programme use the DBT architecture to provide social security.
- DBT under rehabilitation programmes such as the Self Employment Scheme for Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers opens new frontiers that enable social mobility of all sections of society.
Role of DBT during the Pandemic:
- The efficacy and robustness of the DBT network were witnessed during the pandemic.
- It aided the government to reach the last mile and support the most deprived in bearing the brunt of the lockdown.
- From free rations to nearly 80 crore people under the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana, fund transfers to all women Jan Dhan account holders and support to small vendors under PM-SVANidhi,
- DBT helped the vulnerable to withstand the shock of the pandemic.
Way Forward:
- An enabling policy regime, proactive government initiatives and supportive regulatory administration allowed the private and public sector entities in the financial sector to overcome longstanding challenges of exclusion of a large part of the population.
- These are essential which helped in rollout of the ambitious DBT programme, achieving impressive scale in a short span of six years.
- Going forward, the DBT approach is expected to expand further in size and structure as it continues to be the major tool of the government for a more nuanced and targeted intervention towards improving the ease of living.
However, digital and financial literacy, robust grievance redressal, enhancing awareness and an empowering innovation system are some of the aspects that would require continued focus. This would play a vital role for India in meeting the diverse needs of its population and ensuring balanced, equitable and inclusive growth.
Source: Indian Express












