Hello Friends
The 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series is IASbaba’s Flagship Initiative recommended by Toppers and loved by the aspirants’ community every year.
It is the most comprehensive program which will help you complete the syllabus, revise and practice tests on a daily basis. The Programme on a daily basis includes
Daily Prelims MCQs from Static (Monday – Saturday)
Daily Current Affairs MCQs (Monday – Saturday)
Daily CSAT Quiz (Monday – Friday)
Note – Daily Test of 20 static questions, 10 current affairs, and 5 CSAT questions. (35 Prelims Questions) in QUIZ FORMAT will be updated on a daily basis.
To Know More about 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series – CLICK HERE
60 Day Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series Schedule – CLICK HERE
0 of 35 questions completed
Questions:
The following Test is based on the syllabus of 60 Days Plan-2023 for UPSC IAS Prelims 2022.
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
0 of 35 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
The historic Convention on Biological Diversity (‘The Earth Summit’) was held in?
Solution (a)
The historic Convention on Biological Diversity (‘The Earth Summit’) held in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, called upon all nations to take appropriate measures for conservation of biodiversity and sustainable utilisation of its benefits.
Solution (a)
The historic Convention on Biological Diversity (‘The Earth Summit’) held in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, called upon all nations to take appropriate measures for conservation of biodiversity and sustainable utilisation of its benefits.
Consider the following statements regarding Bio-magnification:
How many of the above statements are correct?
Solution (b)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 |
| Correct | Incorrect | Correct |
| Bio-magnification refers to the tendency of pollutants to concentrate as they move from one trophic level to the next. Hence, there is an increase in concentration of a pollutant from one link in a food chain to another. | In order for bio-magnification to occur, the pollutant must be: long-lived, mobile, soluble in fats, biologically active. | Bio-magnification can be checked by measuring the number of pollutants in fatty tissues of organisms such as fish. In mammals, we often test the milk produced by females, since the milk has a lot of fat in it are often more susceptible to damage from toxins (poisons). |
Solution (b)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 |
| Correct | Incorrect | Correct |
| Bio-magnification refers to the tendency of pollutants to concentrate as they move from one trophic level to the next. Hence, there is an increase in concentration of a pollutant from one link in a food chain to another. | In order for bio-magnification to occur, the pollutant must be: long-lived, mobile, soluble in fats, biologically active. | Bio-magnification can be checked by measuring the number of pollutants in fatty tissues of organisms such as fish. In mammals, we often test the milk produced by females, since the milk has a lot of fat in it are often more susceptible to damage from toxins (poisons). |
Consider the following statements regarding Air Pollution:
Which of the above statements is/are true?
Solution (c)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 |
| Correct | Correct |
| Air pollutants deleteriously affect the respiratory system of humans and of animals. Harmful effects depend on the concentration of pollutants, duration of exposure and the organism. The fine particulates (PM 2.5, PM10) in air can be inhaled deep into the lungs and can cause breathing and respiratory symptoms, irritation, inflammations and damage to the lungs and premature deaths. Air pollutants also reduce growth and yield of crops and cause premature death of plants. | Smokestacks of thermal power plants, smelters and other industries release particulate and gaseous air pollutants together with harmless gases, such as nitrogen, oxygen, etc. These pollutants must be separated or filtered out before releasing the harmless gases into the atmosphere. The most widely used of which is the electrostatic precipitator, which can remove over 99 per cent particulate matter present in the exhaust from a thermal power plant and industries. |
Solution (c)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 |
| Correct | Correct |
| Air pollutants deleteriously affect the respiratory system of humans and of animals. Harmful effects depend on the concentration of pollutants, duration of exposure and the organism. The fine particulates (PM 2.5, PM10) in air can be inhaled deep into the lungs and can cause breathing and respiratory symptoms, irritation, inflammations and damage to the lungs and premature deaths. Air pollutants also reduce growth and yield of crops and cause premature death of plants. | Smokestacks of thermal power plants, smelters and other industries release particulate and gaseous air pollutants together with harmless gases, such as nitrogen, oxygen, etc. These pollutants must be separated or filtered out before releasing the harmless gases into the atmosphere. The most widely used of which is the electrostatic precipitator, which can remove over 99 per cent particulate matter present in the exhaust from a thermal power plant and industries. |
Consider the following greenhouse gases that are contributing to total Global Warming:
Choose the correct arrangement in increasing order of their contribution:
Solution (a)
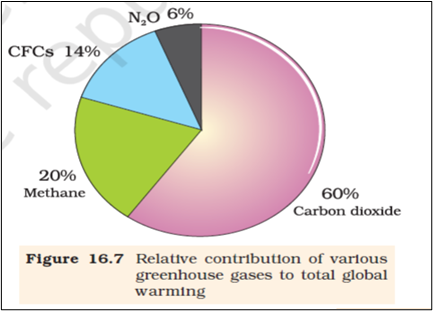
Solution (a)

Consider the following:
Term Refer to
Which of the above are correctly matched?
Solution (b)
| Term | Refer to |
| 1. Refuse | to say No to products that can harm environment |
| 2. Reduce | To use less products by saving the unnecessary wastage |
| 3. Reuse | Using products again and again without further change |
| 4. Re-purpose | Using products for alternative useful purpose |
| 5. Recycle | Using used products to make new things again |
Solution (b)
| Term | Refer to |
| 1. Refuse | to say No to products that can harm environment |
| 2. Reduce | To use less products by saving the unnecessary wastage |
| 3. Reuse | Using products again and again without further change |
| 4. Re-purpose | Using products for alternative useful purpose |
| 5. Recycle | Using used products to make new things again |
Which one of the following takes the maximum time to decompose?
Solution (c)
Decomposition rate of some of the common wastes that we generate on a daily basis:
Solution (c)
Decomposition rate of some of the common wastes that we generate on a daily basis:
Consider the following statements regarding Biosphere Reserve:
Select the correct code:
Solution (c)
To protect our flora and fauna and their habitats, protected areas called wildlife sanctuaries, national parks and biosphere reserves have been earmarked.
The biosphere reserves help to maintain the biodiversity and culture of that area. A biosphere reserve may also contain other protected areas in it. For example, the Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve (M.P) consists of one national park named Satpura and two wildlife sanctuaries named Bori and Pachmarhi.
Solution (c)
To protect our flora and fauna and their habitats, protected areas called wildlife sanctuaries, national parks and biosphere reserves have been earmarked.
The biosphere reserves help to maintain the biodiversity and culture of that area. A biosphere reserve may also contain other protected areas in it. For example, the Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve (M.P) consists of one national park named Satpura and two wildlife sanctuaries named Bori and Pachmarhi.
Consider the Following:
Which of the above are essential nutrients for the crops?
Solution (d)
Nutrients are supplied to plants by air, water and soil. There are several nutrients which are essential for plants. Air supplies carbon and oxygen, hydrogen comes from water, and soil supplies the other thirteen nutrients to plants. Amongst these, some are required in large quantities and are therefore called macro-nutrients. The other nutrients are used by plants in small quantities and are therefore called micro-nutrients.
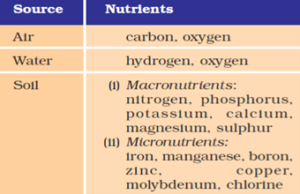
Solution (d)
Nutrients are supplied to plants by air, water and soil. There are several nutrients which are essential for plants. Air supplies carbon and oxygen, hydrogen comes from water, and soil supplies the other thirteen nutrients to plants. Amongst these, some are required in large quantities and are therefore called macro-nutrients. The other nutrients are used by plants in small quantities and are therefore called micro-nutrients.

Consider the following statements with regard to Bioremediation:
How many of the above statements are correct?
Solution (b)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 |
| Correct | Correct | Incorrect |
| Bioremediation is the branch of biotechnology that employs the use of living organisms, like microbes and bacteria, in the removal of contaminants, pollutants, and toxins from soil, water, and other environments. | Typically, this process is economical and sustainable in comparison to other remediation techniques presently available. | Pollutant-reducing microbes which have been modified through recombinant DNA technology (Genetically engineered) have contributed to the bioremediation of contaminated sites. Recombinant DNA technology can facilitate different pathways, for partial or complete degradation of toxic pollutants. |
Solution (b)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 |
| Correct | Correct | Incorrect |
| Bioremediation is the branch of biotechnology that employs the use of living organisms, like microbes and bacteria, in the removal of contaminants, pollutants, and toxins from soil, water, and other environments. | Typically, this process is economical and sustainable in comparison to other remediation techniques presently available. | Pollutant-reducing microbes which have been modified through recombinant DNA technology (Genetically engineered) have contributed to the bioremediation of contaminated sites. Recombinant DNA technology can facilitate different pathways, for partial or complete degradation of toxic pollutants. |
Consider the following statements:
How many of the above statements are correct?
Solution (c)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 | Statement 4 |
| Correct | Incorrect | Correct | Correct |
| A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity with exceptional levels of plant endemism and by serious levels of habitat loss. | The British biologist Norman Myers coined the term ‘biodiversity hotspot’ in 1988. | There are a total of 36 hotspots in the world, the last addition is the North American Coastal Plain. | The current hotspots cover more than 15.7% of the land surface area, but have lost around 85% of their habitat. |
Note:
Solution (c)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 | Statement 4 |
| Correct | Incorrect | Correct | Correct |
| A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity with exceptional levels of plant endemism and by serious levels of habitat loss. | The British biologist Norman Myers coined the term ‘biodiversity hotspot’ in 1988. | There are a total of 36 hotspots in the world, the last addition is the North American Coastal Plain. | The current hotspots cover more than 15.7% of the land surface area, but have lost around 85% of their habitat. |
Note:
Arguments for Biodiversity Conservation are grouped into narrowly utilitarian, broadly utilitarian, and ethical. In context of this, consider the following statements:
How many of the above statements are correct?
Solution (a)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 |
| Incorrect | Incorrect | Correct |
| The narrowly utilitarian arguments to conserve biodiversity are obvious; humans derive countless direct economic benefits from nature. | The broadly utilitarian argument says that nature provides various ecosystem services and other intangible benefits. | The ethical argument says that we have a moral duty to pass on our biological legacy in good order to future generations. |
Solution (a)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 |
| Incorrect | Incorrect | Correct |
| The narrowly utilitarian arguments to conserve biodiversity are obvious; humans derive countless direct economic benefits from nature. | The broadly utilitarian argument says that nature provides various ecosystem services and other intangible benefits. | The ethical argument says that we have a moral duty to pass on our biological legacy in good order to future generations. |
Which of the following is/are the advantages of captive breeding of animal species?
How many of the above statements are correct?
Solution (b)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 |
| Correct | Correct | Incorrect |
| It helps to increase the populations of rare and endangered species of animals and to save these animals from extinction. | This technique helps us to raise the population of wild animals up to the desired level. This technique is useful in developing desired characters or traits in organisms. | One of the disadvantages of captive breeding of animal species is that it does not help in the protection of their natural habitat. It is because the breeding in such case takes place outside their natural habitat.i.e Ex Situ Conservation. |
Captive Breeding
Ex Situ Conservation
Solution (b)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 |
| Correct | Correct | Incorrect |
| It helps to increase the populations of rare and endangered species of animals and to save these animals from extinction. | This technique helps us to raise the population of wild animals up to the desired level. This technique is useful in developing desired characters or traits in organisms. | One of the disadvantages of captive breeding of animal species is that it does not help in the protection of their natural habitat. It is because the breeding in such case takes place outside their natural habitat.i.e Ex Situ Conservation. |
Captive Breeding
Ex Situ Conservation
Consider the following statements regarding Biopiracy:
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Solution (c)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 |
| Correct | Correct |
| Biopiracy refers to the appropriation of traditional knowledge of biodiversity by outsiders and companies. | Under the rules of the CBD, bioprospectors are required to obtain informed consent to access such resources and must share any benefits with the biodiversity-rich country.
|
Biopiracy:
Convention On Biological Diversity (CBD)
Biological Diversity Act, 2002: It was enacted by the Parliament, to provide for:
Nagoya Protocol
Solution (c)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 |
| Correct | Correct |
| Biopiracy refers to the appropriation of traditional knowledge of biodiversity by outsiders and companies. | Under the rules of the CBD, bioprospectors are required to obtain informed consent to access such resources and must share any benefits with the biodiversity-rich country.
|
Biopiracy:
Convention On Biological Diversity (CBD)
Biological Diversity Act, 2002: It was enacted by the Parliament, to provide for:
Nagoya Protocol
With reference to the Sacred Groves, consider the following statements:
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Solution (c)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 |
| Correct | Correct |
| Invasion by exotic weeds is a threat to the Sacred Groves in India.
They threaten ecosystems, habitats, or species with socio-cultural, economic and environmental harm and harm to human health as well. Exotic weeds affect vegetation in terms of native species and thereby bring down the food base of the herbivores. Further, any setback to the herbivore population owing to non-availability of fodder will, in the long run, have a proportionate effect on the carnivore population as well. |
These areas are ecologically significant for the conservation of biodiversity. |
Notes:
Sacred Groves-
Solution (c)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 |
| Correct | Correct |
| Invasion by exotic weeds is a threat to the Sacred Groves in India.
They threaten ecosystems, habitats, or species with socio-cultural, economic and environmental harm and harm to human health as well. Exotic weeds affect vegetation in terms of native species and thereby bring down the food base of the herbivores. Further, any setback to the herbivore population owing to non-availability of fodder will, in the long run, have a proportionate effect on the carnivore population as well. |
These areas are ecologically significant for the conservation of biodiversity. |
Notes:
Sacred Groves-
With respect to International Union for Conservation of Nature’s Red List of Threatened Species, consider the following statements:
How many of the above statements are correct?
Solution (c)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 |
| Correct | Correct | Correct |
| The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species is the global standard for assessing the risk of extinction that individual species of animal, fungus, and plant faces. | The IUCN Green Status of Species complements the Red List by providing a tool for assessing the recovery of species’ populations and measuring their conservation success. In 2020, Green Status of Species assessments became an optional part of Red List assessments. | A species is fully recovered if it is present in all parts of its range, even those that are no longer occupied but were occupied prior to major human impacts/disruption. |
Solution (c)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 |
| Correct | Correct | Correct |
| The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species is the global standard for assessing the risk of extinction that individual species of animal, fungus, and plant faces. | The IUCN Green Status of Species complements the Red List by providing a tool for assessing the recovery of species’ populations and measuring their conservation success. In 2020, Green Status of Species assessments became an optional part of Red List assessments. | A species is fully recovered if it is present in all parts of its range, even those that are no longer occupied but were occupied prior to major human impacts/disruption. |
Which of the following are Agro-biodiversity Hotspots of India?
How many of the above given hotspots are correct?
Solution (d)
| 1. Cold Desert | 2. Brahmaputra Valley | 3. Khasia-Jaintia-Garo Hills | 4. Bundelkhand |
| Correct | Correct | Correct | Correct |
| Agro-biodiversity Hotspot of India. | Agro-biodiversity Hotspot of India. | Agro-biodiversity Hotspot of India. | Agro-biodiversity Hotspot of India. |
Note:
Agro-biodiversity Hotspot:
Benefits of Agrobiodiversity:
Solution (d)
| 1. Cold Desert | 2. Brahmaputra Valley | 3. Khasia-Jaintia-Garo Hills | 4. Bundelkhand |
| Correct | Correct | Correct | Correct |
| Agro-biodiversity Hotspot of India. | Agro-biodiversity Hotspot of India. | Agro-biodiversity Hotspot of India. | Agro-biodiversity Hotspot of India. |
Note:
Agro-biodiversity Hotspot:
Benefits of Agrobiodiversity:
Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding E-Waste in India?
How many of the above given statements are correct?
Solution (b)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 |
| Correct | Incorrect | Correct |
| Toxic elements associated with e waste usually are – Cadmium, Mercury, Lead, nickel, Chromium, Copper, Lithium, Silver and Manganese. | China was the top e-waste generator in the world, producing about 10000 Kt. | Maharashtra is the biggest producer of e-waste in India followed by Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh. |
Solution (b)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 |
| Correct | Incorrect | Correct |
| Toxic elements associated with e waste usually are – Cadmium, Mercury, Lead, nickel, Chromium, Copper, Lithium, Silver and Manganese. | China was the top e-waste generator in the world, producing about 10000 Kt. | Maharashtra is the biggest producer of e-waste in India followed by Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh. |
Consider the following statements:
How many of the above given statements are correct?
Solution (b)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 | Statement 4 |
| Incorrect | Incorrect | Correct | Correct |
| London smog is formed during cold and humid climate. | Oxidizing smog is formed during warm, dry and sunny climate. | Smoke, fog and SO2 form the classical smog. | Photochemical smog is also called as Los Angeles smog. |
Notes:
| Classical Fog | Photochemical Fog |
| Formed during cold and humid climate. | Formed during warm, dry and sunny climate. |
| Constituents: Smoke, Fog and SO2 | Constituents: O3, Nitric Oxide, Acrolein, Proxyacetyl nitrate (PANs), Formaldehyde etc. |
| Chemically it is a reducing mixture: Reducing Smog | Chemically it is a oxidizing mixture: Oxidizing Smog |
| London Smog is the example of Classical Smog | Los Angles Smog is the example of Photochemical Smog |
Solution (b)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 | Statement 3 | Statement 4 |
| Incorrect | Incorrect | Correct | Correct |
| London smog is formed during cold and humid climate. | Oxidizing smog is formed during warm, dry and sunny climate. | Smoke, fog and SO2 form the classical smog. | Photochemical smog is also called as Los Angeles smog. |
Notes:
| Classical Fog | Photochemical Fog |
| Formed during cold and humid climate. | Formed during warm, dry and sunny climate. |
| Constituents: Smoke, Fog and SO2 | Constituents: O3, Nitric Oxide, Acrolein, Proxyacetyl nitrate (PANs), Formaldehyde etc. |
| Chemically it is a reducing mixture: Reducing Smog | Chemically it is a oxidizing mixture: Oxidizing Smog |
| London Smog is the example of Classical Smog | Los Angles Smog is the example of Photochemical Smog |
Consider the following statements regarding Very Short-Lived Halogenated Substances (VSLSs):
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Solution (a)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 |
| Correct | Incorrect |
| They are ozone-depleting halogen-containing substances found in the stratosphere. | Approximately 90% of VSLS are produced by natural processes and their rate of production is increasing. |
Note:
Very Short-Lived Halogenated Substances (VSLSs):
Solution (a)
| Statement 1 | Statement 2 |
| Correct | Incorrect |
| They are ozone-depleting halogen-containing substances found in the stratosphere. | Approximately 90% of VSLS are produced by natural processes and their rate of production is increasing. |
Note:
Very Short-Lived Halogenated Substances (VSLSs):
Which of the following compounds was introduced as a substitute for ozone-depleting substances but turned out to be a potent Greenhouse gas?
Solution (d)
| a) Chloro fluoro carbons (CFCs) | b) Hydro chloro fluoro carbons (HCFCs) | c) Carbon tetrachloride (CC14) | d) Hydro fluoro carbons (HFCs) |
| Incorrect | Incorrect | Incorrect | Correct |
| Ozone-depleting substance | Ozone-depleting substance | Ozone-depleting substance | Greenhouse gas |
Ozone Layer Depletion:
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs):
Examples: HFC-23, HFC-134a
Kigali Agreement:
Solution (d)
| a) Chloro fluoro carbons (CFCs) | b) Hydro chloro fluoro carbons (HCFCs) | c) Carbon tetrachloride (CC14) | d) Hydro fluoro carbons (HFCs) |
| Incorrect | Incorrect | Incorrect | Correct |
| Ozone-depleting substance | Ozone-depleting substance | Ozone-depleting substance | Greenhouse gas |
Ozone Layer Depletion:
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs):
Examples: HFC-23, HFC-134a
Kigali Agreement:
Consider the following statements about Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
How many of the above statements are correct?
Solution (a)
Solution (a)
Consider the following statements:
How many of the given statements are correct?
Solution (c)
Solution (c)
The planetary boundaries framework was first proposed by Johan Rockstrom to define the environmental limits within which humanity can safely operate to maintain Earth’s stability and biodiversity. Which of the following are included in the nine planetary boundaries?
How many of the above statements are correct?
Solution (d)
The planetary boundaries framework was first proposed by Johan Rockstrom to define the environmental limits within which humanity can safely operate to maintain Earth’s stability and biodiversity. The nine planetary boundaries are:
Hence option d is correct.
Solution (d)
The planetary boundaries framework was first proposed by Johan Rockstrom to define the environmental limits within which humanity can safely operate to maintain Earth’s stability and biodiversity. The nine planetary boundaries are:
Hence option d is correct.
Consider the following statements regarding the 7th report on antimicrobial use in animals released by the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH)
Choose the correct code:
Solution (b)
The 7th report on antimicrobial use in animals released by the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) states:
Solution (b)
The 7th report on antimicrobial use in animals released by the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) states:
It is a west-flowing river of the peninsular region flowing through a rift valley between the Vindhya Range on the north and the Satpura Range on the south. Its right tributaries are Hiran, Tendori, Barna, Kolar, Man, Uri, Hatni, and Orsang while its left tributaries are Burner, Banjar, Sher, Shakkar, Dudhi, Tawa, Ganjal, Chhota Tawa, Kundi, Goi, and Karjan. It serves as a traditional boundary between North and South India. Its major dams include Omkareshwar and Maheshwar. It originates from the Amarkantak peak of Maikal Mountain and flows into the Gulf of Khambhat.
The above paragraph refers to which of the following river?
Solution (d)
Narmada River is a west-flowing river of the peninsular region flowing through a rift valley between the Vindhya Range on the north and the Satpura Range on the south. Its right tributaries are Hiran, Tendori, Barna, Kolar, Man, Uri, Hatni, and Orsang while its left tributaries are Burner, Banjar, Sher, Shakkar, Dudhi, Tawa, Ganjal, Chhota Tawa, Kundi, Goi, and Karjan. It serves as a traditional boundary between North and South India. Its major dams include Omkareshwar and Maheshwar. It originates from the Amarkantak peak of Maikal Mountain and flows into the Gulf of Khambhat. It drains areas in Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat. Hence option d is correct.
Solution (d)
Narmada River is a west-flowing river of the peninsular region flowing through a rift valley between the Vindhya Range on the north and the Satpura Range on the south. Its right tributaries are Hiran, Tendori, Barna, Kolar, Man, Uri, Hatni, and Orsang while its left tributaries are Burner, Banjar, Sher, Shakkar, Dudhi, Tawa, Ganjal, Chhota Tawa, Kundi, Goi, and Karjan. It serves as a traditional boundary between North and South India. Its major dams include Omkareshwar and Maheshwar. It originates from the Amarkantak peak of Maikal Mountain and flows into the Gulf of Khambhat. It drains areas in Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat. Hence option d is correct.
Consider the following statements:
Choose the correct code:
Solution (c)
Solution (c)
Consider the following statements regarding the relevance of the Non-Alignment Movement
How many of the above statements are correct?
Solution (c)
The Non-Aligned Movement was formed during the Cold War as an organization of States that did not seek to formally align themselves with either the United States or the Soviet Union but sought to remain independent or neutral. It was founded and held its first conference (the Belgrade Conference) in 1961 under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito of Yugoslavia, Gamal Abdel Nasser of Egypt, Jawaharlal Nehru of India, Kwame Nkrumah of Ghana, and Sukarno of Indonesia.
The Relevance of the Non-Alignment Movement:
Solution (c)
The Non-Aligned Movement was formed during the Cold War as an organization of States that did not seek to formally align themselves with either the United States or the Soviet Union but sought to remain independent or neutral. It was founded and held its first conference (the Belgrade Conference) in 1961 under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito of Yugoslavia, Gamal Abdel Nasser of Egypt, Jawaharlal Nehru of India, Kwame Nkrumah of Ghana, and Sukarno of Indonesia.
The Relevance of the Non-Alignment Movement:
Consider the following statements about Battery energy storage systems (BESS)
Choose the correct code:
Solution (b)
Solution (b)
Consider the following statements regarding the Dadasaheb Phalke Lifetime Achievement Award
How many of the above statements are correct?
Solution (b)
Solution (b)
Consider the following statements regarding the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC)
How many of the above statements are correct?
Solution (c)
Solution (c)
The sum of the digits of a two-digit number is 11. If 45 is added to the number, then the digits are reversed. Find the number.
Solution (c)
x + y = 11………(i)
10x + y + 45 = 10y + x ……….. (ii)
From equation (i) and (ii), we get
X = 3 and y =8
So, the number is 38.
Solution (c)
x + y = 11………(i)
10x + y + 45 = 10y + x ……….. (ii)
From equation (i) and (ii), we get
X = 3 and y =8
So, the number is 38.
The following question is based on the number series given below.
2 4 7 8 9 11 16 19 23 25 28 31 36 40 41 46 49 54 67 73 82 89 97
If all the prime numbers are deleted from the above series, then which element will be 7th from the right end when arranged in descending order?
Solution (b)
Given series:
2 4 7 8 9 11 16 19 23 25 28 31 36 40 41 46 49 54 67 73 82 89 97
Prime numbers in the series are: 2, 7, 11, 19, 23, 31, 41, 67, 73, 89 and 97.
After deleting prime numbers from the given series, we get:
4 8 9 16 25 28 36 40 46 49 54 82
Arranging them in descending order, we get:
82 54 49 46 40 36 28 25 16 9 8 4
Thus, 36 will be the 7th element from the right end in such an arrangement.
Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
Solution (b)
Given series:
2 4 7 8 9 11 16 19 23 25 28 31 36 40 41 46 49 54 67 73 82 89 97
Prime numbers in the series are: 2, 7, 11, 19, 23, 31, 41, 67, 73, 89 and 97.
After deleting prime numbers from the given series, we get:
4 8 9 16 25 28 36 40 46 49 54 82
Arranging them in descending order, we get:
82 54 49 46 40 36 28 25 16 9 8 4
Thus, 36 will be the 7th element from the right end in such an arrangement.
Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
One Amoeba splits into ten Amoeba to form the next generation, but due to the prevailing ecological conditions, only 50% survive. If the number of surviving amoebas in the 6th generation is 3125, what must have been their number in the first generation?
Solution (b)
Let there be ‘x’ Amoeba in the first generation, i.e. n1 = x.
So, n2 = 10x, but only 50% survive,
So, n2, survived = 10x/2 = 5x.
n3 = 10(5x), but only 50% survive,
So, n3, survived = 10(5x)/2 = 25x = 52x.
Similarly, n6,survived = 56-1 x = 55x
Now, it’s given that: 55x = 3125
⇒ 3125x = 3125
∴ x = 1.
Solution (b)
Let there be ‘x’ Amoeba in the first generation, i.e. n1 = x.
So, n2 = 10x, but only 50% survive,
So, n2, survived = 10x/2 = 5x.
n3 = 10(5x), but only 50% survive,
So, n3, survived = 10(5x)/2 = 25x = 52x.
Similarly, n6,survived = 56-1 x = 55x
Now, it’s given that: 55x = 3125
⇒ 3125x = 3125
∴ x = 1.
Find the sum of all four digit numbers that can be formed by the digits 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 without repetition.
Solution (b)
The given digits are 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
Sum of r digit number= n-1Pr-1
(Sum of all n digits)×(1111… r times)
N is the number of non zero digits.
Here n=5, r=4
The sum of 4 digit numbers
4P3 (1+3+5+7+9) (1111) = 666600
Solution (b)
The given digits are 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
Sum of r digit number= n-1Pr-1
(Sum of all n digits)×(1111… r times)
N is the number of non zero digits.
Here n=5, r=4
The sum of 4 digit numbers
4P3 (1+3+5+7+9) (1111) = 666600
In a class of 52 students, 15 failed in the final exams and were not promoted to the next class. The students who were promoted, were assigned roll numbers in accordance with the marks they had obtained in the last class (The student who scored the maximum marks was assigned roll number 1). Ramesh got a roll number 22. What will be his roll number if the roll numbers were to be reversed, i.e. the student who got the least marks was given roll number 1.
Solution (c)
Number of students that passed = 52 – 15 = 37
In the list of passed students, position of Ramesh is 22nd from the top.
So, his position from the bottom = (37 + 1) – 22 = 38 – 22 = 16th
Solution (c)
Number of students that passed = 52 – 15 = 37
In the list of passed students, position of Ramesh is 22nd from the top.
So, his position from the bottom = (37 + 1) – 22 = 38 – 22 = 16th
All the Best
IASbaba


