IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Daily Current Affairs [IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam] – 5th January 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
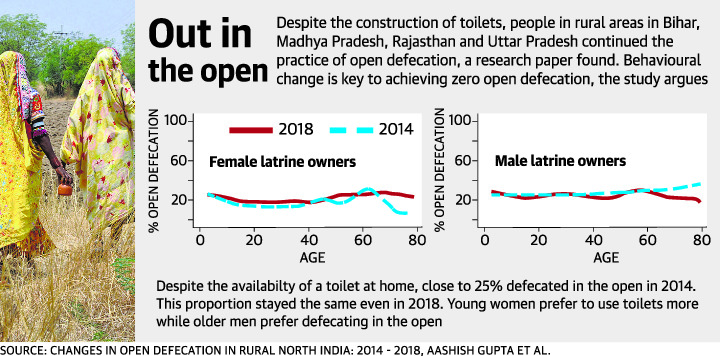
Open defecation continues
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Government schemes and policies; Health issue
In news:
Research and study on the impact of the Swachh Bharat Mission shows that –
- Toilet ownership has increased, however, percentage of people who owned toilets but continued to defecate in the open has remained unchanged between 2014 and 2018.
- Almost 60% of households covered by the survey which did not have a toilet in 2014 had one by 2018.
- Mission has been more successful at toilet construction than at driving behaviour change.
- Approximately 44% of people over two years old in rural Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh still defecate in the open.
Do you know?
- According to the Mission, Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan are already open defecation free or ODF states.
- Bihar has achieved 98.97% coverage of toilets for every household, while Uttar Pradesh has achieved 100%, according to government data, although the state has yet to be declared ODF.
Crux – Open defecation levels are still above 40% in ODF States; Swachh Bharat has not brought behavioural change.
Pic: https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2019/01/05/DEL/Delhi/TH/5_05/0311d6b1_2644582_101_mr.jpg
Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban and ODF++ certification
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Government schemes and policies; Health issue
In news:
According to the Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban:
- Seven cities – all in Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh – have been certified ODF++
- The certification, an extension of the ODF or Open Defecation Free protocol, means that all the faecal sludge and sewage in these cities is treated scientifically before discharge.
Do you know?
- These are the first cities to qualify under the government’s new extended protocol to sustain gains made under the basic ODF protocol.
- Under new norms, cities and towns wanting to be declared ODF+ (Open Defecation Free Plus) must also be free of public urination and not just open defecation.
- The ODF+ and ODF++ protocols (released recently by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs) are the next step for the SBM-U and aim to ensure sustainability in sanitation outcomes.
- The Urban Affairs Ministry is setting up a sub-mission on faecal sludge management under its AMRUT scheme for 500 cities and towns.
Difference between ODF protocol, ODF+ and ODF++
- Original ODF protocol issued in March 2016, said – “A city/ward is notified as ODF city/ward if, at any point of the day, not a single person is found defecating in the open.”
- The new ODF+ protocol, issued last week, says that a city, ward or work circle could be declared ODF+ if, “at any point of the day, not a single person is found defecating and/or urinating in the open, and all community and public toilets are functional and well-maintained.”
- The ODF++ protocol adds the condition that “faecal sludge/septage and sewage is safely managed and treated, with no discharging and/or dumping of untreated faecal sludge/septage and sewage in drains, water bodies or open areas.”
Survey of childcare institutions
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Government schemes and policies; Child issue
In news:
Research and survey of 9,589 shelters across nation found that –
- Most children at childcare institutions are not orphans, but belong to family structures that are unable to look after them.
- More than a lakh inmates are from single parent homes (unwed mothers, abandoned wives, widows and in some cases single fathers).
- In other words, children of single parents constituted a third of the total number of total children in homes.
Miscellaneous
- Wi-Fi facility at 2,000 rail stations soon
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II and III – Government schemes and policies; Infrastructure
In news:
Railway Minister has instructed officials –
- to provide Wi-Fi facilities at a minimum of 2,000 stations as soon as possible.
- to set up a single helpline number for all non-security railway complaints.
- to distribute point of sale (PoS) machines in all trains to each catering staffer to address complaints related to overcharging by the caterer (to ensure transparency in catering services)
- replace conventional coaches with modern LHB (Linke Hofmann Busch) design coaches in all long distance trains
- A.P. recently unveiled second largest petroglyph site
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains I – Indian Art and Heritage; Culture
In news:
- Petroglyphs are images created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art.
- A.P. recently unveiled second largest petroglyph site at Mekala Benchi, in Kurnool district.
- These petroglyphs, or rock carvings, underscore Kurnool’s importance as a major site of Neolithic settlements in south India.
- The term Neolithic Period refers to the last stage of the Stone Age.
- China Chang’e-4 lunar probe and ‘Yutu 2’
- China has named the lunar rover, which was deployed recently to carry out a string of experiments on the unexplored far side of the moon, as ‘Yutu 2’.
- What is a marketplace and inventory based model of e-commerce?
- Marketplace based model of e-commerce means providing an information technology platform by an e-commerce entity on a digital & electronic network to act as a facilitator between the buyer and seller.
- Inventory based model of e-commerce means an ecommerce activity where inventory of goods and services is owned by e-commerce entity and is sold to the consumers directly.
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL
TOPIC:General studies 2
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
India’s role in Afghanistan after the inevitable exit of US
India must be prepared for the potential consequences of withdrawal of American troops from Afghanistan.
Recently, U.S. President Donald Trump suggested that regional players like Russia, India and Pakistan should be more involved in stabilising the situation, and mocked India for not doing enough.
As a result, the U.S. war in Afghanistan, that began as revenge for the 9/11 attacks, evolved into a mission for ensuring democracy and prosperity in Afghanistan.
Challenges:
- Resurgence of the Taliban: The Taliban has re-emerged as a formidable fighting force and are going from strength to strength.
- As Mr. Trump now moves to cutting American presence to a few well-guarded military bases, India must consider the consequences closely.
Do you know?
- Casualties of Afghan National and Defence Security Forces in May-September 2018 were the “greatest it has ever been” compared to corresponding periods since 2001, and the United Nations Assistance Mission in Afghanistan “documented more civilian deaths in the first nine months of 2018 than they had during the same nine-month reporting period since 2014”.
Shift in policy
It is also time to recognise that the U.S.’s South Asia Strategy for Afghanistan (announced by Mr. Trump in August 2017) has been discarded.
Mr. Trump had defined the strategy with three features:
- that U.S. troops would remain involved in the country until “conditions” mandated their return;
- that the U.S. would put Pakistan on notice for its support to the Taliban and a political settlement with the Taliban would only follow “after an effective military effort”; and
- that the policy would hinge on further developing the strategic partnership with India
However, today, we can easily see that each element of the U.S.’s policy on the ground has shifted, if not been entirely reversed.
The appointment of special envoy Zalmay Khalilzad in September to lead talks with the Taliban shows that the U.S. is no longer waiting for military operations to take effect.
Mr. Trump wrote a letter to Pakistan Prime Minister Imran Khan thanking him for his efforts.
Mr. Khalilzad’s direct talks with the Taliban didn’t even have President Ashraf Ghani in the loop and the National Unity government (NUG) in Kabul was cut out. This reversed the previous U.S. position not to engage the Taliban until it engages the NUG.
Exit of Defence Secretary James Mattis is one more concern. Mr. Mattis had pushed most strenuously to keep India in the Afghan game by swinging a waiver for India on Chabahar and Iran oil purchases. It remains to be seen whether Mr. Trump will continue those waivers past May this year.
Conclusion:
- The internal situation in Afghanistan is aggravated now by the uncertainty of the democratic process.
- Doubts have been casted against Government’s inability to conduct Parliamentary elections.
- Presidential elections have been postponed.
For India, these developments may appear discouraging. The removal or reduction of the U.S. presence from most theatres of action has created space for regional players: leaving Syria to Iran and its allies; Yemen to Saudi Arabia; Afghanistan to players like Russia, Pakistan and Iran; and Pakistan to China.
India’s best course with Afghanistan remains its own regional strategy, not becoming a part of any other country’s strategy. Close bilateral consultations has earned India immense popularity and goodwill.
Connecting the dots:
- New challenges confront India and Afghanistan in their bilateral relationship which requires India to tread cautiously. Examine.
- A stable Afghanistan is key to India’s policy towards Central Asian countries. Comment. Also examine the associated challenges.
NATIONAL/POLITY
TOPIC:General studies 2
- Appointment to various Constitutional posts, powers, functions and responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies.
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
NITI Aayog’s proposal for All India Judicial Service
Introduction
- The vision document titled ‘Strategy for New India @ 75’, released by the NITI Aayog proposes a spate of judicial reforms.
- The think-tank recommends for the creation of an All India Judicial Service, akin to the other central services like the IAS and the IPS.
- It believes that All-India Judicial Services (AIJS) will help promote federal governance.
Do you know?
- The idea of an All India Judicial Service (AIJS) has been deliberated since Independence.
- In fact, the first law commission — 14th Report on Reform of Judicial Administration — also suggested for the need for creating a separate all-India service for judicial officers.
- Subsequently, a crucial step towards formalising the process for setting up an AIJS was taken under the infamous 42nd Constitutional Amendment during the Emergency in 1976.
- The Constitution of India was amended in 1977 to provide for an All-India Judicial Services under Article 312.
- The Chief Justices conferences in 1961, 1963, and 1965 favoured creation of All-India Judicial Services and even the Law Commissions (1st, 8th and 11th, 116th) had suggested the creation of the service. However, each time it was faced with opposition.
Arguments in favour of All-India Judicial Services
- Efficiency and efficacy of judiciary would be increased.
- Transparent and efficient method of recruitment would be followed.
- The pendency and issue of delay of cases would be done away with.
- Corruption, nepotism etc would be strongly dealt with.
- Best legal talent across the country would be selected on the basis of merit.
- Public faith in the judiciary would be restored.
- The Supreme Court is not averse to the idea of AIJS as in its 2 judgments of 1991 and1993 it supported the idea of AIJS.
Arguments against All-India Judicial Services
- There will be an issue of local laws differences.
- Local languages and dialects would be a problem.
- Nine High courts are against this proposal and hence disapproving this proposal.
- The conflict between Centre and State would start.
- The status of legal education in India is very much mismanaged. Except for a few national law schools, others do not prioritize the legal education too much. Law is taken as the last report who do not get into medicine, IITs etc.
- Unremunerative pay is a big issue. Despite an effort by the Supreme Court to ensure uniformity in pay scales across States in the All India Judges’ Association case, it is still very low.
- Also, the judiciary has fewer avenues for growth, promotion and limited avenues for career advancement.
- There is low district judge representation in the High Courts, as less than a third of seats in the High Courts are filled by judges from the district cadre. The rest are appointed directly from the Bar.
- It will be difficult for the less privileged background to enter the profession.
- Again coaching institutes etc would flourish and education would be commercialized.
- Currently, the judges of subordinate courts are appointed by the governor in consultation with the High Court which will not be so if AIJS is implemented. Hence it will be against the Independence of Judiciary as some other body will have a control in appointment and integration because in the judiciary, higher level controls and evaluates lower level.
- Both the decentralized approach of each High Court conducting its own appointment and a centralized one seem to have roughly the same efficacy in filling up the vacancy.
Connecting the dots:
- Analyze the merits and demerits of creation of an All India Judicial Services in India.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) Which of the following are not part of Open Defecation Free (ODF) States of India, according to Swachh Bharat Mission?
- Bihar
- Rajasthan
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
Select the correct code
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 5
- 1 and 3
- Only 1
Q.2) Which among the following protocol deals with the condition that “faecal sludge/septage and sewage is safely managed and treated, with no discharging and/or dumping of untreated faecal sludge/septage and sewage in drains, water bodies or open areas?
- Open Defecation Free Plus
- Open Defecation Free
- Open Defecation Free Plus Plus
- Open Urination Free
Q.3) Which of the following is not a part of Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)?
- Every household should have access to tap and sewerage line.
- Developing greenery and well maintained open spaces e.g. Parks
- Reducing pollution by switching to public transport and constructing facilities for non-motorized transport like walking/cycling.
- Providing government broadband internet connection to all households through optical fiber network.
Q.4) The chief characteristic features of the Neolithic culture include:
- Practice of agriculture and domestication of animals
- Polishing of stone tools
- Manufacture of pottery
- The new technology of smelting metal ore and crafting metal artifacts
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
MUST READ
Telangana’s ‘villages of widows’
A global slowdown?
How Dhaka fell in 1971
Citizens and them
We don’t need career judges India
Jobs, in perspective














