IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
HGCO19: India’s first indigenous mRNA vaccine candidate receives approval
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II –Health & GS-III – Sci & Tech
In news
- India’s first indigenous mRNA vaccine candidate, HGCO19, has received approval from Indian Drug regulators to initiate Phase one and two human clinical trials.
Key takeaways
- HGCO19 has been developed by Gennova, Pune and supported with seed grant under the Ind-CEPI mission of the Department of Biotechnology.
- The mRNA vaccines do not use the conventional model to produce immune response.
- Instead, they carry the molecular instructions to make the protein in the body through a synthetic RNA of the virus.
- mRNA-based vaccines are scientifically the ideal choice to address a pandemic because of their rapid developmental timeline.
- The mRNA vaccine is considered safe as is non-infectious, non-integrating in nature, and degraded by standard cellular mechanisms.
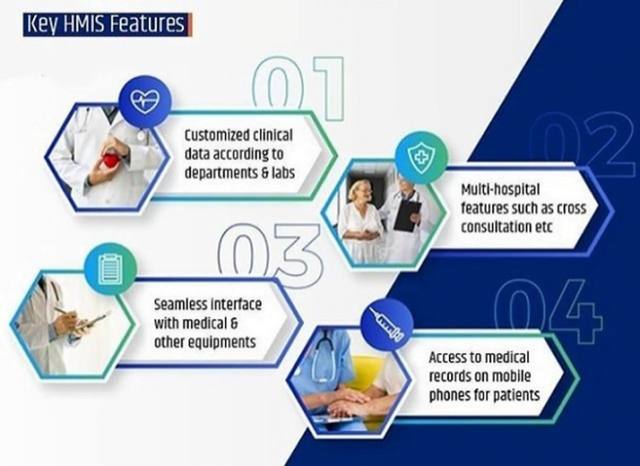
Indian Railways launches Hospital Management Information System (HMIS)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II –Health & GS-III – Infrastructure
In news
- Recently, Indian Railways has launched The Hospital Management Information System (HMIS).
- It is another major IT initiative by Railways to prioritise the well-being of its work force.

Key takeaways
- Developed by: Indian Railways in coordination with RailTel Corporation Limited.
- Objective: To provide a single window of clearance of hospital administration activity such as clinical, diagnostics, pharmacy, examinations, industrial health etc.
- Other objectives: (1) Effectively manage all the health facilities & its resources; (2) Monitor performance of hospitals across the administrative channel; (3) Impart quality health care services to its beneficiaries; (4) Improve the patient turn-around time; (5) Generate and maintain EMR (electronic medical records) of all patients
- Presently, 3 Modules of HMIS – Registration, OPD Doctor Desk & Pharmacy – shall be implemented.
- These shall be implemented on trial basis at Central Hospital, Lallaguda and will progressively be implemented across all Health Units over SCR.
Draft Indian Ports Bill, 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Infrastructure
In news
- Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways has circulated draft of Indian Ports Bill 2020 for public consultation which will repeal and replace the Indian Ports Act, 1908.
Key takeaways
- The Bill seeks to create an enabling environment for the growth and sustained development of the ports sector in India through the following broad methods: (1) Constitution of Maritime Port Regulatory Authority; (2) Formulation of the National Port policy and National Port plan in consultation with Coastal State Governments, State Maritime Boards and other stakeholders; (3) Formulation of specialised Adjudicatory Tribunals namely Maritime Ports Tribunal and Maritime Ports Appellate Tribunal to curb any anti-competitive practises in the port sector and act as a speedy and affordable grievance redressal mechanism.
Real Time Gross Settlement System (RTGS) now available for round the clock transactions
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Banking
In news
- The RBI has announced that the Real Time Gross Settlement System (RTGS) facility will now be available for round the clock transactions, with effect from December 14th, 2020.
Key takeaways
- Round the clock availability of RTGS will provide extended flexibility to businesses for effecting payments.
- The system can also be leveraged to enhance operations of Indian financial markets and cross-border payments.
- RTGS uses ISO 20022 format which is the best-in-class messaging standard for financial transactions.
Important value addition:
- The term real-time gross settlement (RTGS) refers to a funds transfer system that allows for the instantaneous transfer of money and/or securities.
- It is the continuous process of settling payments on an individual order basis without netting debits with credits across the books of a central bank.
- Once completed, real-time gross settlement payments are final and irrevocable.
- RTGS presently handles 6.35 lakh transactions daily.
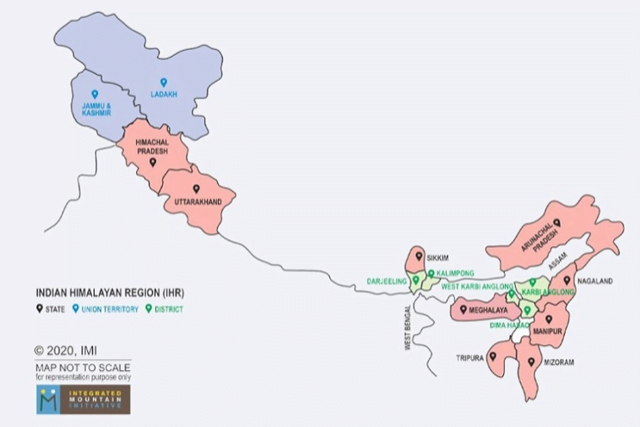
Sustainable Mountain Development Summit (SMDS) begins
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment
In news
- The 9th edition of the Sustainable Mountain Development Summit (SMDS) in Dehradun has begun.
Important value addition
- Organised by: Indian Mountain Initiative (IMI)
- The summit seeks to deliberate on issues such as migration, water security, climate resilience and innovative solutions for the farm sector, and disaster risk reduction in the Indian Himalayas.
- Every year 3-5 salient themes engaging the immediate attention of and relevant to the mountains and hills are taken up for threadbare discussion and debate.
- Conclusions and recommendations emerging from this exercise are pursued by IMI subsequently for actionable output.
- The theme for 2020: Emerging Pathways for Building a Resilient Post COVID-19 Mountain Economy, Adaptation, Innovation and Acceleration.
- The first edition was organized in 2011 in Nainital.
Integrated Mountain Initiative (IMI)
- It is a civil society led network platform.
- Mission: To mainstream concerns of the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR) and its people in the development dialogue of India.
- It functions as a platform to integrate the knowledge and experiences of multiple stakeholders working across the IHR, and uses this to inform and influence policy at the national and state level.
Programme of Socio-Economic Profiling of PM SVANidhi launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions
In news
- A programme of Socio-Economic Profiling of PM SVANidhi beneficiaries and their families was recently launched as an additional component of PM SVANidhi Scheme.
- Ministry: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
Key takeaways
- Under this, a complete profile of each PM SVANidhi beneficiary and their family members will be prepared.
- Based on the profiled data, benefits of the various eligible Central Schemes would be extended to them for their socio-economic upliftment.
- Context: PM SVANidhi scheme should not be seen merely from the perspective of extending loans to street vendors but should also be seen as an instrument for outreach to street vendors and their families for their overall development.
- In the first phase, 125 cities have been selected for the programme.
- The profile will identify potential eligibility of beneficiaries and their family members for select Central Government schemes and facilitate linkages.
Important value addition
Prime Minister Street Vendors AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Scheme
- Implemented by: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
- Objective: To provide affordable working capital loan up to 10 thousand rupees to Street Vendors for facilitating resumption of their livelihoods adversely affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
5th National Family Health Survey (NFHS) released
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health
In news
- Ministry of Health released the 5th National Family Health Survey (NFHS).
- The survey contains detailed information on population, health and nutrition for India and its states and union territories.
Key takeaways
- The results of 17 States and 5 UTs have been released Phase-I.
- Phase II covering the remaining 12 States and 2 UTs had their fieldwork suspended due to Covid-19, which has been resumed from November and is expected to be completed by May 2021.
- Substantial improvement in maternal and child health indicators over NFHS-4 (2015-16) was recorded in the present survey.
- The fertility rate has further declined.
- Contraceptive use has increased and unmet need has been reduced in most phase I states.
- The survey found considerable improvement in vaccination coverage among children age 12-23 months across all states and UTs.
- Malnutrition indicators have worsened.
- Rise in stunting was reported in 11 out of 18 states. Wasting increase was found in 14 states and of those with anaemia in 17 states.
Climate Ambition Summit 2020 held virtually
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment
In news
- The United Nations, United Kingdom and France co-hosted the Climate Ambition Summit 2020 which was held virtually recently.
Key takeaways
- The Summit marked the five years of the adoption of the Paris Agreement on Climate Change.
- The summit aims to bring together leaders to make new commitments to tackle climate change and deliver on the goals of the Paris Agreement.
- The United Kingdom pledged to double its climate finance contribution to USD 15.5 billion over the next five years.
- The European Investment Bank announced a goal of 50% of investments going toward the climate and environment sectors by 2025.
- It also called for climate finance commitments to support the most vulnerable and ambitious adaptation plans and underlying policies.
- According to Indian Prime Minister, India is not only on track to achieve its Paris Agreement targets, but to exceed them beyond expectations.
Do you know?
- India has reduced emission intensity by 21% over 2005 levels.
- Solar capacity has grown from 2.63 GigaWatts in 2014 to 36 GigaWatts in 2020.
- Renewable energy capacity is the fourth largest in the world.
- It will reach 175 GigaWatts before 2022.
- India has also set new target of 450 GigaWatts of renewable energy capacity by 2030.
- On the world stage, India has pioneered two major initiatives: (1) The International Solar Alliance; (2) Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure.
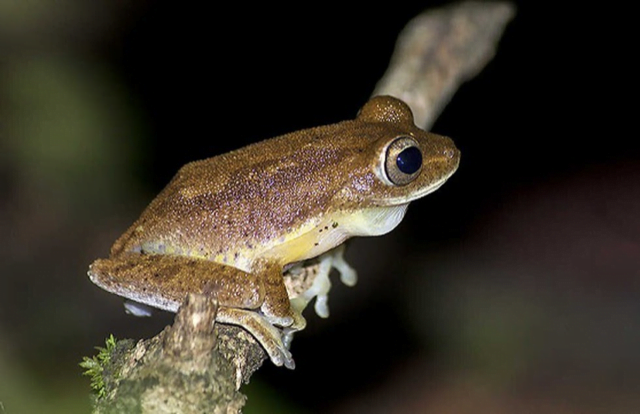
Myristica Swamp Treefrog recorded for the first time
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; biodiversity
In news
- Myristica swamp treefrog, has been recorded for the first time in the Vazhachal Reserve Forest in Kerala’s Thrissur district.
- It is a rare arboreal species endemic to the Western Ghats.

Important value addition
- Scientific name: Mercurana myristicapalustris.
- These frogs are rare and elusive for the reason that they are arboreal and active only for a few weeks during their breeding season.
- During this season, there is a large aggregation of males that descend from the high canopy of the trees.
- The males vocalise in groups from the low perches in the swamps.
- They exhibit unique breeding behaviour.
- The breeding season, unlike for other frogs, starts in the pre-monsoon season (May) and ends before the monsoon.
Plasmodium Ovale: Uncommon type of Malaria
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health & GS-III – Sci & Tech
In news
- A not very common type of malaria, Plasmodium ovale, has been identified in a soldier in Kerala.
- The soldier is believed to have contracted it during his posting in Sudan, from where he returned nearly a year ago, and where Plasmodium ovale is endemic.
Important value addition
- Malaria is caused by the bite of the female Anopheles mosquito, if the mosquito itself is infected with a malarial parasite.
- There are five kinds of malarial parasites — Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax (the commonest ones), Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium knowlesi.
Plasmodium ovale
- P ovale rarely causes severe illness and there is no need for panic because of the case detected in Kerala.
- P ovale is very similar to P vivax, which is not a killer form. It is no more dangerous than getting a viral infection.
- Symptoms: Fever for 48 hours, headache and nausea
- It is termed ovale as about 20% of the parasitised cells are oval in shape.
- P ovale malaria is endemic to tropical Western Africa.
- It is relatively unusual outside of Africa.
Miscellaneous
Eluru illness
- Over 550 people in Eluru town of Andhra Pradesh’s West Godavari district have been suffering from convulsions, seizures, dizziness and nausea.
- The All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) has found traces of lead and nickel in blood samples of some victims.
- The primary suspicion is on water contamination by heavy metals.
- Scientists suspect that pesticide or insecticide has seeped into drinking water sources.
- Eluru receives water through canals from both Godavari and Krishna rivers.
- The canals pass through agricultural fields where runoff laced with pesticides mixes with water in the canals.
- Many aspects of the mystery illness have baffled scientists.
- People who only use packaged drinking water have also fallen sick.
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic: General Studies2:
- International Events and its ramification.
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
Morocco-Israel deal
Context: Morocco has become the fourth Arab country to normalise ties with Israel in five months.
On December 10, U.S. President Donald Trump announced the deal, claiming that the series of normalisation agreements between Arab countries (the UAE, Bahrain, Sudan and now Morocco) and the Jewish state was bringing peace to West Asia.
In October, as parts of its deal to get Sudan to normalise ties with Israel, Washington removed Sudan from its ‘State Sponsor of Terrorism’ list, of which it made been a part for over 27 years.
What does Morocco get in return?
- In return for Morocco’s decision to establish formal ties with Israel, the S. has recognised Moroccan sovereignty over Western Sahara, a disputed territory in northwestern Africa, which has been under Moroccan control for decades.
- Morocco has long been campaigning internationally, using economic pressure and diplomacy, for recognition of its claims to Western Sahara.
- It got what it wanted from the deal with Israel, a country with which it had developed covert ties for decades.
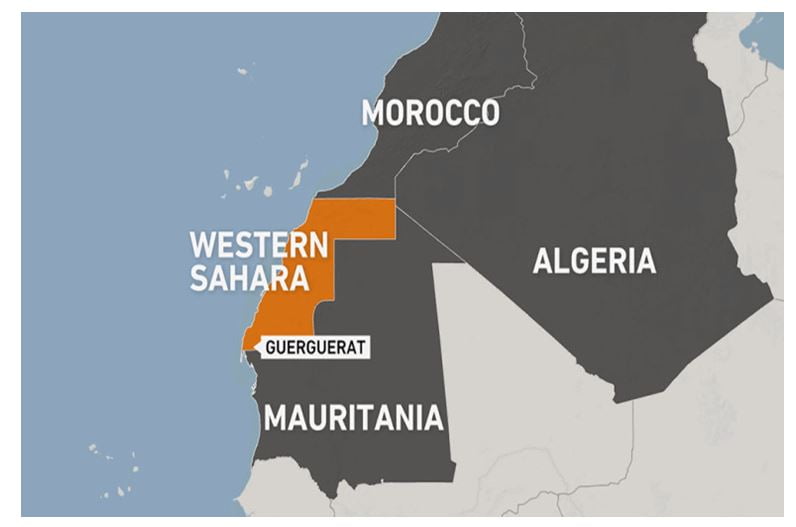
Image Source: Aljazeera
What is the history of Western Sahara dispute?
- Western Sahara is large, arid and sparsely populated region that shares a border with Morocco, Algeria and Mauritania and has a long Atlantic coast was a Spanish colony. The region is home to the Sahrawi tribe.
- In the 1970s, when international and local pressure mounted on Spain to vacate its colonies in Africa, Libya and Algeria helped found a Sahrawi insurgency group against the Spanish rule in Western Sahara.
- In 1975, as part of the Madrid Accords with Morocco and Mauritania, Spain decided to leave the region, which was then called Spanish Sahara.
- According to the accords, Spain would exit the territory before February 28, 1976 and until then, the Spanish Governor General would administer the territory, with help from two Moroccan and Mauritanian Deputy Governors.
- Both Morocco and Mauritania moved troops to Western Sahara to assert their claims.
- Sahrawi insurgency group (Polisario Front) backed by Algeria continued the guerilla resistance, demanding their withdrawal. On February 27, 1976, a day before Spain ended its presence, the Polisario Front declared the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR) in Western Sahara.
- The SADR has been recognised by several African countries and is a member of the African Union.
What is UN Court’s view on the dispute and the basis of Morocco’s claim?
- Morocco and Mauritania had laid claims to Western Sahara even when it was a Spanish colony.
- In 1974, the International Court of Justice was asked by the U.N. General Assembly to look into the legal ties, if any, that existed between Western Sahara and Morocco and Mauritania at the time of its colonisation by Spain in the 19th century.
- The court found no evidence “of any ties of territorial sovereignty” between the Western Sahara and either Morocco or Mauritania, but stated that there were “indications” that some tribes in the territory were loyal to the Moroccan Sultan.
- In its conclusion, the court endorsed the General Assembly Resolution 1541 that affirmed that to ensure decolonisation, complete compliance with the principle of self-determination is required.
- But King Hassan II of Morocco hailed the court’s opinion as vindication of country’s stand and moved troops across the northern border to Western Sahara. Mauritania joined in later. It set the stage for a three-way fight with the Polisario Front resisting both countries.
How did the conflict progress over the decades?
- The three-way conflict lasted for almost four years. In August 1979, Mauritania signed a peace treaty with Polisario, bringing the country’s military involvement in Western Sahara to an end.
- When Mauritanian forces withdrew from the southern part of the desert that they had occupied, Morocco swiftly advanced troops.
- The war continued between Moroccan troops and the Polisario Front.
- In 1991, when a ceasefire was finally achieved, Morocco had taken control of about 80% of the territory. The independence referendum, promised in the 1991 ceasefire, is yet to take place
- The war had forced almost 200,000 Sahrawis to flee the territory to neighbouring Algeria, where Polisario is running squalid refugee camps
- The SADR is operating largely from the eastern flank of Western Sahara and the refugee camps.
- Moroccan troops have built a huge sand wall called Berm, from the Atlantic coast of Western Sahara to the mountains of Morocco, dividing the territories they control from that of Polisario.
What impact will the Israel deal have on the conflict?
- The normalisation deal between Morocco and Israel itself will not have any direct bearing on Western Sahara.
- But the concession the U.S. has given to Morocco — Washington’s recognition of Moroccan occupation of Western Sahara in return for Morocco’s agreement with Israel — could flare up the conflict.
- The uptick in hostilities in the region would further destabilise Western Africa and undermine decades worth of efforts by both the US and France to rid the region of Islamist insurgencies.
- Recently, Morocco launched an offensive into the U.N.-controlled buffer zone between the two sides and in return, Polisario said it would resume armed conflict.
- After the Trump administration’s recognition of Morocco’s claim, Polisario said it would continue fighting until Moroccan troops are forced to withdraw.
- The S. move would upset Algeria, the biggest backer of Polisario.
- Among the countries that condemned the U.S. decision is Russia, which said the recognition of Moroccan sovereignty over Western Sahara “is a violation of international law”.
HEALTH / SOCIETY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Nurses and midwives
Context: The year 2020 has been designated as “International Year of the Nurse and the Midwife”. It is well acknowledged that nurses and midwives will be central to achieving universal health coverage in India.
Do You Know?
- India’s nursing workforce is about two-thirds of its health workforce.
- The ratio of 1.7 nurses per 1,000 population is 43% less than WHO norm; it needs 2.4 million nurses to meet the norm.
Issues
- Heavy Dependence on Private Players: 91% of the nursing education institutions are private and weakly regulated.
- Inadequate Faculty: The faculty positions vacant in nursing college and schools are around 86% and 80%, respectively.
- Structural Issues with Training: There is a lack of job differentiation between diploma, graduate, and postgraduate nurses regarding their pay, parity, and promotion
- Quality of Training:The current nursing education is outdated and fails to cater to the practice needs. The quality of training of nurses is also diminished by the uneven and weak regulation.
- Lack of Specialty Courses: There are insufficient postgraduate courses to develop skills in specialties, and address critical faculty shortages both in terms of quality and quantity.
- Regional Imbalance: Inequities in distribution of nursing education institutions. Around 62% of them are situated in southern India.
- Lack of Comprehensive Policy Focus: The Indian Nursing Act primarily revolves around nursing education and does not provide any policy guidance about the roles and responsibilities of nurses in various cadres.
- Non-standardised practices: Nurses in India have no guidelines on the scope of their practice and have no prescribed standards of care. Mismatch of the role description and remuneration that befits the role sets the stage for the exploitation of nurses.
- Accountability Issues: Nurses are out of the purview of the Consumer Protection Act. This is contrary to the practices in developed countries where nurses are legally liable for errors in their work.
- Social Status: The disabling environment prevalent in the system has led to the low status of nurses in the hierarchy of health-care professionals. In fact, nursing has lost the appeal as a career option.
Way Ahead
- Improvement on Quality: A common entrance exam, a national licence exit exam for entry into practice. Transparent accreditation, benchmarking, and ranking of nursing institutions too would improve the quality.
- Database to know supply-demand:A live registry of nurses, positions, and opportunities should be a top priority to tackle the demand-supply gap in this sector.
- Regular Monitoring: Periodic renewal of licence linked with continuing nursing education would significantly streamline and strengthen nursing education.
- Legislative Amendments: The Indian Nursing Council Act of 1947 must be amended to explicitly state clear norms for service and patient care, fix the nurse to patient ratio, staffing norms and salaries.
- Federal Cooperation: The jurisdictions of the Indian Nursing Council and the State nursing councils must be explained and coordinated so that they are in synergy.
- Promoting Nursing as Career: Incentives to pursue advanced degrees to match their qualification, clear career paths, opportunity for leadership roles, and improvements in the status of nursing as a profession.
- Public-private partnership between private nursing schools/colleges and public health facilities is another strategy to enhance nursing education.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Where is Vazhachal Reserve Forest situated?
- Kerala
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Karnataka
Q.2 Eluru illness, being seen in news, originated in which of the following state of India?
- Tamil Nadu
- Jharkhand
- Andhra Pradesh
- Telangana
Q.3 Plasmodium Ovale is endemic to which of the following region?
- South Asia
- South-east Asia
- Western Africa
- Eastern Africa
ANSWERS FOR 12th December 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
About dangers of hydropower projects in Himalayas:
About innovations for clean air:
About counting workers in India:











