IASbaba's Press Information Bureau
Press Information Bureau(PIB) IAS UPSC – 8th November to 14th November – 2020
GS-2
Aatma Nirbhar Bharat 3.0.
(Topic: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation)
Union Finance Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman has announced 12 key measures, as part of Government of India’s stimulus to the economy, under Aatma Nirbhar Bharat 3.0.
The net stimulus announced today amounts to ₹ 2.65 Lakh crore. The total stimulus announced by the Government and Reserve Bank of India till date, to help the nation tide over the COVID-19 pandemic, works out to ₹ 29.87 lakh crore, which is 15% of national GDP. Out of this, stimulus worth 9% of GDP has been provided by the government.
- Atmanirbhar Bharta Rozgar Yojana: The new employees hired by the EPFO-registered organisations will receive benefits during COVID-19. If the EPFO registered establishments take in new employees or those who lost jobs earlier will get benefits from government.
- Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) for MSMEs, businesses, MUDRA borrowers and individuals (loans for business purposes), has been extended till March 31, 2021.
- New Credit Guarantee Scheme: A credit guarantee support scheme for health care sector and 26 sectors stressed due to COVID-19 pandemic was also launched. Under this new credit scheme, banks will be able to lend to stressed companies from 26 sectors identified by the K.V. Kamath committee earlier this year.
- Production-Linked Incentive: The PLI scheme worth ₹ 1.46 lakh crore is being offered to 10 champion sectors which will help boost the efficiency and competitiveness of domestic manufacturing. A total amount of ₹ 1.5 lakh crore has been earmarked across sectors, for the next five years.
- Pradhan Mantri Awaaz Yojana Urban: An additional outlay of ₹ 18,000 crore over budget estimate towards PM Awaaz Yojana Urban has been announced which will help ground 12 lakh houses and complete 18 lakh houses. This will create additional 78 lakh jobs and improve the production and sale of cement and steel.
- Income Tax Relief for Developers and Home Buyers for houses up to ₹ 2 crore which provides an incentive to the middle class to buy homes.
- Equity Investment in Debt Platform by NIIF: The government will make ₹ 6,000 crore equity investment in debt platform of National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF), which will help NIIF raise ₹ 1.1 lakh crore by 2025 for financing infrastructure project
- Total Support: It comes at a time when the worst seems to be over and the economy seems to be transitioning from the normalisation of economic activity stage to the growth recovery stage. The support totalled ₹2.65 trillion.
IFSC Authority approves the International Financial Services Centre Authority (Banking) Regulations, 2020
(Topic: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation)
The IFSC Authority, after detailed deliberations, approved the International Financial Services Centres Authority (Banking) Regulations, 2020.
Banking constitutes one of the major focus areas of IFSC and is expected to drive and facilitate the other constituent operations in the IFSC in due course. A self-contained regulation laying down the major principles of banking operations at IFSCs is thus an important step in the IFSC reaching its desired potential.
The Authority approved the draft banking regulations at its meeting today, which paves the way for putting in place the rules for the various aspects of banking operations that would be permissible at the IFSC.
The salient aspects of the Banking Regulations include:
- Laying down the requirements for setting up IFSC Banking Units (IBUs)
- Permitting persons resident outside India (having net worth not less than USD 1 Million) to open foreign currency accounts in any freely convertible currency at IFSC Banking Units (IBUs)
- Permitting persons resident in India (having net worth not less than USD 1 Million) to open foreign currency accounts in any freely convertible currency at IFSC Banking Units (IBUs) to undertake any permissible current account or capital account transaction or any combination thereof under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) of the Reserve Bank of India.
- Laying down the permissible activities of IBUs including credit enhancement, credit insurance, and sale , purchase of portfolios, engage in factoring and forfaiting of export receivables and undertake equipment leasing, including aircraft leasing
- Permitting the Authority to determine business that a Banking Unit may be permitted to conduct in INR with persons resident in India and persons resident outside India, subject to settlement of the financial transaction in relation to such business in freely convertible foreign currency.
Cabinet approves Continuation and Revamping of the Scheme for Financial Support to Public Private Partnerships in Infrastructure Viability Gap Funding VGF Scheme
The revamped Scheme is mainly related to introduction of following two sub-schemes for mainstreaming private participation in social infrastructure:
- Sub scheme -1: This would cater to Social Sectors such as Waste Water Treatment, Water Supply, Solid Waste Management, Health and Education sectors etc. These projects face bankability issues and poor revenue streams to cater fully to capital costs. The projects eligible under this category should have at least 100% Operational Cost recovery.
- Sub scheme -2: This Sub scheme will support demonstration/pilot social sectors projects. The projects may be from Health and Education sectors where there is at least 50% Operational Cost recovery. In such projects, the Central Government and the State Governments together will provide up to 80% of capital expenditure and upto 50% of Operation & Maintenance (O&M) costs for the first five years.
Since the inception of the scheme, 64 projects have been accorded ‘final approval’ with Total Project Cost of Rs. 34,228 crore and VGF of Rs. 5,639 crore. Till the end of Financial Year 2019-20, VGF of Rs. 4,375 crore has been disbursed.
Benefits: The aim of the scheme is to promote PPPs in social and Economic Infrastructure leading to efficient creation of assets and ensuring their proper Operation and Maintenance and make the economically/socially essential projects commercially viable. The scheme would be beneficial to public at large as it would help in creation of the Infrastructure for the country.
Impact:
- Revamping of the proposed VGF Scheme will attract more PPP projects and facilitate the private investment in the social sectors (Health, Education, Waste Water, Solid Waste Management, Water Supply etc.).
- Creation of new hospitals, schools will create many opportunities to boost employment generation.
20th Summit of SCO Council of Heads of State
(Topic: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests)
Chaired by: The President of the Russian Federation Mr. Vladimir Putin
This was the first SCO Summit held in Virtual Format and third meeting that India participated after becoming a full member in 2017.
Prime Minister Modi –
- Highlighted the imperative of a reformed multilateralism to meet the expectation of a world suffering from the social and financial after-effects of the pandemic. India, as a non-permanent member of the UNSC, beginning from 1 January 2021, will focus on the theme of ‘reformed multilateralism’ to bring about desirable changes in global governance.
- Reiterated India’s firm belief in regional peace, security and prosperity and raising voice against terrorism, smuggling of illegal weapons, drugs and money-laundering. He mentioned that India’s brave soldiers participated in about 50 UN peacekeeping missions and India’s Pharma industry supplying essential medicines to more than 150 countries during the pandemic.
- Underlined India’s strong cultural and historical connect with the SCO region and reiterated India’s firm commitment towards strengthening connectivity in the region with initiatives like International North-South Transport Corridor, Chabahar Port and Ashgabat Agreement. He also extended full support to observing the 20th anniversary of SCO in 2021 as the “SCO Year of Culture” and spoke of India’s own initiatives to hold the first SCO exhibition on Shared Buddhist Heritage to be organized by National Museum of India, SCO Food Festival in India next year and the translation of Ten regional language literary works into Russian and Chinese.
- Expressed India’s readiness to host the next regular Meeting of SCO Council of Heads of Government on November 30, 2020 in virtual format. India has also proposed to set up a Special Working Group on Innovation and Startups and a Sub Group on Traditional Medicine within SCO. He elaborated on India’s vision of a “Aatma Nirbhar Bharat” (Self-reliant India) in the post-pandemic world that could prove to be a force multiplier for the global economy and the economic progress of the SCO region.
17th ASEAN India Summit
(Topic: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests)
Current chair: H.E. Nguyen Xuan Phuc, Prime Minister of Vietnam
Underlined the centrality of ASEAN in India’s Act East Policy –
- Noted that a cohesive, responsive and prosperous ASEAN is central to India’s Indo-Pacific Vision and contributes to Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR).
- Underscored the importance of strengthening convergence between India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative and the ASEAN Outlook on Indo-Pacific, to ensure a free, open, inclusive and rules-based Indo-Pacific region.
- He also invited the ASEAN countries to cooperate on various pillars of India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
On COVID-19
- Highlighted India’s response and broader support to the international community, and welcomed ASEAN’s initiatives to fight the pandemic.
- Prime Minister announced a contribution of US$ 1 million to the COVID-19 ASEAN Response Fund.
On connectivity
- Underscored the importance of greater physical and digital connectivity between ASEAN and India
- Reiterated India’s offer of US$ 1 billion Line of Credit to support ASEAN connectivity
- On trade and investment, underlined the importance of diversification and resilience of supply chains for post-COVID economic recovery.
The ASEAN leaders –
- Acknowledged India’s contribution towards promoting peace and stability in the region and welcomed India’s support to ASEAN centrality.
- The Leaders also welcomed the adoption of the new ASEAN-India Plan of Action for 2021-2025.
- The discussions also covered regional and international issues of common interest and concern, including South China Sea and terrorism.
- Both sides noted the importance of promoting a rules-based order in the region including through upholding adherence to international law, especially the UNCLOS.
- The leaders affirmed the importance of maintaining and promoting peace, stability, safety and security in the South China Sea,and ensuring freedom of navigation and overflight.
GS-3
Saffron bowl of India extends to the North East
(Topic: Agriculture)
The saffron bowl, which was so far confined to Kashmir, may soon expand to the North East of India. Plants from seeds transported from Kashmir to Sikkim and acclimatized there are now flowering in Yangyang in the Southern part of the North-East state.
Saffron production has long been restricted to a limited geographical area in the Union territory of Jammu & Kashmir. Pampore region, in India, commonly known as Saffron bowl of Kashmir, is the main contributor to saffron production, followed by Budgam, Srinagar, and Kishtiwar districts. Saffron has traditionally been associated with the famous Kashmiri cuisine. It’s its medicinal values were considered as part of the rich cultural heritage of Kashmir. As saffron growing was confined to very specific areas in Kashmir, its production remained limited. Though the National Mission on Saffron focused on several measures to improve its farming, the measures were still limited to the specified areas of Kashmir.
The corms were irrigated during the month of September and October, which ensured timely corm sprouting and good flower yields. The matching of climatic and geographical conditions between Pampore (Kashmir) and Yangyang (Sikkim) led to the successful sample farming of Saffron in Yangyang.
The project also focused on post-harvest management and value addition of saffron so that quality saffron drying and efficient post-harvest processing can improve saffron recovery, thereby improving its production.
Further, detailed analysis and testing of all parameters, including soil testing, quality, quantity, and possible value addition are planned, for immediate results and extrapolation of the project to other parts of the North East Region along with Micro Food Enterprises.
Saffron
- It is a plant whose dried stigmas (thread-like parts of the flower) are used to make saffron spice.
- Saffron cultivation is believed to have been introduced in Kashmir by Central Asian immigrants around the 1st Century BCE.
- It represents the rich cultural heritage of the J&K region.
- It is a very precious and costly product.
- It is referred to as ‘bahukam’ in ancient Sanskrit literature.
- It is cultivated and harvested in the Karewa (highlands) of J&K.
- Uses: (1) It rejuvenates health; (2) It is used in cosmetics and for medicinal purposes.
- It is usually cultivated during June and July and at some places in August and September.
- Saffron grows well at an altitude of 2000 meters above sea level.
- It needs 12 hours of sunlight.
- It grows in many different soil types but thrives best in calcareous (soil that has calcium carbonate in abundance), humus-rich and well-drained soil with a pH between 6 and 8.
- Temperature: Ranging from 35 or 40 degree Celsius in summer to about –15 or –20 degree Celsius in winter.
- It also requires adequate rainfall that is 1000-1500 mm per annum.
Do you know?
- Pampore region, in India, commonly known as Saffron bowl of Kashmir, is the main contributor to saffron production, followed by Budgam, Srinagar, and Kishtiwar districts.
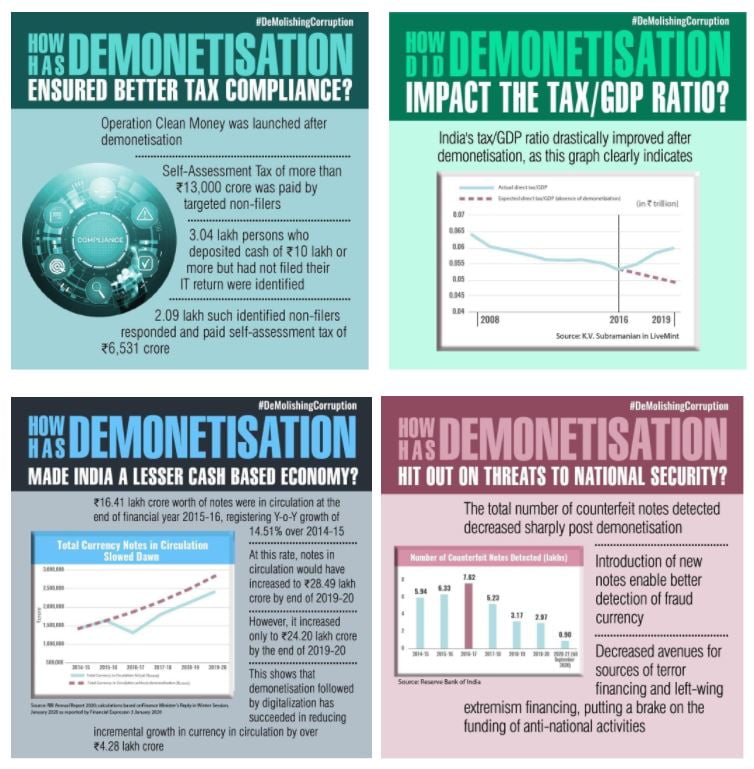
Demonetisation helped to reduce black money
(Topic: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources)
Demonetisation has helped reduce black money, increase tax compliance and formalization and given a boost to transparency. These outcomes have been greatly beneficial towards national progress.
Indian astronomers collaborated with Nobel laureate on Thirty Meter Telescope Project
(Topic: Space)
2020 Physics Nobel Laureate Prof. Andrea Ghez had worked closely with Indian astronomers on the design of back-end instruments and possible science prospects of the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) project being installed at Maunakea in Hawaii, which can revolutionized the understanding of the universe and the enigmas in it.
- The Thirty-meter telescope (TMT) project is an international partnership between CalTech, Universities of California, Canada, Japan, China, and India; through the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and Department of Atomic Energy (DAE).
- To provide facilities with even greater capabilities to gather the observations needed to answer new and emerging questions in astronomy and physics in general.
Indian scientists develop energy efficient smart screens from discarded groundnut shells
(Topic: Science and Technology)
Indian scientists have developed an eco-friendly smart screen from groundnut shells that could help not only in preserving privacy but also in energy conservation by controlling light and heat passing through it and reducing air conditioning load.
- In the smart screen application, liquid crystal molecules were confined in a polymer matrix. The matrix was built using cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) which were prepared from discarded groundnut shells.
- The refractiveindex of the liquid crystal molecules along a particular direction were altered by the application of an electric field. In the absence of the electric field, there was a mismatch between refractive indices between those of the polymer and the liquid crystal, leading to the scattering of light.
- Upon application of a few volts of an electric field, the liquid crystal molecules underwent a direction change resulting in the matching of refractive indices, and the device became transparent almost instantaneously.
- When the field was turned off, the system quickly recovered the scattering state. This reversible change between the two states available at the flip of a switch occurred over thousands of cycles, with essentially no change in contrast or switching speed.
The device they developed, employed the same principle that causes fog on winter mornings. This happens only when the water droplets are of right size, and it can co-exist along with air. The incoming light sees these two as materials of different refractive indices and thus gets scattered, giving a foggy appearance. Similarly, the polymer and the liquid crystal should co-exist in the right size to create the required optical properties for the smart screen.
While, in principal, the device could be developed from any cellulose or agricultural waste, due to certain properties of groundnut waste, the smart screen developed from groundnut waste has been found to be most efficient.
The device can be employed for a whole range of possible applications, especially in energy conservation by controlling the amount and window of infrared light that is permitted to pass. For example, while a window having this technology would remain transparent to the entire visible region, undesirable levels of heat radiation could be significantly reduced, keeping the enclosure cool.
Prelims oriented News
U.S President: Joe Biden
US Vice President: Kamala Harris
Ministry of Shipping renamed: As Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (as in most of the developed countries the Ministry of Shipping handles Ports and Waterways)
National Ayurveda Day: The Ministry of AYUSH, since 2016, has been observing the “Ayurveda Day” every year on the occasion of Dhanwantari Jayanti (Dhanteras).
- Dedicated two future-ready Ayurveda institutions to the nation – the Institute of Teaching and Research in Ayurveda (ITRA), Jamnagar and the National Institute of Ayurveda (NIA), Jaipur. Both the institutes are premier institutions of Ayurveda in the country. The former has been conferred the status of an Institution of National Importance (INI) by an Act of Parliament and the latter that of an Institution Deemed to be University (De novo Category) by the University Grants Commission (UGC)
- Highlights importance of developing evidence-based research structures for Ayurveda for a leading global role in the 21st century
- WHO to set up Global Centre for Traditional Medicine in India
Ro-Pax terminal: At Hazira
- RO-PAX service between Hazira and Ghogha has made dreams come true for the people of Saurashtra and South Gujarat, as the journey is shortened from 10-12 hours to 3-4 hours. This will save time and expenses will also be reduced.
- About 80000 passenger trains and 30000 trucks will be able to take advantage of this new service in a year.
- Fruits, vegetables and milk can now easily be transported and pollution will also be reduced due to this service.
Unveiling of A-Sat Missile Model
- ‘Mission Shakti’ was country’s first ever Anti-Satellite (ASAT) Missile Test successfully conducted, where a fast-moving Indian orbiting target satellite in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) was neutralised with pinpoint accuracy. This was a highly complex mission, conducted at extremely high speed with remarkable precision.
- The successful conduct of Mission Shakti made India the fourth nation in the world with the capability to defend its assets in outer space.
The fifth Scorpene submarine of Project-75 – ‘Vagir’ launched
Vagir, ex-Russia, named after the Sand Fish, a deadly deep sea predator of the Indian Ocean, was commissioned into the Indian Navy on December 3, 1973, and was decommissioned on June 7, 2001, after almost three decades of yeoman service to the nation.
- The state-of-the-art technology utilized in the rebuilt Scorpene has ensured superior stealth features (such as advanced acoustic absorption techniques, low radiated noise levels, hydro-dynamically optimised shape etc.) and the ability to launch an attack on the enemy using precision guided weapons.
- The attack can be launched with both torpedoes and tube launched anti-ship missiles, whilst underwater or on surface.
- The stealth of this potent platform is enhanced by the special attention provided to her characteristic underwater signatures. These stealth features give it an invulnerability, unmatched by most submarines.
- Scorpene submarines can undertake multifarious types of missions i.e Anti-Surface warfare, Anti-Submarine warfare, Intelligence gathering, Mine Laying, Area Surveillance etc. The Submarine is designed to operate in all theatres of operation, showcasing interoperability with other components of a Naval Task Force. It is a potent platform, marking a transformational shift in submarine operations.
With the launch of Vagir, India further cements its position as a Submarine Building Nation and MDL has more than lived up to its reputation as ‘Warship and Submarine Builders to the Nation’ This is totally in sync with the current impetus of the Government towards ‘Make in India’ and ‘Aatma Nirbhar Bharat’.
QRSAM Missile System Achieves Major Milestone
Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile (QRSAM) System has achieved a major milestone by a direct hit on to a Banshee Pilotless target aircraft at medium range & medium altitude. The missile launch took place from ITR Chandipur on 13th Nov 2020 at 1550 hrs off the Odisha Coast.
The missile is propelled by a single stage solid propellant rocket motor and uses all indigenous subsystems. The Missile is canisterised for transportation and launch using a mobile launcher capable of carrying 6 canisterised missiles.
All QRSAM weapon system elements like Battery Multifunction Radar, Battery Surveillance Radar, Battery Command Post Vehicle and Mobile Launcher were deployed in the flight test. The system is capable of detecting and tracking targets on the move and engaging target with short halts. The system is designed to give air defence coverage against strike columns of Indian Army.
The radar tracked the Banshee target from farthest range and missile was launched when target was within kill zone and achieved the direct hit with terminal active homing by RF Seeker guidance. Various DRDO labs DRDL, RCI, LRDE, R&DE(E), IRDE, ITR have participated in the test.
The weapon system elements have been realized through Defence PSUs BEL, BDL and private industry L&T. The missile system is fully indigenous with active RF Seekers, Electro Mechanical Actuation (EMA) systems sourced from various industries. The Radar is four walled Active Phased Array Radar. All range Tracking stations, Radar, EOTs & Telemetry Stations monitored the flight parameters.
NTPC develops Geo-polymer aggregate from fly ash: NTPC Ltd, India’s largest power producer and a PSU under Ministry of Power, has successfully developed Geo-polymer coarse aggregate from fly ash.
- India’s demand for these aggregate touches close to 2000 million metric tons mark every year. The aggregate developed by NTPC from fly ash will help in meeting the demand to a great extent and also will reduce the impact on environment caused by Natural aggregates which require quarrying of natural stone.
- In India, every year, approximately 258 MMT of ash is produced by the coal fired thermal power plants. Out of this around 78% of the ash is utilised and the balance remains unutilised which remain in ash dykes. NTPC is exploring alternate ways to utilise the remaining ash which includes the current research project to generate aggregates using more than 90% ash.
- The Geo-polymer aggregates finds its extensive usage in construction industry turning the ash eco-friendly. These aggregates are extremely environment friendly and does not require any cement for application in concrete where the fly ash based Geopolymer mortar acts as the binding agent. The Geo-polymer aggregates will help in reducing carbon emission and has great potential for reduction of water consumption.
Doorstep Service for submission of Digital Life Certificate through Postman launched
- The facility to submit life certificate online through Jeevan Pramaan Portal was launched in 2014 with the objective to provide a convenient and transparent facility to pensioners for submission of Life Certificate.
- In order to make this facility available across the country, DoPPW roped in the India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) and utilise its huge network of Postmen and Gramin Dak Sevaks in providing doorstep facility to pensioners for submission of life certificate digitally.
Skill India Commences Training of 3 Lakh Migrant Workers From 116 Districts Identified Across 6 States under Garib Kalyan Rozgar Abhiyan
- Aim: To empower migrant workers and rural population in the post-COVID era through demand-driven skilling and orientation under Centrally Sponsored and Centrally Managed (CSCM) component of Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) 2016-2020.
- Over 200 training partners are delivering trainings across 116 districts in6 states
Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme introduced
PLI Scheme has been introduced in the following 10 key sectors for Enhancing India’s Manufacturing Capabilities and Enhancing Exports – Atmanirbhar Bharat
- Will make Indian manufacturers globally competitive
- Attract investment in the areas of core competency and cutting-edge technology
- Ensure efficiencies
- Create economies of scale
- Enhance exports and make India an integral part of the global supply chain
| Priority | Sectors | Implementing Ministry/Department |
|
|
Advance Chemistry
Cell (ACC) Battery |
NITI Aayog and Department of Heavy Industries |
|
|
Electronic/Technology Products | Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology |
| 2. | Automobiles & Auto Components |
Department of Heavy Industries |
| 3. | Pharmaceuticals drugs | Department of Pharmaceuticals |
| 4. | Telecom & Networking Products | Department of Telecom |
| 5. | Textile Products: MMF segment and technical textiles | Ministry of Textiles |
| 6. | Food Products | Ministry of Food Processing Industries |
| 7. | High Efficiency Solar PV Modules | Ministry of New and Renewable Energy |
| 8. | White Goods (ACs & LED) | Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade |
| 9. | Speciality Steel | Ministry of Steel |
Quotes
India has Moved from Tax-Terrorism to Tax-Transparency: Prime Minister
The long period of slavery had made the relationship between tax payer and the tax collector that of exploited and exploiters.
Quoting Goswami Tulsidas “बरसत हरसत सब लखें, करसत लखे न कोय तुलसी प्रजा सुभाग से, भूप भानु सो होय” meaning when clouds rain, the benefit is visible to all of us; but when clouds are formed, the sun absorbs the water but does not cause inconvenience to anyone, the Prime Minister said governance should not cause inconvenience when collecting tax from the common people; but when that money reaches the citizens, then people should feel its benefits in their lives.
Over the years, the government has moved ahead with this vision and today’s taxpayer is witnessing huge changes and transparency in the entire tax system.
When the taxpayer does not have to wait months for a refund and gets a refund within a few weeks, then he feels transparency. When he sees that the department has resolved the age-old dispute on its own, then he feels transparency. When he enjoys faceless appeal, then he feels tax transparency. When he sees that income tax is continuously decreasing, then he feels more tax transparency.
While unveiling statue of Swami Vivekananda at JNU Campus – PM Modi
Ideology should never be put before national interest
- It is natural to be proud of one’s ideology still, on the subjects of national interest, our ideology should be seen standing with the nation not against it.
- In the history of the country, whenever a difficult time arose before the country, people of every ideology came together in the national interest. People of every ideology stood united under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi in the freedom struggle. They fought for the country together. The country saw the same solidarity during the Emergency. Former Congress leaders and activists were also present in the movement against the Emergency. There were RSS volunteers and Jana Sangh people. Socialists and communists too came together.
- In this solidarity, no one had to compromise on ideology. There was only one purpose – national interest. Therefore, whenever there is a question of national unity, integrity and national interest, taking decisions under the burden of any ideology will lead to the loss for the nation.
Idea-sharing and flow of new ideas should remain uninterrupted
Our country is the land where seeds of different intellectual ideas have sprouted and thrived. It is necessary for the youth to strengthen this tradition. Due to this tradition, India is the most vibrant democracy in the world











