IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis, IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs November 2015, International, National, UPSC
Archives
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs – 28th November, 2015
NATIONAL
TOPIC:
- General Studies 1: Urbanization, their problems and their remedies.
- General Studies 2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- General Studies 3: Infrastructure – Energy, Roads.
City infrastructure: With a multifaceted approach we can afford the ‘Housing for All’ dream
- Even as India is rapidly urbanising in the current decade, driven by strong industrial and economic growth, there is a significant shortfall of housing that threatens to hamper our country’s socioeconomic development.
A statistical look into the shortage:
- Nearly 28 per cent of India’s population live in cities and urban areas, a figure that is expected to rise to 40 per cent by 2020.
- Over 300 million people are expected to shift to urban areas over the next decade, which will result in a housing shortage of epic proportions.
- In fact, India’s total housing shortfall is estimated at approximately 19 million units, of which over 95 per cent are supposed to be for the economically weaker sections and low income groups.
Government schemes which promote housing:
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana: The scheme aims at constructing more than two crore houses across the length and breadth of the nation within a span of next seven years (i.e by 2022).The target beneficiaries of the scheme would be poor and people living under Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) and Low Income Categories (LIG) categories in urban establishments of the country.
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation(AMRUT):The purpose of the scheme is to
- Ensure that every household has access to a tap with assured supply of water and a sewerage connection;
- Increase the amenity value of cities by developing greenery and well maintained open spaces (parks); and
- Reduce pollution by switching to public transport or constructing facilities for non-motorized transport (e.g. walking and cycling).
- Housing for all by 2022: It aims at
- Slum rehabilitation of Slum Dwellers with participation of private developers using land as a resource;
- Promotion of affordable housing for weaker section through credit linked subsidy;
- Affordable housing in partnership with Public & Private sectors and
- Subsidy for beneficiary-led individual house construction or enhancement.
Real Estate (Regulatory and Development) Authority Bill 2013: A game changer
Important provisions
- The Bill regulates transactions between buyers and promoters of residential real estate projects. It establishes state level regulatory authorities called Real Estate Regulatory Authorities (RERAs).
- Residential real estate projects, with some exceptions, need to be registered with RERAs. Promoters cannot book or offer these projects for sale without registering them. Real estate agents dealing in these projects also need to register with RERAs.
- On registration, the promoter must upload details of the project on the website of the RERA. These include the site and layout plan, and schedule for completion of the real estate project.
- 70% of the amount collected from buyers for a project must be maintained in a separate bank account and must only be used for construction of that project. The state government can alter this amount to less than 70%.On registration, the promoter must upload details of the project on the website of the RERA. These include the site and layout plan, and schedule for completion of the real estate project.
- The Bill establishes state level tribunals called Real Estate Appellate Tribunals. Decisions of RERAs can be appealed in these tribunals.
What needs to be done?
- It is critical to help the affordable housing sector attract investments and greater capital and investment formation by granting ‘infrastructure’ status and implementing further financial sector reforms.
- A clear and rational procedure to ensure the cost-effective availability of land is a primary condition.
- It is most important to upgrade civic amenities, healthcare services, urban transport and inter-city connectivity for Tier II cities and improve quality of life in Tier I & II cities.
- It is essential that administrative structures and policy frameworks encourage resource mobilisation, including that from the private sector.
Connecting the dots:
- Explain the various initiatives taken by the government to promote housing for all by 2022.
- Critically examine the provisions of Real Estate (Development and Regulatory) Authority Bill 2013.
- Write a note on extent of slum population in India along with measures taken by government to improve socio economic indicators among the slum population.
INTERNATIONAL
TOPIC: General Studies 2
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora.
ASEAN- A new community
- From its inception as a result of the Indonesia-Malaysia conflict over the control of Borneo Island and then the Vietnam war, and the resultant fear of the involvement of external players to constituting a free-trade zone, larger in geographical area than the European Union and, with a combined GDP of $2.57 trillion making it the world’s largest single market; ASEAN has traced a long path full of promises and surprises.
- This collective front has eliminated most of the tariff barriers and is committed to harmonising economic strategies, recognising each other’s professional qualifications and consulting closely on macroeconomic and financial policies.
Success Paradigm:
Economic:
- Removal of non-tariff barriers
- Enhanced transport connectivity- “one corridor connecting 10 cities”, usage of waterways and freer movement of skilled workers, trade and capital to integrate the global plan with the local plan
- Need to establish
- Partnership between state and industry,
- High rates of savings and investments,
- High priority for education, health care, human resources development and infrastructure;
- Need to counter-balance the progress of the markets by rising incomes and
- Strong and efficient regulatory mechanisms to guide a market-friendly economy
Political-Security:
- Respect towards existing diversity in political ideologies by considering country-specific attributes & qualifications
- Make way for Regional integration:
- Pool resources,
- Avoid internecine competition,
- Enhance global competitive edge and
- Reduce security problems
- Series of sovereignty disputes and military issues have led to an uncertain and complex security environment and with new powers emerging and strategic partnerships in the making as well as shifting, a new balance of power needs to be established amongst the rapid changes
- Issues of stable inter-state ties and intra-state ethnic stability are closely intertwined and Asia has to work towards the stability and security of strong, secular, federal multi-ethnic states by taking into account protection of rights of all communities
- Deliberation on the maritime boundaries and commitment to a tension-easing code of conduct in these waters would ease up the countries
- Militancy, insurgency and terrorism have become a common thread linking one country to another and through steady democratisation, decentralisation and with the steady provision of caring and efficient governance, the integrity of state structures and stability be preserved.
Socio-Cultural:
- People to people contact
- Cultural linkages to be established
- More exchange programs for students and teachers collaboration
- Research & Development
- Care for the most disadvantaged
- Values of discipline and frugality
Powerful Interests
- The dynamics of the region with huge trade and investments ties as well as financial and information networks span across the area have led to a heavy concentration of the major powers. The uncertainty over major powers involved in the region as well as the shape of the foreign policy (Assertive foreign policy of China) might attract major clash from the other powers.
- The shift in its policy have led to stability issues as well as disequilibrium established which can be taken care of only via constructive engagement, accompanied by more balanced equilibrium of forces in Asia
- What ASEAN exactly needs is not a reduction of USA’s interests in the region or a far-reaching assertive policy to maintain equilibrium as a whole; but continued engagement to bolster universal norms, cooperative structures, non-use of force, stable ties among all major states, and an end to great power hegemonies
- Even the territorial issues of the region needs to be curbed and the States need to evolve a system of confidence building, peacefully negotiated settlement on the basis of adjustments, and neutral arbitration to resolve some of the issues if the region is to evolve into a zone of peace
- Politico-economic efforts: Existence of Association of South-East Asian States (ASEAN)/the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) and the South Asian Preferential Trade Area (SAPTA)/South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) need to be employed and leveraged positively. Even Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)-seeking to promote free trade and ‘Indian Ocean Rim’ have the capability to enhance their role for major cooperation towards the integration of the economic ties
Indo-ASEAN Ties:
Have enormous prospects to advance cooperative political, economic, technological and military and sustained efforts in the following core areas would present a window of opportunity:
- Regular high-level political dialogue and exchanges (continuing dialogue)
- Rapid expansion of trade, investment and tourism ties
- Improving communication links: Road, Railways, Shipping and Air and Telecommunication
- Expansion of military-to-military ties through high level visits and joint exercises (Steady defence modernisation within a defensive military strategy)
- Control the flow of drugs and illegal arms
IASbaba’s Views:
Current linkages are weak and needs to be worked upon. There is an urgent need to strengthen cooperation, build a community of common interest, common destiny and common responsibility with political mutual trust, integrated economies and inclusive culture for the region to build up in a sustainable way.
Connecting the Dots:
- Discuss the importance of ASEAN for India
- Examine the efforts put in by both India and ASEAN towards Maritime cooperation
- Does there exist a civilizational link between India and the ASEAN countries? Explore and present a case study on them
MUST READ
From non-performing to performing
A well-functioning insolvency resolution framework is fundamental for dealing with business failures
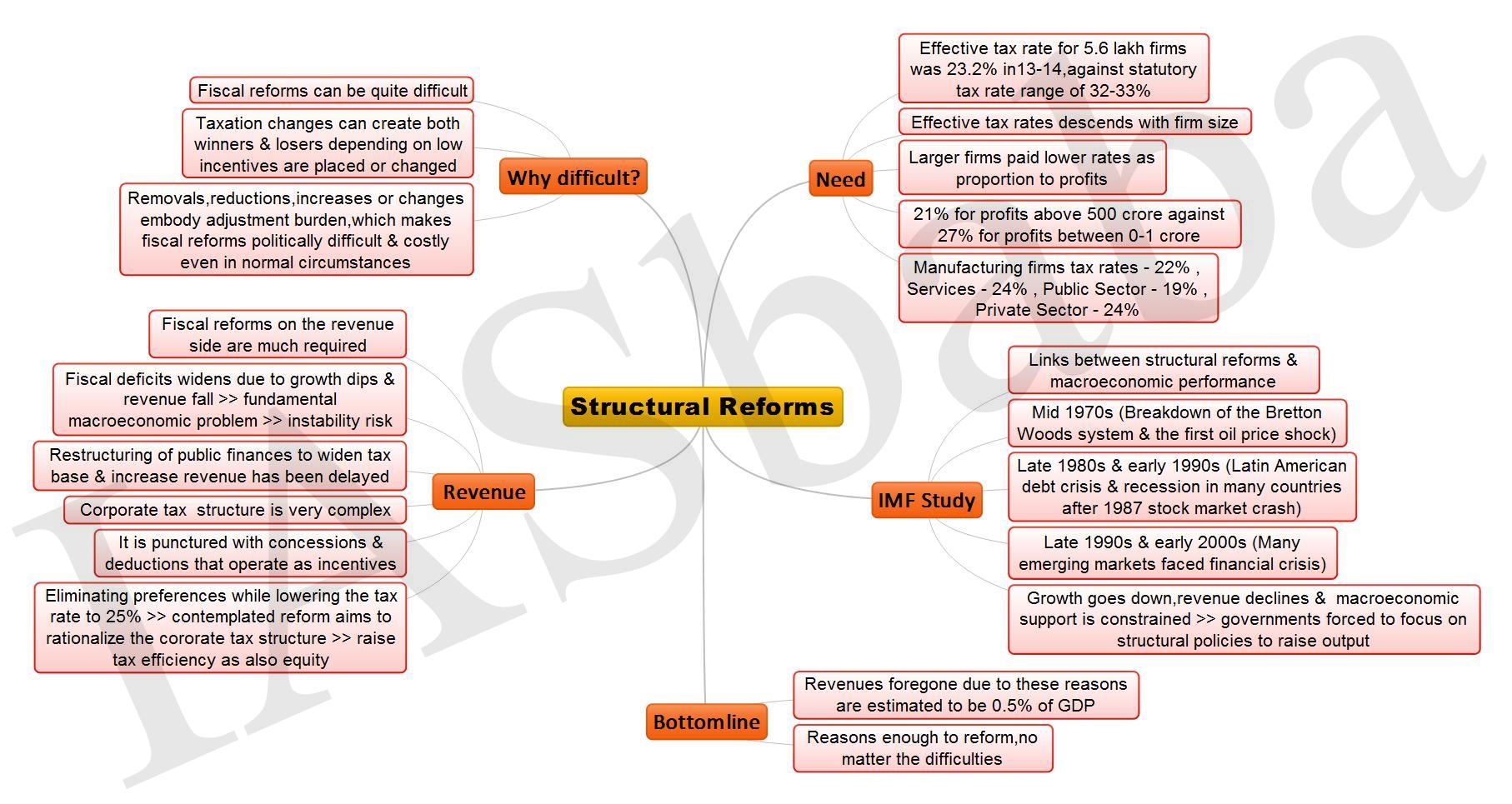
Structural reforms: now the difficult, fiscal part
The angst of the Indian industry to the proposed changes in corporate tax structures reinforces a simple fact: fiscal reforms can be quite difficult
Understanding the CPI-WPI divergence
Unhealthy defiance
MIND MAPS
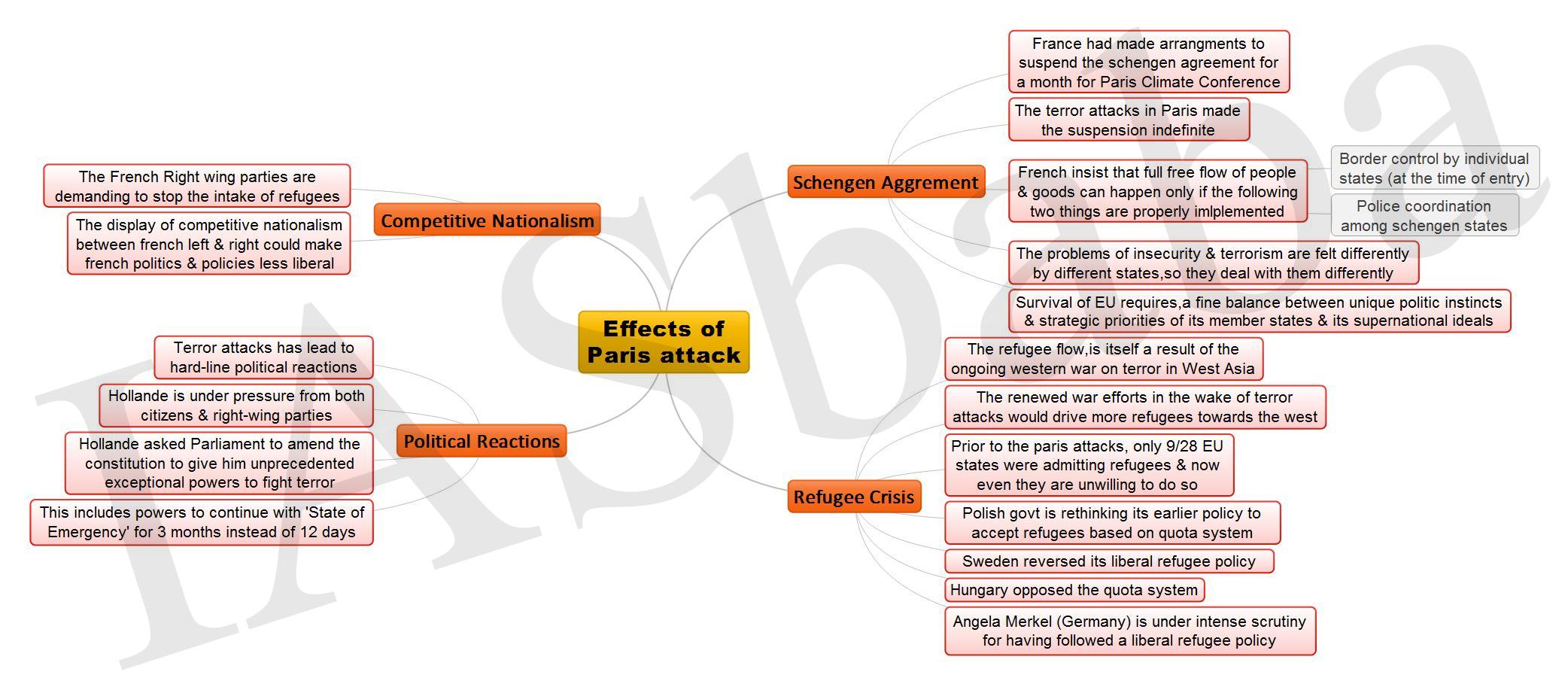
1. Effects of Paris Attack
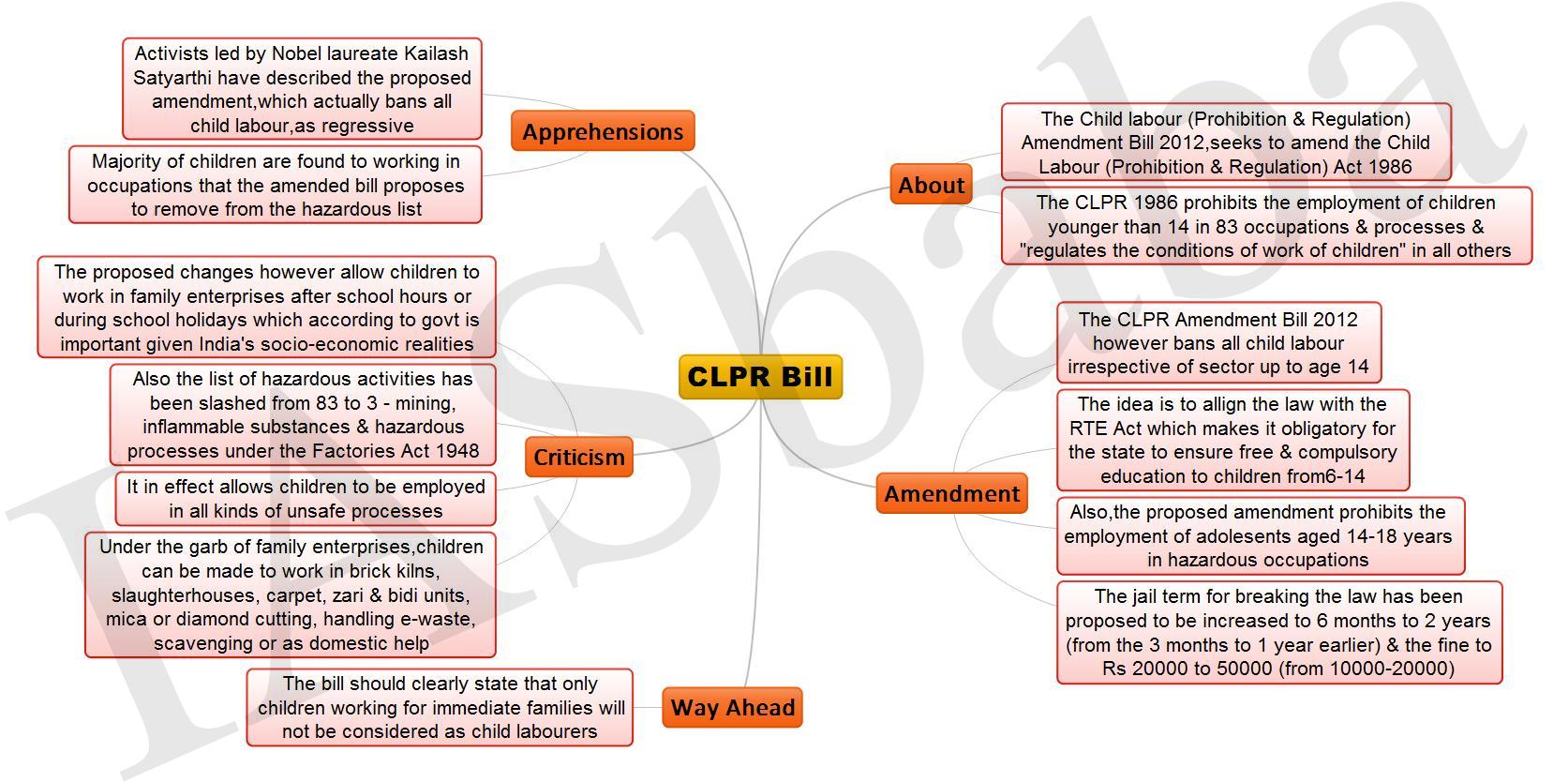
2. CLPR Bill
3. Structural Reforms