IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Status of Kala Azar in Four States reviewed
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health
In news
- Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare recently reviewed the status of the disease Kala-Azar in the four states of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal.
Key takeaways
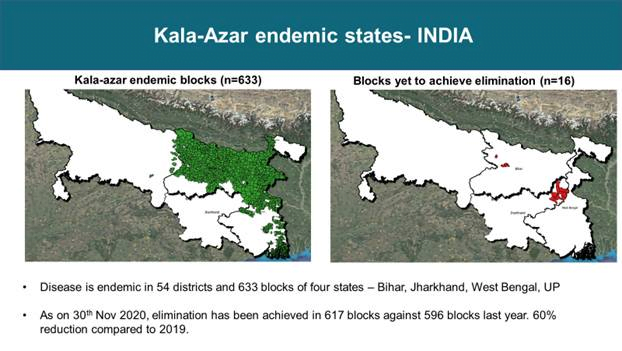
- There are 54 districts in these four states that are currently affected by Kala-azar with sporadic cases in other states like Assam, HP, J&K, Kerala, Sikkim, and Uttarakhand.
- A risk based stratified approach needs to be formulated with clear activities and responsibilities that come with measurable monitoring indicators.
- Kala Azar disproportionately impacts the people at lower socio-economic strata of society whose houses are not sprayed often.
- In addition, they are unable to apply for pucca houses since they don’t own land.
The Central government has underlined the importance of the following activities to target the elimination of the disease:
- Development of a plan for the “unreached poorest” or underprivileged sections in endemic areas.
- Leveraging of Kala-azar elimination programme within POSHAN Abhiyaan for maximum benefit at community level.
- Exploration of the opportunity of providing improved housing under the flagship program of the Prime Minister Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G).
- Exploration of the opportunity of providing improved housing under State Schemes.
- Involvement of Rural Health Practitioners (RHPs)
- Co-ordination with the rural development department and engage with Panchayati Raj functionaries for awareness, community engagement, environment management and social empowerment.
Important value additions
Kala Azar
- A disease caused by infection with leishmania parasites.
- Visceral leishmaniasis is spread by sandfly bites.
- This type of leishmaniasis affects the internal organs, usually the spleen, liver and bone marrow.
- Some people have no symptoms.
- For others, symptoms may include fever, weight loss and swelling of the spleen or liver.
- Medication exists to kill the parasites.
- If left untreated, severe cases are typically fatal.
Do you know?
- Kala Azar is the 2nd largest parasitic killer in the world after Malaria.
- It results in a 95% fatality rate if the patients are not treated.
- Up to 20% of the patients who are correctly treated and cured, develop a skin condition called Post-Kala-Azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL) which surfaces within months to years after treatment.
- These patients can contain large amounts of parasites in their skin lesions, making them an important source of transmission.
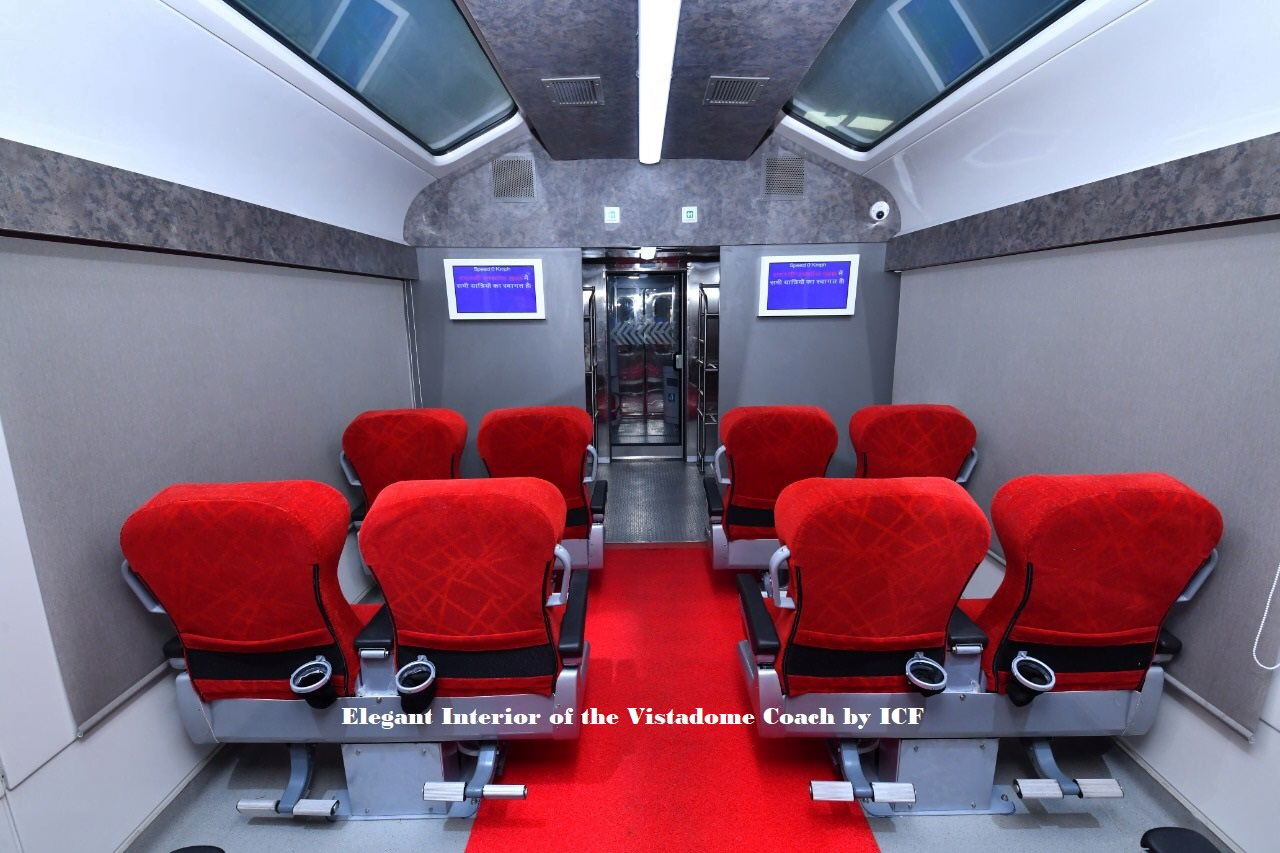
Indian Railway completes successful speed trials of the new design Vistadome Tourist Coaches
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Infrastructure
In news
- In order to provide world class modern travelling experience for the passengers, Indian Railways successfully completed the speed trials of the newly designed Vistadome tourist coach manufactured by Internal Coach Factory.
Key takeaways
- The coach has successfully completed 180 KMPH oscillation trial.
- The Vistadom tourist coach is provided with larger viewing area including roof top glasses with 44 seats for passengers with rotation up to180 degree to face the direction of train movement.
- The coach is also having Wi-Fi based Passenger information system.
- Integral Coach Factory (ICF) is a manufacturer of rail coaches located in Perambur, Chennai, Tamil Nadu.

Progress of Work on Railways National Project in Jammu and Kashmir reviewed
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Infrastructure
In news
- Progress of Work on Railways National Project in Jammu and Kashmir was recently reviewed.
- Work on the Remaining Portion of the Udhampur Srinagar Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) Project to be completed in Mission Mode.
- Focus on Providing All-Weather Connectivity to Kashmir Region from rest of the Country.
Important value additions
- The USBRL is a National project undertaken by the Indian Railways for construction of broad-gauge railway line through the Himalayas.
- Aim: Connecting the Kashmir region with rest of the country.
- The all-weather, comfortable, convenient and cost effective mass transportation system will be the catalyst for the overall development of the region.
- Currently, the line is in operational use for running trains between Baramulla-Banihal in Kashmir valley and Jammu-Udhampur-Katra
ADB, India sign $10 million loan to support horticulture in Himachal Pradesh
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International relations & GS-III – Agriculture
In news
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the Indian Government signed a $10 million project readiness financing (PRF).
- Objective: To help finance piloting activities, and design and capacity building for an ensuing project that aims to expand horticulture production and farm household income in Himachal Pradesh.
Key takeaways
- PRF project will support advance actions to achieve high level of project readiness through detailed design activities, capacity building of state level agencies, and creating an enabling environment for subtropical horticulture development in the state.
- It aims to ensure implementation readiness with prior testing of new production technologies and marketing systems so that the project is cost-effective and gets completed in a timely manner.
- The project will support development of subtropical horticulture, including cultivation of fruits and vegetables, in the state’s southern region which is currently lagging due to limited access to perennial water sources, crops losses due to wild animal encroachment and limited access to high value markets.
- The PRF also supports establishment of water user association (WUAs) on completed irrigation schemes and enhancing women’s participation.
Important value additions
Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- It is a regional development bank.
- Established on: 19 December 1966,
- Headquarter: Ortigas Center, Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines.
- The bank promotes social and economic development in Asia.
- It is modelled closely on the World Bank, and has a similar weighted voting system where votes are distributed in proportion with members’ capital subscriptions.
- As of 31 December 2018, Japan and the United States each holds the largest proportion of shares at 15.571%.
- China holds 6.429%, India holds 6.317%, and Australia holds 5.773%.
ADB, India sign $231 million loan to enhance power generation capacity in Assam
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International relations & GS-III – Infrastructure; Energy
In news
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the Government of India signed a $231 million loan to augment electricity generation capacity in Assam through construction of a 120 megawatts (MW) hydroelectric power plant.
Key takeaways
- This is the third tranche loan for the ongoing Assam Power Sector Investment Programme that was approved by the ADB Board in July 2014.
- The programme, including its two previous tranches, focuses on enhancing capacity and efficiency of the energy generation and distribution systems in Assam to improve electricity service to end users.
- Increased supply of affordable and clean electricity facilitated through the project will help improve living conditions, promote business expansion, and increase employment opportunities in the state beside reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- The project is run-of-the-river project over Kopili river which will help increase electricity supplied from clean energy by 469 gigawatthour (GWh) by 2025 and reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 360,000 tons of carbon dioxide annually.
- A $2 million grant from Japan fund for poverty reduction (JFPR) is also associated with the project to finance equipment and consulting services.
Related articles:
- ADB signs $500 million loan for Delhi-Meerut RRTS Corridor: Click here
- ADB and India sign $177 million loan for Maharashtra roads: Click here
- 15-billion ADB loan to India to fund COVID-19 emergency: Click here
Foundation stone of TiHAN-IIT Hyderabad laid
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Innovation; Sci & Tech
In news
- Union Minister of Education laid foundation stone of ‘TiHAN-IIT Hyderabad’.
- It is India’s first Test bed for Autonomous Navigation Systems (Terrestrial and Aerial).

Key takeaways
- The Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, has sanctioned Rs. 135 crores to IIT Hyderabad under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS) to set up a Technology Innovation Hub on Autonomous Navigation and Data Acquisition Systems (UAVs, RoVs, etc.).
- The Technology Innovation Hub on Autonomous Navigation Systems for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles and Remotely Operated Vehicles at IIT Hyderabad, known as ‘TiHAN Foundation’ has been incorporated as a Section-8 company by the institute in June 2020.
- TiHAN Foundation is a multi-departmental initiative, including researchers from Electrical, Computer Science, Mechanical and Aerospace, Civil, Mathematics, and Design at IIT Hyderabad with collaboration and support from reputed institutions and industry.
- Special Features of this Facility include Test Tracks, Emulation of Real-World Scenarios, State of the Art Simulation Technologies, Road Infrastructure, V2X Communication, Drone Runways and many more.
Meteorological (Met) Centre at Leh (Ladakh) inaugurated
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Sci & Tech
In news
- The Union Minister of Earth Sciences inaugurated Meteorological (Met) Centre at Leh (Ladakh).
Key takeaways
- Located at a height of 3500 m, Meteorological Centre Leh will be the highest meteorological centre in India.
- The Centre will be a world class facility for high altitude meteorology.
- It will cater to the various kinds of weather and climate needs of the people and the administration of Ladakh.
- It will provide forecast for important tourist places like Nubra, Changthang, Pangong Lake, Zanskar, among others.
Need for a Met Centre at Leh
- The Ladakh region has lofty mountains with high slopes and no vegetation and lots of loose soil and debris making the region vulnerable to various kinds of natural hazards like Cloud burst (of 2010), Flash Floods, Avalanches and Glacial Lake Outbursts, etc.
- To avert losses due to such weather events in future, the Government felt the need to establish a State of the Art Meteorological (Met) Centre at Leh to strengthenweather related Early Warning System in Ladakh.
(Mains Focus)
ENVIRONMENT/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Conservation of Environment
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Climate Change and India in 2021
Issues
- High Vulnerability to Climate risks: 75% of districts in India, home to over half the population, were vulnerable to extreme climate risks. Drought-affected districts have increased by yearly average of 13 times over the last two decades. The frequency of cyclones has also doubled.
- Increased Frequency of extreme Climate events: While India witnessed 250 extreme climate events between 1970 and 2005, the country recorded 310 extreme climate events after 2005 alone.
- Financial Losses: Between 1990 and 2019, India incurred losses exceeding $100 billion.
- Enhanced Intensity of Extreme Climate events: The intensity of floods increased eightfold and that of associated events such as landslides and heavy rainfall increased by over 20 times since 1970.
- Swaping Trend: Over 40% of Indian districts now show a swapping trend: flood-prone areas are becoming drought-prone, and vice-versa.
Steps India should take in 2021 to enhance its resilience and adaptive capacity against extreme climate events
- Focused Mission: India should create an Environment and Health De-risking Mission to increase emergency preparedness, secure critical resources and build resilient infrastructure and governance systems to counter the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme climate events.
- Decentralization: Focus on democratising local climate-related and weather-related data along with integrating risk projections in national, sub-national and district disaster and climate plans.
- Focus on Indigenous Communities: Restoration, revival, and recreation of traditional climate-resilient practices, with a special focus on indigenous communities, often on the front lines of ecosystem conservation.
- Creation of Comprehensive Climate Risk Atlas: This Atlas should identify, assess and project chronic and acute risks at a granular level to better prepare against extreme climate events. The Atlas would also help in assessing the resilience and adaptation capabilities of communities & business and act as risk-informed decision-making toolkit for policymakers. It would help in climate-proofing critical infrastructure.
- Financing Tools: To finance climate action at scale, risk financing instruments and risk retention and identification tools should be supplemented by contingency and adaptation funds such as the Green Climate Fund. This will enhance the public finance pool and gear up efficient allocation across sectors at risk by mobilising investments on critical infrastructures and resilient community actions.
- International Collaboration: As the permanent chair of the recently formed Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure, India should play a pivotal role in attracting private investments into climate-proofing of infrastructure. It should also promote adaptation-based infrastructure investment decision making in these countries.
Connecting the dots:
- Paris Climate Deal
- Do you think COVID-19 has enhanced environmental consciousness of the world?
AGRICULTURE / GOVERNANCE/ FEDERALISM
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Issues and challenges pertaining to Agriculture
- Public Distribution System- objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping; issues of buffer stocks and food security
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
To help farmers, right approach is through FPOs, not APMC mandis
Context: Protest by farmers against newly enacted farm bills and their adamant demand of the repeal of these laws. However, government is trying its best to negotiate with agitating farmers and reach an amicable solution
Basic facts about Indian agriculture, which may help negotiators on both sides, with a common objective of benefitting the larger interest of the farming community.
- Implicit Taxation: As per research by ICRIER, Indian agriculture was implicitly taxed to the tune of almost 14% of its value. This was primarily due to restrictive trade and marketing policies, ranging from export controls and stocking limits to the restrictive mandi system.
- Misplaced Fears: The way to improve farmers’ price realisation, therefore, was to liberate agriculture from these various controls. But somehow, a fear has been created that these farm laws will rob farmers of APMC markets, MSP, and they may even lose their lands to big corporate houses through contract farming.
But won’t the APMC face competition from Private Players?
- There is no doubt that APMC markets and MSP will face competition from private markets and out-of-APMC mandi transactions.
- But agricultural experts like Ashok Gulati believe the competition will help the farmers at large, especially small and marginal ones. The creation of an additional 10,000 Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs) and the promised Agri-infrastructure Fund of Rs one lakh crore will aid this process.
- But many among the agitating farmers fear losing the MSP for wheat and paddy that they get in Punjab-Haryana.
- However, in all these years since the MSP was given birth to in 1965 only 6 per cent of farmers and broadly, 6 per cent of the value of agri-produce has benefitted from this system
- The MSP and APMC system primarily helps those who have large surpluses, mainly the large farmers.
- So, if one really wants to help the small and marginal farmers, the right approach is through FPOs at the village level and not in APMC mandis. About 86 per cent of Indian farmers are small and marginal (less than 2 ha), operating roughly 47 per cent of the total operated area in the country.
What about famers demand of making MSP Statutory right & repealing of laws?
- Asking for making MSP a statutory binding even on the private sector will turn out to be anti-farmer as much of the private trade will shun such a system, leading to chaos. It will be worse than repealing these laws.
- Repealing these farm laws would be like robbing more than 90 per cent of farmers — who never gained from the MSP system and who are largely small and marginal — of their rights
Given these basic facts, how do we dispel the fears of agitating farmers?
- First, the government should be ready to give in writing that the existing system of APMC markets and MSP will continue and be strengthened.
- Second, the government can also give in writing that the contract will be for the produce, not the land.
- Third, farmers can take disputes to district courts, if they like.
- Fourth, to add to these written assurances, the government can also commit to creating a fund of Rs 25,000 crores under the Price Stabilisation Scheme, which can be used to support market prices of specified commodities that take a dip of more than 10 per cent below MSP.
- This is akin to NAFED’s operations to support market prices of pulses and oilseeds, or the Cotton Corporation of India (CCI) for cotton prices, and can be extended to maize, sorghum, pearl millet, etc.
- Fifth, if stocks keep piling up, as is the case with wheat and rice today, to correct imbalance in demand and supply, government should either limit the size of procurement or go for price deficiency payments. A further positive step will be to announce a diversification package for the Punjab-Haryana belt.
Conclusion
One must remember that farmers always want a higher price for their produce, but higher food prices can also bring pains to poor consumers. The art of policymaking is to balance the interest of producers and consumers within reasonable financial resources.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Kala Azar is endemic in which of the following states of India?
- Bihar
- Jharkhand
- Chhattisgarh
- Odisha
- West Bengal
Select the correct code:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 4 and 5 only
- 2, 4 and 5 only
- 1,2 and 5 only
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Kala Azar:
- It is caused by infection with leishmania fungus.
- Visceral leishmaniasis is spread by sandfly bites.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Horticulture farming consists of which of the following?
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Nuts
- All of the above
Q.4 Asian Development Bank is headquartered at which of the following?
- China
- India
- Malaysia
- Philippines
Q.5 Consider the following statements regarding Assam Power Sector Investment Programme that was approved by the ADB Board in July 2014:
- The project is run-of-the-river project over Brahmaputra River.
- It will help increase electricity supplied from clean energy by 469 gigawatthour (GWh) by 2030.
- A $2 million grant from Japan fund for poverty reduction (JFPR) is also associated with the project.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
ANSWERS FOR 1st January 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | A |
| 4 | D |
Must Read
On removal of Interconnection Usage Charges in telecom sector:
On U.P. religious conversion ordinance:
About partial reopening of schools:











