Environment & Ecology
In news: The 14th Meeting of the Conference of the Contracting Parties (COP14) to the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands began to discuss the state of wetlands globally.
- Agenda items include waterbird population estimates, Ramsar Convention criteria, lists of wetlands of international importance and conservation of small wetlands.
- The agenda includes a draft resolution by China to host an international mangrove centre which is cosponsored by Cambodia and Madagascar; which will serve as the Secretariat and technical service platform for international mangrove cooperation in the framework of the Ramsar Convention.
Mangroves in China:
- China Mangrove Conservation and Restoration Strategy Research Project in 2020 was China’s first research report to comprehensively assess the state of mangroves in the country.
- Mangrove forests in China are growing in the northern edge of the global mangrove distribution. Limited by the low temperature, China has less mangrove species compared with other Southeast Asian countries.
- Mangroves in China were distributed in the provinces of Hainan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Fujian, Zhejiang, as well as Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan. All these areas are located in the extreme tropical south of the country.
- Mangrove area in China had decreased sharply to 22,000 hectares in 2000, only 45 per cent that of the early 1950s.
About Mangroves:
- Mangroves are a group of halophyte trees and shrubs that live in the coastal intertidal zone, in dense thickets or forests along tidal estuaries, in salt marshes, and on muddy coasts – they can tolerate salt.
- Mangroves are typically tropical in nature than temperate because they cannot withstand freezing temperatures. Indonesia alone contains between 26% and 29% of the entire global mangrove stock.
- These trees grow in areas with low-oxygen soil, where slow-moving waters allow fine sediments to accumulate.
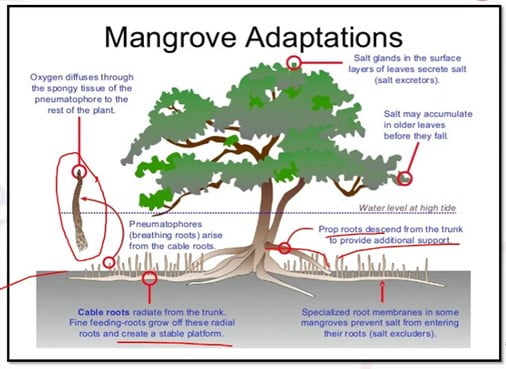
- They have a dense tangle of prop roots —i.e., exposed supporting roots that make the trees appear to be standing on stilts above the water. This intricate root system:-
- allows the trees to handle the daily rise and fall of tides, which means that most mangroves get flooded at least twice per day.
- Filter salt out of sea water, stay upright in soft, waterlogged soils and give them access to oxygen and nutrients.
- slows the movement of tidal waters, causing sediments to settle out of the water and build up the muddy bottom.
- stabilize the coastline, reducing erosion from storm surges, currents, waves, and tides.
- makes these forests attractive to fish and other organisms seeking food and shelter from predators.
- Its flowers are pale yellow in colour.
Significance of Mangroves:
- Biodiversity – Home to an incredible array of species, mangroves are biodiversity hotspots. They provide nesting and breeding habitat for fish and shellfish, migratory birds, and sea turtles. An estimated 80% of the global fish catch relies on mangrove forests either directly or indirectly.
- Livelihoods – fishers and farmers depend on these natural environments to provide healthy fisheries from which to fish, and healthy land on which to farm.
- Water quality – Mangroves are essential to maintaining water quality. With their dense network of roots and surrounding vegetation, they filter and trap sediments, heavy metals, and other pollutants. This ability to retain sediments flowing from upstream prevents contamination of downstream waterways and protects sensitive habitat like coral reefs and sea grass beds below.
- Coastal defence – Mangroves are the first line of defence for coastal communities. They stabilize shorelines by slowing erosion and provide communities from increased storm surge, flooding, and hurricanes. In 2003, it was estimated that a quarter of the world’s population lived within 100 kilometres of the coast and at 100 meters of sea level. Robust mangrove forests are natural protection for communities vulnerable both to sea level rise and the more intense and frequent weather events caused by climate change
- Carbon storage –Cover just 0.1% of the planet’s surface but store up to 10x more carbon per hectare than terrestrial forests. This means that conserving and restoring mangroves is essential to fighting climate change, the warming of the global climate fuelled by increased carbon emissions, that is already having disastrous effects on communities worldwide.
- Materials – In addition to consuming fish and shellfish from the mangroves, communities have historically used mangrove wood and other extracts for both building and medicinal purposes. Their potential as a source for novel biological materials, such as antibacterial compounds and pest-resistance genes, remains largely undiscovered.
- Sustainable development – Intact and healthy mangrove forests have an potential for sustainable revenue-generating initiatives including ecotourism, sport fishing, and other recreational activities.
About Ramsar Convention:
- The Convention on Wetlands is the intergovernmental treaty that provides the framework for the conservation and wise use of wetlands and their resources.
- The Convention was adopted in the Iranian city of Ramsar in 1971 and came into force in 1975. Since then, almost 90% of UN member states have acceded to become “Contracting Parties”.
- Aim: International mangrove cooperation mechanism aims for technical exchanges, collaborative research, education and training, and pilot projects on conservation and restoration, to protect mangrove biodiversity and coastal blue carbon ecosystems, enhance mangrove ecosystem services and resilience to climate change.
- The Convention uses a broad definition of wetlands. It includes all lakes and rivers, underground aquifers, swamps and marshes, wet grasslands, peatlands, oases, estuaries, deltas and tidal flats, mangroves and other coastal areas, coral reefs, and all human-made sites such as fish ponds, rice paddies, reservoirs and salt pans.
- A Ramsar site is a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention
- Criteria: One of the nine criteria must be fulfilled to be the Ramsar Site.
- Criterion 1: If it contains a representative, rare, or unique example of a natural or near-natural wetland type found within the appropriate biogeographic region.
- Criterion 2: If it supports vulnerable, endangered, or critically endangered species or threatened ecological communities
- Criterion 3: If it supports populations of plant and/or animal species important for maintaining the biological diversity of a particular biogeographic region.
- Criterion 4: If it supports plant and/or animal species at a critical stage in their life cycles, or provides refuge during adverse conditions.
- Criterion 5: If it regularly supports 20,000 or more waterbirds.
- Criterion 6: If it regularly supports 1% of the individuals in a population of one species or subspecies of waterbird.
- Criterion 7: If it supports a significant proportion of indigenous fish subspecies, species or families, life-history stages, species interactions and/or populations that are representative of wetland benefits and/or values and thereby contributes to global biological diversity.
- Criterion 8: If it is an important source of food for fishes, spawning ground, nursery and/or migration path on which fish stocks, either within the wetland or elsewhere, depend.
- Criterion 9: If it regularly supports 1% of the individuals in a population of one species or subspecies of wetland-dependent non avian animal species.
MUST READ New Ramsar sites
Source: Down To Earth
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Under Ramsar Convention, it is mandatory on the part of the Government of India to protect and conserve all the wetlands in the territory of India.
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 were framed by the Government of India based on the recommendations of Ramsar Convention.
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 also encompass the drainage area or catchment regions of the wetlands as determined by the authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3













