IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: Recently, the dispute over the Kuril Islands between Tokyo and Moscow came up again in the midst of the Russia -Ukraine war.
Background:-
- As Russia’s invasion of Ukraine drags on, Moscow is forced to funnel more and more of its military and economic resources to its western border.
- In Tokyo, conservative voices are hinting that the war could give Japan a chance to take control of what the Japanese call the Northern Territories.
About the Kuril Islands dispute:-
- Historical Background: Soviet forces seized the strategically located Kuril Islands in Russia, in the closing days of WWII.
- Russia administers all the Kuril Islands.
- However, Japan considers them as part of its Northern Territories.
- These are Iturup (Etorofu in Japanese), Kunashir (Kunashiri), Shikotan, and Habomai Islets.
- No Treaty so far: Moscow and Tokyo have held talks about these islets several times in the past but failed to agree on a solution.
- This led to the two sides never formally signing a peace treaty to end the war.
- China’s interest: There are speculations that China may have a vested interest in taking over the Kuril islands.
- The Kuril Islands would give China access to the Arctic region as well as naval ports directly in the North Pacific.
About the Kuril Islands:-
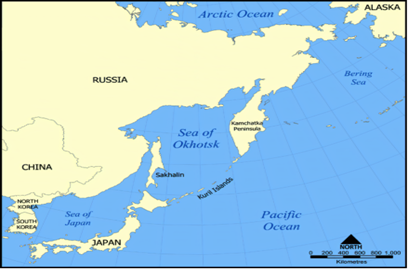
IMAGE SOURCE: bewilderingstories.com
- The Kuril Islands are a chain of islands stretching from the Japanese island of Hokkaido to the southern tip of Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula.
- The islands separate the Okhotsk Sea from the North Pacific Ocean.
- The archipelago comprises 22 major islands, 36 smaller islets, and several rocks covering.
- The Kuril Islands are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, which is a region in the Pacific Ocean that experiences frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
- Administration: Russia administers all the Kuril Islands as part of its easternmost territory.
Importance of South Kuril Islands:-
Natural resources:
- Rich fishing grounds surround the islands.
- They are thought to have offshore reserves of oil and gas.
- Rare rhenium deposits have been found on the Kudriavy volcano on Iturup.
- Nickel-based superalloys of rhenium are used in the combustion chambers, turbine blades, and exhaust nozzles of jet engines.
- Tourism is also a potential source of income, as the islands have several volcanoes and a variety of birdlife.
Strategic Importance:
- Russia has deployed missile systems in the region. (India – Russia Relations)
- Russia also plans a submarine project and intends to prevent any American military use of the islands.
Cultural Importance:
- The Japanese people, especially conservatives in Hokkaido, are emotionally attached to the islands. ( India – Japan Cooperation)
MUST READ: Perspectives on Russia-Ukraine War
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) About three-fourths of the world’s cobalt, a metal required for the manufacture of batteries for electric motor vehicles, is produced by (2023)
- Argentina
- Botswana
- the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Kazakhstan
Q.2) Consider the following countries: (2023)
- Bulgaria
- Czech Republic
- Hungary
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Romania
How many of the above-mentioned countries share a land border with Ukraine?
- Only two
- Only three
- Only four
- Only five
Syllabus
- Prelims –Art and Culture
Context: Recently, seven products from across India, including Jalesar Dhatu Shilp, were given the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
Background:-
- The GI tags were secured by ‘Jalesar Dhatu Shilp’ (a metal craft), ‘Goa Mankurad Mango’, ‘Goan Bebinca’, ‘Udaipur Koftgari Metal Craft’, ‘Bikaner Kashidakari Craft’, ‘Jodhpur Bandhej Craft’, and ‘Bikaner Usta Kala Craft’.
Jalesar Dhatu Shilp:-
- Jalesar is located in the Etah district of Uttar Pradesh.
- It was the capital of Magadha King Jarasandha.
- The metal art of Jalesar is highly esteemed for its intricate designs and exceptional craftsmanship, blending elements of both traditional and contemporary styles.
- Skilled artisans employ various techniques such as casting, molding, hammering, engraving, and filigree work to create a diverse array of metal products.
The Jodhpur Bandhej Craft:-
- It is the Rajasthani art of tying and dyeing.
- It is one of the most famous textile art forms of Rajasthan.
- The fabrics used: muslin, silk, and voile.
- Cotton thread is used for tying the fabric.
The Bikaner Usta Kala Craft:-
- It is also known as gold nakashi or gold manauti
- It shows the prominence of its long-lasting golden colour.
- Untreated raw camel hide is processed and molded by the Dapgar community of leather craftspeople for the requirements of the Usta.
Udaipur Koftgari Metal Craft:-
- The ancient art of Koftgari is used to create exquisitely ornamental weaponry.
- Technique: This damascene technique involves a complex process of etching designs, heating, and cooling the metal, while also embedding gold and silver wire into the surface.
- Unlike inlaid metal ornamentation, the wire does not sink into the iron; instead, it remains on the surface and is mechanically bound through pressing, burnishing, and polishing.
- After the design is complete, burnishing tools known as Opani are used to push and bind the overlaid silver firmly.
- Lastly, the surface is polished using a hakek stone to achieve the final stunning appearance.
- The term ‘Koftgari’ originates from the Persian and Urdu words ‘kuft-gari,’ meaning ‘beaten work’.
- The artisans who practice this art are called ‘kuftgars’ or gilders.
- Historically, Koftgari was brought to India by Persian craftsmen during the 16th century when they served Mughal rulers.
- The Mughal Emperors had a significant iron workshop called the Mughal Silehkhana that produced ornamented swords and weapons for the imperial army.
Bikaner Kashidakari Craft:-
- It is traditionally created on cotton, silk, or velvet with a variety of fine stitches and mirror-work, mainly for objects associated with marriage, especially gift items.
- The mirrors are believed to repel the ‘evil eye’ with their reflective surfaces.
- The weaving of fabrics by hand used to be done by the Meghwal community in Bikaner and nearby districts.
Goa Mankurad mango:-
- The mango was given the name ‘Malcorada’ by the (GI Tag for Mithila Makhana)
- The name translates to ‘poor coloured.
- Over time, this word evolved into ‘Mankurad’.
- In the Konkani language, it came to be known as ‘aamo’, which means mango.
Goan Bebinca:-
- Bebinca, a traditional Indo-Portuguese dessert. ( Pokkali Rice)
- It is a type of pudding widely recognized as the ‘Queen of Goan desserts.’
MUST READ: GI tag for Narasinghapettai nagaswaram
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the “Tea Board” in India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Tea Board is a statutory body.
- It is a regulatory body attached to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The Tea Board’s Head Office is situated in Bengaluru.
- The Board has overseas offices in Dubai and Moscow.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Changpa’ Community of India, consider the following statements: (2014)
- They live mainly in the state of Uttarakhand
- They rear the Pashmina goats that yield fine wool
- They are kept in the category of Scheduled Tribes
Which of the given statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Government Schemes
Context: Recently, it was stated that over 1200 Biogas plants including 320 CBG plants across India registered on the GOBARdhan portal so far.
About GOBARdhan portal:-
- Launched: 2023.
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- Developed by: the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS).
- Objective: to ensure close coordination with various Departments/Ministries for smooth implementation of Biogas schemes/initiatives and its real-time tracking.
- Coordinated by: Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation under the Swachh Bharat Mission – Grameen (SBMG).
Salient Features:-
- The GOBARdhan portal will streamline the process of registration of Biogas plants and under-construction Compressed Biogas plants across the country.
- Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan, which acts as a one-stop repository to assess investment and participation in Biogas/CBG sector at pan India level.
- Any government, cooperative, or private entity operating or intending to set up a Biogas/CBG/Bio CNG plant in India can obtain a registration number by enrolling in this unified registration portal.
- The registration number will enable availing of a multitude of benefits and support from the Ministries & Departments of the Government of India.
- States have been advised to get their CBG/Biogas plant operators registered on the portal on priority to avail existing and upcoming support from the Union Government.
Benefits:-
- The portal will ensure Ease of Doing Business (EODB).
- With aggregated data from all Ministries & Departments across Centre and States, the initiative will also attract greater investment from the private players.
About GOBARdhan scheme:-
- Launched: 2018.
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- Implementation: The scheme is being implemented as part of the Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin).
Objectives of GOBARdhan scheme:-
- Support villages safely manage their cattle waste, agriculture waste and in long run all organic waste.
- Support communities, and convert their cattle and organic waste to wealth using decentralized systems. (Compressed Bio Gas (CBG))
- Promote environmental sanitation and curb vector-borne diseases through effective disposal of waste in rural areas.
- Convert organic waste, especially, cattle waste to biogas and fertilizer for use in rural areas.
- Promote rural entrepreneurship employment and income generation opportunities.
Salient Features of the GOBARdhan scheme:-
- It is an umbrella initiative of the Government of India.
- It covers the entire gamut of schemes/programmes/policies promoting the conversion of organic waste like cattle dung/ agri-residue etc. to biogas/ CBG/ Bio CNG.
Benefits of the GOBARdhan scheme:-
- Promotes circular economy
- An eco-friendly fuel
- Effective waste management
- Protects health and environment
- Reduces GHG emission
- Increases employment
- Saves foreign exchange
- Generates organic manure
- Improves savings
MUST READ: National Bioenergy Programme
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to green hydrogen, consider the following statements: (2023)
- It can be used directly as a fuel for internal combustion.
- It can be blended with natural gas and used as fuel for heat or power generation.
- It can be used in the hydrogen fuel cell to run vehicles.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) According to India’s National Policy on Biofuels, which of the following can be used as raw materials for the production of biofuels. (2020)
- Cassava
- Damaged wheat grains
- Groundnut seeds
- Horse gram
- Rotten potatoes
- Sugar beet
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 5, and 6 only
- 1, 3, 4, and 6 only
- 2, 3, 4, and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: The Centre has announced its plans to launch a fresh infrastructure investment trust (InvIT) for national highways.
About Infrastructure investment trust (InvIT):-
- An Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvITs) is a Collective Investment Scheme similar to a mutual fund.
- It enables direct investment of money from individual and institutional investors in infrastructure projects to earn a small portion of the income as return. ( FPI and InvITs)
- The InvIT is designed as a tiered structure with Sponsor setting up the InvIT which in turn invests into the eligible infrastructure projects either directly or via special purpose vehicles (SPVs).
- Regulated by: SEBI (Infrastructure Investment Trusts) Regulations, 2014.
- An InvIT has four parties namely: Trustee, Sponsor(s) and Investment Manager and Project Manager.
- While the trustee (certified by Sebi) has the responsibility of inspecting the performance of an InvIT, sponsor(s) are promoters of the company that set up the InvIT.
Types of InvITs
As per current SEBI Regulations InvITs can be divided into 5 key types depending on the types of infrastructure they own or operate:
- Energy such as power generation and distribution.
- Transport & Logisticsg. operating highways and other toll roads
- Communicationsg. optical fiber networks and telecom towers
- Social and Commercial Infrastructure g. parks
- Water and Sanitationg. irrigation networks
From the perspective of the source of funds, InvITs can be of two types:
Privately-Held InvITs:-
- This type of InvIT is not listed on the stock exchange and units of this type of infrastructure trust cannot be bought or sold on a stock exchange.
- All units of this type of unit are held privately by a very limited number of individuals or institutions.
Public-Listed InvITs:-
- After an Infrastructure Trust lists itself on the stock exchange, it is known as a public-listed InvIT.
- Units of a public-listed InvIT can be bought and sold on stock exchanges by retail as well as institutional investors.
- Current SEBI regulations do not require a mandatory listing of InvITs on stock exchanges.
NHAI InvIT:-
- It is the infrastructure investment trust sponsored by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) to support the government’s National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP).
- It is a Trust established by NHAI. ( National Highway InvIT)
- It is under the Indian Trusts Act, 1882, and SEBI (Security and Exchange Board of India) regulations.
- The advantages of an InvIT instrument are that it has stable and predictable cash flows and experienced professionals manage the InvIT, operate, and maintain the roads.
MUST READ: Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) model
SOURCE: BUSINESS STANDARD
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I:
Interest income from the deposits in Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InviTs) distributed to their investors is exempted from tax, but the dividend is taxable.
Statement-II:
InviTs are recognized as borrowers under the ‘Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and· Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002’.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q.2) With reference to India’s projects on connectivity, consider the following statements: (2023)
- East-West Corridor under Golden Quadrilateral Project connects Dibrugarh and Surat.
- Trilateral Highway connects Moreh in Manipur and Chiang Mai in Thailand via Myanmar.
- Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor connects Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh with Kunming in China.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Police Reforms in India
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Incidents like an outbreak of communal violence in Delhi region and violence in Manipur’s Imphal Valley raises concerns over the role of law enforcement.
About Police and Policing Framework in India
- The primary role of police forces is to uphold and enforce laws, investigate crimes and ensure security for people in the country.
- In a large and populous country like India, police forces need to be well equipped, in terms of personnel, weaponry, forensic, communication and transport support, to perform their role well.
Constitutional and legal provisions:
- Under the Constitution, ‘Police’ and ‘Public Order’ are state subjects under the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution of India.
- Therefore, each state has its own police force.
- The center is also allowed to maintain its own police forces to assist the states with ensuring law and order.
- The basic framework for policing in India was laid down in the pre-independence era through the Police Act, 1861.
- Apart from the above, several other laws and regulations govern police functioning in India.
- These include the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC), Indian Penal Code (IPC), Evidence Act and various state-specific laws.
Significance of police reforms:
- Low police-to-population ratio: The global average ratio of police-population is 270 to 100,000, where it is 120 in India.
- With far less police –ill-equipped and most of them posted to protect the political representatives, people of India are the least secured people on the globe.
- Corruption: In 2016, the vigilance department had conducted 55% more inquiries against its men.
- A Delhi Police survey found 34% of the cops to be corrupt in 2015, down from 66% in 2014.
- Changing nature of crime: The recent social and technological changes fueled by the internet and the new social media are fast changing the nature, intensity and the reach of crime leading to unprecedented lawlessness and frightening dimensions of global terrorism.
- Insensitive towards backward classes: Representation of women and depressed caste is low which makes them insensitive towards them.
- Escalating violence resulting from caste conflicts including the most recent Dalit uprising, farmers woes across the country.
Issues in Police Forces
Colonial Law: Even at present, the police system in India is based on colonial law.
- Sometimes the British used the police as their instrument to suppress the voice of people and for their personal functions and at present our respected government is doing the same.
Huge vacancies: While the sanctioned police strength was 181 police per lakh persons in 2016, the actual strength was 137 police.
- This is excessively low when compared with the United Nations’ recommended standard of 222 police per lakh persons.
- Further, a high percentage of vacancies within the police forces exacerbates an existing problem of overburdened police personnel.
Custodial Death: There are many cases on custodial death means Death by torture/pressure in police/judicial custody.
- During 1996-1997 in D.K.Basu judgment, the Supreme Court (SC) issued a guideline against custodial death in India.
Police Infrastructure (weapons, vehicle etc.): Modern policing requires strong communication support, state-of-the-art or modern weapons, and a high degree of mobility.
- Even the fund’s allotted face Underutilization.
Law on Torture: India has only signed the “United Nation Convention on torture” but yet to pass by the Parliament.
- India does not have a specific law for torture.
Political Interference: Police officers are not able to do their work due to the interference of political leaders.
- There is no minimum tenure security for officers at the higher post and not even place posting security.
Promotions and working conditions: Qualifications and training of police personnel are not up to the mark, especially for lower levels of officials.
- The lower ranks of police personnel are often verbally abused by their superiors or they work in inhuman conditions.
- This non-harmonious work environment ultimately affects their relationship with the public.
Way Forward: Seven Directives of the Supreme Court (SC)
- Limit political control: Ensure that the state government does not exercise unwarranted influence or pressure on the police.
- Appoint based on merit: Ensure that the Director-General of Police is appointed through a merit-based, transparent process, and secures a minimum tenure of 2 years.
- Fix minimum tenure: Ensure that other police officers on operational duties (Including Superintendents of Police in charge of a district and Station House Officers in charge of a police station) are also provided with a minimum tenure of 2 years.
- Separate police functions: Separate the functions of investigation and maintaining law and order.
- Set up fair and transparent systems: Set up a Police Establishment Board to decide and make recommendations on transfers, postings, promotions and other service-related matters of police officers of and below the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police.
- Establish a Police Complaints Authority in each state: At the state level, there should be a Police Complaints Authority to look into public complaints against police officers of and above the rank of Superintendent of Police in cases of serious misconduct, including custodial death, grievous hurt or rape in police custody.
- At the district level, the Police Complaints Authority should be set up to inquire into public complaints against the police personnel of and up to the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police in cases of serious misconduct.
- Set up a selection commission: A National Security Commission needs to be set up at the union level to prepare a panel for selection and placement of chiefs of the Central Police Organizations with a minimum tenure of 2 years.
Source: LM
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: The Australian Space Agency has confirmed that a large object found on the shores of Western Australia to be the debris of an Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) rocket.
About Space Debris:
- Space debris refers to the artificial objects, including defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and other man-made objects, that are in orbit around the Earth and pose a risk to operational spacecraft and astronauts.
- Kessler Syndrome: It is a theoretical scenario in which a cascade of collisions between artificial objects in low Earth orbit leads to a rapidly increasing amount of space debris, making the use of near-Earth space impossible for an extended period.
- The scenario was first proposed by Donald J. Kessler in 1978 and is considered a major concern for the long-term sustainability of human activities in space.
- The potential for a Kessler Syndrome event underscores the importance of efforts to reduce the generation of space debris and to mitigate its impact on the operational space environment.
Need for removing space debris
- Protecting Active Satellites: Removing space debris will reduce the risk of collisions with operational satellites, protecting them from damage and ensuring their continued functionality.
- Ensuring Safe Human Spaceflight: Space debris removal will create a safer environment for human spaceflight, reducing the risk of collision and damage to spacecraft.
- Cost-Effective: Removing space debris is more cost-effective than constantly avoiding collisions and repairing or replacing damaged satellites.
- Maintaining the Use of Outer Space: By removing space debris, we can maintain the use of outer space for scientific, commercial, and military purposes, ensuring its continued sustainability.
- Protecting the Space Environment: Removing space debris will help to prevent the long-term impacts on the space environment, reducing the potential for a “debris belt” that could limit future missions.
- Compliance with International Regulations: The need for removing space debris is recognized by international agreements, such as the Outer Space Treaty, which requires the responsible use of outer space and the prevention of harmful interference with other nations’ activities in space.
Causes of Space Debris:
- Satellites that are no longer in use: When a satellite’s batteries run out or it experiences a technical issue, it is left drifting in space.
- Equipment loss: Astronauts occasionally misplace tools or other items while on spacewalks. For instance, in 2008, astronaut Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper misplaced a box of gear.
- Phases of a rocket: Some rocket stages crash to Earth shortly after take-off and are lost in low orbits. The higher ones, however, are left to drift in space and occasionally explode because they still carry fuel leftovers. These explosions result in the production of thousands of fragments.
- Weapons: Both the Soviet Union and the United States tested anti-satellite weapons in the 1960s and 1970s. In 1985, the United States utilized one of these weapons, such as Mission Shakti of India, to destroy a one-ton satellite (Sol wind).
- Impacts of micrometeoroids: Micrometeoroids, which are dust-sized fragments of asteroids and comets, collide and naturally produce some trash.
Measures taken at global:
- Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC): IADC is a multilateral organization that was created in 1993 with the aim of coordinating responses to debris in Earth’s orbit.
- NEO-01: The “NEO-01” low-Earth orbit robot prototype has been launched by China.
- It can gather space trash left over by other spacecraft thanks to its enormous net.
- Kounotori experiment: It is a Japanese experiment that uses an original method to get rid of space junk that is in orbit around the earth.
- Get rid of the DEBRIS mission: This satellite research effort aimed to demonstrate several methods for removing space trash. The Surrey Space Centre from the University of Surrey oversaw the project.
- United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UNCOPUOS): It was created by the General Assembly in 1959 with the intention of governing space exploration and usage for world peace, security, and economic growth.
India:
- In 2022, ISRO set up the System for Safe and Sustainable Operations Management (IS 4 OM) to continually monitor objects posing collision threats, predict the evolution of space debris, and mitigate the risk posed by space debris.
- ISRO also carried out 21 collision avoidance maneuvers of Indian operational space assets in 2022 to avoid collisions with other space objects.
- ISRO has also set up a Centre for Space Debris Research to monitor and mitigate the threat of space debris.
- ‘Project NETRA’ is also an early warning system in space to detect debris and other hazards to Indian satellites.
Way Forward:
The issue of space debris highlights the need for continued efforts to mitigate and prevent the growth of debris in orbit to ensure the sustainability and safe use of outer space for future generations.
The need to remove space debris is crucial for the continued safe and sustainable use of outer space. Efforts to remove debris should be a priority for the international community to ensure the continued growth and exploration of space.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Island | Disputing countries |
| 1.Falkland Islands | Argentina and the United Kingdom. |
| 2.Kuril Islands | Russia and South Korea |
| 3.Paracel Islands | China and Russia |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Infrastructure investment trusts (InvIT) are regulated by SEBI.
Statement-II:
They can be used to diversify the investments.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Gobardhan portal will ensure Ease of Doing Business.
Statement-II:
The registration number is required to avail the benefits provided under the scheme.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) Discuss the significance of police reforms in the recent context of rise in crime. (250 words)
Q.2) Discuss hazards and risks associated with space debris. Analyse the steps taken at the global level and India in this context. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 3rd August 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 2nd August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) -b











