IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – Economy
Context: The India Employment Report 2024, prepared jointly by the Human Development and the International Labour Organization, was released recently.
Background:-
- It has analysed trends and patterns of the Indian labour market for two decades, including the COVID-19 years, and listed the “emerging characteristics of the employment challenges now confronting the economy as well as the impact of growth on employment.”
key findings
- Basic long-term feature of the employment situation in the country continues to be insufficient growth of the non-farm sectors and the ability of these sectors to absorb workers from agriculture.
- India’s working-age population (aged 15–59) increased from 61% in 2011 to 64% in 2021 and is projected to reach 65% in 2036.About 7-8 million young people are added each year to the labour force.
- The authors warn that unemployment in the country is “predominantly a problem among youth”, especially those with a secondary level of education or higher, and that it has intensified over time.
- In 2022, the share of unemployed youth in the total unemployed population was 82.9%,” report noted, adding that the share of educated youth among all unemployed people also increased, from 54.2% in 2000 to 65.7% in 2022.
- Also, among the educated (secondary level or higher) unemployed youth, women accounted for a larger share (76.7%) than men (62.2%).
- There is a significant gender gap in the labour market, with low rates of female labour force participation. The gender gap in the LFPR has remained almost consistent over the past two decades.
- In 2022, the LFPR of young men (at 61.2%) was almost three times higher than that of young women (at 21.7%), and the gender gap was similar in both rural and urban areas.
- The ILO and IHD stated that the jobs remained low-productive and low-earning. Real wages and earnings showed a decline or had stagnated.
- While India’s large young workforce is a demographic dividend, the report noted that they don’t appear to have the skills to deliver — with 75% of youth unable to send emails with attachments, 60% unable to copy and paste files, and 90% unable to put a mathematical formula into a spreadsheet.
Reports Recommendations:
- Make production and growth more employment-intensive.
- Improve the quality of jobs.
- Make systems for skills training and active labour market policies more effective.
- Bridge the deficits in knowledge on labour market patterns and youth employment.
- Integrating employment creation with macro and other economic policies to boost productive non-farm employment.
- Micro, small and medium-sized enterprises must be supported and decentralised.
- The ILO and IHD recommended that measures such as crafting policies to boost women’s participation in the labour market including larger provision for institutional care facilities, adaptable work arrangements, improved public transport, improved amenities and enhanced workplace safety must be taken in mission mode to address this gender gap in employment.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – Polity
Context: On March 6, in Leh, Sonam Wangchuk, Ladakh’s famous educationist and environmentalist, began a 21-day hunger strike.The strike was in support of thousands of Ladakh residents who have been demanding safeguards under the Sixth Schedule of the Indian Constitution.Mr. Wangchuk discontinued his hunger strike on March 26; it is currently being continued by women in Leh. If their demands stay unmet, the youth, monks, and the elderly have said they will join the hunger strike as well, in phases.
Background:
- In August 2019, the State of Jammu and Kashmir was split into two UTs: Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. It ended people’s exclusive rights on land and jobs.Under the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019, Ladakh became a UT without a legislature.
Why a hunger strike
- Residents of Ladakh says that the UT is administered by a Lieutenant Governor, who is a not a Ladakh resident.Several bureaucrats in key positions, influencing decisions for the region’s future, were also not residents of Ladakh.
- Further the existing Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Councils (LAHDCs) in Leh and Kargil were rendered powerless after the national government declared Ladakh a UT.
- The draft Ladakh Industrial Land Allotment Policy 2023 is a case in point. While the LAHDCs have the powers to make decisions on land use and its management, the draft policy, which has been designed to attract investments in Ladakh, completely excludes them from having any powers related to land allotment- and lease-related decision-making.
- Protestors contend that Sixth Schedule could help tackle these issues because it enables the establishment of regional and district councils with the authority to make laws regarding land use for grazing, agriculture, residential purposes, and towards other purposes that cater to the residents’ interests.
- Considering more than 97% of Ladakh’s population of over 2.74 lakh (2011 Census) is tribal, the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes recommended in 2019 that Ladakh be brought under the Sixth Schedule.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims- Current Event
Context: Earth was recently hit by an X-class solar flare that was strong enough to ionize part of the planet’s atmosphere.
Background:
- This intense solar outburst was detected by satellites from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), specifically their Space Weather Prediction Center.
About X- CLASS SOLAR FLARE
- The Solar flares are massive eruptions of charged particles on the sun. They emit intense bursts of electromagnetic radiation.
- These flares come in various intensities, with smaller A-class and C-class flares denoting relatively minor events. In contrast, the stronger M-class flares can amplify the auroras visible on Earth.
- The X-class flares are the most powerful type of solar flares.
Effects X-class Solar Flares on Earth
Geomagnetic Storms:
- X-class flares release an immense amount of energy, including charged particles and electromagnetic radiation.
- When these particles reach Earth, they interact with our planet’s magnetosphere, causing geomagnetic storms.
- During a severe geomagnetic storm, the magnetosphere weakens temporarily, allowing solar radiation to penetrate deeper into the atmosphere.
Satellite Disruption:
- Long-lasting radiation storms from X-class flares can harm satellites orbiting Earth.
- Satellites may experience malfunctions or even permanent damage due to increased radiation exposure.
- Airline passengers flying near the poles during such events may receive small radiation doses.
Global Transmission Problems and Blackouts:
- X-class flares have the potential to create global transmission problems.
- Intense bursts of radiation can interfere with communication systems, including radio signals and satellite communication.
- In extreme cases, widespread blackouts could occur if critical infrastructure is affected.
Solar Maximum and Solar Cycle:
- The occurrence of X-class flares is a clear sign that the sun is nearing its solar maximum.
- Solar maximum is part of the sun’s roughly 11-year cycle of activity.
- During this phase, X-class flares become more common, posing challenges for Earth’s technology and space operations.
Source: Live Science
Previous Year Question
Q1. If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth?
- GPS and navigation systems could fail.
- Tsunamis could occur at equatorial regions.
- Power grids could be damaged.
- Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth.
- Forest fires could take place over much of the planet.
- Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed.
- Shortwave radio communication of the aircraft flying over polar regions could be interrupted.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 4 and 5 only
- 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 only
- 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Syllabus
- Prelims : Current Event
Context: Since the announcement of General Elections 2024, the C-Vigil app has been inundated with over 79,000 complaints from vigilant citizens.
Background:
- The term ‘C-VIGIL’ stands for Vigilant Citizen, emphasizing the proactive and responsible role citizens can play in the conduct of free and fair elections.
About C-VIGIL APP
- The C- VIGIL app is an innovative mobile application launched by the Election Commission of India.
- It allows citizens to report violations of the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) and expenditure violations during elections.
- The app provides time-stamped evidentiary proof of violations, including live photos/videos with auto location data.
- This unique combination of timestamping, live photo with auto location can be fairly relied upon by election machinery to navigate to the right spot and take prompt action.
- The app is designed to create a fast-track complaint reception and redressal system.
- It also includes a GIS-based dashboard that provides a strong decision tool to drop and dispose of frivolous and unrelated cases even before they are acted upon, thereby reducing the workload of election machinery on ghost complaints.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: At least seven people have tragically lost their lives in a devastating car bombing that targeted a bustling market in northern Syria.
Background:
- The attack occurred in the town of Azaz. Azaz holds strategic significance in the context of the Syrian civil war due to its proximity to the Turkish border and its role as a crucial supply route. The town is home to the Syrian Interim Government, an opposition group that claims legitimacy as the country’s authority.
About Syria:
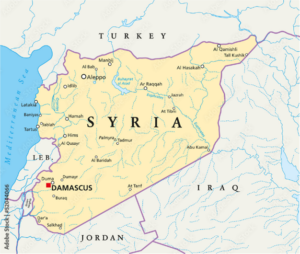
- Syria, officially known as the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant.
- It is bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east and southeast, Jordan to the south, and Israel and Lebanon to the southwest.
- The capital and largest city is Damascus.
- Syria is home to diverse ethnic and religious groups, including the majority Arabs, Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians, Circassians, Armenians, Albanians, Greeks, and Chechens.
- Religious groups include Muslims, Christians, Alawites, Druze, and Yazidis.
- The country has been embroiled in a civil war since 2011, which has resulted in one of the most violent conflicts in the world.
- The war began with large-scale protests and pro-democracy rallies across Syria, as part of the wider Arab Spring protests in the region.
- The ongoing conflict has had a significant humanitarian impact, with many Syrians displaced both internally and externally.
Source: BBC
Previous Year Question
Q1. The term “Levant” often heard in the news roughly corresponds to which of the following regions?
- Region along the eastern Mediterranean shores
- Region along North African shores stretching from Egypt to Morocco
- Region along Persian Gulf and Horn of Africa
- The entire coastal areas of Mediterranean Sea
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2
Context: The Parliamentary Standing Committee on External Affairs recommended legal assistance to Indian nationals imprisoned in Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries.
Background:
- Neighbourhood First construct as a policy came around in 2008.
Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC):
- It was established in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia in 1981.
- It is a political and economic alliance of 6 countries in the Gulf region – Saudi Arabia, UAE, Qatar, Kuwait, Oman, and Bahrain.
- Iran and Iraq are not members.
- Its official language is Arabic.
India-GCC Relations:
- India has strategic interests with GCC countries due to its proximity to important maritime trade routes and its role in countering terrorism and extremism.
- The Gulf has the largest number of Indians abroad (about half of Indian NRIs). GCC countries are the second most prominent contributors to India’s remittance inflow.
- GCC is currently India’s largest trading partner bloc (about one-sixth of India’s total trade). UAE is India’s third largest trade partner while Saudi Arabia is in fourth place.
- GCC countries contribute almost 35% of India’s oil imports and 70% of gas imports.
- India has strong bilateral agreements in the region, such as the defence agreement with Qatar, and intelligence sharing with UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Oman.
- India’s firm stand against terrorism has been acknowledged by GCC countries. UAE, Oman, and Bahrain have conveyed support to India’s claim for a permanent seat at a reformed UN Security Council.
- India also has space cooperation with Saudi Arabia, Oman, and other GCC countries. PSLV launched the UAE’s first nano-satellite, Nayif-I, to collect environmental space data.
Challenges/Issues:
- Geopolitical rivalries and conflicts in the region, such as the Iran-Saudi Arabia rivalry (recently improving), the Yemen civil war, the Syrian civil war, etc. can have spill-over effects and pose security concerns for Indian citizens residing in the region.
- Pakistan’s strong political constituency in ‘West Asia’, fuelled by its Islamic identity and military ties, gives it a favourable political balance in the region compared to India.
- China’s global influence, substantial investments in the Gulf’s oil and gas sector, and successful market penetration have created a power disparity, making Gulf Arabs more inclined to seek Chinese protection.
- The oil and gas prices, along with the rising cost of “war conditions” led to the economic slowdown in Arab Gulf economies, salary cuts, layoffs, and nationalization of workforces at the cost of the expatriate community.
Source: PRS India
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Consider the following countries:
- Turkey
- Iraq
- Jordan
- Israel
- Lebanon
How many of the above-mentioned countries shares border with Syria?
- Only two
- Only three
- Only four
- All five
Q2.) The C- VIGIL app, recently seen in news is launched by:
- The Central Vigilance Commission
- The Election Commission of India
- The Department of Revenue
- The Ministry of Defence
Q3.)With reference to the X-class Solar Flares, consider the following statements:
- The X-class flares are the most powerful type of solar flares.
- It causes geomagnetic storms on the earth.
- X-class flares have the potential to create global transmission problems.
- The occurrence of X-class flares is a clear sign that the sun is nearing its solar maximum.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 1st April 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 30th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – d











