IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
US Justice Department sues Google in Antitrust Case
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Technology; Internet
In news
- Recently, the US Justice Department sued Google.
- It has accused the company of illegally abusing its dominance in internet search.
- It has been harming competitors and consumers.
Key takeaways
- The action against the company comes after a report by the US House of Representatives panel.
- The panel had found that Google, Facebook Inc, Apple Inc and Amazon.com Inc all abused their power as gatekeepers in the digital economy to diminish competitive threats.
- Google is illegally protecting its dominant position in the market for search and search advertising through the deals it has signed with tech companies.
- Google has contracts with smartphone makers that use its Android operating system. These require them to install its search engine as the default.
- All this stifles competition and innovation from smaller startups and harms consumers by reducing the quality of search and limiting privacy protections and alternative search options.
Do you know?
- Many countries have broad laws that protect consumers and regulate how companies operate their businesses.
- The goal of these laws is to provide an equal playing field.
- These are called antitrust laws.
- Also, various antitrust probes are going on against Google in India.
- Google has had run-ins with regulators, especially the Competition Commission of India (CCI).
Punjab becomes the first State to reject Farm Acts
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions; Federalism
In news
- Recently, Punjab became the first State to reject the Central government’s three Farm Acts.
- It also passed three Bills to negate the Union laws.
- It also rejected the proposed Electricity Amendment Bill and demanded their immediate annulment.
Key takeaways
Three farm Bills introduced by the Punjab assembly
- The Farmers Produce Trade and Commerce (Promotion and Facilitation) (Special Provisions and Punjab Amendment) Bill, 2020: (1) Seeks to ensure that sale or purchase of wheat or paddy in Punjab is not allowed below the Minimum Support Price (MSP); (2) Seeks to provide for punishment for harassment of farmers or payment of less price to the farmers.
- The Farmers (Empowerment and Protection) Agreement on Price Assurance and Farm Services (Special Provisions and Punjab Amendment Bill, 2020: (1) It provides for imprisonment of not less than three years and fines for sale-purchase of wheat or paddy under a farming agreement below the MSP.
- The Essential Commodities (Special Provisions and Punjab Amendment) Bill, 2020: (1) It prevents hoarding and black-marketing of agricultural produce; (2) Seeks to ensure status quo ante with regard to implementation of ‘The Essential Commodities (Amendment) Act, 2020’.
- The Punjab bills have reintroduced market fees or licences for private players outside the APMCs which the central law had abolished .
- The Assembly also introduced Code of Civil Procedure (Punjab Amendment) Bill, 2020.
- It seeks to exempt agricultural land not exceeding 2.5 acres from Section 60 of The Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, which provides for attachment of various properties.
- It also seeks to exempt the Properties of the farmers such as cattle, implements, cowsheds, etc from attachment.
China objects to official exchanges between India and Taiwan
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- Recently, China objected to any official exchanges between India and Taiwan.
- China also objected to India wishing Taiwan “Happy National Day” (October 10) and referring to it as a country.
- China is also opposing inclusion of Australia in the upcoming Malabar naval exercise.
Important value additions
Taiwan – the Republic of China (ROC)
- It is an island off the southern coast of China that has been governed independently from mainland China since 1949.
- It is not a member of the United Nations and is the largest economy outside the UN.
- China views it as a province only.
- It has its own democratically elected government
Russia proposes to Extend New START Treaty
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- The Russian President has proposed to extend the New START (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty) by one year.
- It is a Treaty between the USA and Russia expiring in February 2021.
Key takeaways
- It is a treaty on measures for the further reduction and limitation of strategic offensive arms.
- It came into force on 5th February, 2011.
- It is a successor to the START framework of 1991 (at the end of the Cold War) that limited both sides to 1,600 strategic delivery vehicles and 6,000 warheads.
- It continues the process of verifiably reducing the USA and Russian strategic nuclear arsenals by limiting both sides to 700 strategic launchers and 1,550 warheads.
- It will expire in February 2021 unless extended for five more years.
State of Global Air 2020 released by the Health Effects Institute
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Pollution
In news
- Recently, State of Global Air 2020 was released by the Health Effects Institute (HEI).
- HEI is an independent, nonprofit research institute funded jointly by the USA’s Environmental Protection Agency and others.
Key takeaways
- It highlights that air pollution is the largest risk factor for death among all health risks.
- It is the first-ever comprehensive analysis of air pollution’s global impact on new-borns.
- India, Bangladesh, Pakistan and Nepal are among the top ten countries with the highest PM2.5 (particulate matter) exposures in 2019.
- All these countries also experienced increases in outdoor PM2.5 levels between 2010 and 2019.
- India is also among the top ten countries with highest Ozone (O3) exposure in 2019.
- Among the 20 most populous countries, India recorded the highest increase (17%) in O3 concentrations in the past ten years.
- Long-term exposure to outdoor and household (indoor) air pollution contributed to over 1.67 million annual deaths from stroke, heart attack, diabetes, lung cancer, chronic lung diseases, and neonatal diseases, in India in 2019.
Do you know?
- High PM contributed to the deaths of more than 1, 16, 000 Indian infants who did not survive their first month.
- More than half of these deaths were associated with outdoor PM2.5 and others were linked to the use of solid fuels such as charcoal, wood, and animal dung for cooking.
Government working on the formation of Integrated Theatre Command
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Defence; Security
In news
- The government is working on the formation of integrated theatre commands after the appointment of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS).
Key takeaways
- An integrated theatre command envisions a unified command of the three Services, under a single commander, for geographical theatres (areas) that are of strategic and security concern.
- Such a commander will be able to bear all resources at his disposal with greater efficiency.
- The commander will not be answerable to individual Services.
- Integration of the three forces will also avoid duplication of resources.
- The integration will strengthen cohesion in the defence establishment.
Do you know?
- The Shekatkar committee has recommended the creation of 3 integrated theatre commands — northern for the China border, western for the Pakistan border, and southern for the maritime role.
Government expands Production-Linked Incentive Scheme
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions & GS-III – Industry
In news
- The government will extend the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme to eight more sectors to boost domestic manufacturing.
Key takeaways
- All the sunrise and important sectors are proposed to be covered in this.
- The sectors may be automobile, networking products, food processing, advanced chemistry and solar PV manufacturing.
- Through PLI Scheme, incentives will be paid only if the manufacturers make the goods.
- This scheme will give cash incentives for five to seven years.
Important value additions
PLI Scheme for Large Scale Electronics Manufacturing
- The scheme proposes a financial incentive to boost domestic manufacturing and attract large investments in the electronics value chain including electronic components and semiconductor packaging.
- Under the scheme, electronics manufacturing companies will get an incentive of 4 to 6% on incremental sales (over base year) of goods manufactured in India for a period of next 5 years.
- The scheme shall only be applicable for target segments – mobile phones and specified electronic components.
- With the help of the scheme, domestic value addition for mobile phones is expected to rise to 35-40% by 2025 from 20-25%.
- It shall also generate 8 lakh jobs more, both direct and indirect.
Do you know?
- The government has launched the PLI scheme for mobile phones (electronic manufacturing) and it was also extended to pharma products and medical equipment sectors.
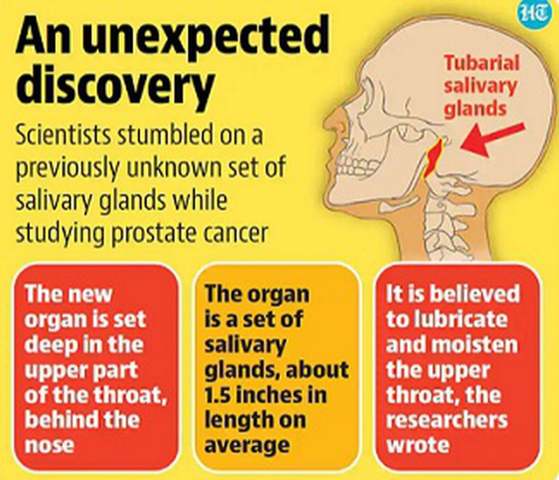
Tubarial Salivary Glands: Potential new organ in the human throat
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Science and Technology
In news
- Scientists in the Netherlands have discovered a potential new organ in the human throat.
- The discovery was made while carrying out research on prostate cancer.
- Researchers at the Netherlands Cancer Institute have identified a set of salivary glands deep in the upper part of the throat and have named them “tubarial salivary glands”.
- The discovery may be important for cancer treatment.
- Till now, this nasopharynx region (behind the nose) was thought to host only microscopic, diffuse, salivary glands.
- However, the newly discovered glands are about 1.5 inches (3.9 centimeters) in length on average.
- Location: These are located over a piece of cartilage called the torus tubarius.
- Function: The glands probably lubricate and moisten the upper throat behind the nose and mouth.
Do you know?
- Till now, there were three known large salivary glands in humans: one under the tongue, one under the jaw and one at the back of the jaw, behind the cheek.

(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 1,2:
- Contemporary World History
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
Greece- Turkey Clash
Context: Greece (EU member) said it would be extending a wall along its border with Turkey (candidate for EU membership) to prevent potential mass crossings by migrants into its territory.
Greece-Turkey Relations
- For centuries, Turkey and Greece have shared a chequered history.
- In 1830, Greece won independence from modern Turkey’s precursor, the Ottoman Empire.
- In 1923, the two countries exchanged their Muslim and Christian populations – a migration whose scale has only been surpassed in history by the Partition of India.
- The two nations continue to oppose each other on the decades-old Cyprus conflict, and on two occasions have almost gone to war over exploration rights in the Aegean Sea.
- Both countries are, however, part of the 30-member NATO alliance
Relations between the two nations have seen a marked downturn this year.
- Issue of Migration
- Consequences of Syrian War: Since the beginning of the Syrian war in 2011, vast numbers of displaced Syrians have sought refuge in Turkey.
- Refugee Crisis: According to the latest known figures, Turkey hosts some 37 lakh refugees from Syria, and is feeling the socio-economic and political strain of their presence in the country.
- Refugee Crisis spilling to EU: In 2015, the refugee crisis reached its peak as thousands drowned while attempting to cross over to the West using water routes. Around 10 lakh reached Greece and Italy.
- Deal with EU: In 2016, Turkey agreed to prevent migrants from crossing into the EU, and the bloc in return promised funds to help the former manage the refugees on its soil.
- Reneging on Deal: However, in February 2020, Turkey said it would not be honouring the 2016 agreement, asserting its inability to sustain another refugee wave. As a result, Turkey had allowed thousands of migrants to cross the border into Greece and the European Union, irking the latter
- Using deal as leverage: Turkey is criticised for using the migrant issue as a means to bring its western allies on board with its military campaign in Syria’s Idlib province, where hostilities had escalated in preceding weeks.
- Greece’s response: Greek government has said it would extend its already existing 10 km long wall with Turkey by an additional 26 km by the end of April 2021, spending EUR 63 million on the project.
- Eastern Mediterranean dispute
- For 40 years, Turkey and Greece have disagreed over rights to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Aegean Sea, which covers significant oil and gas deposits.
- Increasingly assertive under President Erdogan, Turkey in July 2020 announced that it would be exploring a disputed part of the sea for oil and gas.
- Greece responded by placing its air force, navy and coastguard on high alert.
- After brief peace, Greece has once again started conducting seismic surveys near the Greek island of Kastellorizo. Greece considers the waters surrounding the island as its own and described Turkey’s actions as a “direct threat to peace in the region”.
- Greece Stand: A signatory of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), it maintains that its continental shelf should be calculated while considering its island territories in the Eastern Mediterranean.
- Turkey’s stand: Ankara, which has not signed UNCLOS, argues a nation’s continental shelf should be calculated from its mainland, and maintained that its activity was “fully within Turkish continental shelf”
- The Hagia Soophia row
- The Hagia Sophia was originally a cathedral in the Byzantine Empire before it was turned into a mosque in 1453, when Constantinople fell to Ottoman forces.
- In the 1930s, however, Mustafa Kemal Ataturk, the founder of the Republic of Turkey, shut down the mosque and turned it into a museum in an attempt to make the country more secular.
- Many Greeks continue to revere the Hagia Sophia, and view it as a key part of Orthodox Christianity.
- President Erdogan of Turkey converted Hagia Sophia from a museum into a mosque which Greece called the site’s conversion an “affront to civilisation of the 21st century”.
Implications of rising Greece-Turkey Tensions
- Rising Nationalistic tendencies in both the countries which would run against the plans of integration of Turkey with EU
- Another war in the region, especially in the wake of pandemic, will further plunge the countries into recession and poverty.
- All this impacts the stability in the region which further puts strain on International Organisations tasked with maintaining peace in world. UN, whose credibility is already battered due to allegations of politicisation of institution, will be under immense pressure to prove its utility.
- Rule of law in international Politics will be challenged.
- India: The bilateral relation of India-Turkey will be further strained especially after Turkey has voiced its criticism on India’s abrogation of Article 370 and enactment of Citizenship Amendment Act.
Conclusion
All stakeholders in the region – US, EU, Russia, Iran, Syria – should try to help resolve the conflict at the earliest before it blows out of proportion
INTERNATIONAL/ ECONOMY / GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
Reviving WTO
Context: The WTO is on the verge of getting fresh top leadership
Challenges of WTO
- Backlash Against Globalisation: There is a backlash against globalisation, free trade and by extension, against international organisations such as WTO.
- New Negotiating positions by Nations: People who have lost out from technological disruption, globalisation or free trade have found an important voice and have started asserting themselves through political choices made in national elections (electing conservative parties/people to power). These changes are subsequently reflected in country negotiating positions in the WTO.
- Restoring Faith of common man: WTO has to demonstrate that it is on the side of the underdog i.e. it’s mission is to enhance the conditions of poor people and not further the agenda of corporates
- To build New Agenda: It is common knowledge that the Doha Round of trade negotiations has long been dead. The new task for WTO is to build a consensus around a new common work programme and a negotiating agenda.
One solution to overcome above challenges is by announcing that the WTO’s future work programme and negotiating agenda will be based on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) so painstakingly agreed upon by all UN members in 2015.
A new SDG round of trade negotiations has numerous advantages for the WTO.
- First, it is hard to disagree with the SDGs themselves since all countries have publicly committed themselves to achieving it within a definite time frame
- Second, it will be a splendid opportunity for the much-maligned WTO to get its mojo back and secure endorsement for the principle of free trade. After all, it is a matter of consensus among economists of all hues that trade is indeed the best instrument for achieving many of the SDGs.
- Third, the WTO’s future work programme and negotiating agenda must be directly linked to the objectives of the Marrakesh Agreement establishing the WTO, which talks of promoting sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth as well as full and productive employment and decent work for all.
What Steps should WTO take in future?
- Recalibrating Special treatments
- The WTO must carefully recalibrate the Special and Differential Treatment for countries that deserve it.
- The two geographical regions which display “extreme poverty” are: parts of Africa and South Asia. It goes without saying therefore that countries belonging to these two geographical regions must get Special and Differential Treatment without any question.
- Extreme poverty is now well defined and is backed by the Oxford Multidimensional Index of Poverty, so objective criteria may be utilised for deciding countries which are eligible.
- This automatically takes care of the American argument that countries such as Singapore and South Korea (or China for that matter) cannot lay automatic claim to Special and Differential Treatment.
- Conclude negotiations on Fisheries Subsidies
- The multilateral negotiations on Fisheries Subsidies is proceeding apace and must be concluded by the next Ministerial Conference in June 2021.
- Again, these negotiations must be consistent with SDG-14 which is defined thus: Conserve and use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development.
- Developing countries and least-developed countries whose citizens depend on fisheries for their livelihood must be treated appropriately in these negotiations.
- Correct Agriculture Subsidies
- Agriculture has always been a contentious subject in past WTO negotiations.
- SDG-2 provides sufficient guidance in this critical area: End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture.
- The US, EU and other rich countries have long subsidised their agriculture, often with disastrous consequences for the economies of developing and least-developed countries. It is time to make amends.
- Electronic Commerce
- Electronic Commerce poses enormous challenges for developing and least-developed countries. These challenges have to do with digital infrastructure, digital literacy and data sovereignty.
- The SDG-9 that talks of building resilient infrastructure, promotes inclusive and sustainable industrialisation and foster innovation, should guide these negotiations.
- Developed countries need to take into account the serious digital divide that currently exists when they pursue their national interests in these negotiations.
Conclusion
- The above is obviously not an exhaustive list but an illustrative one.
- More crucially, it provides a template for the new round of trade negotiations and the work programme of the WTO by anchoring it in the all-important SDGs.
- Such a move can kill two birds with one stone: to revive the negotiating agenda as well as to resuscitate the WTO itself.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding Taiwan:
- It is a member of United Nations.
- It has its own democratic elected government.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty is a treaty between which of the following countries?
- Russia and India
- USA and Russia
- Japan and Russia
- USA and Japan
Q.3 State of Global Air 2020 was recently released. Consider the following statements regarding the same:
- India is among the top 10 countries with the highest PM2.5 exposures in 2019.
- Among the 20 most populous countries, India recorded the lowest increase in Ozone concentrations in the past 10 years.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4 Which of the following sectors are covered under Production Linked Incentive Scheme?
- Mobile phones (electronic manufacturing)
- Pharma products
- Medical equipment
- Sunrise sectors
Select the correct code
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 and 4 only
- All of the above
Q.5 A new organ was recently discovered in which of the following part of the human body?
- Throat
- Stomach
- Pancreas
- Lungs
ANSWERS FOR 22nd October 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
About indigenously developed COVID-19 test kits:
About US-India 2+2 meeting:
About QUAD needing a definitive blueprint:











