IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Tristan Da Cunha declared the largest fully protected marine reserves in the Atlantic Ocean
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Biodiversity
In news
- Tristan da Cunha was declared the largest fully protected marine reserves in the Atlantic Ocean.
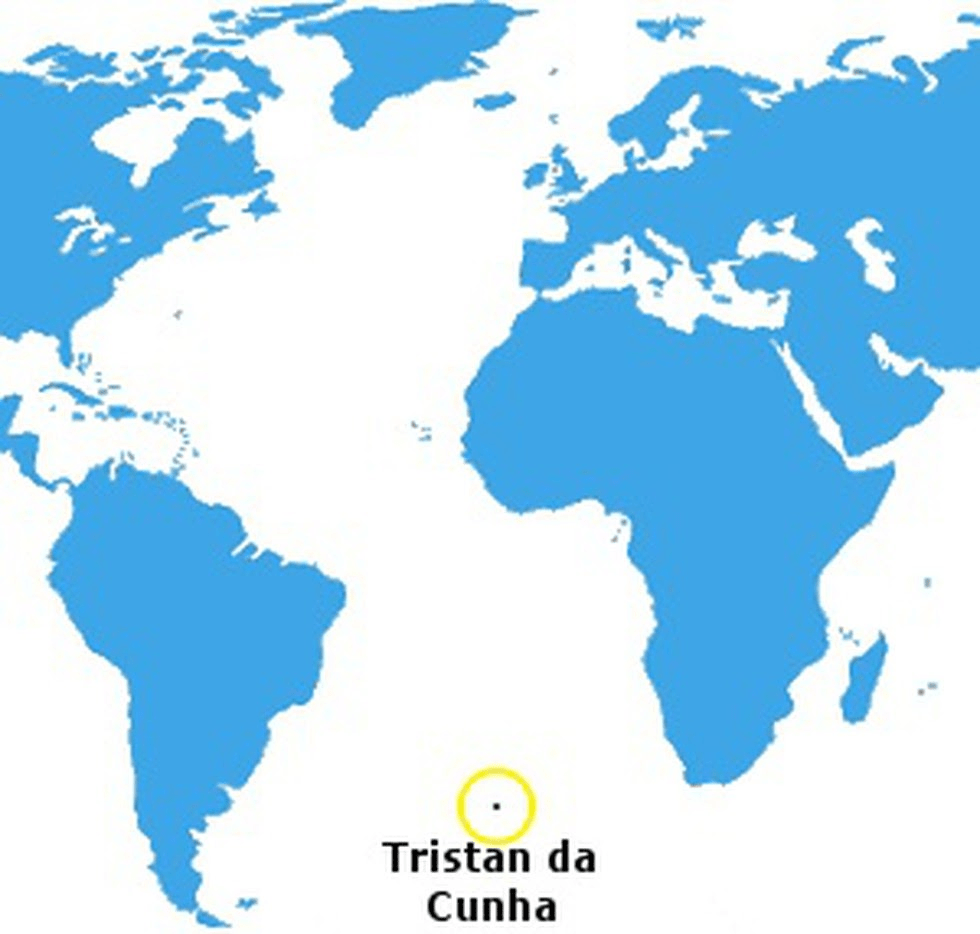
Important value additions
Tristan da Cunha
- It is also home to the world’s most remote human settlement.
- It is also an isolated UK Overseas Territory.
- It is a remote group of volcanic islands in the South Atlantic Ocean.
- It has its own constitution.
- It is also home to tens of millions of seabirds and several unique land birds.
- It is also home to the World Heritage Site of Gough and Inaccessible Islands, which is one of the most important seabird islands in the world.
Do you know?
- After joining the UK’s Blue Belt Programme, it will become the largest no-take zone in the Atlantic and the fourth largest on the planet.
- This means fishing, mining and any such activities will not be allowed.
- This will close over 90% of their waters to harmful activities such as bottom-trawling fishing, sand extraction and deep-sea mining.
Draft Rules notified Under the Code on Social Security, 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions
In news
- Union Ministry of Labour and Employment has notified the draft rules under the Code on Social Security, 2020.
Key takeaways
- The draft rules provide for Aadhaar based registration including self-registration by unorganised workers, gig workers and platform workers, Building and Other Construction Workers on the portal of the Central Government.
- Provision has also been made in the rules regarding gratuity to an employee who is on fixed term employment.
- The rules also provide for single electronic registration of an establishment including cancellation of the registration in case of closure of business activities.
- Provision has also been made regarding manners and conditions for exiting an establishment from EPFO and ESIC coverage.
- The procedure for self-assessment and payment of Cess in respect of building and other construction workers has been elaborated in the rules.
- The rate of Interest for delayed payment of such cess has been reduced from 2% every month or part of a month to 1%.
Emergency Retrieval System (ERS) for Power Lines
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- An indigenous technology, Emergency Retrieval System (ERS), for quick retrieval of power transmission in the event of failure of transmission line towers was recently developed. .
- Developed by: Structural Engineering Research Centre (SERC), constituent laboratory of Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR)
Key takeaways
- At present, the ERS systems are imported and the cost is relatively high.
- This technological development will enable the manufacturing in India for the first time, which will be an import substitute.
- Also, it will cost about 40% of imported systems.
- ERS is a lightweight modular system that is used as temporary support structure to restore power immediately after the collapse of transmission line towers during natural calamities such as cyclone/earthquake, or manmade disruptions.
- It is made of structurally highly stable box sections.
- It is lightweight, modular and reusable.
- It can also be assembled quickly at the disaster site for restoration of power in 2-3 days.
New Chief Information Commissioner (CIC) appointed
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Statutory bodies
In news
- Yashvardhan Kumar Sinha was appointed as the Chief Information Commissioner (CIC) recently.
Important value additions
Central Information Commission
- The RTI Act 2005 provides for the constitution of a Central Information Commission and State Information Commissions in each state.
- The CIC was constituted in 2005 under the Right to Information Act, 2005.
- The jurisdiction of the Commission extends over all Central Public Authorities.
- The Central Information Commission shall consist of:
- The Chief Information Commissioner (CIC)
- Such numbers of Central Information Commissioners (ICs), not exceeding ten, as may be deemed necessary
- Eligibility: (1) The members shall be persons of eminence in public life with wide knowledge and experience in law, science and technology, social service, management, journalism, mass media or administration and Governance.
- The CIC or IC shall not be an MP or MLA or hold any other office of profit or connected with any political party or carrying on any business or pursuing any profession.
- Appointment: The members of the commission are appointed by a committee consisting of the PM (as Chair), Leader of Opposition (LoP) in Lok Sabha and a Union Cabinet Minister appointed by the PM.
- Resignation: The CIC or an IC may, at any time, by writing under his hand addressed to the President, resign from his office.
- Removal: The CIC or an IC may be removed from office only by order of the President on the ground of proved misbehaviour or incapacity after the Supreme Court, on a reference made to it by the President, reports that he/she should be removed on the grounds mentioned.
- The President may also remove them from office if such a person is adjudged insolvent, convicted for certain offences etc.
Miscellaneous
Leonid Meteor Shower
- The Leonid meteor showers are currently making their yearly appearance in India.
- The Leonids emerge from the comet Temple-Tuttle.
- It takes 33 years to revolve once around the Sun.
- These meteors are bright and among the fastest moving.
- The Leonids originate from the constellation Leo the Lion
Meteor shower
- On its journey around the Sun, the Earth passes through large swathes of cosmic debris.
- The debris is essentially the remnants of comets.
- As the Earth wades through this cloud of comet waste, the bits of debris create what appears from the ground to be a fireworks display in the sky — known as a meteor shower.
(MAINS FOCUS)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2, 3:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
- Indian economy and mobilization of resources
Calibrated Economic Package (Atmanirbhar Bharat 3.0) – Part 2
Click here for Part 1 of the article
Merits of the Package
- Objective of Package: The measures are designed to maximise the economic impact of fiscal spending, like the various credit guarantee programmes, where the flows triggered by the guarantee are several times the potential fiscal cost
- Spending is calibrated, as seen in the continued expansion of the MGNREGA budget, which received its second extension, given that three-fourths of the earlier expanded budget had been used up by October.
- Issue of Hunger tackled: The free grains programme was not extended beyond November, as the economy is now more or less fully open, and the risk of abject hunger is lower.
- Success of PLI Scheme: The expansion of the Production-Linked Incentives (PLI) scheme to 10 new sectors is a result of the success thus far of the PLI scheme for handsets. The PLI scheme is as much about self-reliance or cutting down imports, as it is about offering cash incentives to boost domestic production, which is expected to create employment.
- Stresses Sectors recognised: The package expands the supply of loanable funds through enlargement of credit guarantee scheme to support stressed sectors
- Boost to Real Estate Sector: Tax incentives for home buyers could potentially unleash a price discovery in the real estate market. The real estate sector which has a significant multiplier impact on the economy has high employment generation capabilities.
- Boosting Employment: By offering to foot the bill for provident fund contributions, it has nudged companies, big and small, to hire.
- Urban Poor and Demand for Urban NREGA: Unsure of whether an urban MGNREGA could be implemented cleanly, and even if so, what its impact would be on rural-urban migration, the Indian government has chosen to target this problem indirectly, through a sharp increase in the budget for urban affordable housing.
Concerns
- Banks not enthusiastic to lend: The originally envisaged credit guarantee scheme with a target disbursement of ₹3 trillion has seen just about half of the amount being lent out by banks. This shows that despite low risk, banks are uncomfortable to lend.
- Future Risk: Forcing banks to lend to companies where assessing risk has become a challenge due to the pandemic puts banks at a bigger risk, credit guarantee or not.
- Impacts can be felt in medium term: The Rs 1,45,980 crore expenditure in the form of production-linked incentives (PLIs) to 10 new sectors will be over five years, and likely kick in only next financial year
Way Forward
- First, a recalibration of borrowing needs this year, which could provide some relief to the bond markets.
- Second, clearing overdue payments, particularly by state governments — the Centre’s decision to clear fertiliser arrears is a step in right direction. This by itself could provide a stimulus to the economy.
- Third, and most important, would be for state and central governments to build in a stimulus in next year’s budget.
Conclusion
- The package reinforces the ‘fiscal conservatism’ ideology of the government — rather than large cash transfers.
- The growth philosophy centres around creating an ecosystem that aids domestic demand, incentivises companies to generate jobs and boost production, and simultaneously extends benefits to those in severe distress, be it firms or individuals
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
Under Biden, the future of US-India ties
Context: The long drawn out US elections finally resulted in Joe Biden being declared President-elect. The Biden-Kamala Harris administration will be sworn in on 20th January 2021.
For the US, the Indo-US relationship is an extremely consequential one —
- China Factor: India is essential to the US’s hopes of counterbalancing China. As a result, security cooperation has become the cornerstone of any Indo-US strategic partnership.
- New Millennium New Direction: The George W Bush administration first began the US commitment to co-opting India as a “natural ally”, a commitment that resulted in the landmark civil nuclear deal in 2008.
- Since then, while there had been progress, it had also not been as rapid or deep as the US would perhaps have liked.
How has India-US relationship progressed in Trump era?
- Fast Diplomacy: In the past four years under the Donald Trump administration, Indo-US security cooperation moved at breakneck speed.
- Status of Major Defence Partner: In 2016, the US designated India as a Major Defence Partner, which led to, among other things, India being able to receive access to a wide range of military and dual-use American technologies.
- Foundational Defence Agreements Signed: Over the space of three years, three defence agreements – LEMOA, COMCASA, BECA – were reached and signed.
- Institutional Structure for Strategic Dialogue: In 2018, the two countries began the 2+2 strategic dialogue, one of the highest level dialogues ever institutionalised.
- Joint Exercises: In 2019, the US and India conducted Tiger Triumph, the first ever tri-service (ground, naval, and air forces) exercises between them.
- QUAD taking shape: In 2020, Australia joined India, Japan, and the US in conducting the India-led Malabar naval exercises, giving a big impetus to the Quad.
- Chinese aggressiveness acted as catalyst: In the US view, while it had always been ready to engage in this level of cooperation, it was the border clashes with China that made India more willing to engage deeply with the US.
Despite both the US and India being on the same page in terms of the deepening relationship, there are obstacles that have remained like:
- Indian Military’s systemic dependence on Russia: The US believes that India, which is still 60% to 70% dependent on Russia for military resupplies and hardware, will, in the future, have to choose with the kind of warfare that India wants to align itself with. India can no longer choose from an à la carte military menu; rather it has to choose a system.
- India’s insistence on Strategic Autonomy: The real Achilles’ heel is, as experts have pointed out, is India’s economics and the continuing harping on strategic autonomy. PM Modi’s use of power (full majority) to promote a nationalistic agenda is viewed by US as a lost opportunity which has not brought the expected economic growth.
- Domestic Issues: President Biden would be more committed to human rights which could lead to a rift with India, on, for example Kashmir.
Potential for India-US Relationship under President Biden
- Despite these obstacles, a Biden administration will not particularly change the relationship. And, in many ways, it may even come out stronger.
- Any US concerns, like that of Kashmir, are more likely to be conveyed privately rather than publicly.
- Under President Trump, decision-making was more ad hoc and at times chaotic. The dismantling of US national security decision structure by Trump, due to his deep suspicion of bureaucracy, added to this chaos.
- President Biden will restore the US national security decision structure – like regular inter-agency meetings, National Security Council meetings – and a process by which bureaucracy recommendations and decisions will make its way up to the President’s office.
- Biden is also more likely to be considerate when it comes to Climate funding, which India needs so as to fulfil its Paris Climate Commitments
- President Biden will reverse the US withdrawal of leadership role in International affairs and help in resurrecting the rules-based international order under the leadership of US. This is in the interest of India because the space left by US will be occupied by China (which is against India’s interest)
Conclusion
While it is undeniable that Trump and Modi had a bond, both Biden and Modi are likely to be extremely pragmatic about a relationship which is really about the geopolitical compulsions.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following remote group of volcanic islands was recently declared the largest fully protected marine reserves in the Atlantic Ocean?
- Balleny Islands
- American Samoa
- Antipodes Islands
- Tristan da Cunha
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Central Information Commission:
- The Central Information Commission shall consist of the Chief Information Commissioner (CIC) and such numbers of Central Information Commissioners (ICs), not exceeding five, as may be deemed necessary.
- The CIC or an IC may be removed from office only by order of the President on the ground of proved misbehaviour or incapacity after the Supreme Court’s report on the same.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 14th November 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | D |
Must Read
About Labour laws
About recent Pakistan’s ceasefire violations














