IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 10th February 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Supreme court on reservations in Job
Part of: GS Prelims –Polity and GS-II- Judiciary
In news:
- The Supreme Court has ruled that reservation in the matter of promotions in public posts is not a fundamental right
- A state cannot be compelled to offer the quota if it chooses not to.
- No mandamus can be issued by the court directing state governments to provide reservations
From Prelims Point of View :
Prerogative writs:
- “prerogative writs” meaning the extraordinary writs or orders granted by the Sovereign when ordinary legal remedies are inadequate
- prerogative writs are habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, certiorari, and quo warranto.
- In India, the Supreme Court can issue prerogative writs under Article 32 of the Constitution, and the High Courts under Article 226.
- The writ can also be issued against inferior courts or other judicial bodies when they have refused to exercise their jurisdiction and perform their duty.
Mandamus :
- Mandamus literally means ‘we command’.
- When issued to a person or body, the writ of mandamus demands some activity on their part
- It orders the person or body to perform a public or quasi-public duty, which they have refused to perform, and where no other adequate legal remedy exists to enforce the performance of that duty.
- The writ cannot be issued unless the legal duty is of public nature, and to whose performance the applicant of the writ has a legal right.
- Under Article 361, mandamus cannot be granted against the President or Governor of a State,
Four-fold jump in Li-ion battery imports since 2016
Part of: GS Prelims –Science & Tech and GS-III- Technology
In news:
- India has quadrupled its imports of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries
- lithium-ion are vital for powering a range of devices from cellphones to electric vehicles
- India lacks manufacturing capacity;
- India is world’s largest importer
- Imports from China, Japan and South Korea
- To promote indigenous development of such batteries, the Union Cabinet in 2019 approved a programme, called a National Mission on Transformative Mobility and Battery
- Electric vehicles are expected to account for a significant share in the growth of the Li-ion battery demand in India
- The government has announced investments worth $1.4 billion to make India one of the largest manufacturing hubs for electric vehicles by 2040.
From Prelims point of view :
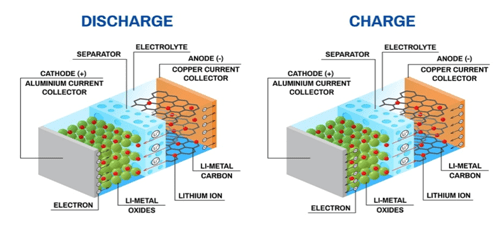
lithium-ion
- Rechargeable battery.
- Used for portable electronics and electric vehicles
- Developed by John Goodenough, Stanley Whittingham, Rachid Yazami and Akira Yoshino
- Lithium ions move from the negative electrode through an electrolyte to the positive electrode during discharge, and back when charging.
- Li-ion batteries use an intercalated lithium compound as the material at the positive electrode and typically graphite at the negative electrode.
- There is a safety hazard since they contain a flammable electrolyte, and if damaged or incorrectly charged can lead to explosions and fires.
- Samsung were forced to recall Galaxy Note 7 handsets following lithium-ion fire
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 10th February 2020
National Mission on Transformative Mobility and Battery:
- Recommend and drive the strategies for transformative mobility and Phased Manufacturing Programmes for EVs, EV Components and Batteries.
- A Phased Manufacturing Program (PMP) will be launched to localize production across the entire EV value chain.
- Determine the contours of PMP, and will finalise the details of such a program.
- The details of the value addition that can be achieved with each phase of localisation will be finalised by the Mission with a clear Make in India strategy for the electric vehicle components as well as battery.
- The Mission will coordinate with key stakeholders in Ministries/ Departments and the states to integrate various initiatives to transform mobility in India.
Electric vehicles:
- An electric vehicle, uses one or more electric motors or traction motors for propulsion.
- An electric vehicle may be powered through self-contained battery, solar panels or an electric generator to convert fuel to electricity.
*** E vehicles and policy related to it will be soon dealt in the mains section
Pangolins be the source of novel coronavirus
Part of: GS Prelims –Environment and GS-III- Conservation
In news:
- Pangolins could be responsible for the spread of the virus to humans in China.
- The genome sequence of the coronavirus isolated from pangolins was 99 per cent identical with that separated from infected humans.
From Prelims Point of view:

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 10th February 2020
Pangolins:
- Pangolins are considered to be one of the most trafficked animals in the world and are classified as a critically endangered species
- People who sell pangolins can be imprisoned for a period of 10 years or morepoached every year due to their “medicinal value” and the consumption of their meat in countries such as China and Vietnam.
- It is believed that the novel coronavirus spread from the seafood market in Wuhan, where live animals are sold
- The SARS coronavirus, which was identified in 2003, is believed to have spread from bats to civet cats to human beings.
Storm, named ‘Ciara’
Part of: GS Prelims –Polity and GS-II- Constitution
In news:
- The storm, named ‘Ciara’ ,referred to as ‘Sabine’
- Hit in UK, Ireland, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Switzerland, and Germany.
- The storm has two names because there isn’t yet a pan-European system in place for labelling weather systems.
From Prelims Point of view:
How cyclones are named?
- The tradition started with hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean, where tropical storms that reach sustained wind speeds of 39 miles per hour were given names.
- (Incidentally, hurricanes, typhoons, cyclones are all the same, just different names for tropical storms in different parts of the world;
- Hurricane in the Atlantic, Typhoon in the Pacific and Cyclone in the Indian Ocean). If the storm’s wind speed reaches or crosses 74 mph, it is then classified into a hurricane/cyclone/typhoon.
- Tropical storms are given names and they retain the name if they develop into a cyclone/hurricane/typhoon.
(MAINS FOCUS)
Science & Technology
Topic: General Studies 2 & 3:
- Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Purifiers – Draft notification by Government
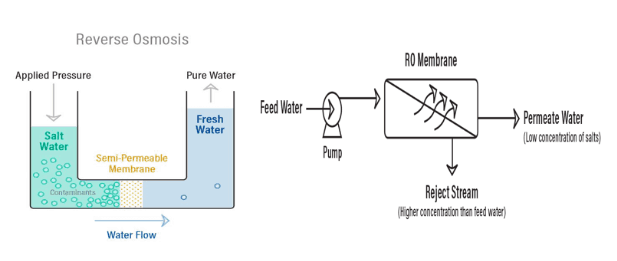
About Reverse Osmosis
- Reverse Osmosis is a technology that is used to remove a large majority of contaminants from water by pushing the water under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane.
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 10th February 2020
- It works by using a high-pressure pump to increase the pressure on the salt side of the RO and force the water across the semi-permeable RO membrane, leaving around 95% to 99% of dissolved salts behind in the reject stream.
- The amount of pressure required depends on the salt concentration of the feed water. Higher the concentration of salt, higher is the pressure required.
- An RO membrane rejects contaminants based on their size and charge
- Reverse Osmosis is also used to produce water that is suitable for many industrial applications that require demineralized or deionized water
Issues with RO System
- Wastage: RO systems now recover only 20 per cent of water while 80 per cent go waste
- Can remove beneficial mineral: The process can cut the levels of calcium and magnesium, which are vital nutrients.
- Membranes get clogged easily which happens when materials build up on the membrane and slow down the flow of water. Thus it requires constant replacement which increases operational costs
- Not 100% purification capability: BIS standards clearly state that RO system is not recommended for treatment of raw water having Arsenic level above 0.1 mg/l and Fluoride level above 8.0 mg/l.
May 2019 NGT order had stated that
- RO Purifiers should be prohibited where TDS (total dissolved solids) – which covers trace chemicals, certain viruses, bacteria and salts – in water was less than 500 miligram per litre (mg/l)
- It had asked the government to redesign the RO system in a way that treated water would have a minimum 150 mg/l TDS concentration.
- It also stressed on remineralisation to compensate for loss of minerals during RO treatment
- It asked RO manufacturers to increase efficiency of systems to recover 60% of water inputs
Draft notification by the Union Environment Ministry (MoEFCC)
- The notification issued on February 3, 2020 mentions that use of membrane-based water purification system (MWPS), mainly RO purifiers, shall be prohibited where drinking water complies with the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
- Enforcement will largely be the responsibility of CPCB and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs), taking water supply agencies on board to certify whether they provide potable drinking water in a particular area as per the prescribed BIS standard.
Concerns with the notification
- The notification does not mention any limits prescribed in NGT order
- The notification implies, these filters are only prohibited if the home gets water supply that conforms to BIS standards for Drinking Water.
- Although several State and city water boards claim BIS standards, the water at homes falls short of the test parameters
- The resort to prohibition (to restrict home filters) may cause consumer apprehension
Conclusion
- The case for restricting people’s choices on the means they employ to ensure potable water is thus weak in view of above concern
- Government’s primary aim should be to persuade authorities to upgrade and supply BIS-standard water at the consumer’s end and it should be done without additional costs.
Do You Know?
- The BIS norms are voluntary for public agencies which supply piped water but are mandatory for bottled water producers.
- The Composite Water Management Index (CWMI) of NITI Aayog says that 70% of water supply is contaminated.
- India is ranked 120th among 122 countries in an NGO, WaterAid’s quality index.
Connecting the dots!
- Nal Se Jal: Government’s mission to ensure piped drinking water to every rural Households by 2024
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q 1. The power of the Supreme Court of India to decide disputes between the Centre and the States falls under its
- advisory jurisdiction
- appellate jurisdiction
- original jurisdiction
- writ jurisdiction
Q 2. Which one of the following pairs of metals constitutes the lightest metal and the heaviest metal, respectively?
- Lithium and mercury
- Lithium and osmium
- Aluminium and osmium
- Aluminium and mercury
Q 3. Consider the following statements:
- Toothless mammals such as Pangolins are not found in India.
- Gibbon is the only ape found in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 08 FEB 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | C |
MUST READ
About India’s refugee treatment:
About abortion law:
About Victim Justice:











