IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
About Compensatory Afforestation :
- It seeks to ensure that forest lands getting ‘diverted’ for non-forest purposes, like industrial or infrastructure development, is mandatorily accompanied by afforestation effort on at least an equal area of land.
- This compensatory afforestation was made a legal requirement through the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Act of 2016.
About THE COMPENSATORY AFFORESTATION FUND ACT, 2016 :
- The Compensatory Afforestation Fund Act was passed by the centre in 2016 and the related rules were notified in 2018.
- The Act was enacted to manage the funds collected for compensatory afforestation, which till then was managed by ad hoc Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA).
- ad hoc Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA)
- A temporary structure of CAMPA functioning on the orders of the Supreme Court. In 2002, the Supreme Court of India observed that collected funds for afforestation were under-utilized by the states and it directed that an “ad hoc CAMPA” consisting of three officials and one representative of the Central Empowered Committee be set up till the final one is created.
Objective: It seeks to establish the National Compensatory Afforestation Fund under the Public Account of India, and a State Compensatory Afforestation Fund under the Public Account of each state.
These Funds will receive payments for:
- compensatory afforestation
- net present value of forest (NPV)
- other project-specific payments.
- The determination of Net Present Value (NPV) will be delegated to an expert committee constituted by the central government.
- Net Present Value (NPV) quantifies the services provided by the forest like goods and services (tourism and timber); regulating services (climate change); and non-material benefits (recreation).
- It seeks to provide safety, security, and transparency in the utilization of CAMPA funds which are currently kept in Nationalized Banks and managed by an ad-hoc body.
- The National Fund will receive 10% of these funds, and the State Funds will receive the remaining 90%.
- These funds would be brought under the focus of Parliament and State Legislatures by transferring them to non-lapsable interest-bearing funds.
- According to the recently revised calculations, companies have to pay NPV at rates ranging between Rs 9.5 lakh and Rs 16 lakh per hectare, depending on the quality of forests getting diverted.
- The Act also establishes the National and State Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authorities to manage the National and State Funds
CAMPA funds can be used for the following purposes:
- Artificial regeneration (plantation)
- Assisted natural regeneration
- Forest management
- Forest protection
- Infrastructure development
- Wildlife protection and management
- Supply of wood
- Other forest produces saving devices.
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- As per law, the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority exists at both National and State levels.
- People’s participation is mandatory in the compensatory afforestation programmes carried out under the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Act, 2016.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- As per the recent amendment to the Indian Forest Act, of 1927, forest dwellers have the right to fell the bamboo grown on forest areas
- As per the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006, bamboo is a minor forest produce
- The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition Forest Rights) Act, 2006 allows ownership of minor forest produce to forest dwellers
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and technology
Context: Recent studies reported that combination therapy can save more lives in Scrub typhus.
About Scrub typhus :
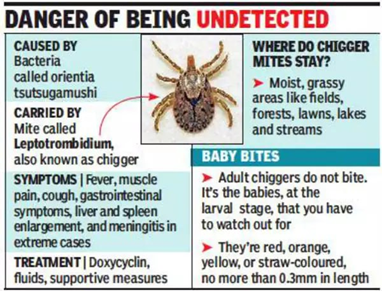
- Scrub typhus is also known as bush typhus.
- It is a disease caused by a bacteria called Orientia tsutsugamushi.
- Scrub typhus is spread to people through bites of infected chiggers (larval mites).
- The most common symptoms of scrub typhus include fever, headache, body aches, and sometimes rash. .
- No vaccine is available to prevent scrub typhus.
About Doxycycline :
- Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic used in the treatment of some bacterial and parasitic infections such as bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus, and syphilis.
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent the COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Serum Institute of India produced a COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using an mRNA platform.
- The Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using a vector-based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen-based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following statements is not correct? (2017)
- Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV.
- Hepatitis B, unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine.
- Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses is several times more than those infected with HIV.
- Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context : Recent reports show that ‘Hippocampus kelloggi’ or sea horse, could be migrating toward coastal Odisha due to fishing pressures.
About Sea horses :

- A seahorse is any of 46 species of small marine fish in the genus Hippocampus.
Characteristic feature :
- Having a head and neck suggestive of a horse,
- They also feature segmented bony armor, an upright posture, and a curled prehensile tail.
Habitat and Distribution across India :
- Seahorses are mainly found in shallow tropical and temperate saltwater throughout the world, from about 45°S to 45°N.
- They live in sheltered areas such as seagrass beds, estuaries, coral reefs, and mangroves.
- Seahorses range in size from 1.5 to 35.5 cm.
- They are named for their equine appearance, with bent necks and long-snouted heads, and distinctive trunks and tails.
- The species are distributed along the coasts of eight States and five Union Territories from Gujarat to Odisha, apart from Lakshadweep and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Conservation status :
- IUCN status : Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix II
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following kinds of organisms: (2021)
- Copepods
- Cyanobacteria
- Diatoms
- Foraminifera
Which of the above are primary producers in the food chains of oceans?
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Q.2) Which of the following are detritivores? (2021)
- Earthworms
- Jellyfish
- Seahorse
- Woodlice
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 2, 3, 4 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims – Government initiatives (Polity)
Context: The Gujarat government recently told the High Court, that it was in the process of setting up virtual traffic courts in the state under the ‘One Nation One Challan’ initiative.
About One Nation One Challan :
- One Nation, One Challan is an initiative of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
Objective :
- to bring all related agencies, such as the traffic police and the Regional Transport Office (RTO), on one platform, to enable the seamless collection of challans as well as data transfer.
- involves the detection of traffic violations through the CCTV network
- involves getting the registration number of the erring vehicle from applications like VAHAN (detecting the vehicle’s ownership details) and SARATHI (compilation of driving licenses).
- An e-challan is then generated with the relevant penalty amount and sent to the mobile number linked with the vehicle.
About VAHAN (detecting the vehicle’s ownership details) :
- VAHAN is a software that enables the processes at RTO/DTO/MLO/SDM involving Vehicle Registration, Fitness, Taxes, Permits & Enforcement to get computerized.
- The State Transport Department is governed by both Central Motor Vehicle Regulation (CMVR) and state-specific Motor Vehicle Regulation (State MVR).
VAHAN Services:
- Vehicle Registration.
- Permit
- Taxes
- Fitness
- Enforcement
About Virtual traffic courts:
- If a challan amount is not paid within 90 days, it will be automatically forwarded to a virtual court and proceedings will begin.
- The accused will receive a summons on their mobile phone.
- The virtual court aims to eliminate the physical presence of litigants.
- The accused can search for their case on the virtual court’s website and pay the fine.
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) In India under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defense in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) Consider the following statements : (2020)
- Aadhaar metadata cannot be stored for more than three months.
- State cannot enter into any contract with private corporations for sharing of Aadhaar data.
- Aadhaar is mandatory for obtaining insurance products.
- Aadhaar is mandatory for getting benefits funded out of the Consolidated Fund of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
About The Special Window for Affordable and Mid-Income Housing (SWAMIH) Investment Fund :
- The Special Window for Affordable and Mid-Income Housing (SWAMIH) Investment Fund I is a social impact fund specifically formed for completing stressed and stalled residential projects.
- Sponsors : the Ministry of Finance, Government of India, and is managed by SBICAP Ventures Ltd., a State Bank Group company.
- This is a government-backed fund that was set up as a Category-II AIF (Alternate Investment Fund) debt fund
- It is registered with SEBI in 2019.
- Objectives: formed to complete construction of stalled, RERA-registered affordable and mid-income category housing projects which are stuck due to paucity of funds.
Eligibility criteria:
- Real estate projects seeking last-mile finance from SWAMIH must be registered under the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act (RERA) and have been halted due to a lack of sufficient money.
- Each of these initiatives must be on the verge of being completed.
- They must also fall into the category of ‘Affordable and Middle-Income Projects’ (any housing projects wherein housing units do not exceed 200 sq.m.).
- SWAMIH funding is also available for initiatives with net worth-positive projects.
- The value of their receivables (debts due to them by buyers) plus the value of their unsold inventories is more than their completion expenses and outstanding liabilities for net-worth-positive projects.
About Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act (RERA):
- Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act (RERA) is an act that came into effect fully in 2017.
- The Act establishes Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA) in each state for regulation of the real estate sector and also acts as an adjudicating body for speedy dispute resolution.
- It seeks to protect home-buyers as well as help boost investments in the real estate sector by bringing efficiency and transparency in the sale/purchase of real estate.
Key Provisions of RERA Act
- Compulsory registration: According to the central act, every real estate project (where the total area to be developed exceeds 500 sq metres or more than 8 apartments is proposed to be developed in any phase), must be registered with its respective state’s RERA.
- Establishment of state level regulatory authorities.
- Render advice to the government and ensuring compliance with its Regulations and the Act
- Establishment of Real Estate Appellate Tribunal: Decisions of RERAs can be appealed in these tribunals.
- Mandatory Registration: All projects with plot size of a minimum 500 sq.mt or eight apartments need to be registered with Regulatory Authorities.
- Deposits: Developers needs to keep 70% of the money collected from a buyer in a temporary pass through account held by a third party (escrow account) to meet the construction cost of the project.
- Liability of the developer: A developer’s liability to repair structural defects would be for 5 years.
- Cap on Advance Payments: A promoter cannot accept more than 10% of the cost of the plot, apartment or building as an advance payment or an application fee from a person without first entering into an agreement for sale
- Carpet Area over super built-up: Clearly defines Carpet Area as net usable floor area of flat. Buyers will be charged for the carpet area and not super built-up area.
- Punishment for non-compliance: Imprisonment of up to three years for developers and up to one year in case of agents and buyers for violation of orders of Appellate Tribunals and Regulatory Authorities.
MUST READ : About Alternative Investment Fund (AIF)
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to the ‘National Investment and Infrastructure Fund’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- It is an organ of NITI Aayog.
- It has a corpus of Rs. 4, 00,000 crores at present.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Who among the following can join the National Pension System (NPS)? (2017)
- Resident Indian citizens only
- Persons of age from 21 to 55 only
- c)All State Government employees joining the services after the state notification by the respective State Governments
- All Central Government employees including those of Armed Forces joining the services on or after 1st April 2004
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: According to a recent study, anthropogenic threats like illegal fishing and sand mining pose a threat to the mugger crocodiles (Crocodylus plaustris) of the Rapti river.
About mugger crocodiles :

- The mugger crocodile (Crocodylus palustris ) is a medium-sized broad-snouted crocodile, also known as the mugger and the marsh crocodile.
- It inhabits marshes, lakes, rivers, and artificial ponds.
- Geographic Range:
- They are found all over south Asia — India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Nepal, and Bangladesh — as well as south-eastern Iran.
- The mugger is found in 15 Indian states, with the largest populations in the middle Ganges (Bihar-Jharkhand) and Chambal (Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Rajasthan) basins.
Conservation Status:
- CITES Appendix I
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
Conservation Projects:
- Mugger Project At Ramatirtha
- Kakra Crocodile Trail: it is going on in Terai Eastern Forest Division at Khatima, Uttarakhand.
- The Indian Crocodile Conservation Project: it was launched in 1975 in different states in the country.
Other crocodiles species in India
Saltwater or Estuarine Crocodile
- Habitat: Blackish and freshwater regions of eastern India, Southeast Asia, and northern Australia.
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern
- Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus)
- It is the longest among all living crocodilians.
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
- CITES : Appendix I
About Valmiki Tiger Reserve :
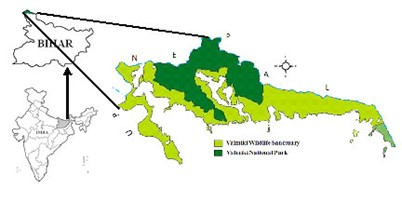
- Valmiki Tiger Reserve forms the easternmost limit of the Himalayan Terai forests in India.
- It is the only tiger reserve in Bihar.
- It is situated in the Gangetic Plains bio-geographic zone of the country; the forest has a combination of Bhabar and terai tracts.
- It lies in the northwestern portion of the West Champaran district of Bihar.
- Wild mammals found in the forests of Valmiki Tiger Reserve include tiger, sloth bear, leopard, wild dog, bison, wild boar, etc.
About Chitwan National Park:
- Chitwan National Park (CNP), established in 1973, was Nepal’s first National Park.
- It is located in the Southern Central Terai of Nepal.
- The park is the last surviving example of the natural ecosystems of the ‘Terai’ region and covers subtropical lowland, wedged between two east-west river valleys at the base of the Siwalik range of the outer Himalayas.
- The core area lies between the Narayani (Gandak) and Rapti rivers to the north and the Reu River and Nepal-India international border in the south, over the Sumeswar and Churia hills, and from the Dawney hills west of the Narayani, and borders with Parsa Wildlife Reserve to the east.
- The Chitwan National Park (CNP) is a world heritage property. Beeshazar within it were designated as a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
- In 2003, and associated lakes the buffer zone
About the Gandak River :
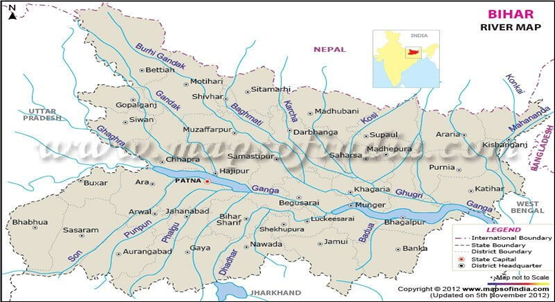
- It is also known as the Kali Gandaki and Narayani after the confluence with the Trisuli river in Nepal.
- It is a north-bank tributary of the Ganga in India.
- Origin — It rises in Tibet near the Nepal border.
- It flows southwest into India and then turns southeast along the Uttar Pradesh–Bihar state border and across the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
About Rapti River:
- The West Rapti River is a tributary of the Ghaghara River.
- It has its origins in Nepal.
- The West Rapti River originates at a summit in the Western Himalayas and the Mahabharat range of mountains.
- It joins Ganga River near Patna, Bihar.
- Lungri Khola, Jhimruk Khola, Ami River, Rohini River are the major left-bank tributaries of Rapti.
- Arun Khola is the right bank tributary of the Rapti.
Source: DOWN TO EARTH
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Two important rivers — one with its source in Jharkhand (and known by a different name in Odisha), and another, with its source in Odisha — merge at a place only a short distance from the coast of the Bay of Bengal before flowing into the sea. This is an important site of wildlife and biodiversity and a protected area.
Which one of the following could be this? (2011)
- Bhitarkanika
- Chandipur-on-sea
- Gopalpur-on-sea
- Simlipal
Q.2) A sandy and saline area is the natural habitat of an Indian animal species. The animal has no predators in that area but its existence is threatened due to the destruction of its habitat. Which one of the following could be that animal? (2011)
- Indian wild buffalo
- Indian wild ass
- Indian wild boar
- Indian gazelle
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and technology
About Bio computers :
- Researchers at the JHU have developed a technique wherein brain organoids are integrated with modern computing technologies to create “bio-computers”.
- The 3D cultures of brain tissue being created in the lab are called brain organoids or mini-brains.
- These are up to 4 mm in size.
- These are developed using human stem cells and thus they have the ability to capture various functional and structural features of a human brain.
- Such brain cultures that are created or developed are then coupled to the real world through various sensors and input/output devices.
- Plans are in place to also integrate rain organoids or mini-brains with machine learning (ML) techniques by developing such organoids inside flexible structures affixed with multiple electrodes (similar to the ones used to record EEG readings).
- Such a mechanism will help record the firing patterns of various neurons and deliver electrical stimuli to mimic sensory stimuli.
- Brain organoids will be grown inside flexible structures affixed with multiple electrodes to record the firing patterns of neurons and deliver electrical stimuli.
- Machine-learning techniques will be used to analyze the response patterns of neurons and their effect on human behavior or biology.
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- Biofilms can form on medical implants within human tissues.
- Biofilms can form on food and food processing surfaces.
- Biofilms can exhibit antibiotic resistance.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the carbon nanotubes, consider the following statement : (2020)
- They can be used as the carriers of drugs and antigens in the human body.
- They can be made into artificial blood capillaries for an injured part of the human body.
- They can be used in biochemical sensors.
- Carbon nanotubes are biodegradable.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2, 3, and 4 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy – Agriculture)
Context: Centre has recently notified nano Di-Ammonia Phosphate (DAP) in the Fertilizer Control Order, allowing its commercial release for farmers.
About Nano DAP:
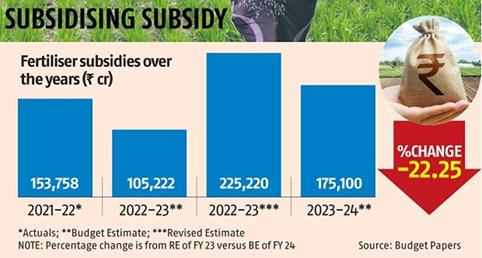
- Nano-DAP is jointly manufactured by IFFCO in association with a private player Coromandel and is expected to contribute to bringing down the annual subsidy on non-urea fertilizers.
- DAP is a type of fertiliser that contains both nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Nano DAP is a variation of DAP that has been modified at the nano-scale to improve its effectiveness in agriculture to enhance crop growth and yield.
- It is produced by reducing the size of the DAP particles to the nano-scale (1-100 nanometres).
- The small size of the particles allows for better absorption of the fertiliser by plant roots, resulting in increased crop growth and yield.
- It is more efficient than traditional DAP, which means that less fertiliser is needed to achieve the same results.
Significance of Nano DAP for India:
- Nitrogen Use Efficiency: Nano-DAP has a high nutrient use efficiency of more than 85%, which helps to fulfil the nitrogen requirement of plants.
- Cost Advantage: Nano-DAP is expected to be priced at around half the subsidized rate of traditional DAP, thus providing cost advantages to farmers.
- Better crop quality: The use of Nano-DAP is expected to improve crop quality, leading to better prices for farmers.
- Contribution to reducing subsidies: With the inclusion of Nano-DAP in the Fertilizer Control Order, it is expected to bring down the annual subsidy on non-urea fertilizers.
- Reduction in Chemical Fertilizers: Nano-DAP can help reduce the injudicious use of chemical fertilizers like urea by 50%, thus promoting efficient use of plant chemicals.
- Increase in Farmer Income: Nano-DAP is expected to lead to an increase in farmer income by reducing input costs, increasing crop yield, and improving crop quality.
Issues associated with Nano-DAP:
- Cost: While Nano-DAP is expected to be cost-effective in the long run, the initial investment can be higher for farmers who may not have the resources to invest in new fertilizers.
- Awareness and education: The government and private sector will need to invest in educating farmers about the benefits of the new fertilizer and how to use it correctly.
- Limited availability: The production of Nano-DAP is currently limited and may not be sufficient to meet the demand of all farmers across India.
- Infrastructure: The government and private sector will need to invest in building the necessary infrastructure to ensure that the fertilizer reaches farmers in a timely and efficient manner.
- Resistance: While Nano-DAP is expected to be more efficient than traditional fertilizers, farmers will need to use it responsibly to prevent resistance from developing.
Way Forward:
Nano DAP is a promising technology that has the potential to revolutionize the agriculture industry, especially for a country like India which needs to ensure food security for its billion-plus population.
However, further research is needed to fully understand these risks and ensure that the benefits of this technology outweigh any potential drawbacks. Thus, Overall, Nano DAP presents a promising solution for improving crop productivity and addressing food security challenges around the world.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which of the following activities constitute real sector in the economy? (2022)
- Farmers harvesting their crops
- Textile mills converting raw cotton into fabrics
- A commercial bank lending money to a trading company
- A corporate body issuing Rupee Denominated Bonds overseas.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) Under the Kisan Credit Card scheme, short-term credit support is given to farmers for which of the following purposes ? (2020)
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets harvesters,
- Purchase of combine tractors and mini trucks requirements of farm
- Consumption households
- Post-harvest expenses
- Construction of family house and setting up of village cold storage facility
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 5 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2,3,4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Security Issues)
Context: ‘Cyber Warrior’ Teams and Help Desks to Combat Rising Cybercrime in Visakhapatnam.
- During the year 2022, Visakhapatnam had reported as many as 610 cybercrime cases, as against 316 during the year 2021, which is almost a 93% increase.
About Cyber Warriors:
- As part of the initiative, around 70 police personnel, including around 20 sub-inspectors and several ASIs will be undergoing virtual and offline training on various aspects of cybercrime.
- The cyber warriors team will be headed by a Sub-Inspector and staff.
Cybercrime in India as per NCRB Report:
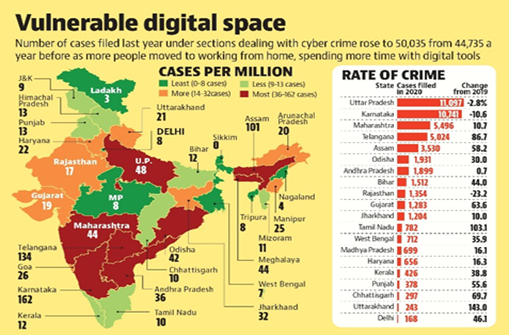
- India reported nearly 52,974 cybercrime incidents in 2021 which was an increase of nearly 6% from 2020.
- Telangana was the state with the highest number of cybercrime cases, accounting for more than 19% of the total.
- Uttar Pradesh and Karnataka saw a decrease in the number of cybercrime cases by 20% and 24%, respectively.
- The main challenges in prosecuting cybercrime cases are jurisdictional issues and difficulty in obtaining electronic logs from foreign service providers.
- Bengaluru had the highest number of cybercrime cases, but there has been a decline in cases over the past three years.
- Fraud was the most common motive for committing cybercrime, accounting for nearly 61% of cases.
- Karnataka recorded the highest number of cybercrimes against women in 2021, with 2,243 cases.
- The police pendency percentage in cybercrime cases improved from 3% in 2020 to 56.4% in 2021.
- The conviction ratio for cybercrime cases remains poor, and the charge-sheeting rate declined from 5% in 2020 to 33.8% in 2021.
- The court pendency percentage remained high, with 81.4% of total cases in trial in 2021 remaining. pending at the end of the year.
Challenges of cybercrime:
- Lack of Awareness: Many people in India are still not aware of the risks associated with cybercrime, making them more vulnerable to attacks.
- Rapidly Evolving Cyber Threat Landscape: Cybercrime is evolving at a rapid pace, with new threats emerging regularly. It is challenging for law enforcement agencies to keep up with these developments.
- Low Cybersecurity Awareness: A large number of individuals and organizations in India lack basic cybersecurity awareness, making them easy targets for cybercriminals.
- Increasing Use of Technology: With the widespread adoption of technology in India, more people are becoming vulnerable to cybercrime, making it even more challenging to combat.
- Lack of Cybercrime Laws: India has outdated cybercrime laws that are not in line with current threats. There is a need for updated laws to be enacted to combat the ever-changing cybercrime landscape.
- Limited Cybersecurity Infrastructure: India’s cybersecurity infrastructure is still developing, and many organizations do not have adequate security measures in place to protect their networks and data.
Need for controlling cybercrimes in India:
- Increasing Digitalization: With the growing digitalization of India, more people are using online services and technology, which has led to an increase in cybercrime incidents.
- National Security: Cybercrime can have severe consequences for national security, as it can compromise sensitive information and infrastructure, leading to potential political instability.
- Personal Privacy: Cybercrime can violate personal privacy, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and other forms of cyberstalking.
- Economic Impact: Cybercrime has a significant economic impact on India, with losses amounting to billions of dollars annually. The country is also losing out on potential investments due to concerns about cybersecurity.
- Digital India Initiative: The Indian government’s Digital India initiative aims to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy. However, cybercrime can hinder the initiative’s progress and undermine public trust in digital technologies.
- Cyber Security Jobs: With the growing importance of cybersecurity, there is a need for skilled professionals in the field, creating job opportunities in India.
Government Initiatives To Tackle Cyber Crime in India:
- Banning of unsafe apps: India had banned apps that posed a threat to security.
- India had banned many apps (mostly of Chinese origin), which were found to be unsafe for usage by Indian citizens.
- The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In): It operates as the national agency for tackling the country’s cybersecurity, and has helped in lowering the rate of cyber-attacks on government networks.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C):
- To act as a nodal point in the fight against cybercrime
- To prevent misuse of cyber space for furthering the cause of extremist and terrorist groups
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC):
- It is a central government establishment, formed to protect critical information of India, which has an enormous impact on national security, economic growth, or public healthcare.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: Cyber Swachhta Kendra helps users to analyse and keep their systems free of various viruses, bots/ malware, Trojans, etc.
- Launched in early 2017.
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat: It was launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in 2018 with an aim to
- spread awareness about cybercrime and
- building capacity for safety measures for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT staff across all government departments.
- The Cyber Warrior Police Force: It was organised on the lines of the Central Armed Police Force in 2018.
- Information Technology Act, 2000 (Amended in 2008): It is the main law for dealing with cybercrime and digital commerce in India.
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) was created under Section 70A of IT Act 2000 to protect Cyberinfrastructure.
Way Forward:
Cybercrime is a crucial issue in India due to its economic, national security, and personal privacy implications. It is necessary to take proactive steps to combat cybercrime and create a safe and secure digital environment in the country. Therefore, Cyber warriors are significant especially when India ranks fifth globally in terms of the number of incidents reported.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding The Special Window for Affordable and Mid-Income Housing (SWAMIH) Investment Fund:
- It is a social impact fund specifically formed for completing stressed and stalled residential projects.
- It is managed by SBICAP Ventures Ltd., a State Bank Group company.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) It forms the easternmost limit of the Himalayan Terai forests in India. It is the only tiger reserve in Bihar. It is situated in the Gangetic Plains bio-geographic zone of the country; the forest has a combination of Bhabar and terai tracts.
Which of the following tiger reserves is described in the above passage?
- Pakke Tiger Reserve
- Valmiki Tiger Reserve
- Dudhwa Tiger Reserve
- Buxa Tiger Reserve
Q.3) Consider the following species:
- Gharials
- Mugger crocodile
- Saltwater crocodile
Which of the above finds natural habitat in India?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 7th March 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 6th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – b











