IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Kochi-Mangaluru natural gas pipeline
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Infrastructure
In news
- The Prime Minister Narendra Modi will dedicate the Kochi-Mangaluru Natural Gas Pipeline to the nation on January 5 at 11 am via video conferencing.
Key Highlights
- The 450-km pipeline has been built by GAIL (India) Ltd
- It has transportation capacity of 12 million standard cubic metres per day
- It will carry natural gas from the liquefied natural gas (LNG) regassification terminal at Kochi to Mangaluru
- Laying of the pipeline was an engineering challenge as the route of the pipeline necessitated it to cross water bodies at more than 100 locations. This was done through a special technique called horizontal directional drilling method.
- The pipeline will supply environment friendly and affordable fuel to households, transportation sector and to commercial and industrial units across the districts along the pipeline.
UK to abolish the ‘tampon tax’
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I- Society; GS-III- Economy
In news
- The UK began 2021 by abolishing a 5 per cent Value Added Tax (VAT) on women’s sanitary products, often referred to as the “tampon tax” and which many activists had described as sexist.
- It now joins the list of countries which have already eliminated this tax, which includes India, Australia and Canada.
Key Highlights
- Until December 31, the UK was a part of the EU, where period products such as sanitary napkins and tampons are classified as non-essential, and member states are required to levy a 5 per cent tax on them.
- Now that the UK is out of the 27-member bloc, it is not bound by its directives, under which sanitary products had been subjected to five different VAT rates since 1973– with the lowest 5 per cent slab being applicable since 2001.
- The removal of the tax has thus been praised by women’s right activists and Brexit proponents at the same time.
- EU itself has been in the process of removing the tax on period products. In 2018, the bloc published proposals to change the tax rules, but these are yet to be accepted by all members
- The British government has estimated that the move to abolish the tampon tax would save the average woman about 40 pounds during her lifetime – as a pack of 20 pounds will be cheaper by around 7 pence and 12 sanitary pads by 5 pence.
FSSAI slashes limit for trans fat levels in foods
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Governance
In news
- FSSAI has capped the amount of trans fatty acids (TFA) in oils and fats to 3% for 2021 and 2% by 2022 from the current permissible limit of 5% through an amendment to the Food Safety and Standards (Prohibition and Restriction on Sales) Regulations.
- The FSSAI notified the amendment on December 29, more than a year after it issued a draft on the subject for consultation with stakeholders.
- The revised regulation applies to edible refined oils, vanaspati (partially hydrogenated oils), margarine, bakery shortenings and other mediums of cooking such as vegetable fat spreads and mixed fat spreads.
Key takeaways
- While the regulation comes into effect immediately, industry players were made to take a pledge back in 2018 that they would comply with WHO’s call for action to reduce TFA by 3% by 2021 allowing them three years to comply with the latest regulation.
- It was in 2011 that India first passed a regulation that set a TFA limit of 10% in oils and fats, which was further reduced to 5% in 2015.
- Trans fats, or trans-fatty acids, are a form of unsaturated fat. They come in both natural and artificial forms.
- Trans fats are associated with increased risk of heart attacks and death from coronary heart disease.
- As per the World Health Organisation (WHO), approximately 5.4 lakh deaths take place each year globally because of intake of industrially produced trans fatty acids. The WHO has also called for global elimination of trans fats by 2023.
Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- International Affairs
In news
- Iran has informed the International Atomic Energy Agency that it intends to produce uranium enriched to up to 20 percent purity, well beyond the threshold set by the 2015 Vienna accord (also known as JCPOA).
About JCPOA
- Commonly as the Iran nuclear deal or Iran deal, is an agreement on the Iranian nuclear program reached in Vienna on July 14, 2015, between Iran and the P5+1 (the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council—China, France, Russia, United Kingdom, United States—plus Germany) together with the European Union.
- Under JCPOA, Iran agreed to eliminate its stockpile of medium-enriched uranium, cut its stockpile of low-enriched uranium by 98%, and reduce by about two-thirds the number of its gas centrifuges for 13 years.
- For the next 15 years Iran will only enrich uranium up to 3.67%. Iran also agreed not to build any new heavy-water facilities for the same period of time.
- Uranium-enrichment activities will be limited to a single facility using first-generation centrifuges for 10 years. Other facilities will be converted to avoid proliferation risks.
- To monitor and verify Iran’s compliance with the agreement, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) will have regular access to all Iranian nuclear facilities.
- The agreement provides that in return for verifiably abiding by its commitments, Iran will receive relief from U.S., European Union, and UNSC nuclear-related sanctions.
- On 5 January 2020, in the aftermath of the Baghdad Airport Airstrike that targeted and killed Iranian general Qassem Soleimani, Iran declared that it would no longer abide by the limitations of the deal but would continue to coordinate with the IAEA, leaving open the possibility of resuming compliance.
Miscellaneous
Banana Grit
-
Scientists have come up with a new product, banana grit or granules, developed from raw Nendran bananas.
- Billed as an ideal ingredient for a healthy diet, banana grit can be used for making a wide range of dishes.
- The product resembles to ‘rava’ and broken wheat.
- The concept was introduced to utilise the presence of resistant starch in bananas, which is reported to improve gut health.
Nendran Banana
- Changalikodan Nendran Banana or famously known as Changalikodan is a banana variety originated and cultivated in Chengazhikodu village of Thrissur District in Kerala.
- Changalikodan, now are cultivated on the banks of the Bharathapuzha river.
- Changalikodan got Geographical indication registration from the Geographical Indications Registry, Chennai.
Pong Dam
- Nearly 1,400 migratory birds were found dead recently due to an unexplained cause in the Pong Dam area of Kangra district in Himachal Pradesh. The local authorities have suspended all tourism activities in the reservoir precincts
- The Pong Dam, also known as the Beas Dam, is an earth-fill embankment dam on the Beas River in the state of Himachal Pradesh.
(Mains Focus)
GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
COVID-19 Vaccine Dry Run
Context: With two vaccine candidates — Covishield from the Pune-based Serum Institute of India and Covaxin of Bharat Biotech — at final stages of emergency use authorisation (EUA) in India, several States and Union Territories conducted a dry run for a COVID-19 vaccination programme.
India’s Immunization Experience
- Under India’s ‘Expanded Programme on Immunization’, which was initiated in 1978, the country has gathered experience in administering essential vaccines to children and pregnant women.
- In 1985, the programme was renamed ‘Universal Immunisation Programme’, under which about 12 different vaccines are provided through the government health system.
- Other than inoculation, there is a three-tier system at the district, State and national levels to monitor coverage and adverse events and to ensure that the vaccines adhere to quality norms.
- Roughly 9 million immunisation sessions are conducted annually in India, according to the UNICEF. Despite that, only about 60% of eligible children are fully immunised, with wide variations among States.
Why was it necessary?
- Because a COVID-19 vaccine will involve two jabs spaced at least four weeks apart, and will need to be administered to potentially over a billion Indians, it requires more planning, personnel and logistical arrangements.
- India’s priority list of beneficiaries includes healthcare workers, municipal workers, police personnel, those over 50 years of age, and younger people with identified co-morbidities.
- This, the government has calculated, works out to 300 million people, and given the pace of vaccine production and administration, it will be August till all on the priority list are inoculated.
- With at least two vaccines on the EUA list, the whole exercise involves an unprecedented level of digitisation (Co-WIN Application).
- The purpose of the dry run was to assess operational feasibility of using Co-WIN application in field environment, to test the linkages between planning, implementation and to identify the challenges and guide way forward prior to actual implementation.
- This is also expected to give confidence to programme managers at various levels
What has been the experience of the trial run?
- The Punjab government successfully completed the exercise at 12 sites in two districts.
- Health officials in Assam said they focused on “software efficacy” and would be carrying out the physical part of the drill involving 300 people in two districts.
- The two-day exercise in Andhra Pradesh was conducted at five session sites, including public and private medical institutions, with 25 dummy beneficiaries (healthcare workers) at each site.
Following the dummy run, are actual vaccines ready to be rolled out?
- So far, only two vaccine candidates — Covishield, developed by the Serum Institute-Pune and based on the AstraZeneca ‘Oxford’ vaccine, and Covaxin, developed by Bharat Biotech and the Indian Council for Medical Research (ICMR) — have been cleared by an expert panel of the Drug Controller General of India.
- A formal approval by the DCGI is imminent, which will then allow the companies to supply doses to the government for distribution.
- The SII has said it has already stockpiled 50 million doses and will have another 50 million ready by next week.
Challenges Ahead
- The dummy runs are useful as a warm-up exercise, but they will reveal little about the toughest parts of the vaccination process, namely the actual inoculation, reactions, severe adverse reactions and potential hospitalisation.
- So far, as part of vaccine trials in India, thousands of people have been administered test vaccines in hospital settings.
- Many future inoculations are expected to be conducted in rural settings, where necessary healthcare infrastructure is absent.
- The United States, which has approved the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, had expected to vaccinate 20 million people within a month, but has barely progressed to 2.8 million.
INTERNATIONAL
Topic: General Studies 2:
- International events.
GIBRALTAR (UK-Spain Deal)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- International Affairs
In news
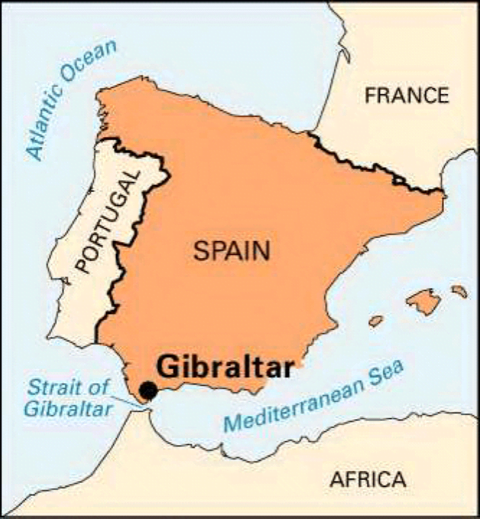
- Hours before the Brexit transition period ended on New Year’s Eve, Spain announced it had struck a deal with the UK to maintain free movement to and from Gibraltar
- Gibraltar is a small portion of land on the southern tip of the Iberian peninsula that Britain controls but Spain claims as its own.
About the deal
- Officially remaining a British Overseas Territory, Gibraltar will now be part of the Schengen zone and follow EU rules, thus ensuring that a hard border does not separate it from the rest of Europe
- The result of the 2016 Brexit referendum gave rise to the possibility of a hard border coming up between Gibraltar and the rest of Europe, despite 96 per cent of the vote in Gibraltar being in favour of remaining in the EU.
- Gibraltarians mainly voted ‘Remain’ because the territory’s economy depends on an open border with Spain, which sends over 15,000 workers and 200 trucks there daily.
- However, free movement will now continue thanks to the Spain-UK deal, as Gibraltar is being placed in the Schengen area, with Spain acting as a guarantor.
- The Schengen passport-free zone includes 22 countries from the EU, and four others –Norway, Switzerland, Iceland and Liechtenstein. The UK has never been a part of this zone
- The EU will now place Frontex border guards for the next four years to ensure free movement to and from Gibraltar, and the territory’s port and airport would become the external borders of the Schengen area.
- The deal would mean the EU’s fair competition rules in areas such as the labour market and the environment would continue to apply to Gibraltar.
- Although the deal covers free movement, it does not address the sovereignty dispute between Spain and the UK. Britain has called the deal a “political framework” for a separate treaty that it wants to sign with the EU concerning Gibraltar.
Source: Britannica
About Gibraltar
- Gibraltar, with an area of just 6.8 sq km and a population of around 34,000 people, has been the subject of intense dispute between Spain and Britain for centuries. This is mainly because of its strategic location.
- The territory, which is connected to Spain by a small strip of land and surrounded by sea on three sides, serves as the only opening from the Atlantic Ocean into the Mediterranean Sea, making it a key location on the shortest sea route between Europe and Asia via the Suez Canal.
- Gibraltar fell into British hands after a war in 1713, and has since remained with Britain despite several attempts by Spain to retake it.
- Due to its strategic importance, Gibraltar came to be highly fortified by Britain since the 18th century, thus earning its commonly known name– “the Rock”.
- Even during World War II, Gibraltar’s port was critically important for the Allies, and it continues to be a key base for NATO.
- When Britain joined the EU in 1973, Gibraltar was a “crown colony”, but was reclassified as a British Overseas Territory in 2002.
- In two referendums, one in 1967 and the other in 2002, Gibraltarians overwhelmingly voted to remain a British territory.
- Currently, the territory is self-governing in all aspects, except for defence and foreign policy, which are managed by London, and Gibraltarians have British citizenship.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Pong Dam is located in which state?
- Andhra Pradesh
- Odisha
- Kerala
- Himachal Pradesh
Q.2 consider the following statements regarding Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA)
- It was an agreement signed between Iran and the P5+1 (the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council—China, France, Russia, United Kingdom, United States—plus Germany) together with the European Union.
- Under JCPOA, Iran agreed to eliminate its stockpile of medium-enriched uranium, cut its stockpile of low-enriched uranium by 98%, and reduce by about two-thirds the number of its gas centrifuges for 13 years.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Gibraltar:
- Gibraltar is a small portion of land on the southern tip of the Iberian peninsula.
- There is a sovereignty dispute regarding Gibraltar between Spain and France
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 02 JANUARY 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | D |
| 5 | A (Kopili is tributary of Brahmaputra) |
Must Read
On record GST inflows:
On military reforms:











