IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recent reports have suggested that the global energy transition has made progress but it falls short of the 1.5°C pathway.
About World Energy Transitions Outlook report:-
- It is taken out by International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).
- The World Energy Transitions Outlook outlines a vision for the transition of the energy landscape to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement.
- It presents a pathway for limiting global temperature rise to within 1.5°C of pre-industrial levels and bringing CO2 emissions to net zero by mid-century.
- It outlook charts an evolving pathway to achieving a climate-safe future in line with the goals of the Paris Agreement.
- Its 1.5°C pathway offers a roadmap for accelerating the global energy transition by positioning electrification and efficiency as key drivers of change, backed by renewables, hydrogen and sustainable biomass.
- This Preview presents high-level insights from the forthcoming 2023 report, which builds on two of IRENA’s key scenarios to capture global progress toward meeting the 1.5°C climate goal: the Planned Energy Scenario (PES) and the 1.5°C Scenario.
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA):-
- It is an intergovernmental organisation.
- It was officially founded in Bonn, Germany, in 2009.
- It has 167 members and India is the 77th Founding Member of IRENA.
- It has its headquarters in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates.
MUST READ: Renewable Energy Transition
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) “Climate Action Tracker” which monitors the emission reduction pledges of different countries is a: (2022)
- Database created by a coalition of research organisations
- Wing of “International Panel of Climate Change”
- Committee under “United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change”
- Agency promoted and financed by United Nations Environment Programme and World Bank
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The International Solar Alliance was launched at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in 2015.
- The Alliance includes all the member countries of the United Nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Recently, in the India Justice Report (IJR) 2022 the State of Karnataka has achieved the top rank.
About India Justice Report 2022:-
- It was initiated by Tata Trusts in 2019.
- This is the third edition.
- The foundation’s partners include the Centre for Social Justice, Common Cause, Commonwealth Human Rights Initiative, DAKSH, TISS-Prayas, Vidhi Centre for Legal Policy and How India Lives, IJR’s data partner.
- This report is based on overall data of 4 pillars of justice delivery namely Police, Judiciary, Prisons, and Legal Aid.
- It also separately assesses the capacity of the 25 State Human Rights Commissions in the country.
Findings of the report:-
Few number of judges:
- High courts: As of December 2022, against a sanctioned strength of 1,108 judges, the High Courts were functioning with only 778 judges.
- Subordinate courts: The subordinate courts were found functioning with 19,288 judges against a sanctioned strength of 24,631 judges.
Rising pendency:
- The number of cases pending per judge is rising in most States over the past five years.
- At High Court level: Uttar Pradesh has the highest average pendency – cases remain pending for an average of 11.34 years,
- West Bengal for 9.9 years.
- The lowest average High Court pendency is in Tripura (1 year), Sikkim (1.9 years) and Meghalaya (2.1 years).
Number of cases per judge:
- The number of cases a judge has to deal with has steadily increased.
- Between 2018 and 2022, the caseload per judge increased in 22 States and Union Territories.
Case clearance rate:
- The case clearance rate (CCR), or the number of cases disposed of in a year measured against the number filed in that year, is a common metric used to determine the rate at which cases are disposed of.
- The report found that the High Courts are clearing more cases annually than the subordinate courts.
- Between 2018-19 and 2022, the national average improved by six percentage points (88.5% to 94.6%) in High Courts, but declined by 3.6 points in lower courts (93% to 89.4%).
- Tripura is the only State where the CCR in district courts remained above 100%, with the exception of 2020 — the year of the pandemic.
Number of court halls:
- Nationally, the number of court halls appears sufficient for the number of actual judges.
- However, that space will become a problem if all the sanctioned posts are filled.
Caste based reservation:
- Though caste-based reservations vary from State to State, at the district court level, no State or Union Territory could fully meet all its Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and Other Backward Classes quotas.
- State-wise data on caste diversity in High Courts remains unavailable.
Representation of Women:
- There are more women judges at the district court level than at the High Court level, with 35% of the total number of judges at the district court level and only 13% of judges in the High Courts across the country being women.
- Goa, with 70%, has the highest percentage of women judges at subordinate courts, followed by Meghalaya and Nagaland at 63% each.
- Among the High Courts, Sikkim, with a total strength of just three judges, has the highest national average at 33.3% of women judges.
- Bihar, Tripura, Manipur, Meghalaya, and Uttarakhand continued to have no women judges in their High Courts.
MUST READ: Judicial Accountability
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- Pursuant to the report of the H.N. Sanyal Committee, the Contempt of Courts Act, 1971 was passed.
- The Constitution of India empowers the Supreme Court and the High Courts to punish for contempt of themselves.
- The Constitution of India defines Civil Contempt and Criminal Contempt.
- In India, the Parliament is vested with the power to make laws on Contempt of Court.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 3 only
Q.2) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Government law officers and legal firms are recognized as advocates, but corporate lawyers and patent attorneys are excluded from recognition as advocates.
- Bar Councils have the power to lay down the rules relating to legal education and recognition of law colleges.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and technology
Context: Recently, India has initiated an anti-dumping probe into imports of the poisonous chemical sodium cyanide from China, the European Union, Japan and Korea.
About Sodium cyanide:-
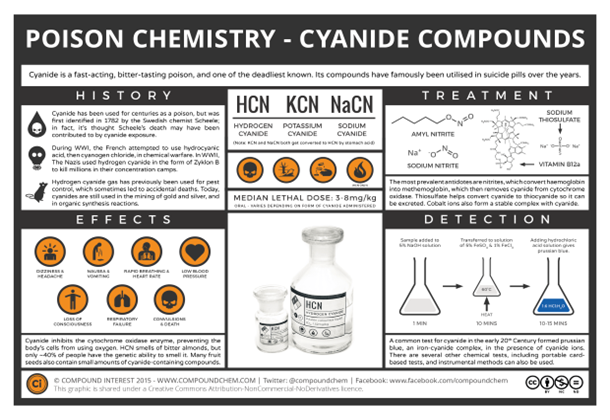
IMAGE SOURCE: The Chemistry of Poisons – Cyanide – Compound Interest (compoundchem.com)
- This sodium salt is white in colour and is soluble in water.
- It is one of the highly toxic salts as it has a high affinity (highly reactive) for metals.
- Sodium cyanide is also a moderately strong base, and when it is treated with an acid (such as sulfuric acid).
- It forms a highly toxic gas known as hydrogen cyanide.
Sodium Cyanide Uses:-
- Gold Mining: In the mining industry sodium cyanide has exorbitant uses.
- Chemical Feedstock: Sodium cyanide helps in producing a number of commercially significant chemical compounds such as cyanogen chloride, many types of nitriles and also cyanuric chloride.
- Pharmaceutical industry: Nitriles are present in many chemicals which it has vast usage in the industry.
- Other industries:
- it is used for cleaning metals.
- In the dye industry, the chemical is used to produce dyes.
- This said the chemical can also be used for producing hydrocyanic acid.
- In many other sectors, the chemical is used to manufacture the electroplating solution.
- It is also used as an agricultural chemical and farmers use it as a pesticide to kill pests that damage the crop.
MUST READ: Shortcomings of Indian Chemical Industry: TIFAC and Anti-Dumping Duty
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) “Triclosan” considered harmful when exposed to high levels for a long time, is most likely present in which of the following? (2021)
- Food preservatives
- Fruit-ripening substances
- reused plastic containers
- Toiletries
Q.2) Bisphenol A (BPA), a cause of concern, is a structural/key component in the manufacture of which of the following kinds of plastics? (2021)
- Low-density polyethene
- Polycarbonate
- Polyethene terephthalate
- Polyvinyl Chloride
Syllabus
- Prelims – Disaster Management
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi, underlined the need for an integrated response to disasters recently.
About International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure 2023:-
- It is the annual conference of the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) and its partners.
- International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure 2023 is being hosted by India.
- The Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI):-
- It is a multi-stakeholder global partnership of national governments, UN (United Nations) agencies and programmes, multilateral development banks and financing mechanisms, the private sector, and knowledge institutions.
- The Prime Minister of India launched CDRI during his speech at the UN Climate Action Summit in 2019.
- It aims to promote the resilience of new and existing infrastructure systems to climate and disaster risks in support of sustainable development.
- Members: 30 countries and 8 organizations.
- The CDRI Secretariat is based in New Delhi, India.
- It brings together member Countries, organizations, institutions and infrastructure actors and stakeholders to strengthen the global discourse on disaster and climate-resilient infrastructure.
- The ICDRI 2023 will focus on charting these solutions and pathways to Shaping Resilient Infrastructure.
- It aims at delving into practices of creating risk-informed systems, resilient infrastructure assets and innovative financing to deliver infrastructure needs.
- The conference will feature the progress of the Biennial Report on Global Infrastructure Resilience, the collaborative delivery mechanism of IRIS with SIDS, and the operationalization of IRAF.
- IRAF: multi-partner trust fund for DRI, and feature the launch of the DRI Academic Network and Partnership.
Objectives of ICDRI 2023 are:-
- To provide a platform for Member Countries to engage and contribute to DRI solution pathways.
- To bring together infrastructure actors for building partnerships, knowledge sharing and fostering complementarity on DRI solutions.
- To convene DRI stakeholders for enhanced collective action on infrastructure resilience.
Thematic Focus:-
- Pillar 1: Delivering Resilient Infrastructure
- Inclusive and Risk-Informed Systems
- Pillar 2: Delivering Resilient Infrastructure
- Providing Reliable Services through Resilient Infrastructure Assets
- Pillar 3: Delivering Resilient Infrastructure
- Realising Finance and Investments for Infrastructure Resilience
MUST READ: National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2020)
- Jet streams occur in the Northern Hemisphere only.
- Only some cyclones develop an eye.
- The temperature inside the eye of a cyclone is nearly 10°C lesser than that of the surroundings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The Barren Island volcano is an active volcano located in the Indian territory.
- Barren Island lies about 140 km east of Great Nicobar.
- The last time the Barren Island volcano erupted was in 1991 and it has remained inactive since then.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 3 only
- 1 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, a rescued black panther was released in Netravali Wildlife Sanctuary.
About Netravali Wildlife Sanctuary:-
IMAGE SOURCE: Erasing the dots (downtoearth.org.in)
- It is located in South Eastern Goa.
- Netravali Wildlife Sanctuary is the largest sanctuary in Goa and probably the most bio-diverse.
- It constitutes one of the vital corridors of the Western Ghats.
- Netravali or Neturli is an important tributary of River Zuari, which originates in the sanctuary.
- It has two important waterfalls namely, Savari and Mainapi.
- It has some of the finest yet relatively unexplored forests in the state.
- The typical forest here is mixed deciduous to semi-evergreen with a good network of streams and tabletop grasslands.
- Fauna: Leopard, Giant Squirrel, Mouse Deer, Nilgiri Wood Pigeon and Ceylon Frogmouth.
MUST READ: Panther
SOURCE: THE PRINT
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following Protected Areas are located in the Cauvery basin? (2018)
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) Which one of the following protected areas is well-known for the conservation of a sub-species of the Indian swamp deer (Barasingha) that thrives well on hard ground and is exclusively graminivorous? (2020)
- Kanha National Park
- Manas National Park
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Tal Chhapar Wildlife Sanctuary
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Recently, an avalanche struck Sikkim’s capital Gangtok.
About Avalanche:-
- It is a mass of snow, rock, ice, soil, and other material sliding swiftly down a mountainside.
- Avalanches of rocks or soil are often called landslides.
- Snow slides are the most common kind of avalanche.
- It can sweep downhill faster than the fastest skier.
- A snow avalanche begins when an unstable mass of snow breaks away from a slope.
- It occurs as layers in a snowpack slide off.
- A snowpack is simply layers of snow that build up in an area, such as the side of a mountain.
- There are two main types of snow avalanches:
- Sluff avalanches: occur when the weak layer of a snowpack is on top.
- A sluff: is a small slide of dry, powdery snow that moves as a formless mass.
- Sluffs are much less dangerous than slab avalanches.
- A slab avalanche occurs when the weak layer lies lower down in a snowpack.
About important passes in Sikkim:-
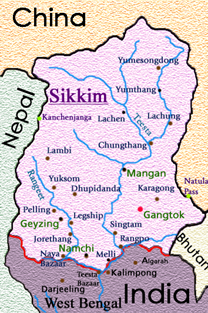
IMAGE SOURCE: important passes in Sikkim upsc – Bing images
Nathu La (Pass)-Nathu La
- It is a mountain pass in the Himalayas in the East Sikkim district.
- It connects the Indian state of Sikkim with China’s Tibet Autonomous Region.
- Nathu means “listening ears” and La means “pass” in Tibetan.
Jalep La (Pass)-Jelep La or Jelep Pass
- It is at an elevation of 4,267 m or 13,999 ft.
- It is a high mountain pass between East Sikkim District, Sikkim, India, and Tibet Autonomous Region, China.
- It is on a route that connects Lhasa to India.
MUST READ: Snow and Avalanche Study Establishment (SASE)
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements: (2017)
- The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim.
- River Rangeet originates in Sikkim and is a tributary of river Teesta.
- River Teesta flows into the Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following is/are tributary/ tributaries of Brahmaputra? (2016)
- Dibang
- Kameng
- Lohit
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: Recently, the Prime Minister expressed happiness about GI Tag for Ladakh’s Wood Carving.
About Ladakh’s Wood Carving:-
- Ladakh’s wood carving has been known for its intricate designs and unique patterns.
- The designs and unique patterns, are mostly inspired by Buddhist themes and motifs.
- The wood carvings are made from local wood such as willow and apricot.
- They are often used for decorating doors, windows, and other household items.
- The unique form of wood carving which has received a GI tag is concentrated in the Wanla and Cjoglamasar districts of Leh.
- The craft has a distinct cultural and religious influence.
MUST READ: India’s first-ever night sky sanctuary in Ladakh
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2018)
Crafts Heritage of
- Puthukkuli Shawls Tamil Nadu
- Sujni Embroidery Maharashtra
- Uppada Jamdani saris Karnataka
Which of the pairs given above is /are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
- 2 and 3
Q.2) Kalamkari painting refers to (2019)
- a hand-painted cotton textile in South India
- a handmade drawing on bamboo handicrafts in North East India.
- a block-painted woollen cloth in the Western Himalayan region of India
- a hand-painted decorative silk cloth in North-Western India
Syllabus
- Prelims –Modern Indian History
Context: Recently, the 116th birth anniversary of Babu Jagjivan Ram was celebrated.
About Babu Jagjivan Ram:-
- He was a national leader, a freedom fighter, a social justice crusader, a champion of the depressed classes, and an outstanding Parliamentarian.
- In 1925, Jagjivan Ram met scholar Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya and was greatly inspired by him.
- On Malaviya’s invitation, he joined the Banaras Hindu University.
- He organized a number of Ravidas Sammelans and celebrated Guru Ravidas Jayanti in different areas of Calcutta (Kolkata).
- In 1931, he became a member of the Indian National Congress (Congress Party).
- He was instrumental in the foundation of the All India Depressed Classes League.
- All India Depressed Classes League: an organisation dedicated to attaining equality for untouchables, in 1934-35.
- He was a champion of social equality and equal rights for the Depressed Classes.
- In 1935, he proposed at a session of the Hindu Mahasabha that drinking water wells and temples be open to untouchables.
- In 1935, Babuji also appeared before the Hammond Commission at Ranchi and demanded, for the first time, voting rights for the Dalits.
- He was jailed twice in the early 1940s for his political activities associated with the Quit India movement against British rule.
- When Jawaharlal Nehru formed the provisional government, Jagjivan Ram became its youngest minister.
- After independence he held the labour portfolio until 1952.
- He served in Nehru’s cabinet in the posts of minister for communications (1952–56), transport and railways (1956–62), and transport and communications (1962–63).
- He served as minister for food and agriculture (1967–70).
- In 1970 he was made minister of defence.
- He later served as the Deputy Prime Minister of India (1977–79).
- Jagjivan Ram was a member of the Parliament uninterrupted from 1936 to 1986 (40 years) and this is a world record.
- He also holds another record for being the longest-serving cabinet minister in India (30 years).
- His memorial at his cremation place is named Samta Sthal (Place of Equality).
MUST READ: Mahatma Gandhi
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following freedom fighters: (2022)
- Barindra Kumar Ghosh
- Jogesh Chandra Chatterjee
- Rash Behari Bose
Who of the above was/were actively associated with the Ghadar Party?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Q.2) Who among the following is associated with ‘Songs from Prison’, a translation of ancient Indian religious lyrics in English? (2021)
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
- Sarojini Naidu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity and Governance)
Context: The Lokpal of India the country’s first anti-corruption body instituted four years ago to investigate complaints against public functionaries , recently submitted to a parliamentary panel that “it has not prosecuted even a single person accused of graft till date.”
Key highlights of the report:
- According to data provided by the Lokpal office to a parliamentary panel on the Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT), since 2019-20, the anti-corruption body received 8,703 complaints.
- Out of them, 5,981 complaints were disposed of.
- As many as 6,775 complaints were rejected for not being in the correct format.
- The office informed that only three complaints were fully investigated, and 36 complaints were at a preliminary stage.
- In 2022-23, as many as 2,760 complaints were received, out of which only 242 were in the prescribed format.
- The Parliamentary committee recommends Lokpal not to reject genuine complaints merely on the technical ground that the complaint is not in the prescribed format.
About Lokpal:
- The word “Lokpal” is derived from the Sanskrit word “loka” meaning people and “pala” meaning protector or caretaker. Together it means “protector of people”.
- The Lokpal and Lokayukta Act, 2013 provided for the establishment of Lokpal for the Union and Lokayukta for States.
- The Act states that not less than 50% of the members of the Lokpal should be from among persons belonging to the SCs, the STs, OBCs, minorities and women.
- Lokpal is appointed by the President on the recommendation of a committee headed by Prime Minister which includes the Chief Justice of India, Speaker, Lok Sabha and Leader of Opposition, Lok Sabha and an eminent Jurist as its member.
- Salaries, allowances and service conditions of the Lokpal chairperson will be the same as those for the Chief Justice of India; those for other members will be the same as those for a judge of the Supreme Court.
- These institutions are statutory bodies without any constitutional status.
- The Lokpal and Lokayuktas (Amendment) Bill, 2016 was passed by Parliament in July 2016 and amended the Lokpal and Lokayukta Act, 2013.
- It enables the leader of the single largest opposition party in the Lok Sabha to be a member of the selection committee in the absence of a recognized Leader of Opposition.
Powers of the Lokpal
- It has the powers to superintendence over, and to give direction to CBI and its officers.
- The Inquiry Wing of the Lokpal has been vested with the powers of a civil court.
- The Lokpal and Lokayuktas (Amendment) Bill, 2016 also incorporates provisions for attachment and confiscation of property acquired by corrupt means, even while the prosecution is pending.
- Lokpal has the power to recommend transfer or suspension of public servants connected with allegations of corruption.
- Lokpal has the power to give directions to prevent the destruction of records during the preliminary inquiry.
Need for Lokpal
- Lack of Independence: Most of our agencies like CBI, state vigilance departments, internal vigilance wings of various departments, Anti-corruption Branch of state police etc are not independent.
- Powerless: Some bodies like CVC or Lokayuktas are independent, but they do not have any powers.
- They have been made advisory bodies.
- They give two kinds of advice to the governments: to either impose departmental penalties on any officer or to prosecute him in court.
- Lack of Transparency and internal accountability: In addition, there is the problem of internal transparency and accountability of these anti-corruption agencies.
- Presently, there is not any separate and effective mechanism to check if the staff of these anti-corruption agencies turns corrupt.
Challenges:
- Political Influence: The appointing committee of Lokpal consists of members from political parties that put Lokpal under political influence.
- Judiciary excluded: One of the biggest lacunae is the exclusion of the judiciary from the ambit of the Lokpal.
- No criteria to decide eminent Jurist: There are no criteria to decide who is an ‘eminent jurist’ or ‘a person of integrity’ which manipulates the method of the appointment of Lokpal.
- No proper immunity to Whistle Blowers: The Lokpal and Lokayukta Act 2013 failed to provide any kind of concrete immunity to the whistleblowers.
- No provisions of appeal: There are no adequate provisions for appeal against the actions of Lokpal.
- No constitutional backing: The Lokpal does not have any constitutional backing.
Way Forward:
The institution of ombudsman must be strengthened in respect of functional autonomy and workforce availability to fight against corruption. The appointment of Lokpal is not the real solution to problems; instead the government should focus on eliminating the root causes because of which the general public is demanding a Lokpal.
There should be complete transparency when nominating a Lokpal and Lokayukta as it will increase the chances for the right person to be appointed. At this juncture when India is heading the G20 Anti-Corruption Working group, Lokpal should rise to the occasion and make every effort to strengthen the anti-corruption landscape in the country.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently a new study conducted by Journal of Health Management, on the burden of mental illness highlighted expenditure on treatment of mental illness pushes 20% Indian households into poverty.
Key findings of the study:
- 20 % of Indian households become poor as a result of spending money on the treatment of mental illnesses.
- India’s national average healthcare burden due to mental illness is 10.4 %.
- States and UTs with a higher burden: Daman and Diu (19.4 %), Himachal Pradesh (18.0 %), Sikkim (17.4 %), Lakshadweep (14.6 %), Maharashtra (13.7 %), Telangana (13.3 %), Punjab (12.7 %) and Uttarakhand (12.5 %).
- States and UTs with a lower burden: Mizoram (0.5 %), Andaman and Nicobar Islands (1.2 %), Puducherry (1.7 %), Dadra and Nagar Haveli (2.0 %), Arunachal Pradesh (3.0 %) and Nagaland (3.5 %).
- Majority of people in low- and middle-income countries with mental illness do not receive healthcare, leading to chronicity, suffering, and increased costs of care.
OOPE, CHE, and Poverty:
- Study estimated the out-of-pocket expenditure (OOPE), catastrophic health expenditure (CHE), and poverty impact due to mental illness in India.
- OOPE usually refers to expenses that one has to pay for with their own money rather than an alternative source.
- CHE is money spent on healthcare that exceeds some specified critical level of tolerance or threshold from the household total income in a given specified period.
- Those aged 60 years and above reported the highest OOPE on mental illness in the last 365 days across all age groups.
- 5 % and 32.5 % of the households were exposed to CHE based on 10 % and 20 % thresholds.
- 20 % of households forced into poverty due to expenses on mental illness treatment were rural (22.5 %) as compared to urban (17 %).
About Mental Health and illness
- Mental health is a state of mental well-being that enables people to cope with the stresses of life, realize their abilities, learn well and work well, and contribute to their community.
- It is an integral component of health and well-being that underpins our individual and collective abilities to make decisions, build relationships and shape the world we live in.
- Mental health is a basic human right.
- It is crucial to personal, community and socio-economic development.
- World Mental Health Day is observed on 10th October every year
- The term ‘mental disorders’ is used to denote a range of mental, behavioral disorders and psychosocial disabilities.
- They are generally characterised by a combination of abnormal thoughts, perceptions, emotions, behaviour and relationships with others.
- Mental Disorders include depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia and other psychoses, dementia, and developmental disorders including autism.
Determinants of Mental Health:
- Multiple social, psychological, and biological factors determine the level of mental health of a person at any point of time.
- For example, violence and persistent socio-economic pressures are recognized risks to mental health. The clearest evidence is associated with sexual violence.
- Poor mental health is also associated with:
- rapid social change,
- stressful work conditions,
- gender discrimination,
- social exclusion,
- unhealthy lifestyle,
- physical ill-health and
- human rights violations.
- There are specific psychological and personality factors that make people vulnerable to mental health problems. Biological risks include genetic factors.
Issues and Concerns:
- Mental health problems have been growing rapidly over the last few decades.
- In 2015, the GOI carried out a National Mental Health Survey — 2015-16 to assess the prevalence of mental health in the country.
- The report showed mental disorders at 10.6 per cent among above 18-year-olds, 16 per cent among the productive age group of 30-49-year-olds — and lifetime morbidity affecting 150 million people with one per cent reporting high suicidal risk.
- The human resources and treatment facilities are woefully low.
- For policymakers, mental health is a low priority.
- Such poor policy attention is often ascribed to indifference among bureaucrats and politicians.
- Designing a policy is the most challenging piece of policy-making.
Government of India Initiatives:
- Constitutional Provision: The Supreme Court has held healthcare to be a fundamental right under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- National Mental Health Program (NMHP): To address the huge burden of mental disorders and shortage of qualified professionals in the field of mental health, the government has been implementing the National Mental Health Program (NMHP) since 1982.
- The Program was re-strategized in 2003 to include two schemes, viz. Modernization of State Mental Hospitals and Up-gradation of Psychiatric Wings of Medical Colleges/General Hospitals.
- Mental HealthCare Act 2017: It guarantees every affected person access to mental healthcare and treatment from services run or funded by the government.
- It has significantly reduced the scope for the use of Section 309 IPC and made the attempt to commit suicide punishable only as an exception.
- Kiran Helpline: In 2020, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment launched a 24/7 toll-free helpline ‘Kiran’ to provide support to people facing anxiety, stress, depression, suicidal thoughts and other mental health concerns.
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2017: The Act acknowledges mental illness as a disability and seeks to enhance the Rights and Entitlements of the Disabled and provide effective mechanism for ensuring their empowerment and inclusion in the society
- Mano Darpan Initiative: An initiative under Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, aims to provide psycho-social support to students for their mental health and well-being.
Way Forward:
To promote mental health, there is a need to create such living conditions and environment that support mental health and allow people to adopt and maintain healthy lifestyle. A society that respects and protects basic, civil, political, and cultural rights is needed to be built to promote mental health.
The National mental health policies should not be solely concerned with mental disorders, but should also recognize and address the broader issues which promote mental health. This includes education, labour, justice, transport, environment, housing and health sector.
Source: DTE
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Which of the following statements is not correct regarding Babu Jagjivan Ram?
- He was instrumental in the foundation of the All-India Depressed Classes League.
- He was jailed twice in the early 1940s for his political activities associated with the Quit India movement against British rule.
- He was the longest-serving cabinet minister in India
- All statements are correct
Q.2) Consider the following passes:
- Jalep La
- Khardung la
- Nathu La
- Banihal pass
Which of the above are located in Sikkim?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
Q.3) Netravali Wildlife Sanctuary is often mentioned in the news located in
- Goa
- West Bengal
- Odisha
- Karnataka
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 6th April 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 5th April – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – a











