Science and Technology
Context: According to Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation officials, Mumbai has reported 11 fresh measles cases and one suspected death amid the outbreak of the viral infection in the city. With this the infection tally in the metropolis so far this year has gone up to 303.
About Measles:
- Measles is caused by a virus in the paramyxovirus family and it is normally passed through direct contact and through the air. The virus infects the respiratory tract, then spreads throughout the body.
- Measles is a human disease and is not known to occur in animals.
- Before the introduction of measles vaccine in 1963 and widespread vaccination, major epidemics occurred approximately every 2–3 years and measles caused an estimated 2.6 million deaths each year.
Signs and symptoms:
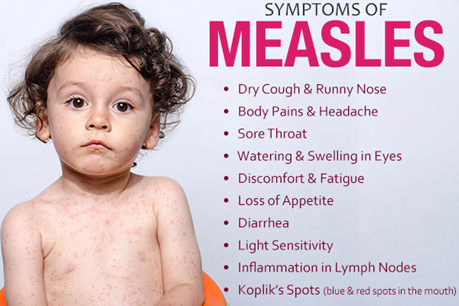
- The first sign of measles is usually a high fever, which begins about 10 to 12 days after exposure to the virus, and lasts 4 to 7 days.
- A runny nose, a cough, red and watery eyes, and small white spots inside the cheeks can develop in the initial stage.
- After several days, a rash erupts, usually on the face and upper neck.
- Serious complications are more common in children under the age of 5, or adults over the age of 30.
- Severe measles is more likely among poorly nourished young children, especially those with insufficient vitamin A, or whose immune systems have been weakened by HIV/AIDS or other diseases.
Transmission:
- It is spread by coughing and sneezing, close personal contact or direct contact with infected nasal or throat secretions.
- It can be transmitted by an infected person from 4 days prior to the onset of the rash to 4 days after the rash erupts.
- Measles outbreaks can result in epidemics that cause many deaths, especially among young, malnourished children.
- In countries where measles has been largely eliminated, cases imported from other countries remain an important source of infection.
Treatment:
- Routine measles vaccination for children, combined with mass immunization campaigns in countries with low routine coverage, are key public health strategies to reduce global measles deaths.
- WHO recommends immunization for all susceptible children and adults for whom measles vaccination is not contraindicated.
- Reaching all children with 2 doses of measles vaccine, either alone, or in a measles-rubella (MR), measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), or measles-mumps-rubella-varicella (MMRV) combination, should be the standard for all national immunization programmes.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body? (2022)
- They protect the body from environmental allergens.
- They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
- They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
- They protect the body from the diseases caused by pathogens.
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
- Adenoviruses have single-stranded DNA genomes whereas retroviruses have double-stranded DNA genomes.
- Common cold is sometimes caused by an adenovirus whereas AIDS is caused by a retrovirus.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2021)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2













