IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – ENVIRONMENT
Context: Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), a global group of scientific experts, has released an Assessment Report on the Interlinkages among Biodiversity, Water, Food and Health – known as the Nexus Report.
Background: –
- This is a first-of-a-kind report looking at the interconnections between the multiple crises. The group examined five major challenges — climate change, biodiversity loss, food insecurity, water scarcity, and health risks — and found that they were strongly interconnected.
What is IPBES?
- IPBES is to biodiversity and natural ecosystems what Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is to climate change. It periodically examines all the existing scientific knowledge on biodiversity and nature to make an assessment of their current state.
- Just like IPCC, IPBES too does not produce new science. It only evaluates the existing knowledge to make consolidated assessments.
- IPBES, set up in 2012, informs several multilateral environmental processes, including the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), the Convention on Combating Desertification (CCD), the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands, Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species, and the Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety.
- IPBES produced its first report in 2019 in which it assessed the threat to global biodiversity. The information in this report became the basis for the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
What does the latest report say?
- Nexus Report has highlighted the strong interlinkages between the five identified global challenges. Its key takeaway is that responses to all these challenges need to be harmonised so that positive actions taken on any one of these does not result in negative impacts on others.
- For example, an attempt to scale up food production, a positive action to deal with hunger and malnutrition, could have the unintended consequence of increasing stress on land and water resources and biodiversity. Exclusive focus on climate change could also go down on the same pathway.
- The report, therefore, argues that it was important to adopt synergistic approaches that deliver benefits across the spectrum.
- Report identified over 70 synergetic approach response options that produced positive outcomes across the five elements. Examples of such response measures included restoration of carbon-rich ecosystems such as forests, soils and mangroves, effective management of biodiversity to reduce risks of diseases spreading from animals to humans, promotion of sustainable healthy diets, and reliance on nature-based solutions wherever possible.
- The report pointed out that more than half of the global GDP — was moderately to highly dependent on nature.
Transformative Change Report
- In another report released simultaneously, IPBES called for fundamental and transformative shifts in the way people view and interact with the natural world in pursuit of its well-being.
- This report, being called the Transformative Change Report, said current, and previous, approaches to deal with ecological decline had failed, and a new and different approach was needed.
- This new and transformative approach, it said, must be based on four fundamental principles — equity and justice, pluralism and inclusion, respectful and reciprocal human-nature relationships, and adaptive learning and action.
- It said the world needed to act immediately on new approaches because the cost of delaying action would increase the costs. There were also benefits to be had from immediate action. It said recent estimates suggested that more than 10 trillion dollars in business opportunities, and about 400 million jobs, could be generated by 2030 through sustainable economic approaches that rely on nature-positive economic models.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Mains – GS 2
Context: Kuwait and India elevated their relationship to a “strategic partnership” and signalled that trade and defence cooperation would form the key pillars of their ties.
Background: –
- PM Modi arrived in Kuwait on Saturday for a two-day visit — the first by an Indian PM in 43 years. The last Indian PM to visit Kuwait was Indira Gandhi in 1981.
Key takeaways
Defence Cooperation
- The two sides institutionalised defence cooperation through an overarching agreement that includes training, exchange of personnel and experts, joint exercises, supply of defence equipment, and collaboration in research and development, among others.
Cooperation in Other Sectors
- Besides defence, three other MoUs (Memoranda of Understanding) were inked to facilitate cooperation in the areas of: Sports, Culture and Solar energy.
India-GCC Cooperation
- India showed keen interest in intensifying its cooperation with the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) through Kuwait’s presidency of the influential grouping, which includes the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, Saudi Arabia, Oman, and Qatar.
- The total volume of India’s trade with GCC countries stood at US$ 184.46 billion in the financial year 2022-23. Both sides also stressed the importance of early conclusion of the India-GCC Free Trade Agreement.
India-Kuwait Relations
- Kuwait is among India’s top trading partners, with bilateral trade valued at US$ 10.47 billion in 2023-24.
- The Indian community forms the largest expatriate group in Kuwait.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims – SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: The satellites for the SpaDeX mission are set to launch onboard the PSLV C60 mission on December 30, 2024.
Background:
- If the SpaDeX test is successful, India will become the fourth country in the world to have a space programme capable of docking in space.
Key takeaways:
- The SpaDeX mission (Space Docking Experiment) is an ambitious project by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) aimed at demonstrating in-space docking technology.
- The primary goal of the SpaDeX mission is to develop and demonstrate the technology required for rendezvous, docking, and undocking of two small spacecraft in low-Earth orbit.
- ISRO needs to master in-space docking so that satellites launched in separate rocket launches can link up to perform more sophisticated tasks. The technology will be essential for the ‘Bharatiya Antariksh Station,’ a new India-made space station ISRO has begun work on.
- Mission Details:
- Spacecraft: The mission involves two small spacecraft, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), each weighing approximately 220 kg.
- Launch: The spacecraft will be launched aboard the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C60) from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre.
- Orbit: Both spacecraft will be injected into a 470 km circular orbit at a 55° inclination.
- Docking Process: The mission will demonstrate the docking of the two spacecraft, followed by the transfer of electrical power between them. After successful docking, the spacecraft will undock and operate their respective payloads for up to two years.
Source: ISRO
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – ECONOMY
Context: Considering the threat that climate change poses globally, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in April last year issued a comprehensive framework for lenders to accept green deposits. However, more than 20 months after the framework has been issued, lenders have made little to no progress in garnering green deposits.
Background: –
- Bankers say a reduction in cash reserve ratio (CRR) requirement for green deposit will help.
What is green deposit?
- Green deposits are essentially interest-bearing deposits, received by the lenders for a fixed period and the proceeds of which are earmarked for being allocated towards green finance.
- The deposits shall be denominated only in Indian rupees as per RBI norms.
- Capital raised via green deposits can be used in funding projects related to solar, wind, biomass, and hydropower energy projects that integrate energy generation and storage. Further, the funds can be used in sectors which enable energy efficiency, clean transportation, climate change adaptation and sustainable water and waste management. Green deposits also can be used for funding green buildings, projects relating to coastal and marine environments, certified organic farming, among others.
- To ensure compliance, RBI said that allocation of funds raised through green deposits during a financial year shall be subject to an independent third-party audit.
Challenges to Green Deposits in India
- Limited Customer Interest and Awareness : Many customers lack awareness of these products and their potential impact. Without a strong alignment of values or incentives, green deposits fail to attract interest from the general public.
- Lower Interest Rates : Green deposits typically offer lower interest rates compared to standard deposit products.
- Slow Adoption Among Private Banks : While most public sector banks have started offering green deposits, private banks have been slower to adopt these products. This hesitance limits the overall availability and visibility of green deposit options.
- Competing Priorities for Lending : Given the country’s population and economic structure, banks must prioritize lending to sectors like small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and job creation. This focus can divert attention and resources away from green projects.
Source: Hindu Businessline
Syllabus:
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: Incoming U.S. President Donald Trump slammed unfair fees for U.S. ships passing through the Panama Canal and threatened to demand that control of the waterway be returned to Washington.
Background: –
- Trump’s comments were an exceedingly rare example of a U.S. leader saying he could push a sovereign country to hand over territory.
Key takeaways
- The Panama Canal is an artificial 82-kilometer (51-mile) waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean, cutting across the Isthmus of Panama.
- It greatly reduces the time for ships to travel between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, enabling them to avoid the lengthy, hazardous route around the southernmost tip of South America via the Drake Passage, the Strait of Magellan or the Beagle Channel.
History:
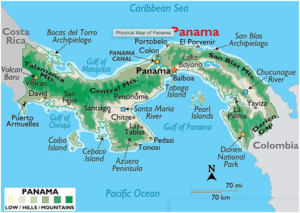
- Early Attempts: The idea of creating a water passage across the isthmus of Panama dates back to at least the 1500s. The French first attempted to build a canal in the 1880s but failed due to disease and financial difficulties.
- U.S. Construction: The United States took over the project in 1904, and the canal was completed in 1914. The U.S. maintained control over the canal zone until 1999, when it was handed back to Panama.
- Modern Era: Panama took full control of the canal in 1999, and it continues to be a vital artery for international shipping.
Structure:
- Locks: Locks at each end lift ships up to Gatun Lake, an artificial fresh water lake 26 meters above sea level, created by damming up the Chagres River and Lake Alajuela to reduce the amount of excavation work required for the canal. Locks then lower the ships at the other end.
- Water Usage: An average of 200 million liters (52 million gallons) of fresh water is used in a single passing of a ship.
Source: Reuters
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Consider the following statements regarding the SpaDeX Mission:
- The SpaDeX mission is aimed at demonstrating in-space docking technology by ISRO.
- The mission involves two spacecraft that will dock and undock in a geostationary orbit.
- If successful, India will become the fourth country to achieve space docking capability.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q2.) Which of the following best describes “Green Deposits”?
(a) Deposits made exclusively by public sector banks for renewable energy projects.
(b) Interest-bearing deposits received by lenders for funding green projects.
(c) Government bonds issued for the purpose of promoting sustainable infrastructure.
(d) Savings accounts providing tax benefits for investments in green projects.
Q3.) With reference to the Panama Canal, consider the following statements:
- It connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean, cutting across the Isthmus of Panama.
- The canal was built by the United States and handed over to Panama in 1999.
- The waterway includes locks to lift and lower ships, making it a unique engineering structure.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 21st December – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – a














