IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
India-Bangladesh Inland Waterways
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- International relations
In news
- The trial run on a new river route from Daudkandi in Bangladesh to Sonamura in Tripura started recently.
- Distance covered will be 93 km through river Gumti or Gomati.
- The route will connect Tripura with Bangladesh using the inland waterways for the first time.
- It will greatly enhance connectivity between Bangladesh and the North Eastern states of India boosting bilateral trade with Bangladesh.
- The opening of the new route follows the signing of the 2nd addendum to the Protocol for Inland Water Trade & Transit (PIWTT) in May 2020 which opened two new routes.
Do you know?
- The PIWTT was signed between India and Bangladesh in 1972 to connect the two countries through inland waterways.
Coal Gasification and Liquefaction webinar held
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Energy resources
In news
- The Union Coal Ministry organised a webinar on Coal Gasification and Liquefaction recently.
Key takeaways
- India aims for 100 million tonnes (MT) coal gasification by 2030 with investments worth over Rs. 4 lakh crores, said Pralhad Joshi, Union Minister of Coal and Mines.
- For encouraging use of clean sources of fuel, the government has provided for a concession of 20% on revenue share of coal used for gasification.
- This will boost production of synthetic natural gas, energy fuel, and urea for fertilisers and production of other chemicals.
Do you know?
- For development of Surface Coal Gasification in India, a Steering Committee has been constituted under the chairmanship of Dr. V.K. Saraswat, Member, NITI Aayog comprising members from the Ministry of Coal.
- CIL has also planned to set up at least 3 gasification plants (besides Dankuni) on BOO basis (Build-Own-Operate) through global tendering and has signed an MOU with GAIL for marketing synthetic natural gas.
Important value additions
Coal gasification
- It is the process of producing syngas—a mixture consisting primarily of carbon monoxide, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, natural gas, and water vapour —from coal and water, air and/or oxygen.
Coal liquefaction
- It is a process of converting coal into liquid hydrocarbons: liquid fuels and petrochemicals.
Protests Against Farm Ordinances
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Centre-state Relations; Policies and interventions
In news
- Recently, the Punjab Assembly passed a resolution and rejected the Centre’s recent farm ordinances and the proposed Electricity (Amendment) Bill 2020.
Key takeaways
The ordinances include:
- Farmers’ Produce Trade and Commerce (Promotion and Facilitation) Ordinance, 2020
- Farmers (Empowerment and Protection) Agreement on Price Assurance and Farm Services Ordinance, 2020
- Essential Commodities (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020.
- These ordinances are expected to allow free movement of agricultural produce between states and let the farmers decide to whom they want to sell their crops.
- The Electricity (Amendment) Bill 2020 centralizes the power sector through establishment of Electricity Contract Enforcement Authority.
- Recognition of franchisees and sub- licensees under the Bill might open the sector to private players.
Punjab’s Stand:
- Entry 14 of List II of the Constitution comprises agriculture as the subject of the states.
- Therefore, the three ordinances passed by the Centre are against the Constitution of India.
- These ordinances are a direct encroachment upon the functions of the states and against the spirit of cooperative federalism enshrined in the Constitution.
Important value additions
- Article 246 adopts a threefold distribution of legislative power between the Union and the states.
- The subject-wise distribution of this power is given in the three lists of the Seventh Schedule of the constitution:
- List-I- the Union List
- List-II- the State List
- List-III- the Concurrent List
SC Decision on UGC Guidelines on Conduct of Examinations
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Judiciary; Education
In news
- The Supreme Court ruled that the states are empowered under the Disaster Management Act, 2005 (DM Act) to override University Grants Commission (UGC) exam guidelines in order to protect human lives amid the Covid-19 pandemic.
Key takeaways
- It held that universities and other institutions of higher education will have to conduct the final-year exams and cannot promote students on the basis of internal assessment or other criteria.
- In case of a disaster, the priority of all authorities under the DM Act is to immediately combat the disaster and contain it to save human life.
- In future, if any State found it impossible to conduct the exams by the deadline given by UGC and wanted to postpone them, it could apply to the UGC.
- The States and universities cannot dismiss UGC guidelines as being merely advisory.
- SC rejected the argument that compelling attendance by holding physical examination is a violation of the ‘Right to Life’ under Article 21.
Foundation Day of AREAS
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Energy resources; Renewable sources of Energy
In news
- On the 6th Foundation Day (27th August 2020) of the Association of Renewable Energy Agencies of States (AREAS), the government has launched a website and telephone directory for AREAS.
Important value additions
AREAS
- Agenda Behind AREAS: State Nodal Agencies (SNAs) for Renewable Energy (RE) interact and learn from each other’s experiences and also share their best practices and knowledge regarding technologies and schemes/programmes.
- Members: The Union Minister for New & Renewable Energy (NRE) is the Patron of the Association and Secretary, MNRE is the ex-officio President of the Association. All SNAs are members of the Association.
- Formation: It got registered under Society Registration Act, 1860 on 27th August 2014.
NIDHI-EIR program launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Entrepreneurship; Innovation
In news
- A brochure featuring Entrepreneurs in Residence (EIR) was recently launched.
- Launched under: National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI) programme.
- Concerned department: Department of Science & Technology (DST) Secretary.
- The brochure details what the EIRs are working on and some highlights about them.
- It is also meant to be a directory of all EIRs.
Important value additions
- NIDHI supports aspiring entrepreneurs for pursuing a promising technology business idea over a period up to 18 months with a subsistence grant up to Rs 30000 per month with a maximum cap for total support of Rs 3.6 lakh to each EIR over a maximum of 18 months.
- The NIDHI-EIR programme provides tremendous opportunities for innovative entrepreneurs to expand their networks and get critical feedback on their ventures in order to promote their entrepreneurial career goals and aspirations.
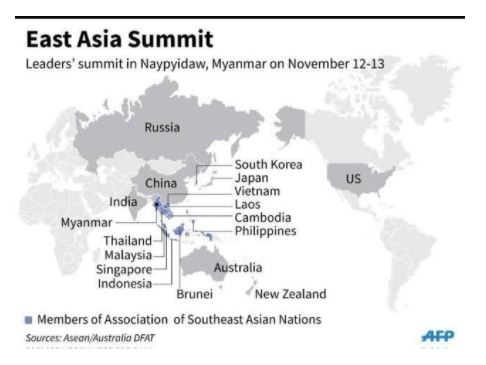
Eighth East Asia Summit Economic Ministers’ Meeting
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Global Groupings; International relations & GS-III – Trade
In news
- Recently, the 8th East Asia Summit Economic Ministers’ Meeting (EAS-EMM) was held virtually.
- Attended by: 10 ASEAN members and eight other nations, including India, the USA, and China.
Key takeaways
- The importance of strengthening regional supply chains to make them resilient in times of Covid-19 pandemic and to increase economic growth was highlighted.
- Any trade-restrictive emergency measures put in place to address the impact of Covid-19 must be consistent with the WTO rules.
- They must not create unnecessary barriers to trade.
- Support for the necessary reforms in the WTO was also discussed.
- Facilitating the essential movement of people across borders.
- Commitment to facilitate supply chain connectivity and inclusion of essential goods.
- Harness the opportunities of the digital economy to overcome the challenges posed by restricted movement.
Important value additions
- It was established in 2005.
- It is a forum of 18 regional leaders for strategic dialogue and cooperation on the key political, security, and economic challenges facing the Indo-Pacific region.
- India is one of the founding members of the East Asia Summit.
- Membership: ASEAN members and 8 other countries namely Australia, China, Japan, India, New Zealand, South Korea, Russia and USA.
- It is an ASEAN-centred forum so it can only be chaired by an ASEAN member.
- ASEAN members: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Miscellaneous
MEDBOT
- Indian Railways has developed a remote-controlled medical trolley named ‘MEDBOT’ to help deliver food and medicines to COVID-19 patients.
- It is providing service in the Central Hospital of the Diesel Rail Engine Factory of Indian Railways.
Indra 2020
- It is a bilateral naval exercise India and Russia.
- It is to be held in the Andaman Sea close to the Strait of Malacca instead of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- It will be the first bilateral naval exercise since all such engagements were suspended due to Covid-19 pandemic.
- The Strait of Malacca connects Indian Ocean to the South China Sea.
- It is also a prominent trade route between East Asia and West Asia-Europe.
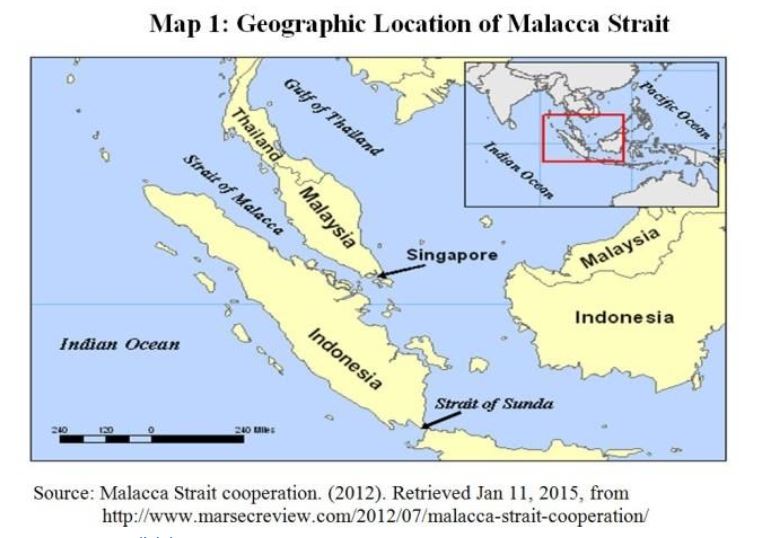
Image source: Click here
(MAINS FOCUS)
EDUCATION / GOVERNANCE/ SCIENCE & TECH
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Education, Human Resources
- e-governance- applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential;
Digital Education
Context: COVID-19 pandemic has put spotlight on the need to push Digital Education as well as the challenges that lie ahead with it.
Challenges to Education Sector due to Pandemic
- Suspension of Learning Centres: Most schools and colleges campuses will be closed through 2020 due to an increasing number of COVID cases. This could even extend to 2021.
- Safety and security of students, teachers and staff will be challenging whenever educational institutes reopen
- Increased Maintenance Cost: Schools and Colleges need to ensure hygiene to check the COVID-19 spread and this involves increased usage of disinfectants and sanitizers
- Redesign Classrooms: Some of the educational institutes have started online classes to ensure continuum of learning. When these institutes reopen they need to upgrade their school digital infrastructure to deal effectively with future such breaks
- Financial Difficulties: Institutes are finding it difficult to pay teachers without students and parents are finding tough to pay fees without work
The answer to the education crisis during the pandemic has been to offer online education. However, there are serious issues related to it, some of which are
- Internet Access: It is estimated that only about 25 per cent of Indian households have an internet facility. For rural households, that number drops to 15 per cent.
- Teacher Training: Teachers are not adequately trained to impart education through online mediums.
- Underprepared: Government schools and colleges do not have the resources to provide digital education.
- Regulation: In India there is lack of a proper policy on digital education, infrastructure and multiple languages.
- Parenting Issues: Additional burden on parents to ensure that their Children attend the online classes and this impacts the productivity of their work
- Students Discipline: There is inadequate space and peace at home for students to concentrate on learning.
- Logistical Issues: Digital education requires uninterrupted broadband connectivity for several hours a day
- Lacks Holistic Approach: Digital education is not about videos of lectures on blackboards by teachers on the internet. It is about appropriate platforms, technology, tools, interactivity, curation, content and a lot more.
Government Initiatives in past to help digital education
- NOFN — National Optical Fibre Network (Now called Bharat Network)
- The objective of this programme is to connect all 2,50,000 panchayats at the cost of over Rs 40,000 crore
- It was conceptualised as a bulk broadband common infrastructure for the country. Overlaying education and health services up to panchayats and villages was an important component of the strategy.
- It has reached many rural areas telecom operators did not want to serve due to lack of profitability. The Universal Service Obligation (USO) fund was used to build NOFN.
- However, the NOFN is still not completely operational, after almost eight year
- National Knowledge Network (NKN)
- The NKN was established as a high bandwidth, low latency network to connect all knowledge-creating organisations comprising IITs, IIMs, universities, research labs and other e-governance institutions up to the district level.
- It was aimed at encouraging collaborative development and building a repository of knowledge in all fields.
- This network exists and is fully functional.
- However, only a few institutions take full advantage of it because of a lack of understanding, local facilities, funding and technical expertise.
Way Ahead
- The driving force behind NOFN and NKN was to build an IT-based teaching system, which could address the shortage of quality teachers and school infrastructure at the bottom of the economic pyramid
- There is need to relook at the NOFN and make it a core component of digital education ecosystem of our country.
Connecting the dots:
POLITY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Parliament and State legislatures—structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers & privileges and issues arising out of these.
Question Hour and Democracy
Context: The Union Government has announced that in the forthcoming session of Parliament (monsoon session that starts on September 14) there will be no Question Hour. The stated reason for this is the situation created by the COVID-19 pandemic
What is Parliamentary Form of Government?
- A parliamentary form of government in the one in which the executive is accountable to the electorate through a legislature which in turn is periodically elected by the electorate.
- This accountability lies at the heart of democratic government and is implemented through procedures put in place by the legislature whose functions include
- Lawmaking
- Controlling the national finances
- Approving taxation proposals
- Having discussions on matters of public interest and concern
- Each of these functions is discharged, daily or periodically, during sittings of the legislature and cover questions, adjournment motion, calling attention, half-an-hour discussion, motion of no confidence, questions of privilege, etc
What is Question Hour?
- The first hour of every parliamentary sitting is slotted for the Question Hour where Members of Parliament raise questions about any aspect of administrative activity.
- In a starred question, a member seeks an oral answer from the concerned minister and this can be followed by supplementary questions, whereas in the case of unstarred questions, a written answer is provided, and no supplementary question can be asked
- Short notice question is one that is asked by giving a notice of less than ten days. It is answered orally.
- Ministries receive the questions 15 days in advance so that they can prepare their ministers for Question Hour.
- The presiding officers of the both Houses (Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha) are the final authority with respect to the conduct of Question Hour.
- Question Hour is regulated according to parliamentary rules
- Question Hour in both Houses is held on all days of the session. But there are two days when an exception is made (Day of President’s address & During Budget presentation)
- With the broadcasting of Question Hour since 1991, Question Hour has become one the most visible aspects of parliamentary functioning
Significance of Question Hour
- Instrument of Accountability: During the Question hour, Members of Parliament (MPs) ask questions to ministers and hold them accountable for the functioning of their ministries.
- Regularity: The daily ‘Question Hour’ has an unmatched criticality on account of its regularity and its availability on a basis of equality to every Member of the House, Rajya Sabha or Lok Sabha.
- Broad Scope: It has a special significance in the proceedings of Parliament since it covers every aspect of government activity, domestic and foreign.
- Leads to Wider Debate: Though questions are pointed & specific, our parliamentary history records instances of answers given to questions leading to wider debates, inquiries, and even administrative scandals.
- Public Awareness: The information made available through Question Hour adds to public information essential to informed debates on matters of interest or concern.
- Stance of Executive: The advantage of Question Hour to the government is that its position in the matter is authoritatively explained
What is the criticism of government’s move to suspend Question Hour?
- Reduced Space for Opposition: The rest of the business of Houses was tightly controlled and set by the government, leaving only Question Hour to hold the government accountable.
- Against the Spirit of Democracy: Suspension of Question Hour is not good sign in democratic principles especially in a parliamentary democracy.
- Bad Precedence: Parliament is the beacon of legislative functioning and its functioning will set the precedent for Vidhan sabhas to follow in the future.
- Lacks Consensus: The move to suspend Question Hour due to pandemic and to find alternate options was not discussed with leaders of political parties and groups
How has government responded to above criticisms?
- The government has later clarified that the Unstarred Questions will continue to be received and answered and that the change will relate only to Starred Questions and the Supplementary questions emanating from them that require to be answered orally.
Conclusion
The test of a functioning democracy is its ability to face crises — social, economic, political — and seek correctives premised on institutions of democracy. A resort to what has been called ‘the politics of avoidance’ does not help the process.
Value Addition
Zero Hour
- Zero Hour is an Indian parliamentary innovation. It is not mentioned in the parliamentary rules book.
- Under this, MPs can raise matters without any prior notice.
- The zero hour starts immediately after the question hour and lasts until the agenda for the day (i.e. regular business of the House) is taken up.
- In other words, the time gap between the question hour and the agenda is known as zero hour.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following are not the members of ASEAN?
- Cambodia
- Indonesia
- Laos
- India
- South Korea
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 3 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding river Gomati or Gumti:
- It is a tributary of the Ganges.
- It flows through Tripura and Bangladesh.
- Trial run of inland waterway was recently done through this river for the first time.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
Q.3 Indra 2020 is to be held between which of the following countries?
- India and Japan
- India and USA
- India and Russia
- India and Thailand
Q.4 Strait of Malacca is a strait between which of the following countries?
- Malaysia and Thailand
- India and Sri Lanka
- Malaysia and Indonesia
- Indonesia and Philippines
ANSWERS FOR 3rd September 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | A |
Must Read
About relief for telecom operators:
About gaps in India’s health care digital push:
About raising the marriage age for women:











