IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Recently, the Finance Bill, 2023, has proposed to amend Section 56(2) VII B of the Income Tax Act, related to Angel tax.
About Angel Tax:
- A term used to refer to the income tax payable on the capital raised by unlisted companies.
- It is levied on the capital raised via the issue of shares from an Indian investor.
- This tax predominantly affects start-ups and the angel investments they attract.
- It derives its genesis from section 56(2) (viib) of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Section 56(2) (viib) in the IT act:
- Introduced by the finance act, 2012
- It taxes any investment, received by any unlisted Indian company, valued above the fair market value by treating it as income.
- The investment in excess of fair value is characterized as ‘Income from other sources.
- If the fair market value of a start-up share is Rs 50 apiece, and in a subsequent funding round they offer it to an investor for Rs 60, then the difference of Rs 10 would be taxed as income.
Proposed changes
- For Angel Tax exemptions:
- The government has exempted investments made by the domestic investors in companies approved by an inter-ministerial panel from Angel Tax.
- Criteria for exemption:
- The paid-up capital and share premium of the startup should not exceed Rs. 10 crores after issuing shares.
- The startup should procure the fair market value certified by a merchant banker.
- The investor should have a minimum net worth of Rs. 2 crores and the average income in the last 3 financial years should not be less than Rs. 50 lakhs.
- For foreign Investors:
- New changes include foreign investors, meaning that when a start-up raises funding from a foreign investor, that too will now be counted as income and be taxable.
- Foreign investors are a key source of funding for the start-ups and have played a big role in increasing the valuation.
Significance of provision:
- The provision aims to deter the generation and use of unaccounted money through the subscription of shares of a closely held company at a value that is higher than the fair market value of the firm’s shares.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to the expenditure made by an organisation or a company, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2022)
- Acquiring new technology is capital expenditure.
- Debt financing is considered capital expenditure, while equity financing is considered revenue expenditure.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements:
- A share of the household financial savings goes towards government borrowings.
- Dated securities issued at market-related rates in auctions form a large component of internal debt.
Which of the above statements is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: The United States opened an embassy in the Solomon Islands recently in its latest move to counter China’s push into the Pacific.
About Solomon Islands:
- Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania.
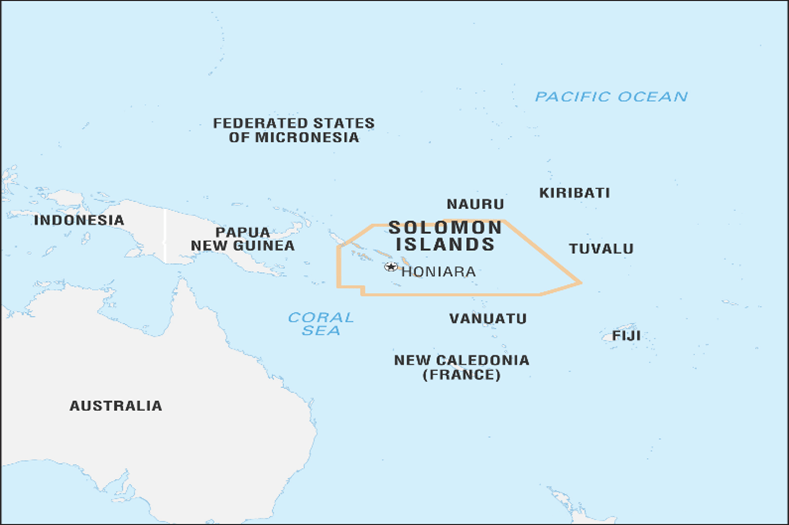
- Capital city Honiara, is located on the largest island,
- According to the World Risk Report 2021, the island state ranks second among the countries with the highest disaster risk worldwide.
- More than 90% of the islanders are ethnic Melanesians, but there has been intense and bitter rivalry between the Isatabus on Guadalcanal, the largest island, and migrant Malaitans from the neighbouring island.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following pairs:
Region often mentioned in the news: Country
- Anatolia Turkey
- Amhara Ethiopia
- Cabo Delgado Spain
- Catalonia Italy
How many pairs given above are correctly matched? (2022)
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Q.2) Consider the following countries:
- Azerbaijan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Tajikistan
- Uzbekistan
- Turkmenistan
Which of the above have borders with Afghanistan? (2022)
- 1, 2 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
- 3, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims – History and Art and Culture
Context: Two sacred Shaligram stones, weighing 31 tonnes and 15 tonnes, arrived in Ayodhya in Uttar Pradesh. The stones are expected to be used for constructing the idols of Lord Ram and Janaki at the Ram Temple.
About Shaligram Stones:
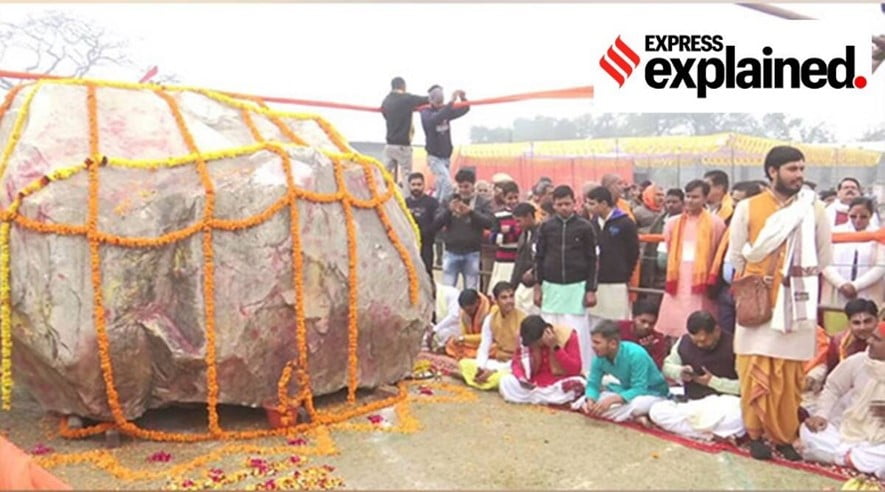

- Shaligram stones are fossils of ammonite, which is a type of mollusc that lived between 400 million and 65 million years ago.
- Shaligram stones date specifically from the Early Oxfordian to the Late Tithonian Age near the end of the Jurassic Period some 165-140 million years ago.
- It is mostly found in riverbeds or banks of the Kali Gandaki, a tributary of the Gandaki River in Nepal.
- This stone is revered by Hindus who believe it to be a representation of Lord Vishnu.
- The stone is considered to have divine powers and is seen as a symbol of good luck and prosperity.
- Significance:
- Lord Ram is believed to be the reincarnation of Lord Vishnu, and the use of the Shaligram stone symbolises the connection between the two gods.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following pairs:
Site of Ashoka’s major rock edicts Location in the State of
- Dhauli Odisha
- Erragudi Andhra Pradesh
- Jaugada Madhya Pradesh
- Kalsi Karnataka
How many pairs given above are correctly matched? (2022)
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pair
Q.2) With reference to Chausath Yogini Temple situated near Morena, consider the following statements:
- It is a circular temple built during the reign of Kachchhapaghata Dynasty.
- It is the only circular temple built in India.
- It was meant to promote the Vaishnava cult in the region.
- Its design has given rise to a popular belief that it was the inspiration behind the Indian Parliament building.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2021)
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 4
- 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Research
Joint Parliamentary Committee
ers at the Microsoft Research (MSR) lab in India have been working towards creating Project ELLORA.
About Project ELLORA:
- The project aims to bring ‘rare’ Indian languages online.
- It is also known as Enabling Low Resource Languages that was launched in 2015.
- It is a digital resource for Indian languages that do not have enough presence online.
- Some of the languages that’s its researching includes: Gondi, Mundari, and Idu Mishmi.
Gondi:
- It is a South-Central Dravidian language spoken by Gond tribes.
- It is spoken in Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- It is written in Devanagari and Telugu scripts.
Mundari:
- It belongs to Austroasiatic language family spoken by the Munda tribes.
- It is spoken in Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal.
- Scripts: Mundari bani.
- It is written in the Devanagari, Odia, Bengali, and Latin writing systems.
Idu Mishmi:
- It is spoken in Arunachal Pradesh and in Tibet Autonomous Region, China.
- It uses the Tibetan script and Idu Azobra script.
- It is also known as Sulikata, Midu, Mindri and Mithu.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity and Governance
Context: The Opposition joined hands to demand a probe either by a Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC), headed by the Supreme Court or monitored by the Chief Justice of India, into the allegations of fraud and stock manipulation against the Adani Group.
About Joint Parliamentary Committee:
- A Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC) is set up by the Parliament for a special purpose, like for the detailed scrutiny of a subject or Bill.
- It has members from both the Houses and from both the ruling parties and the opposition.
- Members of the JPC are decided by the Parliament.
- There is no fixed number of members in the committee.
- It is dissolved after its term ends or its task has been completed.
- The recommendations made by the committee are in recommendatory in nature not binding on the government.
Powers of the committee:
- A JPC can obtain evidence of experts, public bodies, associations, individuals or interested parties suo motu or on requests made by them.
- If a witness fails to appear before a JPC in response to summons, his conduct constitutes a contempt of the House.
- Ministers are not generally called by the committees to give evidence.
- However, with the permission of the Speaker, the JPC can seek information on certain points from ministers and call the ministers.
- The JPC can take oral and written evidence or call for documents in connection with a matter under its consideration.
The Joint Parliamentary Committees are formed till date include the following cases:
- Bofors scandal (1987)
- Harshad Mehta Stock market scam (1992)
- Ketan Parekh share market scam (2001)
- Soft drink pesticide issue (2003)
- 2G spectrum case (2011)
- VVIP Chopper scam (2013)
- Land Acquisition (2015)
- NRC (2016)
- Personal Data Protection Bill (2019)
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- The Constitution of India classifies the ministers into four ranks viz. Cabinet Minister, Minister of State with Independent Charge, Minister of State and Deputy Minister.
- The total number of ministers in the Union Government, including the Prime Minister, shall not exceed 15 percent of the total number of members in the Lok Sabha.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) We adopted parliamentary democracy based on the British model, but how does our model differ from that model? (2021)
- As regards legislation, the British Parliament is supreme or sovereign but in India, the power of the parliament to legislate is limited.
- In India, matters related to the constitutionality of the Amendment of an Act of the Parliament are referred to the Constitution Bench by the Supreme Court.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims: Government schemes and policies
In News: The scheme will continue till 2025-26 with an allocation of Rs.2400 crore.
About Rashtriya Gokul Mission
- The “Rashtriya Gokul Mission” aims to conserve and develop indigenous breeds in a focused and scientific manner.
- The potential to enhance the productivity of the indigenous breeds of India through professional farm management and superior nutrition is immense, for this it is essential to promote conservation and development of indigenous breeds.
- The Rashtriya Gokul Mission is a focussed project under National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development.
- The Mission will be implemented with the objectives to:
- Development and conservation of indigenous breeds
- Undertake breed improvement programme for indigenous cattle breeds so as to improve the genetic makeup and increase the stock;
- Enhance milk production and productivity;
- Upgrade nondescript cattle using elite indigenous breeds like Gir, Sahiwal, Rathi, Deoni, Tharparkar, Red Sindhi
- Distribute disease-free high genetic merit bulls for natural service.
News Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims: Governance
About: One District One Product Scheme is an initiative that is seen as a transformational step forward towards realizing the true potential of a district, fuel economic growth, and generate employment and rural entrepreneurship, taking us to the goal of AtmaNirbhar Bharat.
- This scheme is basically a Japanese business development concept, which gained prominence in 1979.
- It is aimed at promoting a competitive and staple product from a specific area to push sales and improve the standard of living of the local population.
- Over time, it has been replicated in other Asian countries as well.
- In India, Uttar Pradesh government was the first state of India to launch the concept of One District One Product in 2018.
Components of the Scheme:
- Identify one product per district based on the potential and strength of a district and national priorities
- Develop a cluster for that product in the district which is capable of producing a world-class product with quality, scalability, and a brand
- Provide market linkages
- Address bottlenecks for exporting these products
- Support local exporters/manufacturers to scale up manufacturing
- Find potential buyers outside India with the aim of promoting exports
- Promoting manufacturing & services industry in the District
- Generate employment in the District
GIS One District One Product (ODOP) Digital Map of India:
- By The Ministry of Food Processing
- The digital ODOP map provides detailed information about ODOP products to all states and facilitates the stakeholders.
- The digital map also has indicators for tribal, SC, ST, and aspirational districts.
- It will enable stakeholders to make concerted efforts for its value chain development.
Few products identified include:
Uttar Pradesh
- The ancient and nutritious ‘Kala namak’ rice of Siddharthanagar
- The rare technique of wheat-stalk craft, handicraft in Bahraich
- The famous chikankari and zari-zardozi work garments
- Banana fibre of Kushinagar,
- Banana of Kaushambi,
- Jaggery of Ayodhya,
- Aamla of Pratapgarh,
- Pulses of Balrampur and Gonda,
- Desi ghee of Auraiya,
- Wooden toys of Chitrakoot
- Wooden artifacts of Saharanpur, Basti, Bijnor, Rae Bareli
- The horn and bone work that uses the remains of dead animals rather than living ones, making it a nature-friendly replacement for ivory.
- Sunahri Kand: To support the production of horticultural items under the “One District One Product (ODOP)” scheme and provide better nutrition to school children
Rajasthan: Blue Pottery (Jaipur) and MarkhanaMarbels (Nagaur)
Maharashtra: Wine from the Nashik valley
Karnataka:
- The hilly district in Malnad region of Karnataka is known for its coffee production and accounts for 30-40% of the total coffee production in India. It is also nicknamed the ‘coffee cup’ of India.
- In Chikkamagaluru, spices were earmarked, while pineapples were chosen in Shivamogga district.
- Other products included are Kalaburagi (red gram), Mandya (jaggery), Vijayapura (lemon), Haveri (mango), Gadag (Byadagi chillies), Bidar (ginger), Ballari (fig), Mysuru (bananas), and Koppal (guava).
News Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims: International Affairs
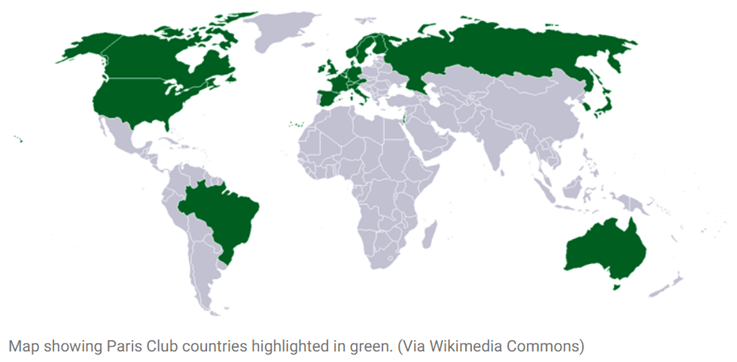
In News: The Paris Club, an informal group of creditor nations, will provide financial assurances to the International Monetary Fund on Sri Lanka’s debt.
The Paris Club
- It is a group of mostly western creditor countries that grew from a 1956 meeting in which Argentina agreed to meet its public creditors in Paris.
- Objective is to find sustainable debt-relief solutions for countries that are unable to repay their bilateral loans.
- It describes itself as a forum where official creditors meet to solve payment difficulties faced by debtor countries. All 22 are members of the group called Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- The members are: Australia, Australia, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Israel, Japan, Netherlands, Norway, Russia, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, the United Kingdom and the United States.
How has Paris Club been involved in debt agreements?
- Since its beginnings, the Paris Club has reached 478 agreements with 102 different debtor countries.
- Since 1956, the debt treated in the framework of Paris Club agreements amounts to $ 614 billion.
- It operates on the principles of consensus and solidarity. Any agreement reached with the debtor country will apply equally to all its Paris Club creditors.
- A debtor country that signs an agreement with its Paris Club creditors, should not then accept from its non-Paris Club commercial and bilateral creditors such terms of treatment of its debt that are less favourable to the debtor than those agreed with the Paris Club.
The role of the Paris Club over time: The Paris group countries dominated bilateral lending in the last century, but their importance has receded over the last two decades or so with the emergence of China as the world’s biggest bilateral lender.
News Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims: Elections
In News: The Supreme Court has refused to set aside a provision in the election law that allows candidates to contest polls from two constituencies simultaneously.
Why: SC feels that it is a policy matter and an issue concerning political democracy. Hence, it is for the Parliament to take a call.
Background: The petition filed by advocate Ashwini Upadhyay, represented by senior advocate Gopal Sankaranarayanan, had sought the court to declare Section 33(7) of the Representation of People Act invalid and ultra vires.
- Like one-person-one-vote, one-candidate-one-constituency is the dictum of democracy.
- Section 33(7) of the Act allows a person to contest a general election or a group of by-elections or biennial elections from two constituencies.
- But the court chose to leave the issue to the wisdom of the Parliament.
In 2018, the government had objected to the petition in court.
- It had argued that law cannot curtail the right of a candidate to contest elections and curtail the polity’s choice of candidates.
- The government had further told the Supreme Court that one-candidate-one-constituency restriction would require a legislative amendment. It had supported Section 33 (7).
- Before the amendment, candidates could contest from any number of constituencies. The government had said the restriction to two constituencies was reasonable enough, and there was no need to change the law now.
The Election Commission had, in an affidavit in 2018, supported the petition. It had informed the Supreme Court that it had proposed an amendment to Section 33(7) in July 2004.
- There have been cases where a person contests election from two constituencies, and wins from both.
- In such a situation he vacates the seat in one of the two constituencies.
- The consequence is that a by-election would be required from one constituency involving avoidable expenditure on the conduct of that bye-election.
- Conclusion:
- Law should be amended to provide that a person cannot contest from more than one constituency at a time.
- A candidate should deposit an amount of ₹5 lakh for contesting in two constituencies in an Assembly election or ₹10 lakh in a general election.
- The amount would be used to cover the expenses for a by-election in the eventuality that he or she was victorious in both constituencies and had to relinquish one.
News Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following pairs:
Indigenous tribal language and script
- Gondi – Telugu
- Mundari – Mundari bani
- Idu Mishmi – Idu Azobra
How many pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- None
- One pair only
- Two pairs only
- All three pairs
Q.2) Consider the following countries:
- Australia
- Switzerland
- China
- Russia
- India
Which of the above are part of Paris Club of Nations?
- 1 2 and 5 only
- 1 3 and 4 only
- 1 2 and 4 only
- 2 3 and 5 only
Q.3) Consider the following pairs:
Famous product and region
- Markhana marbles – Pune
- Kala namak – Siddharth Nagar
- Byadagi chillies – Gadag
How many pairs given above is/are correctly matched ?
- None
- One pair only
- Two pairs only
- All three pairs
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 4th February 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 3rd February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – a











