IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs (Prelims + Mains Focus)- 7th June 2018
Archives
(PRELIMS+MAINS FOCUS)
RBI MPC Policy Highlights and REPO RATE
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains Paper III – Indian Economy – Monetary Policy; RBI Reforms and its functions
In News:
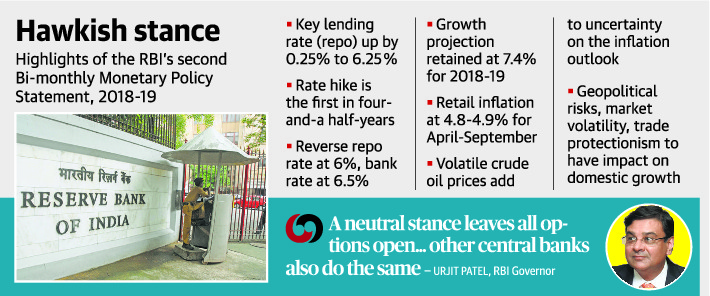
- The six-member monetary policy committee (MPC) of the RBI increased the repo rate by 25 basis points to 6.25%.
- This is the first rate hike in four-and-a-half years; the last was in January 2014.
Key pointers:
- Reasons for increase of repo rate – RBI raised rates after 4.5 years as crude price surges and due to inflation.
- Immediate effect – RBI lends money to commercial banks at higher rate and banks will raise their lending rates. Since, lending rates are high, people abstain from borrowing and consequently it leads to decrease in money supply in economy and decrease in inflation rate.
Do you know?
What is Repo rate?
- Repo rate is the rate at which the central bank of a country (RBI in case of India) lends money to commercial banks in the event of any shortfall of funds. Repo rate is used by monetary authorities to control inflation.
- RBI increases the repo rate during inflation and decreases it during deflation.
Important value additions:
Let’s see what happens when RBI increases and decreases Repo rate –
When RBI increases repo rate
- In order to control excess money supply and inflation in the economy, central bank increases repo rate and lends to commercial banks at a higher rate.
- Now, because of increased repo rate, funds come to commercial banks at a higher cost, so in order to cover those increased costs of acquiring funds, commercial banks increase their lending rates for loans and advances.
- Since, lending rates are increased, people abstain from borrowing and postpone their purchases thereby decreasing demand for products and services, consequently it leads to decrease in money supply in economy and decrease in inflation rate.
When RBI decreases repo rate:
- In order to cure depression and lack of effective demand, central bank decreases repo rates and lends to commercial banks at a reduced rate.
- Because of reduced rates, commercial banks can acquire funds at a lower cost and in order to acquire new consumers and markets they pass their benefit of lower cost to consumers by decreasing their prime lending rates on loans and advances.
- Since, lending rates are reduced by banks, credit is cheap and this induces people to venture in new business activities and purchase of capital goods leading to increased demand for capital goods and increased employment rates.
Key takeaways from RBI MPC Policy
- Repo rate: 6.25%
- Reverse repo: 6%
- FY19 growth projection retained at 7.4 %
- RBI increased its inflation projection to 4.8%-4.9%
- It sees major upside risk to the inflation path as crude prices rose 12%
- Says volatile crude oil prices adds uncertainty to its inflation outlook
- Geo-political risks, financial market volatility, trade protectionism to impact domestic growth
- Adherence to budgetary targets by the Centre and states will ease upside risks to the inflation outlook
Pic link: https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2018/06/07/DEL/Delhi/TH/5_01/75e6c72c_2154768_101_mr.jpg
Article link: RBI hikes repo rate by 25 basis points to 6.25%
Co-op banks can become small finance banks
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains Paper III – Indian Economy – Monetary Policy; RBI Reforms and its functions
In news:
- RBI has decided to allow urban co-operative banks (UCB) to convert into small finance banks (SFB)
- Detailed scheme will be announced shortly.
- UCBs currently face regulation by both the RBI and the respective State governments. By turning into SFBs, they will be regulated only by the RBI.
Article link: Co-op banks can become small finance banks, says RBI
Maternal mortality ratio drops
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Welfare and health; Social issue
In news:
- Maternal mortality ratio in the country drops to 130 from 167, according to latest Sample Registration System (SRS) data
- MMR (number of maternal deaths per 1,00,000 live births)
Do you know?
- Maternal death is the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management but not from accidental or incidental causes.
Key points:
- Kerala remains at the top with an MMR of 46 (down from 61). Maharashtra retains its second position with 61. Tamil Nadu with 66 is in the third position.
- Three States have already achieved the UN’s Sustainable Development Goal of MMR 70.
- Fresh impetus is required to bring the MMR below 30 for all States.
Article link: Maternal mortality ratio in the country drops to 130 from 167 – The Hindu
World Bank to fund Atal Bhujal Yojana
Part of: Prelims and Mains – Government schemes
In news:
- World Bank and Indian Government join hands to address concerns about depleting groundwater reserves in India.
- World Bank nod for ₹6,000 cr. scheme called the Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY).
Important Value Additions
About Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY)
- Central Sector Scheme
- to be implemented over a period of five years from 2018-19 to 2022-23
- aims to improve ground water management in priority areas in the country through community participation
- The priority areas identified under the scheme fall in seven States – Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh
- Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA) is regulating ground water development in 23 States/UTs.
Do you know?
- Water being a State subject, steps for augmentation, conservation and efficient management of water resources to ensure sustainability and availability are primarily undertaken by the respective State Governments.
Difference between Central sector schemes and Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS)
Under Central sector schemes, it is 100% funded by the Union government and implemented by the Central Government machinery. Central sector schemes are mainly formulated on subjects from the Union List. In addition, the Central Ministries also implement some schemes directly in States/UTs which are called Central Sector Schemes but resources under these Schemes are not generally transferred to States.
Under Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) a certain percentage of the funding is borne by the States in the ratio of 50:50, 70:30, 75:25 or 90:10 and the implementation is by the State Governments. Centrally Sponsored Schemes are formulated in subjects from the State List to encourage States to prioritise in areas that require more attention.Funds are routed either through consolidated fund of States and or are transferred directly to State/ District Level Autonomous Bodies/Implementing Agencies.
Article link: World Bank nod for ₹6000 cr. groundwater recharge plan
India improves in global peacefulness rankings
Part of: GS Prelims
In news:
- India’s rank has marginally improved in global peacefulness, according to the Global Peace Index (GPI)
- India’s GPI rank was 137 out of 163 countries in 2017, when the year 2016 was assessed. India’s rank moved up to 136 for 2017.
- Pakistan’s rank too has improved marginally. Pakistan’s rank moved from 152 to 151.
- However, the best performer of South Asia, Bhutan, slipped from 13th to 19th position, while Bangladesh’ peace index deteriorated sharply. Bangladesh moved from 84th to 93rd position.
About Global Peace Index (GPI)
- Global Peace Index (GPI) is released by Australia-based Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP).
- The GPI gauges global peace using three broad themes: the level of societal safety and security, the extent of ongoing domestic and international conflict and the degree of militarization.
Do you know?
- Peace continues to record a “gradual, sustained fall” across the world, the report noted.
- Syria remained the least peaceful country in the world, a position that it had held for the past five years.
- Iceland continues to remain the most peaceful country in the world, a position it has held since 2008.
Article link: India’s rank marginally improves in peace index
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL
TOPIC:General Studies 2:
- India and its International relations.
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora.
India-US Relations: No longer seeing eye to eye?
India and the U.S. “shares similar vision” of an open and secure Indo-Pacific region. However, their equation is not quite balancing out recently.
Concerns for US:
- According to US, Indian government views its relation with the U.S., Russia and China in equal measure.
- Last year, the NDA government had hinted at challenging the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), and to back a Quadrilateral grouping of India, the U.S., Japan and Australia to maintain an open Indo-Pacific.
- Today, the Doklam issue has been buried, the BRI isn’t as much a concern as before, and the government’s non-confrontational attitude to the Maldives and Nepal indicates a softened policy on China in the neighbourhood.
- India’s closer engagement with Chinese President Xi Jinping and a relationship reset with China after the Wuhan meeting.
- The Quad formation has been given less attention. India rejected an Australian request to join maritime exercises along with the U.S. and Japan this June. Indian Navy Chief alsi hinted that there was no plan to “militarise” the Quad.
- India’s acceptance of military exercises with countries of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), the Russia-China led grouping.
- Delay in signing of outstanding India-U.S. foundational agreements.
- India intends to continue energy deals with Iran and Venezuela in defiance of American sanctions.
Concerns for India:
There has been a surge in disputes between the two countries:
- Trade protectionism is clearly the other big point of divergence between India and the U.S.
- Several issues/disputes in World Trade Organisation (WTO)
- Disputes on the new American steel and aluminium tariffs
- the proposed cuts in H1B professional visas and cancellation of H4 spouse visas,
- disputes on India’s tariffs and resistance to U.S. exports of dairy and pork products,
- disputes on Indian price reductions on medical devices, and
- Reserve Bank of India rules on data localisation on Indian servers for U.S. companies.
- The row over Harley-Davidson motorcycles, where US calling for India to scrap its 75-100% tariffs, given that the U.S. imposes zero tariffs on the import of Indian Royal Enfield motorcycles.
- India’s plans to acquire the Russian S-400 missile system.
The biggest challenges to a common India-U.S. vision are now emerging from the new U.S. law called Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act and the U.S.’s withdrawal from the Iran nuclear deal with the threat of more secondary sanctions.
Both actions have a direct impact on India, given its high dependence on defence hardware from Russia and its considerable energy interests in Iran.
Conclusion:
From the above differences, it is equally clear that the India-U.S. equation isn’t balancing out quite the way it did last year.
Connecting the dots:
- India-Us trade relation holds huge potential. However the key to tap this potential lies in focusing on reaping low hanging fruits rather than trying to address major concerns. Discuss.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Q.1) Consider the following statements about the reverse repo rate
- It is an interest rate at which the Banks deposit their cash with the RBI
- If reverse repo rate is increased the bank’s lending rates to customers will also increase
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Match the following statements with the related terms given below:
- It is rate at which scheduled banks can borrow funds overnight from RBI against government securities.
- It is amount that banks have to maintain a stipulated proportion of their net demand and time liabilities (NDTL) in form of liquid assets.
- It is amount of funds that banks have to keep with RBI.
- It is rate at which banks lend funds to RBI.
Terms:
- Reverse Repo Rate
- Repo Rate
- Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) Rate
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR)
Select the correct answer using the following codes:
- 1-E; 2-C; 3-B; 4-A
- 1-E; 2-C; 3-A; 4-B
- 1-C; 2-E; 3-D; 4-A
- 1-C; 2-E; 3-D; 4-B
Q.3) Consider the following:
- Currently, urban co-operative banks are regulated by both the RBI and the respective State governments.
- Currently, urban co-operative banks are regulated only by the RBI.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4) Consider the following statements with regard to Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY):
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation is the Nodal Ministry for the overall policy, planning, funding and coordination of the programme.
- It aims at providing every person in both rural and urban India with adequate safe water for drinking and cooking.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- None
Q.5) The primary entry in the Constitution relating to water is in the –
- State List
- Union List
- Concurrent List
- None
Q.6) Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY), a ₹6,000 cr. scheme is collaboration between –
- India and UN Environment
- India and World Bank
- India and Israel
- India and IMF
Q.7) Global Peace Index (GPI) is released by –
- World Justice Project
- International Court of Justice
- The Office of UN Commissioner for Human Rights
- None of the above
MUST READ
Pre-emptive strike
What RBI’s rate hike indicates
Nagaraj: The law on SC/ST promotions
Merge ideas, not cadres
The plastic ban needs a management plan
Is the great FII sell-off a cause for concern?
Informal enterprises should be encouraged











