IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Ministry of Defence (MoD) seeks to exempt armed forces personnel from the ambit of decriminalization of adultery
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Defence and Security
In news
- The Supreme Court recently admitted a petition filed by the Ministry of Defence (MoD).
- MoD has sought to exempt armed forces personnel from the ambit of a Constitution Bench judgment of 2018 that decriminalised adultery.
Key takeaways
- A three-judge Bench led by Justice Rohinton Fali Nariman said the plea had to be considered by a Constitution Bench because the original verdict, striking down Section 497 (adultery) of the IPC, was pronounced by a five-judge Bench in September 2018.
- The court referred the case to the Chief Justice to pass appropriate orders to form a five-judge Bench to clarify the impact of the 2018 judgment on the armed forces.
Reason given by the government for seeking exemption:
- There will always be a concern in the minds of the Army personnel who are operating far away from their families under challenging conditions about the family indulging in untoward activity.
- Personnel of the Army, Navy and the Air Force were a “distinct class”.
- They were governed by special legislation, the Army Act, the Navy Act and the Air Force Act.
- Adultery amounted to an unbecoming conduct and a violation of discipline under the three Acts.
- The three laws were protected by Article 33 of the Constitution, which allowed the government to modify the fundamental rights of the armed forces personnel.
RBI Working Group constituted on digital Lending
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The RBI has constituted a working group on digital lending — including online platforms and mobile apps — to study all aspects of digital lending activities in the regulated financial sector and by unregulated players.
Key takeaways
- The working group consists of both internal and external members and is chaired by Jayant Kumar Dash, Executive Director, RBI.
- Functions of the working group will: (1) Evaluate digital lending activities and assess the penetration and standards of outsourced digital lending activities in RBI regulated entities; (2) Identify the risks posed by unregulated digital lending to financial stability, regulated entities and consumers; (3) Suggest regulatory changes to promote orderly growth of digital lending; (4) t Fasds measures for expansion of specific regulatory or statutory perimeter and suggest the role of various regulatory and government agencies; (5) Recommend a robust fair practices code for digital lending players.
- EpThe group will submit its report within three months.
Procurement of LCA Tejas approved
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Defence and Security
In news
- The Union Cabinet has approved procurement of 73 LCA Tejas Mk-1A fighter aircrafts and 10 LCA Tejas Mk-1 Trainer aircrafts.
Key takeaways
- Light Combat Aircraft Mk-1A variant is an indigenously designed, developed and manufactured state-of-the-art modern 4+ generation fighter aircraft.
- This aircraft is equipped with critical operational capabilities of Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) Radar, Beyond Visual Range (BVR) Missile, Electronic Warfare (EW) Suite and Air to Air Refuelling (AAR) would be a potent platform to meet the operational requirements of Indian Air Force, IAF.
- It is the first “Buy (Indian-Indigenously Designed, Developed and Manufactured)” category procurement of combat aircrafts with an indigenous content of 50% which will progressively reach 60% by the end of the programme.
- The Cabinet has also approved infrastructure development by IAF under the project to enable them handle servicing at their base depot so that the turnaround time would get reduced for mission critical systems and would lead to increased availability of aircraft.
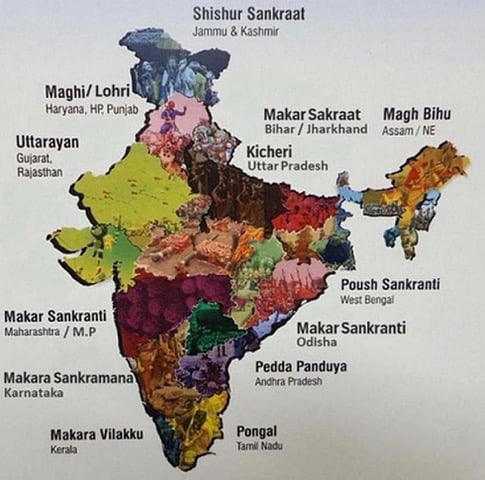
Makar Sankranti being celebrated all over India
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I – Culture
In news
- The Vice President of India greeted fellow citizens on the eve of the festivals of Lohri, Makar Sankranti, Pongal, Bhogali Bihu, Uttarayan and Paush Parbon.
- These festivals are celebrated in diverse yet similar ways, across India.
Key takeaways
- Makar Sankranti is a festival day in the Hindu calendar, in reference to deity Surya (sun).
- Makar Sankranti is observed according to solar cycles.
- It is held normally on the 14th of January, or a day before or after.
- In certain regions celebrations can go on for even four days and vary a lot in the rituals.
- It marks the – first day of sun’s transit into the Makara (Capricorn), marking the end of the month with the winter solstice and the start of longer days.
- It is also celebrated as a harvest Festival.
Do you know?
Different names of the same festival
- Makar Sankranti – Odisha, Maharashtra-Goa, Andhra-Telengana, Kerala and most of the north India
- Paush Parbon – Bengal
- Pongal – Tamil Nadu
- Bhogali Bihu – Assam
- Lohri – Punjab and Jammu
- Maghi – Haryana and Himachal
- Khichdi Parwa – parts of Bihar, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh
SC sets up Farm Laws Committee
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Judiciary
In news
- The Supreme Court has put a stay on the implementation of the three farm laws until further orders.
- It has also set up a committee of agricultural experts to facilitate talks between the Centre and farmers’ unions to resolve the impasse.
Key takeaways
- The members include: (1) Bhupinder Singh Mann, the national president of the Bhartiya Kisan Union and All India Kisan Coordination Committee; (2) Dr Parmod Kumar Joshi, an agricultural economist who is also the Director for South Asia, International Food Policy Research Institute; (3) Ashok Gulati, agricultural economist and former chairman of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices; (4) Anil Ghanwat, the chief of Shetkari Sanghatana, who in articles written in the media have expressed views in favour of the farm laws.
- The Chief Justice said that the committee will not pass an order or punish and submit a report to the Supreme Court.
- The SC has said the committee is the judicial process in this case.
Related articles :
- Your views on farm laws: Click here
- Failed negotiations on farm laws: Click here
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) successfully completes 5 Years of operations
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions
In news
- Crop Insurance Scheme- The Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yajana (PMFBY) successfully completes 5 Years of operations on 13th January 2021.
Important value additions
- The Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) was launched in 2016.
- It is an insurance service scheme for farmers for their yields.
- It aims to reduce the premium burden on farmers and ensure early settlement of crop assurance claim for the full insured sum.
- It was formulated in line with One Nation–One Scheme theme by replacing earlier two schemes National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (NAIS) and Modified National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (MNAIS).
- The Scheme covers all Food & Oilseeds crops and Annual Commercial/Horticultural Crops for which past yield data is available and for which requisite number of Crop Cutting Experiments (CCEs) are being conducted under General Crop Estimation Survey (GCES).
- Implemented by: Empanelled general insurance companies.
- Administered by: Ministry of Agriculture
- The scheme is compulsory for loanee farmers availing Crop Loan /KCC account for notified crops and voluntary for others.
Manipur 4th Sate to undertake Urban Local Bodies Reforms
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Urban Local Bodies
In news
- Manipur has become the 4th State in the country to successfully undertake “Urban Local Bodies (ULB)” reforms
- The reforms were stipulated by the Department of Expenditure, Ministry of Finance in its letter to the States dated 17th May, 2020.
Key takeaways
- Manipur has now become eligible to mobilise additional financial resources of Rs.75 crore through Open Market Borrowings.
- It has now joined the three other States namely, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Telangana, who have completed this reform.
Reforms in the Urban Local Bodies and the urban utilities reforms are aimed at financial strenghtening of ULBs in the States and to enable them to provide better public health and sanitation services.
Economically rejuvenated ULBs will also be able to create good civic infrastructure.
Do you know?
- The State will notify (a) floor rates of property tax in ULBs which are in consonance with the prevailing circle rates (i.e. guideline rates for property transactions) and (b) floor rates of user charges in respect of the provision of water-supply, drainage and sewerage which reflect current costs/ past inflation.
- The State will put in place a system of periodic increase in floor rates of property tax/ user charges in line with price increases.l
Place in news: India expresses serious concern over the security situation in the Sahel and Lake Chad region
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- India has expressed serious concern over the security situation in the Sahel and Lake Chad region in West Africa.
- India also condemned terrorist attacks by Boko Haram in Nigeria and Lake Chad region and by Islamic State in West Africa.
Important value additions
- Lake Chad is a historically large, shallow, endorheic lake in central Africa, which has varied in size over the centuries.
- An endorheic basin is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water.
- The freshwater lake is located in the Sahelian zone of West-central Africa.
- Lake Chad is mainly in the far west of Chad, bordering on northeastern Nigeria.
- It is the largest lake in the Chad Basin.
- The Chari River, fed by its tributary the Logone, provides over 90% of the lake’s water, with a small amount coming from the Yobe River in Nigeria/Niger.
- Despite high levels of evaporation, the lake is fresh water.
Miscellaneous
Khelo India Zanskar Winter Sport & Youth festival 2021
-
Zanskar Winter Sports & Youth Festival 2021 is being organized from 18th to 30th January 2021 by the Dept. of Sports & Youth Services under the Khelo India banner in collaboration with the Ladakh Tourism Department.
- Zanskar, Zahar (locally) or Zangskar is also known as Janskar or Jangskar.
- The Zanskar Range is a mountain range in the union territory of Ladakh that separates Zanskar from Ladakh.
- Geologically, the Zanskar Range is part of the Tethys Himalaya, an approximately 100-km-wide synclinorium (synclinal form that includes a series of smaller folds) formed by strongly folded and weakly metamorphosed sedimentary series.
- The average height of the Zanskar Range is about 6,000 m.
- Its eastern part is known as Rupshu.
First ever ice climbing festival
- In Leh, the first ever Ice climbing festival was celebrated in Nubra valley.
- Nubra is a subdivision and a tehsil in the union territory of Ladakh.
- Its inhabited areas form a tri-armed valley cut by the Nubra and Shyok rivers.
- The Shyok River meets the Nubra River (or Siachan River) to form a large valley that separates the Ladakh and Karakoram Ranges.
- The Shyok river is a tributary of the Indus river.
Shijiazhuang
- Shijiazhuang has become China’s new hotspot of Coronavirus surge.
- It is the capital and largest city of North China’s Hebei Province.
- It is situated east of the Taihang Mountains.
- The city stands at the edge of the North China Plain, which rises to the Taihang Mountains to the west of the city, and lies south of the Hutuo River.
Kayakalp awards
- Public and Private Health Facilities were felicitated with Kayakalp award for high standards of Sanitation and Hygiene.
- The government had launched a National Initiative ‘Kayakalp’ on 15th May 2015 to ensure hygiene, sanitation and cleanliness in Public Health Facilities in India
(Mains Focus)
AGRICULTURE / GOVERNANCE/ FEDERALISM
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
Farm laws, their constitutional validity, and hope
Context: The Supreme Court of India staying the operation of new farm laws and setting up a committee of experts to negotiate with the government and the farmers.
Why farmers are protesting against farm laws: Click here and here
Why earlier government negotiations have failed: Click here
What is the long term solution advocated by experts: Click here
What has been the reaction by farmers to SC decision to set up committee?
- The farmers’ unions have not reacted favourably to the formation of the experts’ committee.
- They allege that the committee does not comprise entirely impartial experts. Most of them are well known and strong defenders of the farm laws, and are critical of the agitation.
- Thus, the agitation being carried on by the farmers is entering a new phase.
Critical Analysis of SC’s decision
- Challenge for the Committee to gain confidence of parties: For conducting negotiations with both the government and the farmers, the members of the committee ought to and should be known to have an open mind on the core issues, which alone will create a necessary confidence in the parties concerned.
- Maximalist Position by farmers: The farmers have made it clear that they will not agree to anything less than the repeal of these laws. This would mean that the present agitation is likely to continue indefinitely.
- SC’s decision Lacks Clarity: It is not yet clear what impact the report of this committee will have on the final decision of the Supreme Court on the question of the constitutional validity of the farm laws. So whatever the experts’ committee recommends, the question of the constitutional validity of the farm laws can be decided only after a proper hearing of the matter before the Court.
- Political Investment by ruling party: While the repeal of a law is a simple legislative act, having to repeal a law in which the government has invested a lot of its prestige is not so easy.
On what basis can farm laws be further challenged in Supreme Court?
- Violation of Federalism
- The constitutional validity of the farm laws has been challenged in the Supreme Court mainly on the ground that Parliament has no legislative competence to enact these laws, the subject matter of which is essentially in the State list.
- Violation of rules of the House
- It is a universally acknowledged fact that the voting on the Farm Bills in the Rajya Sabha was not done in accordance with the rules of the House.
- These rules require the Chair to order the recording of votes (division) by members even when one member demands it.
- The Deputy Chairman of the House, who was conducting the proceedings at that time, did not order division although a few members openly and loudly demanded it.
- Thus, there was a violation of the rules of the House in passing the Bills by voice vote when there was a demand for division.
- Violation of Constitution with regard to procedures adopted for passage of bills
- Article 100 says that all questions at any sitting of either House shall be determined by a majority of votes of the members present and voting.
- Majority can be determined only in terms of number, and therefore what this Article requires is that all questions in the House should be determined by recording the votes of the members present and voting.
- Majority cannot be determined through voice vote. In fact, the Constitution does not recognise voice vote to determine majority in a legislature.
- However, deciding a question by voice vote is a practice prevailing in all legislatures. This was devised for the sake of convenience and there is always an assumption that since the government of the day has a majority, any proposal before the House has the support of the majority.
- But that assumption goes when a member demands voting in the House and the Chair has, then, no option but to order the actual voting. Since this was not done and the Bills were all passed by voice vote, there is a violation of the rules as well as the Constitution (Article 100)
What are the options before the Supreme Court if and when above challenges are made?
- Strike down laws on violation of Article 100 & 107
- The Court can strike down the whole laws as the requirement of Article 107 has not been fulfilled. This Article says that a Bill shall not be deemed to have been passed unless it has been agreed to by both Houses.
- As has been explained above, the Bills have not in fact been passed by the Rajya Sabha because the majority had not been determined in accordance with Article 100.
- Invalidate the proceedings of Rajya Sabha
- The Court may also invalidate the proceedings of the Rajya Sabha and send the three ‘Acts’ back to that House for further proceedings in accordance with the constitutional provisions.
- If this happens, it may provide a good opportunity to the government to revisit these laws.
- These can then be referred to a Select Committee of the Rajya Sabha which can invite the farmers and all other stakeholders and finally produce better Bills.
Conclusion
The issue that needs to be settled by the top court is the constitutional validity of the laws and adherence to the Procedures established by law & Constitution.
GOVERNANCE/ SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
National Science, Technology and Innovation Policy (STIP 2020)
Context: In a difficult year, government has managed to complete an expert-driven, bottom-up, evidence-based and inclusive draft of the fifth National Science, Technology and Innovation Policy (STIP 2020)
Need of National Policy: STIP 2020 is the collective aspiration to ensure that we get the benefits of our national investments in science and technology. It is a comprehensive policy framework the guides & promotes investment in Science & Technology.
The Science, Technology and Innovation Policy will be guided by the following broad vision;
- Atmanirbhar Bharat: To achieve technological self-reliance and position India among the top three scientific superpowers in the decade to come.
- Human Capital: To attract, nurture, strengthen and retain critical human capital through a ‘people centric’ science, technology and innovation (STI) ecosystem.
- Investment: To double the number of Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) researchers, Gross Domestic Expenditure on R&D (GERD) and private sector contribution to the GERD every 5 years.
- Globally Competitive: To build individual and institutional excellence in STI with the aspiration to achieve the highest level of global recognitions and awards in the coming decade.
Key features of draft STIP are:
- Objective:
- STIP 2020 by way of its decentralized, bottom-up, and inclusive design process aims to restrategize priorities, sectoral focus, and methods of research and technology development for larger socio-economic welfare.
- STI Observatory and Centralised Database
- STIP will lead to the establishment of a National STI Observatory that will act as a central repository for all kinds of data related to and generated from the STI ecosystem.
- It will encompass an open centralised database platform for all financial schemes, programmes, grants and incentives existing in the ecosystem.
- The Observatory will be centrally coordinated and organized in distributed, networked and interoperable manner among relevant stakeholders.
- Open Science Framework
- A future-looking, all-encompassing Open Science Framework will be built to provide access to scientific data, information, knowledge, and resources to everyone in the country and all who are engaging with the Indian STI ecosystem on an equal partnership basis.
- All data used in and generated from publicly-funded research will be available to everyone under FAIR (findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable) terms.
- A dedicated portal to provide access to the outputs of such publicly-funded research will be created through Indian Science and Technology Archive of Research (INDSTA).
- STU Education to be made more inclusive
- Online learning platforms will be developed using Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to address the issue of accessibility and to promote research and innovation at all levels.
- Teaching-learning centres (TLCs) will be established to upskill faculty members which in turn will improve the quality of education.
- Engaged Universities will be created to promote interdisciplinary research to address community needs.
- Higher Education Research Centres (HERC) and Collaborative Research Centres (CRC) will be established to provide research inputs to policymakers and bring together stakeholders.
- Increasing Investments
- With an aim to expand the financial landscape of the STI ecosystem, each department/ ministry in the central, the state and the local governments, PSUs, private sector companies and startups will set up an STI unit with a minimum earmarked budget to pursue STI activities.
- Each State will earmark a percentage of the state allocation for STI-related activities under a separate budget head.
- STI investments will be increased through boosting fiscal incentives, enhancing support to industry, especially Medium Small Micro Enterprises (MSMEs), for pursuing research through innovation support schemes and other relevant means on a need basis.
- To ensure systematic governance of the expanded STI financing landscape, an STI Development Bank will be set up to facilitate a corpus fund for investing in direct long term investments in select strategic areas
- Translational Research and Promotion of Innovation
- The policy aims to create a fit for purpose, accountable research ecosystem promoting translational as well as foundational research in India in alignment with global standards.
- An institutional architecture to integrate Traditional Knowledge Systems (TKS) and grassroots innovation into the overall education, research and innovation system will be established.
- Grassroots innovators will also be supported for registration, claiming the Intellectual Property Right (IPR), filing of patent, or any type of legal claim with the help of Higher Education Institute (HEIs).
- Technology self-reliance and indigenization
- A two-way approach of indigenous development of technology as well as technology indigenization will be adopted and focused upon in alignment with national priorities, like sustainability and social benefit, and resources
- A Technology Support Framework will be created to facilitate this development. A Strategic Technology Board (STB) will be constituted to act as a link connecting different strategic departments.
- Inclusivity an integral part of STIP
- An India-centric Equity & Inclusion (E&I) charter will be developed for tackling all forms of discrimination, exclusions and inequalities in STI leading to the development of an institutional mechanism.
- An inclusive culture will be facilitated through equal opportunity for women along with candidates from rural- remote areas, marginalised communities, LGBTQ+ Communities and differently-abled individuals including Divyangjans.
- International Engagement
- Engagement with the Diaspora will be intensified through attracting the best talent back home through fellowships, internships schemes and research opportunities expanded and widely promoted across different ministries.
- Appropriate facilitating channels will be created for remote contribution as well.
- An engagement portal exclusively for the Indian scientific diaspora will be created. ‘S&T for Diplomacy’ will be complemented with Diplomacy for S&T ’.
- STI Policy Institute
- To serve all the aspects of STI policy governance and to provide the knowledge support to institutionalised governance mechanisms , a STI Policy Institute will be established to build and maintain a robust interoperable STI metadata architecture.
- It will conduct and promote nationally and internationally relevant STI policy research and strengthen the science advice mechanism at national, sub-national and international levels.
- It will develop long term capacity building programs for STI policy through training and fellowships.
- An implementation strategy and roadmap will be devised for STI policy and programs along with continuous monitoring and timely evaluation mechanisms.
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”
Q.1 Bihu is a harvest festival of which of the following state of India?
- Odisha
- Tamil Nadu
- Assam
- Punjab
Q.2 Lake Chad is a fresh water lake of which of the following region?
- West Africa
- North America
- Himalayan region
- South Africa
ANSWERS FOR 13th January 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
Must Read
About US Policy reversal on Cuba:
On Building trust in vaccines:
About challenges in vaccination drive:














