IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Mains – GS 2 & GS 3
Context: The Paris Agreement was supposed to save the world from the worst impacts of climate change. But nine years after it was finalised — on December 12, 2015 — it is perhaps more fragile than ever, appearing increasingly ineffective and helpless in containing worsening climate situation.
Background: –
- The main goal of the Paris Agreement — holding global annual average temperatures within 1.5 degree Celsius of pre-industrial averages, two degrees Celsius in the worst case scenario — seems more distant than ever.
Key takeaways
- In the nine years, annual global emissions have grown 8% from about 49 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent to 53 billion tonnes. Average annual global temperatures have increased from 1.1 degree Celsius above the pre-industrial average to 1.45 degree Celsius above that level.
Erosion of Trust Among Developing Nations
- Unmet Financial Obligations:
- Developed countries failed to meet the $100 billion annual climate finance goal by 2020.
- A finance deal in Baku only proposed increasing this to $300 billion by 2035, which is grossly inadequate given the trillions needed annually by developing nations.
- Equity Concerns:
- The Paris Agreement replaced the Kyoto Protocol, which held developed countries primarily accountable for emissions reductions.
- The Kyoto Protocol had assigned specific emissions reduction targets on developed countries, but placed virtually no responsibilities on the rest of the world. The Paris Agreement mandated everyone to take climate actions, but only in a “nationally-determined” manner, essentially freeing developed countries of their assigned responsibilities.
Geopolitical Dimensions
- Role of Developed Nations:
- Developed nations have consistently resisted stringent climate obligations, fearing economic repercussions.
- The United States’ potential withdrawal under Donald Trump’s presidency could further weaken global climate action.
- Emerging Economies: The growing economic power of countries like China has shifted the climate narrative, with developed nations demanding greater contributions from such nations while ignoring their historical emissions.
Alternative Strategies by Developing Nations
- Vanuatu’s Initiative: The resolution passed by the UN General Assembly to seek the ICJ’s advice on defining countries’ climate obligations is a significant step by vulnerable nations.
- Small island nations aim to establish clearer legal consequences for failing to meet climate commitments.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – ECONOMY
Context: The Social Dialogue Report of the International Labour Organisation (ILO), released recently, has recommended the governments to uphold fundamental principles and rights at work, especially freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining.
Background: –
- Report found that countries’ compliance with freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining had deteriorated by 7% between 2015 and 2022.
Key takeaways
What is Social Dialogue?
- Definition: Social dialogue refers to discussions, consultations, negotiations, and other interactions between governments, employers, and workers on issues related to economic and social policy.
- Purpose: To promote consensus-building, resolve workplace conflicts, and ensure equitable economic and social development.
- The International Labour Organisation (ILO), a United Nations agency, champions social dialogue as one of its four strategic objectives under the Decent Work Agenda.
- The Social Dialogue Report provides a global perspective on:
- The effectiveness of social dialogue in different countries.
- The role of tripartite structures (governments, employers, and workers) in promoting decent work.
- Best practices and challenges in achieving workplace harmony.
Highlights of the Latest Social Dialogue Report:
- The report has highlighted the experience of Rajasthan that brought in the Platform Based Gig Workers (Registration and Welfare) Bill to provide for the establishment of the Rajasthan Platform Based Gig Workers Welfare Board.
- The report argues that social dialogue can enable countries to pursue economic development alongside social progress, while ensuring fair and inclusive low-carbon and digital transitions.
- The ILO has also recommended the national social dialogue institutions (NSDIs) of various countries to expand their outreach to under-represented groups.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: Israel Defense Forces (IDF) has attacked Syria’s naval fleet at the ports of Al-Bayda and Latakia.
Background:
- Attacks are part of Israel’s effort to neutralise military assets in the country after the fall of the Assad regime.
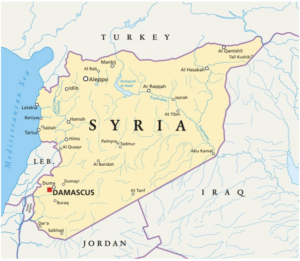
Key Concerns:
- The Port of Latakia is a significant seaport located on the Mediterranean coast in the city of Latakia, Syria.
- When Syria became independent in 1945 it was the only seaport in the country.
- Since 2019, Iran leases parts of the port of Latakia for civilian and military use. This was followed closely by Russia, which operates its only naval base in the Mediterranean in nearby Tartus.
Source: BBC
Syllabus:
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: Romania and Bulgaria will become full members of Europe’s Schengen free-travel area from next month.
Background: –
- Although the Schengen agreements guarantee free travel, several members including Germany and the Netherlands have recently increased controls to stem illegal immigration.
About Schengen Area
- The Schengen Area is a zone comprising 29 European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their mutual borders.
- Establishment: The Schengen Area was established on March 26, 1995.
- Member Countries: The Schengen Area includes 25 EU member states and 4 non-EU countries (Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland).
Key Features:
- Free Movement: Citizens of Schengen countries can travel freely within the area without needing to show a passport or go through border checks.
- Common Visa Policy: The Schengen Area has a common visa policy, allowing travelers to use a single visa to visit multiple Schengen countries.
- External Borders: Schengen countries have harmonized controls at their external borders, ensuring security while allowing free movement within the area
Significance:
- Economic Benefits: The Schengen Area facilitates trade and tourism, benefiting the economies of member states.
- Cultural Exchange: It promotes cultural exchange and strengthens ties between European countries.
- Security: Harmonized external border controls enhance security while maintaining the freedom of movement within the area.
Source: Reuters
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – ECONOMY
Context: The Prime Minister recently emphasised that Jal Jeevan Mission was furthering women empowerment, especially in rural areas.
Background: –
- PM Modi pointed out that women, who previously had to travel long distances to fetch clean water, can now access it right at their doorstep. This shift, he said, allows women to focus more on skill development and self-reliance.
Key takeaways
- Jal Jeevan Mission, is envisioned to provide safe and adequate drinking water through individual household tap connections by 2024 to all households in rural India.
- The mission was launched on August 15, 2019.
- Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) is a centrally sponsored scheme
- As of October 2024, the mission has extended tap water connections to 15.20 crore rural households, covering over 78% of all rural households in India.
Key Features:
- Community Approach: The mission emphasizes a community approach to water management, including extensive Information, Education, and Communication (IEC) activities.
- Source Sustainability: Measures such as recharge and reuse through grey water management, water conservation, and rainwater harvesting are mandatory components.
- Water Supply: Supply 55 liters of water per person per day (lpcd) in every rural household.
- Focus on Quality: Ensure safe and adequate water that meets Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) norms.
Additional Information
- A recent report by the State Bank of India highlighted the broader impact of the initiative.
- Rural households across India have seen an 8.3 percentage point reduction in the need to fetch water from outside their premises. This has led to a 7.4 percentage point rise in women’s participation in agriculture and other productive activities.
- The report also noted significant progress in states like Bihar and Assam, where female workforce participation has surged by over 28 percentage points.
- WHO projects that ensuring safely managed drinking water for all households in India could prevent nearly 400,000 deaths from diarrheal diseases, saving approximately 14 million Disability Adjusted Life Years (DALYs).
- The Indian Institute of Management Bangalore, in partnership with the International Labour Organization (ILO), estimates that JJM will generate 59.9 lakh person-years of direct and 2.2 crore person-years of indirect employment during its capital expenditure phase. Additionally, the operation and maintenance phase could generate 13.3 lakh person-years of direct employment.
Source: PM INDIA
Practice MCQs
Q1.) With reference to the Jal Jeevan Mission, consider the following statements:
- It aims to provide 100 liters of water per person per day to all urban households.
- It involves a 90:10 funding pattern for Himalayan and North-Eastern states.
- It is implemented by the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q2.) With reference to the Port of Latakia, consider the following statements:
- It is located on the Mediterranean coast of Syria.
- It is the only operational seaport in Syria since its independence.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Q3.) With reference to the Schengen Area, consider the following statements:
- It includes all member states of the European Union.
- It allows for free movement of people without border checks between member countries.
- Bulgaria and Romania is set to join the Schengen Area.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 13th December – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – a














