IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – Agriculture
Context: Earlier this month, Agriculture Minister Arjun Munda inaugurated a Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC) set up at Krishi Bhavan in New Delhi, a big-screen dashboard of all digital innovations in the sector.
Background:-
- ICCC is a “significant leap forward” in leveraging technology for the advancement of agricultural practices.
About Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC):
- The ICCC is a tech-based solution involving multiple IT applications and platforms, which is designed to help in making informed decisions.
- The centre is housed in the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare, which is responsible for legislation, policy formation, and implementation of initiatives in the agriculture sector.
- The ICCC uses state of the art technologies such as artificial intelligence, remote sensing, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to collect and process large amounts of granular data — on temperatures, rainfall, wind speed, crop yields and production estimations — and presents it in graphical format.
- On eight large, 55-inch LED screens installed at the ICCC, you can see information on crop yields, production, drought situation, cropping patterns (geographic region-wise and year-wise) in map, timeline, and drill-down views.
- You can also see the relevant trends (periodic and non-periodic), outliers, and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), and receive insights, alerts, and feedback on agriculture schemes, programmes, projects, and initiatives.
- The ICCC uses platforms including the Krishi Decision Support System (DSS) to collect micro-level data, process it, and present the macro picture.
What is the objective of the ICCC?
- The ICCC will enable comprehensive monitoring of the farm sector by making available at one place geospatial information received from multiple sources, including remote sensing; plot-level data received through soil survey; weather data from the India Meteorological Department (IMD); sowing data from Digital Crop Survey; farmer- and farm-related data from Krishi MApper, an application for geo-fencing and geo-tagging of land; market intelligence information from the Unified Portal for Agricultural Statistics (UPAg); and yield estimation data from the General Crop Estimation Survey (GCES).
Can the command and control centre generate individual farmer-specific advisories?
- Going forward, the ICCC can create an ecosystem based on which individual farmer-level advisories can be generated through apps like Kisan e-mitra, a chatbot developed for PM-Kisan beneficiaries.
- The AI-/ machine learning-based system will identify a farmer through his/ her mobile number or Aadhaar, and match it with the farmer’s field information obtain through land records, historical crop sowing information from the crop registry, weather data from IMD, etc. It will then generate a customised advisory in the local language of the farmer. For this, the system will use the Bhashini platform that allows translation into several Indian languages.
PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS
- FARMER’S ADVISORY: The ICCC allows visualisation of GIS based soil carbon mapping as well as soil health card data for a particular district together at one place. This, when visualised with weather-related data from IMD for the selected district, will allow a customised and authentic advisory to be sent to the farmer about the type of crops that can be grown, and water and fertiliser requirements.
- DROUGHT ACTIONS: According to officials, increase or decrease in yield from a specific region (as per GCES data) can be correlated with weather, rainfall, and other information visualised through the Drought Portal, enabling the administration to understand the reason for increase/ decrease in yield and to take decisions proactively.
- CROP DIVERSIFICATION: An analysis of crop diversification maps, together with field variability for paddy, will enable decision-makers to identify regions with scope for diversified cropping.
- FARM DATA REPOSITORY: Krishi Decision Support System (K-DSS), a platform under development, will act as an agriculture data repository. Integrated spatial and non-spatial data will be superimposed as a layer on the GIS map, and various AI/ ML models would be run on the data. The K-DSS will help in evidence-based, efficient, and data-driven decision-making.
- VALIDATION OF YIELD: Yield as captured through Krishi MApper can be analysed with the yield generated through GCES application for a plot.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: Since 2020, a highly pathogenic type of bird flu, H5N1, has been spreading across the globe, posing an existential threat to birds and wildlife. The virus has infected birds in more than 80 countries (as of December 2023) and resulted in culling of millions of chickens and turkeys at commercial poultry farms. It also struck numerous species of wild birds.
Background:
- The worrying sign, however, is the rapid spread of the flu — once largely confined to birds — among mammals. The infection has also infiltrated mainland Antarctica for the time in history.
About Bird flu:
- The Bird flu, also known as avian flu, refers to an infectious viral illness that mainly infects and spreads among poultry and some wild birds.
- There are different strains of bird flu virus, which have been circulating for a very long time among at least 100 bird species, including wild waterfowl, such as ducks and geese, without much harming them.
- From time to time, a form of the flu virus jumps from wild birds to poultry farms, and replicates in cramped warehouses of farmed birds. It then quickly evolves into a highly pathogenic flu virus that causes a larger wave of illness and death than usual among birds.
- The currently circulating type of H5N1 is one such highly pathogenic flu virus. It has descended from a virus that caused an outbreak on a goose farm in Guangdong, China, in 1996.
- The new version of H5N1 first emerged in Europe in 2020 and then rapidly reached Europe, Africa, and Asia. By late 2021, it had spread to North America and in the fall of 2022, it appeared in South America. In February 2024, the virus stormed through mainland Antarctica.
How has H5N1 impacted animals across the world?
- Apart from the farm birds, the virus has severely impacted wild birds.
- Some wild birds, which are already on the verge of extinction, have also been hit. At least 21 of the endangered California condors have died from the virus in 2023 alone, which is nearly 6 per cent of the population of the roughly 330 birds that were believed to live in the wild as of the end of 2021.
- The biggest concern is the spread of the virus among mammals, though. Outbreaks among foxes, pumas, skunks, and both black and brown bears in North America have been reported.
- The worst affected are marine mammals. More than 20,000 sea lions and a handful of dolphins have died in Chile and Peru due to the infection.
- Humans are also at riskbut they rarely contract bird flu. Most of the cases of human infection involve people who have come in contact with a large number of sick birds at poultry farms. This means that humans are likely to get infected when there is a huge viral load.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims- Current Event
Context: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will conduct the Space science and Technology Awareness Training (START) 2024 programme during April and May.
Background:
- The START programme is part of the ISRO’s efforts to enable Indian students to become professionals in Space Science and Technology, as the organisation’s Space Science exploration programme continues to expand into new domains.
About SPACE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY AWARENESS TRAINING (START)
- The Space Science and Technology Awareness Training (START) is an initiative by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO).
- It is an online introductory-level awareness program in space science and technology.
- The START program intends to equip students with foundational knowledge in space-related domains.
- It is specifically designed for undergraduate and postgraduate students of science and technology.
- START will cover various domains, such as space science, that includes Astronomy and Astrophysics, Heliophysics, Instrumentation, Aeronomy, and Sun-Earth interaction.
- The lectures are delivered by scientists from Indian academia and ISRO centres.
- This program is part of ISRO’s efforts to train Indian students to become professionals in the fields of space science and technology.
Source: ISRO
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: The National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) has made significant reforms in its accreditation process for higher educational institutions (HEIs).
Background:
- NAAC has introduced a binary accreditation system that categorizes HEIs into two classifications: “Accredited” or “Not accredited”. The primary goal is to encourage all institutions to participate in the accreditation process.
About NATIONAL ASSESSMENT AND ACCREDITATION COUNCIL (NAAC):
- The National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) is an autonomous body established by the University Grants Commission (UGC) of India.
- Its primary purpose is to assess and accredit institutions of higher education in the country.
- The establishment of NAAC was advocated by the National Policy on Education (NPE, 1986) and the Programme of Action (PoA, 1992) to address concerns about the quality and relevance of higher education in India.
NAAC’s mandate includes:
- Performance evaluation: Assessing the performance of universities and colleges.
- Accreditation: Granting accreditation to institutions based on their quality status.
- Quality Assurance: Making quality assurance an integral part of higher education functioning.
Structure:
- NAAC operates through its General Council (GC) and Executive Committee (EC).
- The GC and EC include educational administrators, policy makers, and senior academicians.
- The Director serves as the academic and administrative head of NAAC.
Source: Hindustan Times
Previous Year Question
Q1. What is the aim of the programme ‘Unnat Bharat Abhiyan’?
- Achieving 100% literacy by promoting collaboration between voluntary organizations and government’s education system and local communities.
- Connecting institutions of higher education with local communities to address development challenges through appropriate technologies.
- Strengthening India’s scientific research institutions in order to make India a scientific and technological power.
- Developing human capital by allocating special funds for health care and education of rural and urban poor, and organizing skill development programmes and vocational training for them.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: India has recently submitted an application to the International Seabed Authority (ISBA), seeking rights to explore two extensive regions in the Indian Ocean seabed that fall outside its jurisdiction.
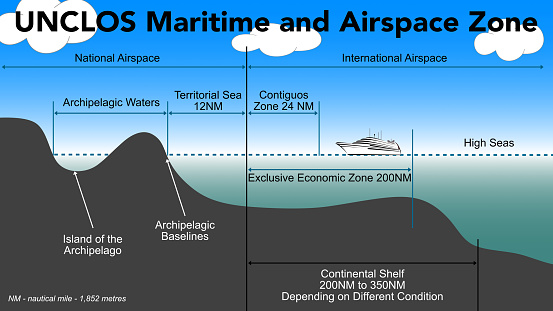
Background:
- This strategic move is motivated in part by Chinese activity in the area and aims to secure valuable resources. The regions India seeks to explore are the Afanasy Nikitin Seamount (AN Seamount) and Carlsberg Ridge.
About INTERNATIONAL SEABED AUTHORITY(ISA) :
- The International Seabed Authority (ISA) is an autonomous international organization.
- The ISA was established in 1994 under the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
Purpose:
- Its primary purpose is to regulate mining and related activities in the international seabed beyond national jurisdiction.
- This area encompasses most of the world’s oceans.
- The ISA is responsible for granting licenses and regulating activities related to the exploration and exploitation of mineral resources in the international seabed.
- The ISA aims to protect the marine environment from harmful effects arising from deep-seabed-related activities.
- The ISA is headquartered in Kingston, Jamaica.
- As of March 2024, the ISA has 169 Members, including 168 Member States and the European Union.
Structure:
- The supreme authority within the ISA is the assembly, where all ISA members are represented.
- The assembly sets general policies, establishes budgets, and elects a 36-member council, which serves as the ISA’s executive authority.
- The secretary-general of the ISA is nominated by the council and elected by the assembly for a four-year term.
Source: Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3
Context: The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) recently unveiled draft road maps for Critical Tech Sectors.
Background:
- India needs to focus on research and development to build its technology independence.
Critical Technologies
- Critical Technologies are those technologies identified by government as ‘Critical’ for a nation’s future economic growth, national security, and technological advancement.
- These often involve: cutting-edge research, innovation, and strategic importance.
- These sectors typically receive heightened oversight from the government and improving technology investment environment.
- They are important for the state’s critical infrastructure.
- Examples of Critical Technology Sectors include Artificial Intelligence (AI), Quantum computing, Internet of Things, and Blockchain.
Significance of Critical Tech Sectors:
- They promote India’s technological leadership; and cooperation with partners to advance and maintain shared technological advantages, making India a trustworthy international technology partner.
- They help deter foreign hostile forces from economic espionage and strengthen the protection of key technologies. It avoids the damage to national and industrial interests caused by illegal technology outflows.
- It drives innovation and competitiveness across key industries creates job opportunities and boosts GDP growth.
- Enterprise-grade security systems are particularly crucial for businesses to safeguard their intellectual property, customer data, and operational continuity.
- Robust cryptographic techniques are essential for protecting sensitive data, securing online transactions, and maintaining trust in digital interactions.
- It is crucial to mitigate risks like disrupting critical services and ensure the resilience of IoT ecosystems.
Issues/Challenges in Developing Critical Tech Sectors:
- Despite producing a large number of STEM graduates, there’s often a gap between the skills taught and those required by industries.
- India faces a brain drain in AI algorithms and hardware accelerators as many opt for post-graduate training in the USA and Europe.
- While India has made strides in R&D, there’s still a need for increased funding and investment in R&D to foster innovation and technological breakthroughs.
- India faces stiff competition from other countries like China, the USA, etc., particularly in emerging technology sectors such as AI and quantum computing.
- Technology sector growth requires addressing energy consumption, electronic waste management, and sustainable manufacturing practices.
Source: Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:
The International Seabed Authority (ISA)is an autonomous international organization.
Statement-II:
ISA is responsible for granting licenses and regulating activities related to the exploration and exploitation of mineral resources in the international seabed.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
Q2.) Consider the following statements about National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC):
- NAAC is an autonomous body established by the University Grants Commission (UGC) of India.
- The NAAC was set up to assess and accredit institutions of higher education in the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q3.)With reference to Space Science and Technology Awareness Training (START), consider the following statements:
- Space Science and Technology Awareness Training (START) is an initiative by the Ministry of Science & Technology.
- START intends to equip students with foundational knowledge in space-related domains.
- It is specifically designed for undergraduate and postgraduate students of science and technology.
How many of the statements given above are not correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 28th March 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 27th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – b











