IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 12th May 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
A project to develop human monoclonal antibodies (hmAbs) approved
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health & GS-III – Science and Technology
In News:
- Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) has approved a project to develop human monoclonal antibodies (hmAbs) through New Millennium Indian Technology Leadership Initiative (NMITLI) programme.
- These antibodies can neutralize SARS-CoV-2 in patients.
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is responsible for causing coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
Key takeaways:
- hmAbs shall be generated from convalescent phase of COVID-19 patients.
- High affinity and neutralizing antibodies shall be selected.
- The project aims to anticipate future adaptation of the virus and generate hmAbs clones that can neutralize the mutated virus and combat future SARS-CoV infections.
Important value additions:
New Millennium Indian Technology Leadership Initiative (NMITLI)
- It is the largest public-private-partnership effort within the Research & Development field in the country.
- It seeks to act as a catalyst in innovation-centered scientific and technological developments.
- It also aims to help Indian industry achieve a global leadership position.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb)
- They are antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell.
- They can have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody).
COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In News:
- Recently, India and the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) signed a $500 million “COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project” to strengthen India’s public health preparedness.
- The project was launched in New Delhi, India.
- This is the first ever health sector support from AIIB to India.
Key takeaways:
- This will cover all States and Union Territories across the country and
- It will address the needs of:
- infected people,
- at-risk populations,
- medical and emergency personnel and service providers,
- medical and testing facilities,
- national and animal health agencies.
- It will help strengthen the country’s Integrated Disease Surveillance Program and revamp infectious disease hospitals and medical colleges.
- It will be implemented by:
- the National Health Mission (NHM)
- the National Center for Disease Control (NCDC)
- the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare will be the responsible Ministry for the program.
- The project is being financed by the World Bank and AIIB:
- $1.0 billion – World Bank
- $500 million – AIIB.
Important value additions:
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB)
- It is a multilateral development bank.
- Mission: To improve social and economic outcomes in Asia by investing in sustainable infrastructure and other productive sectors.
- Headquarters: Beijing.
- It began operations in 2016.
Potential distribution of the Sal forest tortoise over unprotected areas
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment
In News:
- According to a recent study by ecologists in the Wildlife Institute of India, Dehradun, over 90% of the potential distribution of the Sal forest tortoise falls outside the current protected area’s network.

Image source :The Hindu
Important value additions:
Sal forest tortoise
- It is a species of tortoise.
- It is also known as Elongated tortoise and Yellow Tortoise.
- It is found in Southeast Asia and parts of the Indian Subcontinent, particularly Northeast India.
- IUCN Status: Critically Endangered.
- It is heavily hunted for food and collected both for local use, such as decorative masks, and international wildlife trade.
- In china, a mixture, made by grinding up the tortoise’s shell, also serves as an aphrodisiac.
Miscellaneous
Shekatkar Committee
- Recently, Indian Defence Minister has approved a proposal for the abolition of numerous posts in the Military Engineering Service (MES).
- This was done according to recommendations of the Lt. Gen. D.B. Shekatkar (Retd.) Committee.
- It was appointed in 2016,
- The recommendations ranged from optimising defence budget to the need for a Chief of the Defence Staff.
(MAINS FOCUS)
POLITY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Parliament and State Legislatures – structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers & privileges and issues arising out of these.
- Separation of powers between various organs dispute redressal mechanisms and institutions.
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Is the Rajya Sabha essential?
Context:
Below editorial covers the following areas –
- Basics or key facts about Rajya Sabha
- Whether we need Rajya Sabha? – Arguments in favour and arguments in against
- Views of proponents and opponents
Key facts about Rajya Sabha
- The Rajya Sabha is the Upper House (Second Chamber or House of Elders) and it represents the states and union territories of the Indian Union.
- It came into being on April 3, 1952 and held its first session on May 13 the same year.
- Government of India Act of 1919 introduced, for the first time, bicameralism. Government of India Act, 1935 proposed an elaborate and improved version of the second chamber, but this never materialised.
- Bicameralism is a specific feature of Federal form of government and was borrowed from the British Constitution.
Do we need Rajya Sabha?
Arguments in favour
- The Rajya Sabha is required to maintain the federal equilibrium by protecting the interests of the states against the undue interference of the Centre.
- The second chamber enables a second and reflective expression of representative opinion.
- Both the Houses check one another and hence instances of parliamentary tyranny can be avoided. In other words, it can ensure that the majoritarian thrust of the Lower House does not undermine rule of law and public institutions.
- Legislation is checked by members who are expected to be sober, wise and well-informed with domain knowledge.
- It represents the interests of the States as a federal chamber. (Promotes Federalism)
- It acts as a deliberative body holding high-quality debates on important issues.
- It helps to initiate proposals for public policy.
- Rajya Sabha can be the voice of sanity, of the excluded, and of citizen rights.
Arguments against
- In 2006 in Kuldip Nayar v. Union of India and Others, the SC held that – Rajya Sabha has turned out to be another chamber of the Parliament akin to the Lok Sabha, except for the mode of selection of its members.
- The deadlock between both Houses on parliamentary matters is a major setback to India’s progress and shows the leadership of all parties in a bad light.
- Cronyism and patronage appointments are increasing.
- Only some members have the necessary qualifications that will do justice to the role of the Rajya Sabha, others do not measure up.
- Many parties are now using the Rajya Sabha as a backdoor to get members elected, most of whom will not be able to win a Lok Sabha election.
- People get in from States they are least connected with.
- Parliamentary logjams and stalling of legislation can be avoided.
Opponents view
- According to Mr. Mohd. Tahir (Constiuent Assembly member) – “Upper House was not essential and viewed it as a creation of imperialism.”
- According to Professor Shibban Lal Saksena – “the second chamber acts as an obstruction in the wheel of progress of the nation as it doesn’t enable quick law-making.”
Proponents view
- According to Naziruddin Ahmad – a second chamber would introduce an element of sobriety and second thought besides lending voice to the constituent units in the legislative scheme of things.
- According to M. Ananthasayanam Ayyangar – a second chamber would check hasty legislation and it can make place for genius people “who may not be able to win a popular mandate”.
- According to N. Gopalaswami Ayyangar – a second chamber will help to “hold dignified debates on important issues and to delay legislations which might be the outcome of passions of the moment until the passions have subsided and calm consideration could be bestowed on the measures which will be before the Legislature.”
- According to Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan, the first Chairman of the Rajya Sabha – Because of Rajya Sabha, Parliament is not just a mere legislative body but also a deliberative one. It enables the members to debate major issues of public importance.
- Lokanath Mishra described it as “a sobering House, a reviewing House, a House standing for quality and the members will be exercising their right to be heard on the merits of what they say, for their sobriety and knowledge of special problems.”
- Rajya Sabha largely duplicates the functions of the Lok Sabha and is unnecessary. – Abbé Sieyès
Conclusion:
The council of states emerged after it was subjected to serious argumentation and underdoing severe scrutiny in the Constituent Assembly. It should be our responsibility to make it an effective and time-bound contributor to India’s parliamentary system.
It has the role of a watchdog, it must assert itself as a House of correction. Its function is to improve legislation passed by the Lower House and is not one of obstruction.
Connecting the dots:
- What measures are needed to make the Council of States more effective and a deliberative body?
- Do you think Rajya Sabha needs reforms? If yes, why and what type of reforms are needed?
- Rajya Sabha is the repository of diverse intellect that ensures in depth scrutiny and wide ranging debates. Even though, it has limited functional powers, its role in India’s polity can’t be belittled. Critically comment.
POLITY/GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and the States and the performance of these schemes.
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health
- Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability, e-governance- applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential
Arogya Setu app: Advantages and Issues
Below editorial covers the following areas –
- What is arogya setu app?
- Its advantages
- Issues concerning the app
- How to overcome the issues
Aarogya Setu
- It is Indian COVID-19 tracking mobile application.
- It is developed by the National Informatics Centre which comes under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- Purpose:
- To spread awareness of COVID-19
- To connect essential COVID-19 – related health services to the people of India.
- It uses the smartphone’s GPS and Bluetooth features to track the coronavirus infection.
- With Bluetooth, it determines the risk if one has been near (within six feet of) a COVID-19 – infected person, by scanning through a database of known cases across India.
- Using location information, one can determine whether a particular location is one of the infected areas.
- It is an updated version of an earlier app called Corona Kavach (now discontinued).
For which category of people has the installation of the app been made compulsory?
- As per the directive issued under the Disaster Management Act, it is compulsory for following people to install the app:
- all people residing in ‘containment zones’,
- all government and public sector staff,
- all employees, both public and private, who are allowed to work during the lockdown,
- Stranded Indians in abroad, once they landed in India through Vande Bharat Mission.
- Travelers who will be traveling in special passenger trains.
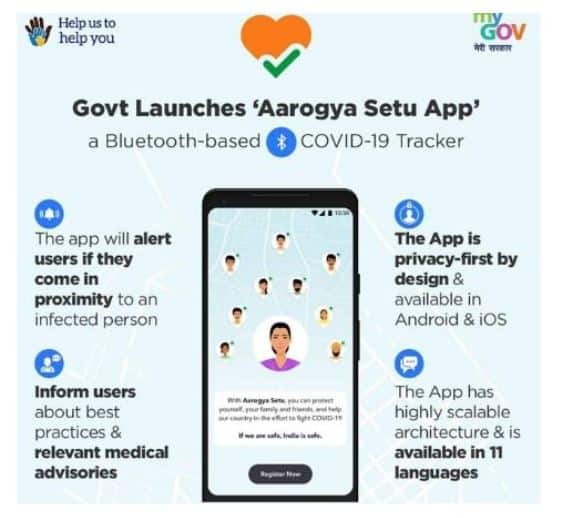
Image source: Click Here
Advantages of the app:
- Individuals and authorities shall remain informed in case they have crossed paths with someone who has tested positive for coronavirus.
- It works on Bluetooth-based technology. Absence of internet connectivity won’t pose a problem.
- The app recommends several measures such as Self Assessment Test, Social distancing, do’s and don’t.
- It informs about the precautionary measures.
- As per the statement by the Prime Minister’s Office, it could also be used as an e-pass for traveling.
- In case, a user is at high risk, the app will advise him/her to go for a test at a nearby testing centre and call the toll-free number 1075 immediately.
- The helpline number for each state is also available.
Issues with the app
- It is imposed through executive order without any legalisation.
- It is being regarded as sophisticated surveillance system.
- Recently, Robert Baptiste tweeted that security vulnerabilities in Aarogya Setu allowed hackers to know who is infected or unwell in the area of his choice. He also gave details of how many people were unwell and infected at the Prime Minister’s Office, the Indian Parliament and the Home Office.
- The app’s Terms of Service (TOS) provides blanket limited liability on the government. Thus, there is no government accountability in case of data theft of users.
- The app breaches the fundamental right to privacy. There is no legal framework to show the breach as reasonable.
- If users have no control over their data, it is a complete violation of their right to informational self-determination and the right to be forgotten.
- The closed source architecture of the app violates transparency principles.
- Under the TOS, the government is obligated to delete certain personal data after a 30-day time period. However, there exists no framework to check compliance of the same.
- Ever-changing rules add to the problem. Recently, the app updated its privacy policy without notifying users. Such actions do not inspire trust.
- There are no safeguards against data theft and other breaches.
- It is not clear if the government has conducted scenario analyses of how the app can be misused or abused. This is crucial in India given how much stigmatisation has already occurred (communities refusing to bury bodies of COVID patients and an instance of the lynching of a person suspected to be positive).
- There are no guidelines about how the government plans to deal with cases of false positives.
- There are no clear instructions to deal with people who may make wrong inference or stigmatise someone on the basis of faulty algorithms.
- The app is useless for the low-income non-smartphone users. There exists no alternative for them as well.
How to overcome the issues?
- The government must heed privacy concerns raised by the Opposition,
- It should look at the experiences and experiments in other countries.
- The app code must be opened so that they can be audited for design and programming flaws. For example, Singapore’s TraceTogether app was made open source, thus allowing researchers and experts to test the architecture and suggest measures to correct vulnerabilities.
- It will help in bringing transparency and deal with bugs.
- India must contemplate a legal design around the app, which strikes a balance between disease containment and privacy.
- It should address fears among the public that it may become a permanent mass surveillance instrument.
- It should also ensure that there is sufficient anonymity of data and access is limited.
- It must resort to methods that cause the least harm.
Conclusion
Across India, there are efforts to build databases of people’s health records to enable easier treatment, including through telemedicine.
If instances of misuse of the Aarogya Setu app emerge, then people will not trust other government initiatives involving health records, even if they are undertaken with due care, inclusive consultations, and respect for privacy.
Connecting the dots:
- How well is India equipped to deal with the COVID-19 pandemic post the lockdown? Examine.
- What are the controversies surrounding the Arogya Setu app? Discuss in detail.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 With regard to new Millennium Indian Technology Leadership Initiative Program, consider the following statements:
- It is an initiative launched by private Research and Development companies of India.
- A project to develop human monoclonal antibodies was recently approved by CSIR through this program
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding monoclonal antibodies:
- They are all made by immune cells which are identical.
- They have multivalent affinity to the same epitope.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project was launched between India and which of the following organisation/Bank?
- The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
- International Monetary Fund
- World Health Organisation
- Asian Development Bank
Q.4 Consider the following statements regarding Sal forest tortoise:
- It is critically endangered according to IUCN status.
- It is also used as an aphrodisiac
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 11th May 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
About U.S – China confrontation over international trade
About India’s first war of Independence
About EU fiscal stimulus
About Indian states’ consensus over special trains












