IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 12th December 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Shore temple
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains I– Culture& Geography
In News
- The shoreline on the northern side of the Shore Temple in Mamallapuram, Tamil Nadu is facing severe sea erosion.
- The Public Works Department is awaiting funds to construct groynes for coastal protection at a cost of ₹95.95 crore.
- According to PWD, every year, nearly 4-5 m of the shoreline near the temple is declining.
Groynes
- A groyne is a shore protection structure built perpendicular to the shoreline of the coast (or river), over the beach to reduce longshore drift and trap sediments. A groyne functions as a physical barrier by intercepting sand moving along the shore.
- Rock is often used as construction material, but wooden groynes, steel groynes, rubble-mound and sand-filled bag groynes, or groynes made of concrete elements can also be found. Rock groynes are generally preferred as they are more durable and absorb more wave energy due to their permeable nature.

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 12th December 2019
River Pollution
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III – Environment Conservation
In News
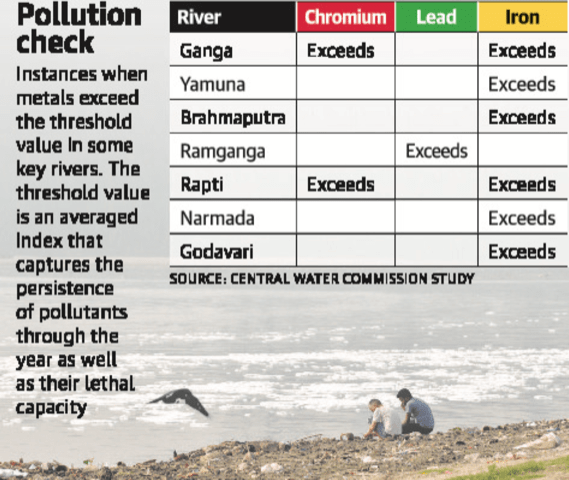
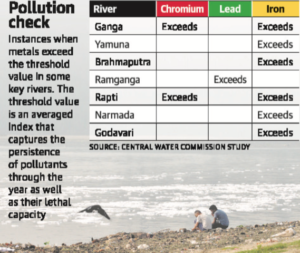
- Samples taken from two-thirds of the water quality stations spanning India’s major rivers showed contamination by one or more heavy metals, exceeding safe limits set by the Bureau of Indian Standards.
- The study spanned 67 rivers in 20 river basins and was conducted by Central Water Commission (CWC) from May 2014 to April 2018.
- Iron emerged as the most common contaminant with 156 of the 442 sampled sites registering levels of the metal above safe limits.
- None of the sites registered arsenic levels above the safe limit.
- The other major contaminants found in the samples were lead, nickel, chromium, cadmium and copper.
- Source of metal pollution: Mining, milling, plating and surface finishing industries that discharge a variety of toxic metals into the environment.
- The presence of metals in drinking water is to some extent unavoidable and certain metals, in trace amounts, required for good health. However, when present above safe limits, they are associated with a range of disorders.
- Health Impact: Long-term exposure to the above-mentioned heavy metals may result in slowly progressing physical, muscular, and neurological degenerative processes that mimic Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, muscular dystrophy and multiple sclerosis.
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 12th December 2019
RISAT
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III – Space
In News
- India’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, in its 50th flight (PSLV-C48), successfully launched RISAT-2BR1, an earth observation satellite, along with nine commercial satellites of Israel, Italy, Japan and USA from Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR, Sriharikota.
- These satellites were launched under commercial arrangement with NewSpace India Limited (NSIL), the commercial arm of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
RISAT-2BR1:
- It is a radar imaging earth observation satellite weighing about 628 kg.
- The satellite will provide services in the field of Agriculture, Forestry and Disaster Management. The mission life of RISAT-2BR1 is 5 years.
- It is believed that RISAT-2BR1 along with Cartosat-3, a remote sensing satellite which was launched on November 27, 2019, will also be used for military reconnaissance.
- Before the launch of RISAT (Remote Imaging Satellite), India relied on images provided by Canadian satellites as the current domestic remote sensing spacecraft are not equipped to capture images of the earth during cloud cover.
PSLV
- Initially, the PSLV had a carrying capacity of 850 kg, and over the years it has been enhanced to 1.9 tonnes.
- The PSLV is very versatile, having various mission options.The PSLV had helped take payloads into almost all the orbits in space, including the the Geo-Stationary Transfer Orbit (GTO), the moon and mars, and would soon be launching a mission to the Sun
- The PSLV has failed only twice — the maiden flight of the PSLV D1 in September 1993 and the PSLV C-39 in August 2017.
USMCA trade deal
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II- International Relations
In News
- The US, Mexico and Canada have finalised the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) that will replace the 25-year-old North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).
- But the deal needs approval by legislatures in the three countries before it can move forward.
Salient Features ofU.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA)
- USMCA is intended to last 16 years and will be reviewed every 6 years.
- Agriculture: Farmers of major crops no longer have to worry about President Trump potentially pulling out of the existing Nafta and leaving them fewer major export markets. USMCA also gives dairy farmers more access to Canada.Tariffs of up to 275% have kept most foreign milk out of the Canadian market.
- Auto Rules: Compared with Nafta, USMCA significantly tightens the rules that the auto industry has to follow in order to trade vehicles duty free in North America. A certain proportion of a car will have to be produced by workers with higher wages, and a greater proportion of components will have to originate in North America.
- Pharma: The new dealremoves requirements for a 10-year exclusivity period for biologic drugs [medication derived from or containing components of biological organisms, rather than having been totally synthesized], which would have benefited large pharmaceutical companies.
- It also includes stronger protections for workers, tough environmental rules, updates the trade relationship to cover the digital economy and provides tougher intellectual property protections.
- Digital Freedom: USMCA, unlike the current Nafta, includes rules mandating the free flow of data among the three countries.
- Canada managed to preserve the dispute-settlement mechanism as a protection for its wood industry.
- It also adds provisions to prevent “manipulation” of the trade rules, including covering currency values, and controls over outside countries trying to take advantage of the duty-free market.
Electric commercial aircraft
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Science & Technology
In News
- World’s first fully-electric commercial aircraft took its inaugural test flight in Vancouver, Canada.
- It involved a six-passenger aircraft fitted with an electric motor.
- Seattle-based Engineering firm magniX designed the plane’s motor and worked in partnership with Harbour Air.
- The push to electric could help slash carbon emissions in the high-polluting aviation sector.
- The technology would mean significant cost savings for airlines
- An aircraft like the one flown in Vancouver could only fly about 160km (100 miles) on lithium battery power. Still, electric aircraft that can travel long distances remain a big challenge for the sector.
- The e-plane has to be tested further to confirm it is reliable and safe. In addition, the electric motor must be approved and certified by regulators.
Voice over Wi-Fi (VoWiFi)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Science & Technology
In News
- Bharti Airtel, which recently removed its FUP (Fair Usage Policy) on calls to other networks, has introduced Voice over Wi-Fi (VoWiFi), a first for India
- Wi-Fi Calling makes use of high speed Internet connection, available via broadband, to make and receive high definition (HD) voice calls. Users don’t have to pay extra for these calls as it is using a Wi-Fi network.
- Wi-Fi Calling is aimed especially for areas where cellular networks are not strong.
- This is not much different from a voice call using WhatsApp or any other over-the-top messaging platform, but here the call is from one number to another, and not using an app.
- Wi-Fi Calling can be configured on compatible smartphones by upgrading operating systems to the version that supports Wi-Fi Calling, and enabling this in Settings.
- Airtel says it will soon be compatible with all broadband services and Wi-Fi hotspots, and rolled out in other locations.
(MAINS FOCUS)
SOCIETY
TOPIC: General Studies 1:
- Role of women and women’s organization, population and associated issues, poverty and developmental issues, urbanization, their problems and their remedies.
Rape and sexual crimes law in India

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 12th December 2019
Context:
- There has been an outcry for justice for the victims after the rape and murder of a veterinarian in Hyderabad and the burning of a rape survivor in Unnao, Uttar Pradesh.
History of Rape law:
- First introduced in the Indian Penal Code in 1860.
- The first Law Commission under the chairmanship of Lord Macaulay decided to put the criminal law of the land in two separate codes. (Indian Penal Code & Code of Criminal Procedure )
Indian Penal Code IPC :
- Section 375 of the IPC made punishable the act of sex by a man with a woman if it was done against her will or without her consent.
- Her consent has been obtained by putting her or any person in whom she is interested, in fear of death or of hurt is considered to be Rape
- Sex with or without her consent, when she is under 18 years is considered rape.
- Exception : sexual intercourse or sexual acts by a man with his wife, the wife not being under 15 years of age, is not rape.
- Section 376 provided for seven years of jail term to life imprisonment
Mathura custodial rape case 1972
- In 1972 a young Adivasi girl named Mathura was allegedly raped by policemen in the Desai Gunj Police Station in Maharashtra.
- In the trial that ensued, the sessions court came to the conclusion that she had sexual intercourse while at the police station but rape had not been proved and that she was habituated to intercourse.
- The sessions court acquitted both the policemen, the High Court reversed the order of acquittal.
- When the case reached the Supreme Court, it overturned the High Court verdict saying that “the intercourse in question is not proved to amount rape”.
- SC 1978 verdict, said no marks of injury were found on the girl after the incident and “their absence goes a long way to indicate that the alleged intercourse was a peaceful affair”.
Controversy and Criminal Law (Second Amendment) Act 1983
- Controversial SC 1978 verdict sparked widescale protests across the country seeking a change in existing rape laws. This led to Criminal Law (Second Amendment) Act of 1983.
- Section 114A in the Indian Evidence Act of 1872 was inserted which presumed that there is absence of consent in certain prosecutions of rape if the victim says so. This applied to custodial rape cases.
- Section 228A was added which makes it punishable to disclose the identity of the victim in Rape case
Law Commission:
- Law Commission in its 172th report recommended widening the scope of rape law to make it gender neutral.
- While the rape law in India even today remains gender specific, as the perpetrator of the offence can only be a ‘man’, the 172nd report led to the amendments in the Indian Evidence Act in 2002.
Nirbhaya case in Delhi 2012 &Criminal Law (Amendment) Act in 2013
- Parliament made the amendments on the recommendation of the Justice J.S. Verma Committee, which was constituted to re-look the criminal laws in the country and recommend changes.
- The 2013 Act, increased jail terms in most sexual assault cases and also provided for the death penalty in rape cases that cause death of the victim or leaves her in a vegetative state.
- It also created new offences, such as use of criminal force on a woman with intent to disrobe, voyeurism and stalking.
- Unwelcome physical contact, words or gestures, demand or request for sexual favours, showing pornography against the will of a woman or making sexual remarks stalking was made punishable acid attack was increased to 10 years of imprisonment.
Offences against minors (Kathua Rape case in Jammu and Kashmir)
- Led to the passing of the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2018 which for the first time put death penalty as a possible punishment for rape of a girl under 12 years;
- The minimum punishment is 20 years in jail.
- The minimum jail term for rape, which has remained unchanged since the introduction of the IPC in 1860, was increased from seven to 10 years.
National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) 2017 report:
- A total of 3,59,849 cases were reported against women in 2017.( 2016, 3.38 lakh , 3.2 lakh cases 2015) The number of cases reported has increased. U
- Uttar Pradesh has again topped the list with 56,011 cases of crime against women, followed by Maharashtra with 31,979 cases and West Bengal at 30,002.
- Crimes against women constitute murder, rape, dowry death, suicide abetment, acid attack, cruelty against women and kidnapping.
- ‘Cruelty by husband or his relatives’ accounts for 27.9 per cent of the crimes against women.
- ‘Assault on women with intent to outrage her modesty’ comprise 21.7 per cent, followed by ‘kidnapping and abduction of women’ with 20.5 per cent and ‘rape’ with 7.0 per cent of reported cases.
Rape data :
- ‘Rape’ stands with 7.0 per cent of reported cases.
- A total of 32,559 rapes were reported in 2017 in India.
- Madhya Pradesh has recorded the highest number of rape cases at 5,562 cases being reported in 2017. Uttar Pradesh is second to MP.
- Delhi, saw a decline in reporting of rape cases, in 2017, 13,076 were reported, which is the lowest in the last three years.
- 93.1 percent cases the accused were known to the victims.
- Arunachal Pradesh, Goa, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura can be seen as moderately safer than other states as they recorded the lowest number of cases.
Way forward:
- Make the criminal justice system tougher on an offender committing sexual crimes against women and children.
Connecting the dots:
- Punishments must reinforce people’s faith in the rule of law, not undermine it. Analyse
DEVELOPMENT
TOPIC: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Assam protests against Citizenship Amendment Bill (CAB)
Context:
- In the protests in the Northeast against the Citizenship Amendment Bill (CAB), 2019, the outrage has been most intense, sustained and widespread in Assam.
- Large parts of the other Northeastern states have been exempted from the ambit of the CAB, although there have been protests there too. On the other hand, the larger part of Assam is under CAB.
Reason for protests in Assam
- Angst against the Citizenship (Amendment) Bill rooted in a fear that illegal Bengali Hindu migrants from Bangladesh, if regularized, will threaten cultural and linguistic identities.
- Students, activists, writers, actors, musicians and people from all walks of life thronged the streets to voice their angst against the bill since they believe the bill will pose a serious threat to their livelihood and political destiny.
- Though this provision covers refugees from three nations, the people in the North-East fear that it will primarily benefit the illegal Bengali Hindu migrants from Bangladesh who have settled in “large numbers” across the region.
- Though the BJP has tried to hard sell the bill projecting it as a strategy to protect the Hindu identity of Assam against the influx of Muslims from Bangladesh, it failed to take into account the fear among the Assamese people of cultural hegemony of Hindu Bengalis
- The Assamese fear that if Bengali Hindus and Bengali Muslims join hands, Bangla speakers will easily outnumber Assamese-speaking people in the state, as it has happened in Tripura where Bengali-Hindu immigrants from East Bengal now dominate political power, pushing the original tribals to the margins.
Areas which are exempted
There are two categories that have been given exemption — states protected by the ‘Inner Line’, and areas covered under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution.
- Inner Line Permit (ILP): This is a special permit that citizens from other parts of India require to enter a state protected by the ILP regime. Without an ILP granted by the state government, an Indian from another state cannot visit an state that is under the ILP regime.
- Sixth Schedule: The Sixth Schedule relates to special provisions in administration of certain Northeastern states. It provides special powers for Autonomous District Councils (ADCs) in these states. ADCs have powers to enact laws in areas under their jurisdiction on a variety of subjects, one of its objectives being to boost self-governance by tribal communities.
State by state
- Assam: The state has three Autonomous District Councils, two of which are geographically contiguous. While these are protected, CAB will be in effect in a larger area.
- Meghalaya: This state too has three ADCs. Unlike in Assam, the ADCs in Meghalaya cover almost the entire state. Only a small part of Shillong is not covered. CAB will be effective in that part of Shillong while the rest of the state is protected.
- Tripura: One ADC covers around 70% of the state’s area. However, the remaining 30% holds about two-thirds of the population. CAB is effective in the smaller, more densely populated regions.
- Arunachal Pradesh: Entire state covered under ILP regime, protected from CAB.
- Nagaland: Entire state covered under ILP regime, protected from CAB. So far, only Dimapur used to be outside the regime. Now, ILP has been extended to Dimapur, too, so the whole state is now exempt.
- Mizoram: Entire state covered under ILP regime, protected from CAB. Additionally, the state has three ADCs that are also protected under the Sixth Schedule.
- Manipur: Entire state gets new ILP protection. The state was not protected under either option, but following the introduction of CAB in Parliament, the government has introduced ILP in Manipur too.
Do you know?
- The new amendment to the Citizenship Act of 1955 aims to provide Indian citizenship to Hindu, Sikh, Buddhist, Jain, Parsi and Christian refugees from Afghanistan, Bangladesh and Pakistan.
- A person belonging to any of these faiths – who entered India on or before December 31, 2014 and have lived in the country for six years – can apply for Indian citizenship.
Connecting the dots:
- Citizenship Amendment Bill not only excludes Muslims but creates other complications. Analyse.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1) Consider the following statements about VoWiFi
- It uses high speed Internet connection, available via broadband, to make and receive high definition (HD) voice calls.
- This is not much different from a voice call using WhatsApp or any other over-the-top messaging platform which requires the usage of unique app designed for the purposei.e call cannot be made from one number to another
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Groynes
- A groyne is a shore protection structure which functions as a physical barrier by intercepting sand moving along the shore.
- Groynes made of concrete are generally preferred as they are more durable and absorb more wave energy due to their permeable nature.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements about River Pollution
- The presence of metals in drinking water in trace amounts is required for good health. However, when present above safe limits, they are associated with a range of disorders.
- Mining, milling, plating and surface finishing industries that discharge a variety of toxic metals into the environment are the main source of metal pollution in rivers.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4) Consider the following statements about RISAT-2BR1
- It is a radar imaging earth observation satellite
- Itis meant for applications in various fields like agriculture, forestry, disaster management support and would also serve military purposes
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.5) Consider the following statements about E-plane
- World’s first fully-electric commercial aircraft took its inaugural test flight in Bengaluru, India
- The technology would mean significant cost savings for airlines and could help slash carbon emissions in the high-polluting aviation sector.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 11 DEC 2019 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | B |
MUST READ
Strength in numbers: On judge vacancies
Testing judicial reforms
Brute majority
PMJAY can help bridge the gender gap in availing of healthcare services
Rethink the Social Security Code 2019
Stop Toxic Dope in Its Track and Field











